carbonyl compounds as electrophiles
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
how do aldehydes and ketones react as both nucleophiles and electrophiles
what consequence does this have for their reactions (name)
they react as nucleophiles through their enol/enolate forms and as electrophiles through attack at the carbonyl
this means they can undergo self-condensation known as the aldol reaction
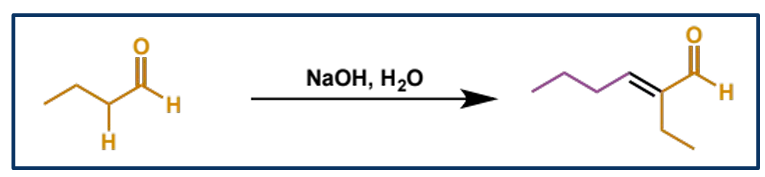
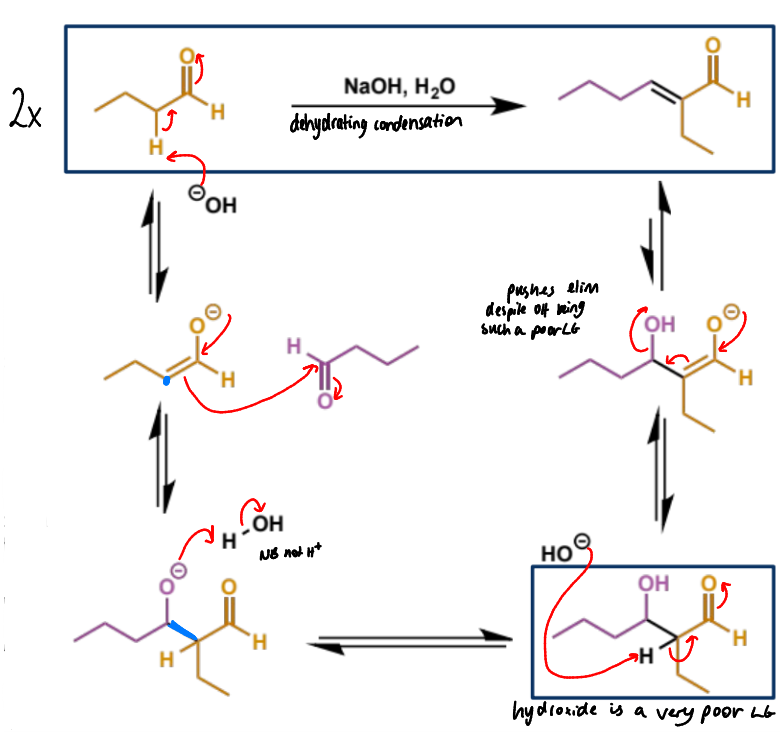
overall equation for the aldol reaction of butanal

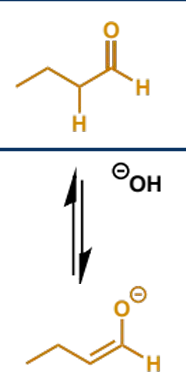
mechanism + product
comment on equilibrium?
only a small equilibrium population of enolate is formed, but aldehydes + ketones are powerful electrophiles and can trap the enolates
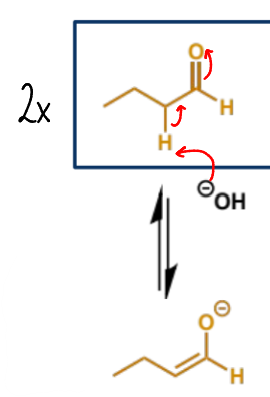
mechanism + product
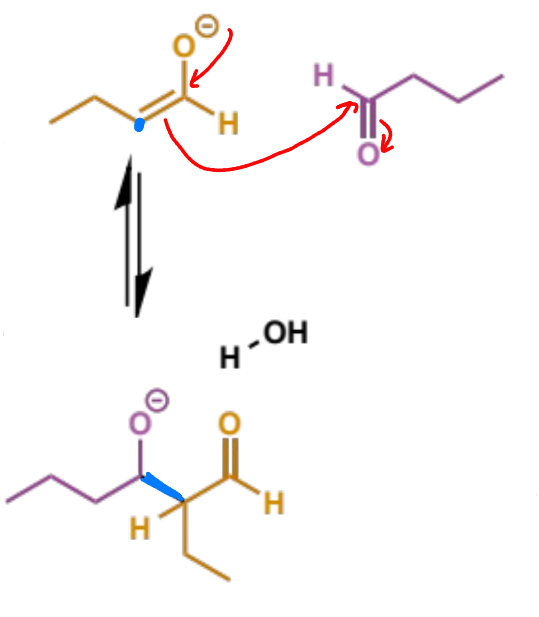
mechanism + product

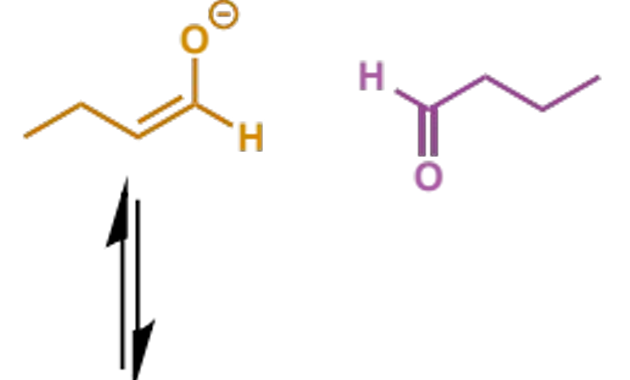
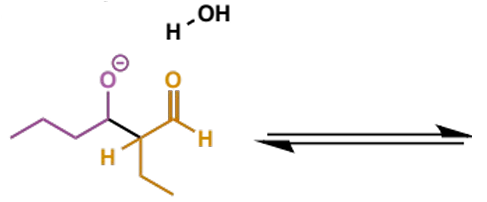
where does the name aldol come from
initial adduct from aldehydes is an aldehyde-alcohol (although this name is also used for the reactions of ketones)
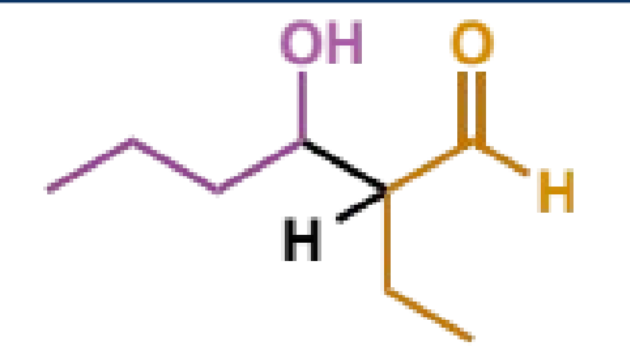
mechanism + product
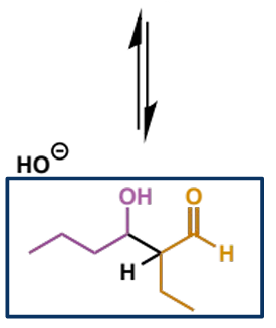
why is this step important
rather than stopping at the aldol, the reaction will usually continue to enolate formation which triggers E1cb elimination (next step)
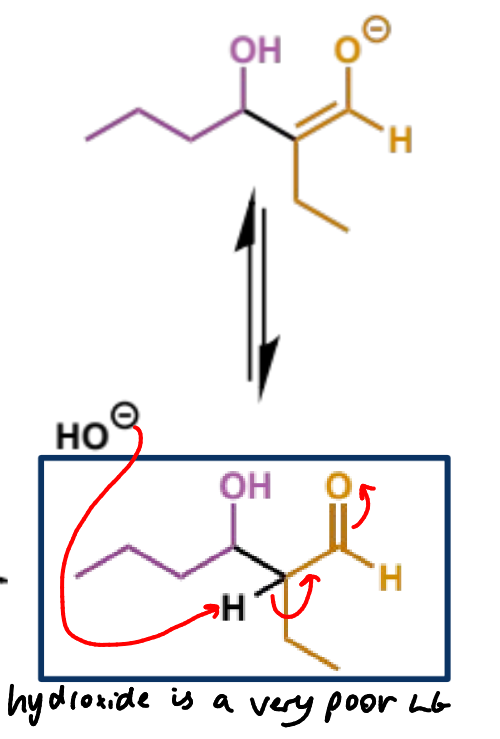
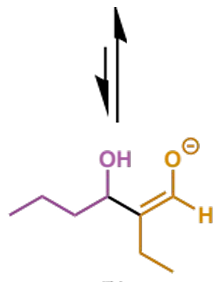
mechanism + product
name of mechanism
name of product
what drives this step
E1cb (conjugate base) elimination which gives the stable, conjugated enal product - note this is different to an E2 elimination
