Week 2 Stress&Adaptation/ Neoplasia/ Tissue Repair&Wound Healing
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Patho 500
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Homeostais
body maintaining a stable balanced environment
Negative Feedback
a self-regulating process where a system responds to a change by counteracting it, reducing the effect, and maintaining stability or equilibrium
General Adaptation Syndrome
three-stage physiological response to stress
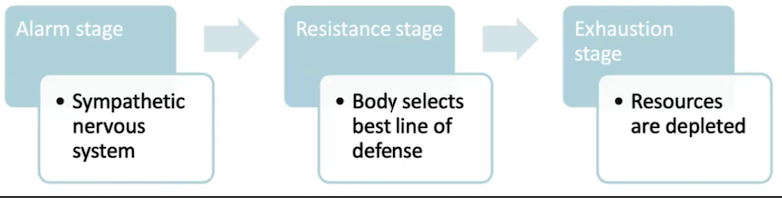
Neuroendocrine response (to stress)
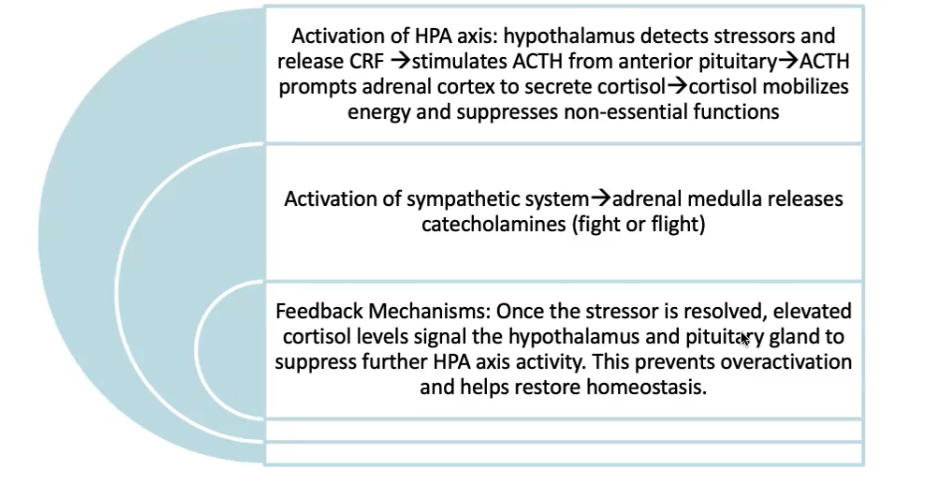
Immune System (in response to stress)
Immune cells (lymphocytes) send messages to the brain (cytokines) through the blood brain barrier to complete a stress response
how are the nervous and immune systems linked?
Nerves from the autonomous nervous system supply immune organs (lymph nodes/thymus/spleen) through inhibition of catecholamines and cortisol
process may lead to illness!
Acute Stress response
“fight or flight” short term response
alertness, vigilance from physiological or psychological stressors
Chronic Stress Response
prolonged stress that overwhelms the feedback system
leads to chronic or long term health problems such as PTSD
Adaptation to Stress
ability for the body to respond to challenges of physical or psychological homeostasis return to a balanced state
what is tissue repair
process that restores structure and function after healing
goal: restore look, structure and strength
tissue repair occurs through…
regeneration- replacement with original cells
fibrous tissue repair- replacement with scar tissue (collagen)
Regeneration
same type of cells replace injured ones
occurs in labile and stable tissues such as the skin or liver
fibrous repair
scar tissue replaces injured cells
occurs when tissue cannot regenerate (w the same cells)
ex such as when an MI occurs
scars limit organ function
Regulations on Healing
controlled by growth factors, cytokines, and ECM
depends on cell proliferation, migration and differentiation
key: PDGF & TGF-Beta
Local Factors of Wound Healing
response to tissue injury
Homeostasis
Inflammation
Proliferation
Remodeling
Healing Types (Wound Healing)
Primary Intention and Secondary Intention
Primary Intention
edges of wound are well-approximated
-minimal tissue loss
-clean incision
-quick healing
-small scar
ie. surgical wounds
Secondary Intention
open wounds that are not approximated
-large tissue loss
-slower healing
-large scar
ie burns or ulcer
Inflammatory Phase

Proliferation Phase
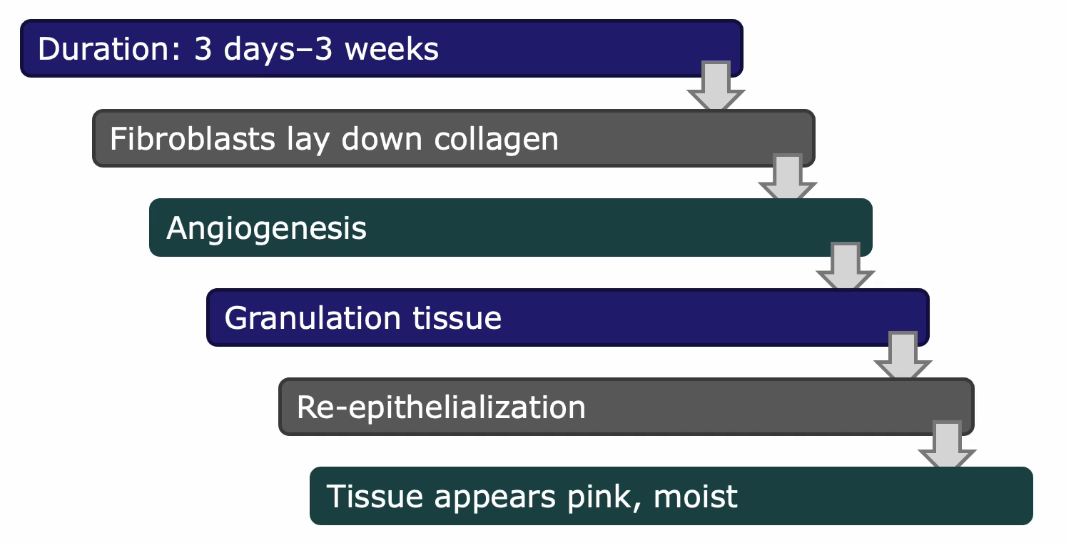
Wound Contraction & Remodeling
takes weeks to months
Myofibroblasts contract the wound
Collagen Type 3 → Type 1
strength increases
final tissue is ~80% Strength
Local Factors that affect wound healing
infection
blood supply
moisture
Systemic factors of wound healing
age
diabetes