OH leaving pushes the elimination despite it being a poor leaving group
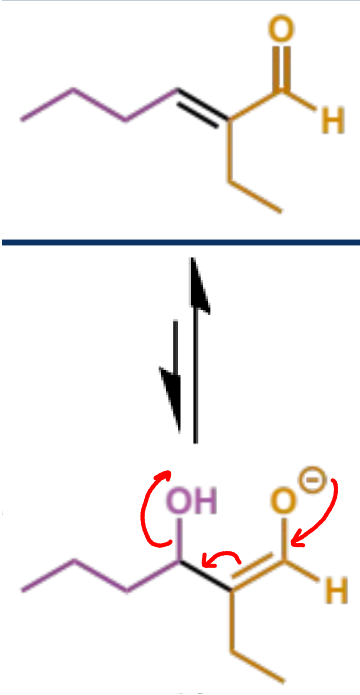
mechanism
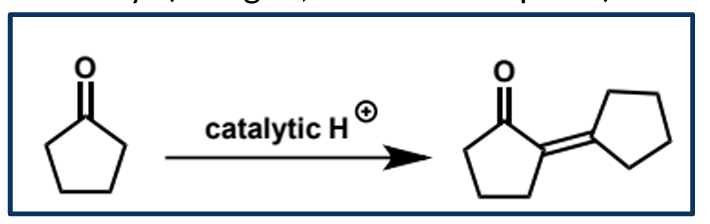
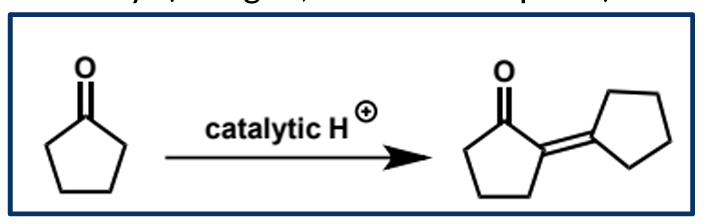
acid catalysed aldol condensation - what type of acid is needed and why
enols act as electrophiles in the presence of strong acid - strong acid is needed since the enol is not nucleophilic enough to attack the neutral carbonyl so a protonated carbonyl is needed as it is charged and more electrophilic
overall equation for acid-catalysed aldol condensation
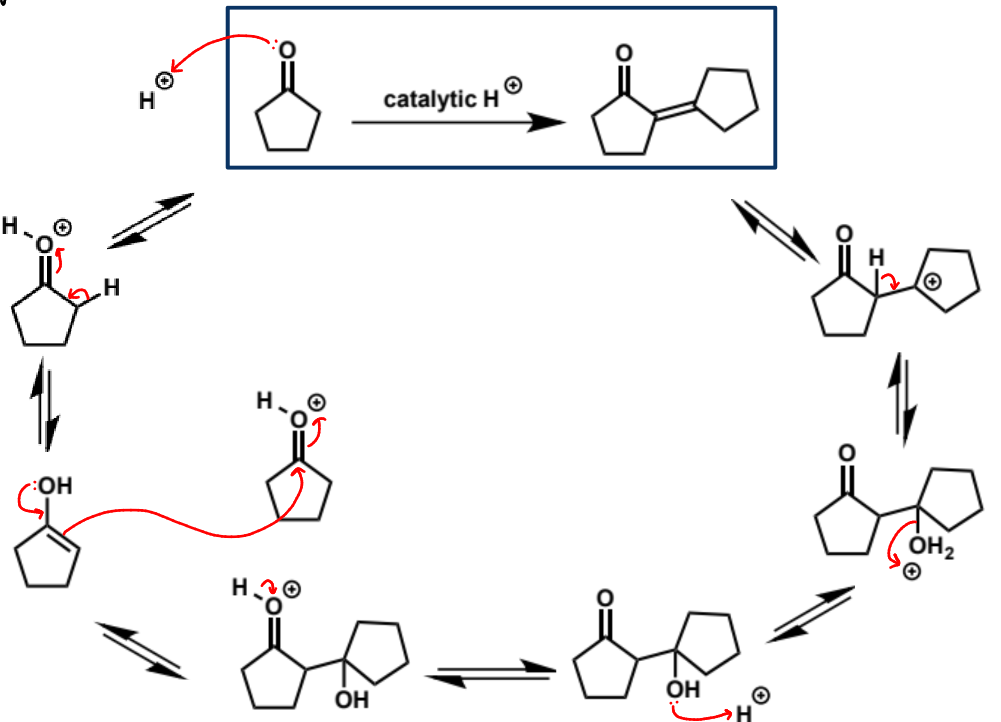
step 1 in acid catalysed aldol condensation

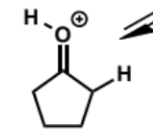
next stage of aldol condensation
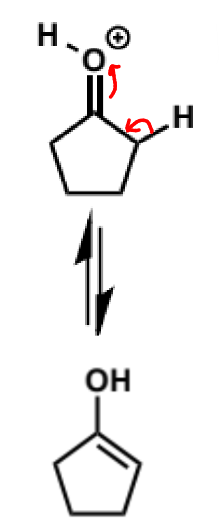
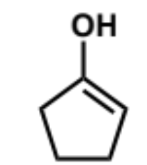
next step of aldol mechanism + product + conditions
this molecule is a good nucleophile but it is not as reactive as enolates - carbonyls don’t react alone with enols as they are not electrophilic enough but they will when they are catalysed and hence protonated - the second molecule MUST be protonated for the reaction to happen
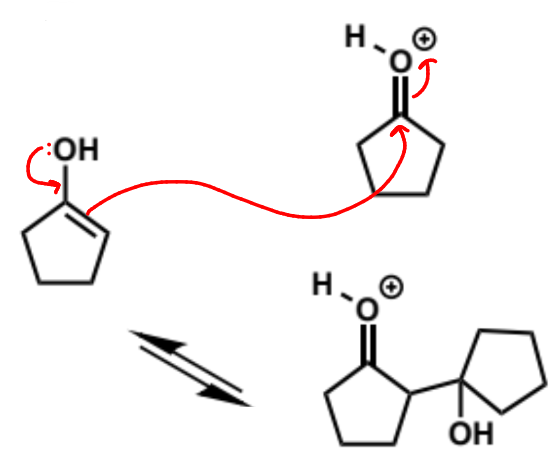
mechanism + product


mechanism + product
why is this step necessary
makes OH into a viable leaving group

next step in aldol condensation
E1 elimination (part 1)
mechanism + products
full mechanism
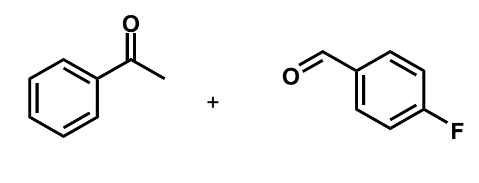
what are crossed aldol reactions
reactions where the enolate and carbonyl come from different starting materials
these are much more useful but can lead to problems
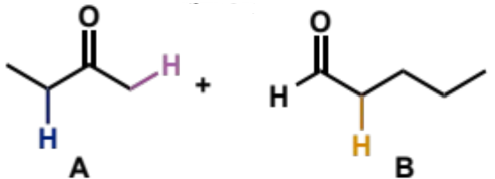
when do crossed aldol reactions work and why (think choice of reactants)
only work well when only one partner can form an enolate to prevent a mixture of products from forming, and additionally the compounds are well distinguished as electrophiles as if there are multiple enolates or electrophiles, this will lead to the complex mixture of products
this usually means choosing a monoenolisable or symmetrical ketone and reacting it with a non-enolisable aldehyde
show product + conditions and identify nucleophile and electrophile
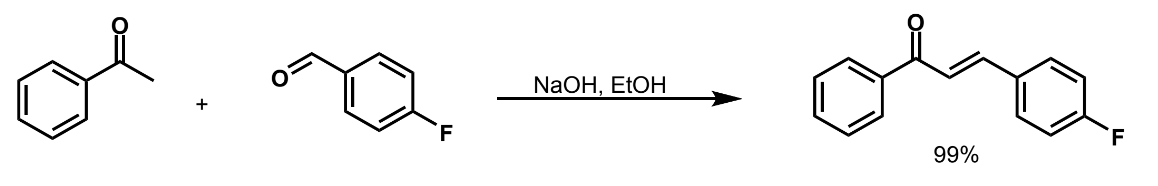
what makes a position enolisable
the presence of H atoms on a C next door to the carbonyl
how to achieve crossed aldol reactions with problematic carbonyls
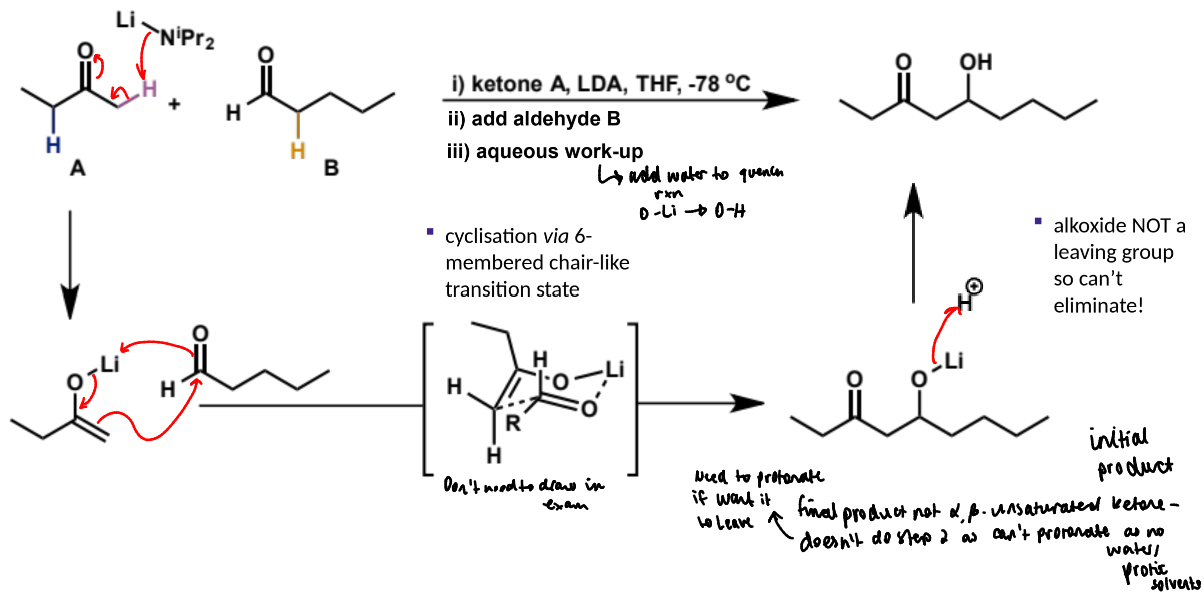
irreversibly form the lithium enolate of one carbonyl (usually the ketone) first
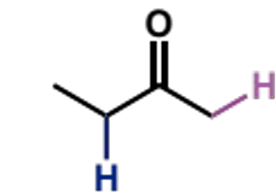
show mechanism for the pre-formed lithium enolate
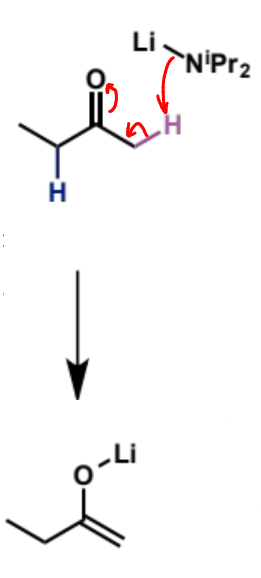
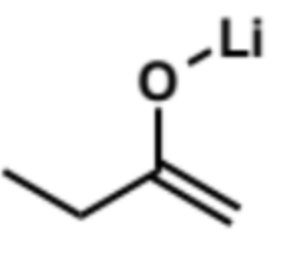
reaction with pentanal
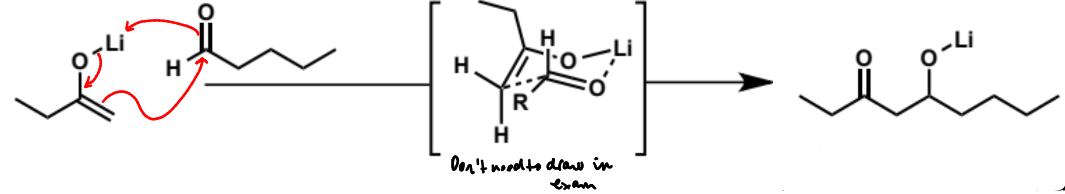
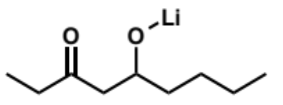
final step of crossed aldol reaction, why done and what is product
final product is not an α,β-unsaturated ketone as the alkoxide group is not a leaving group so cannot eliminate. in order for it to eliminate it would need to be protonated but there is no water or protic solvent to do this
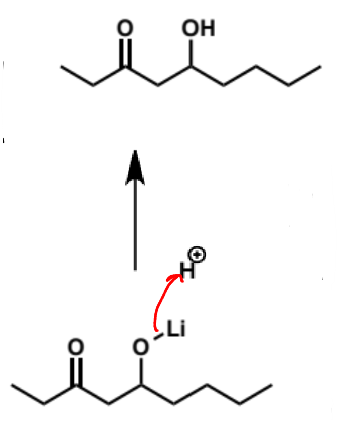

what is step (i)
ketone A, LDA, THF, -78°C

what is step (ii)
add aldehyde B

what is step (iii)
aqueous work-up (add water to quench reaction and convert O-Li to O-H)