nutrition
corticosteroids
smoking
Clinical Manifestations of Poor Healing
persistent inflammation
non-healing edges
purulent drainage
keloids
wound dehiscence
chronic pain
Neoplasia
Tumors
growth of new, uncontrollable cells
Tumor
mass of cells due to overgrowth
can be defined as Malignant or Benign
adding the suffix -oma to the parenchymal tissue type from which the growth originated
Adenoma
benign tumor of glandular epithelial tissue
Adenocarcinoma
malignant tumor of glandular epithelia tissue
Carcinoma
malignant tumor of epithelia tissue
osteoma
benign tissue of bone tissue
sarcoma
malignant tumors of mesenchymal origin (loosely organized connective tissue made of unspecialized cells)
Papillomas
benign microscopic or macroscopic finger-like projections growing on a surface
Benign Neoplasms
slow and do not spread - may standstill or regress
cannot invade surrounding tissues
Malignant Neoplasms
grow fast and have potential to kill no matter their original location
take essential nutrients from normal tissues
destroy normal tissue
Factors differentiating benign and malignant neoplasms
cell characteristics
manner of growth
rate of growth
potential for metastasizing or spreading
tendency to cause tissue damage
capacity to cause death
Anaplasia
describes the loss of cell differentiation in cancerous tissue
undifferentiated cells are marked by different morphologic changes, such as size, shape or condition
pleomorphism
undifferentiated cell changes in size or shape
Methods by which cancer spreads
direct invasion and extension
seeding of cancer cells in body cavities
metastatic spread through the blood or lymph pathways
Factors affecting tumor growth
number of cells dividing or moving
length of cell cycle
number of cells lost vs new cell production
growth fraction (ratio of dividing cells to resting cells in a tissue mass)
doubling time- time it takes for mass of cells in a tumor to double
genes that control cell growth and replication
protooncogenes genes
tumor supressor genes
geenes that control programmed cell death or apoptosis
genes that regulate repair of damaged dna
Initiation of Cancer cell formation
cells exposed to doses of carcinogenic agents making them susceptible to malignant transformation
Promotion of Cancer cell formation
unregulated accelerated growth in already initiated cells caused by chemicals and growth factors
Progression of cancer cell formation
where cells get more mutations and allows them to invade, metastasize and resist control mechanisms
Factors leading to cancer
Heredity - hormones, carcinogens, chemicals, radiation, viruses
Immunologic- stem cells, angiocentesis, microenvironmental effects
Clinical Manifestations of Cancer
tissue integrity
cancer cachexia - weight loss of body fat / tissues / anorexia / anemia
paraneoplastic syndromes - innapropriate hormone release or other circulation issues