overall equation for reaction between these carbonyls


full mechanism for reaction between these carbonyls
for crossed aldol reactions with pre-formed lithium enolates, how can you ensure the crossed-aldol is the only product
prevent equilibrium using solvent and temperature choice
for crossed aldol reactions with pre-formed lithium enolates, whic product is formed
the less hindered/substituted enolate due to kinetic control
alternative approach to pre-formed lithium enolates for problematic crossed aldol reactions
silyl enol ethers - a stable equivalent of enols
how is silicon effective in making silyl enol ethers
forms very strong bonds to oxygen and can be used to trap very small concentrations of enolates formed when using a very weak base
favoured enolate from silyl enol ethers and why
at high temperatures, equilibrium is achieved so the more substituted thermodynamic enolate is favoured and more of this is trapped by the silicon to form more of the more substituted silyl enol ether
why does the conversion from enolate to silyl enol ether work
O-C = ca. 360 kJ mol-1
O-Si = ca. 450 kJ mol-1
reagents and conditions for production of silyl enol ethers
explain choice of solvent and temperature
solvent chosen as polar, temp chosen as DMF has high BP
equation for production of silyl enol ethers
what is unusual about this reaction
the nucleophile attacks the O and not the C, which is unusual in organic reactions
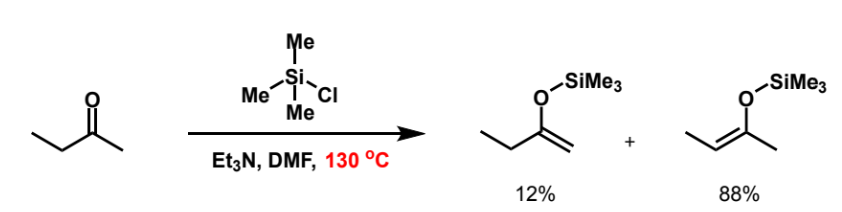
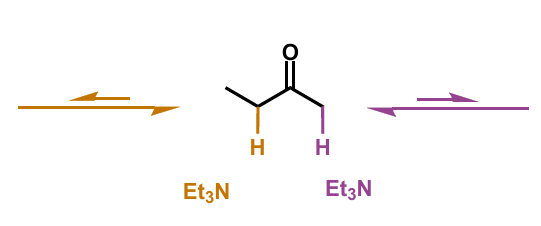
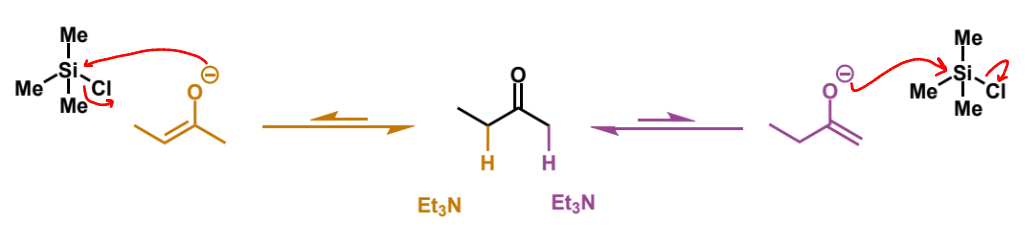
complete to show possible products
which is favoured?
left hand product is more substituted and thermodynamic product so it is favoured
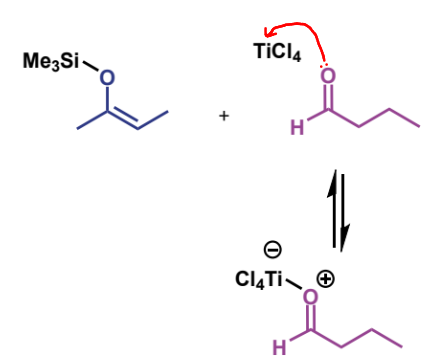
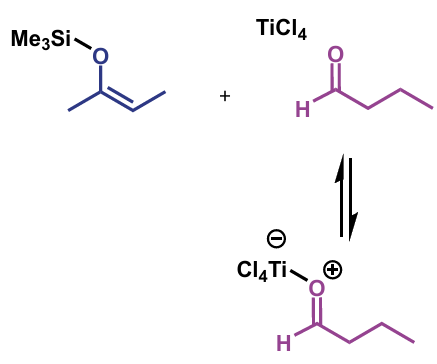
conditions for reaction between silyl enol ether and carbonyl
example? how does it react?
silyl enol ethers are not nucleophilic enough to attack a carbonyl compound on their own so the reaction is promoted by Lewis acid catalysts
example = TiCl4. O donates lone pair to Ti giving it a negative charge (and the O is positive)
product of crossed aldol with silyl enol ethers
non-eliminated aldol adducts, as with pre-formed lithium enolates

first step of crossed-aldol reaction
next step in mechanism
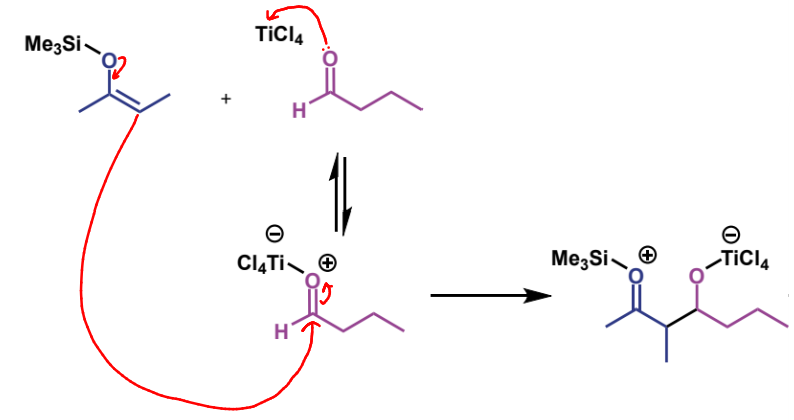
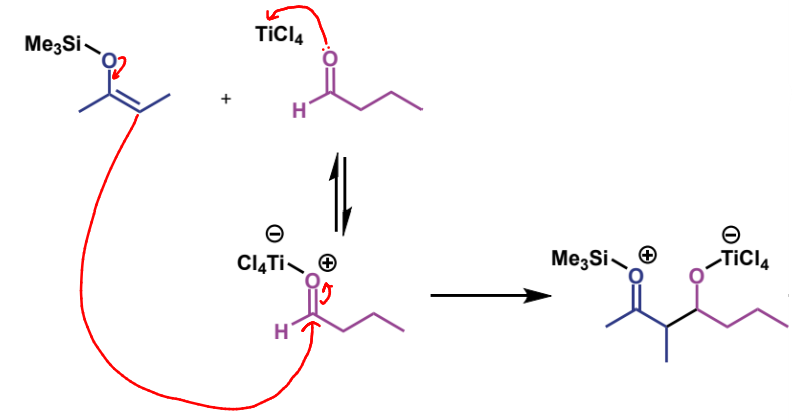
next step in mechanism
name of product
trimethylsilyl ether
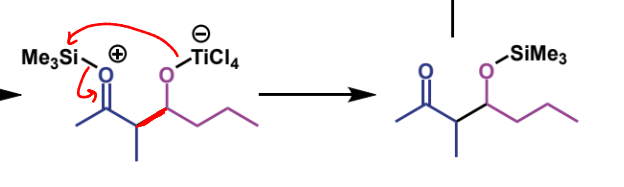
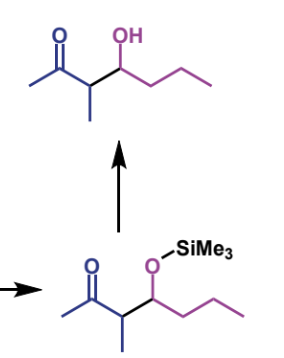
how is this final step achieved + how does it work
water workup - hydrolyses ether
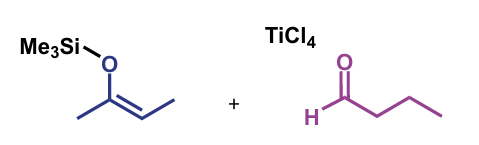
full mechanism for crossed aldol
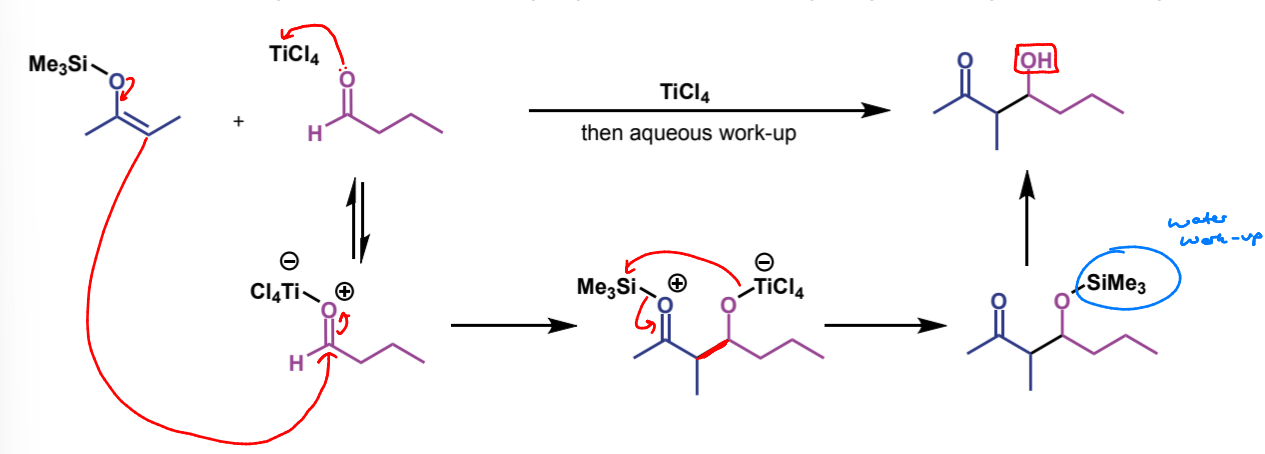
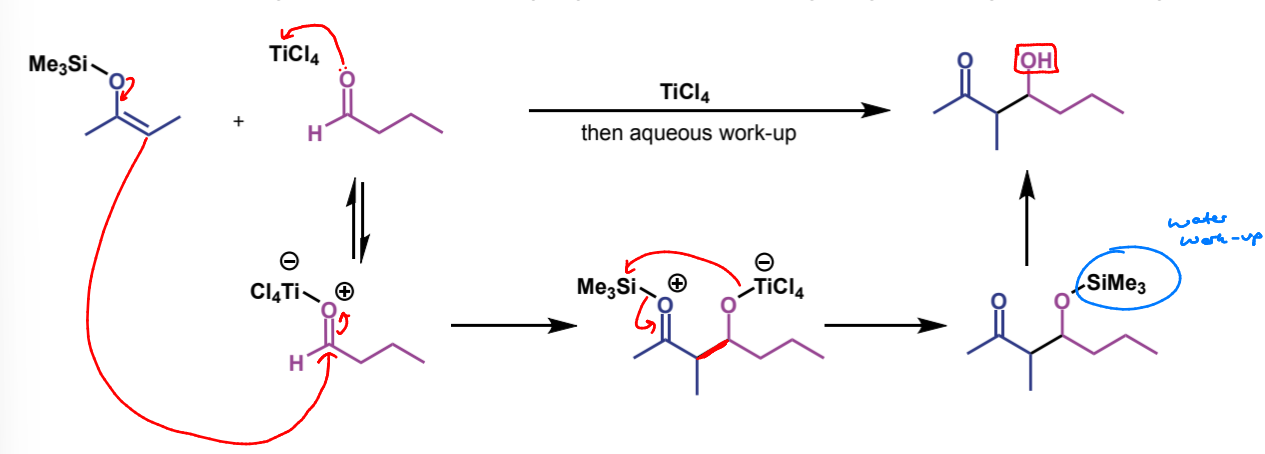
how would the product be different if LDA was used instead
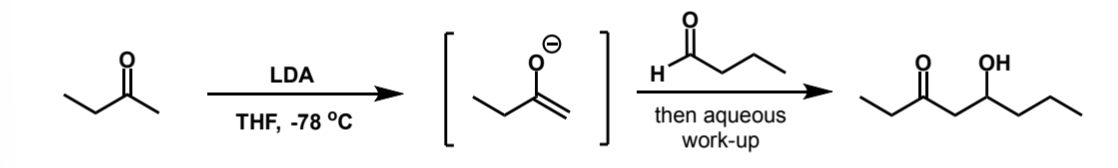
how are the products of crossed aldol reactions with LDA vs silyl enol ethers
LDA gives the less-substituted kinetic enolate, whereas silyl enol ethers give the more substituted thermodynamic enolate
what are intramolecular aldol reactions useful for? are they selective?
how are they catalysed?
powerful way to construct rings - selectivity is observed for forming five or six membered rings - smaller or larger rings are disfavoured. this is because five and six membered rings have less strain than smaller rings and are more substituted than larger rings
the reactions work under acid or base catalysis
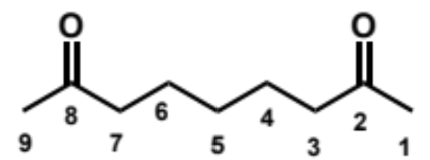
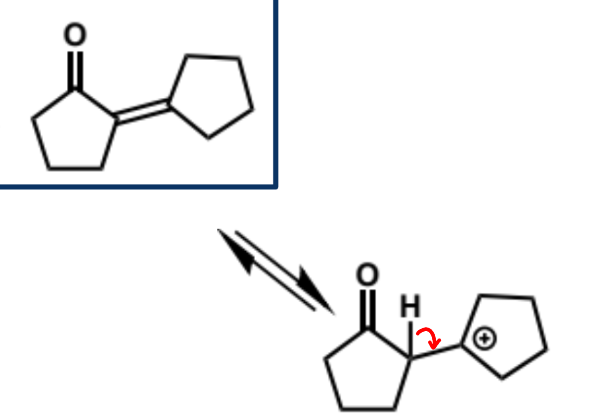
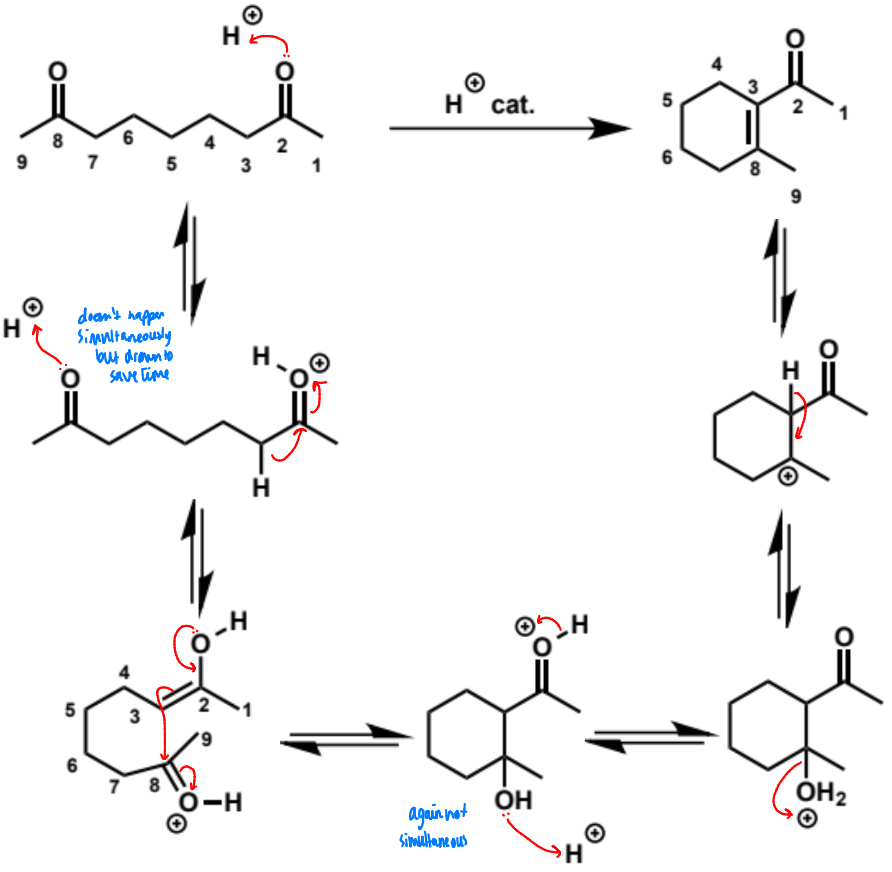
overall equation for intramolecular aldol here (acid conditions)
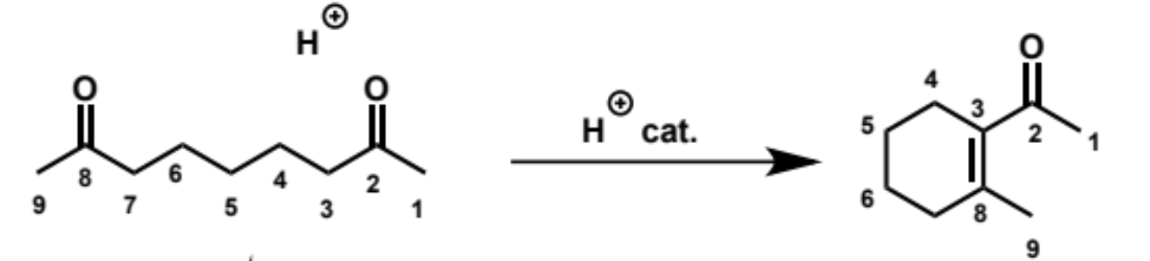
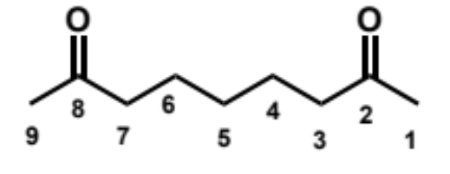
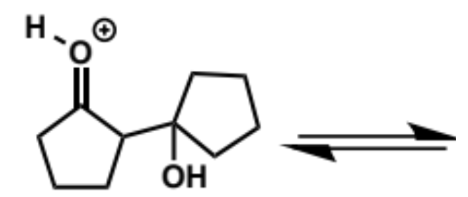
first step in intramolecular aldol reaction (acid conditions)

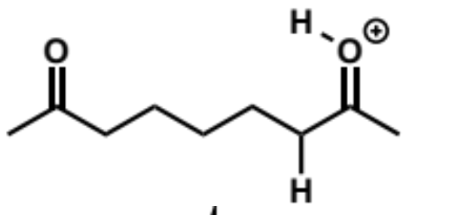
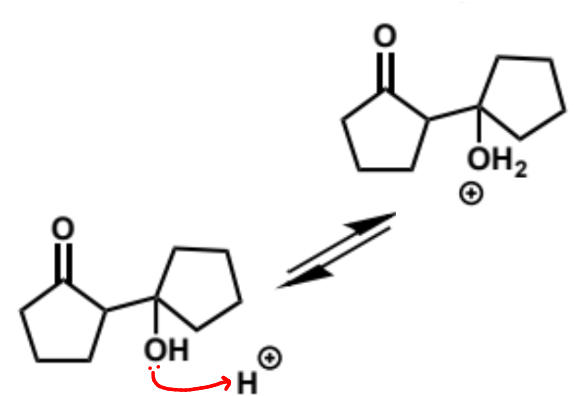
next stages of intramolecular aldol (acid conditions)
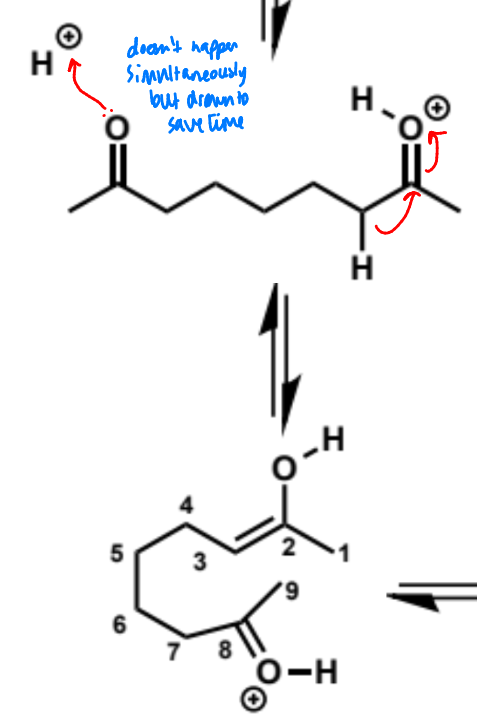
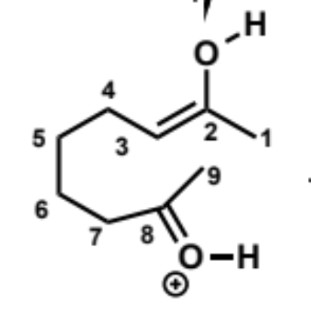
next stage of intramolecular aldol (acid conditions)
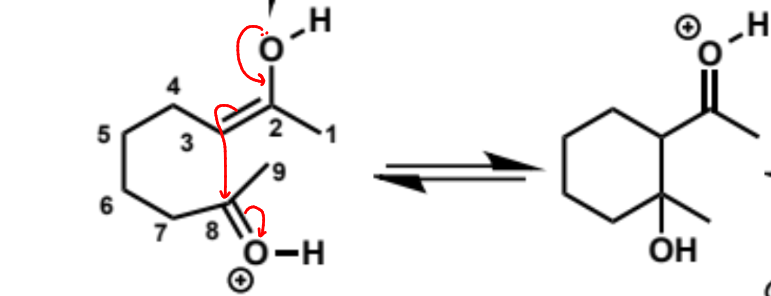
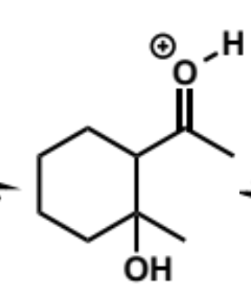
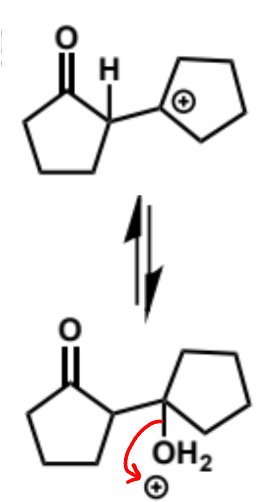
next stages of intramolecular aldol (acid conditions)
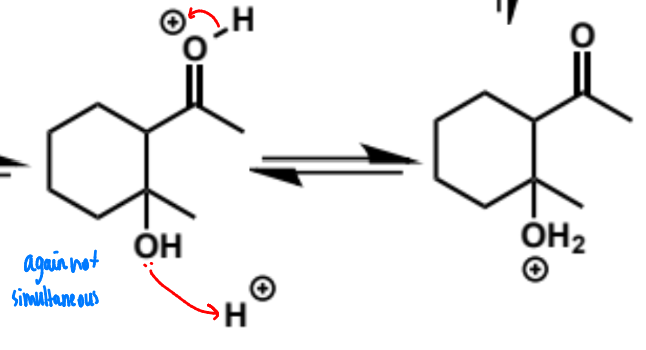
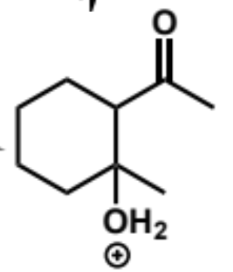
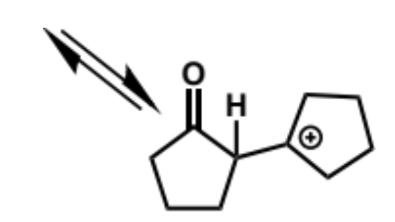
next stage of intramolecular aldol (acid conditions)
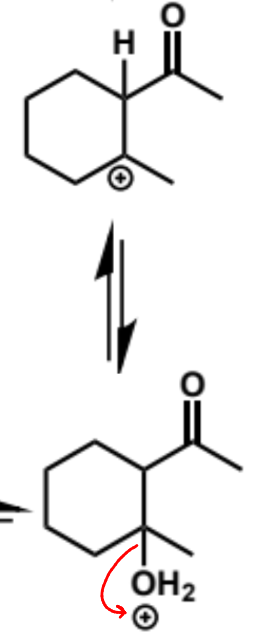
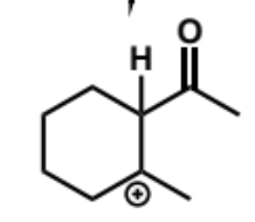
final stage of intramolecular aldol (acid conditions)
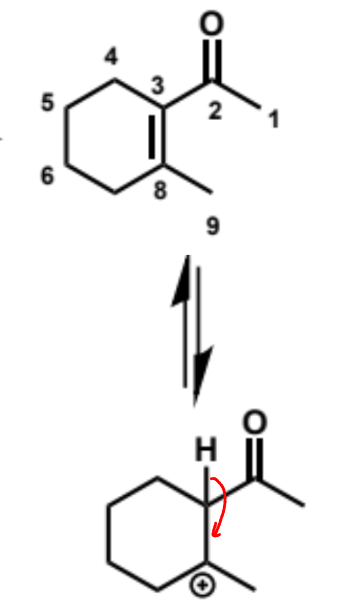

show mechanism
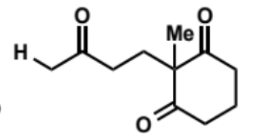
overall equation for intramolecular aldol (basic conditions)
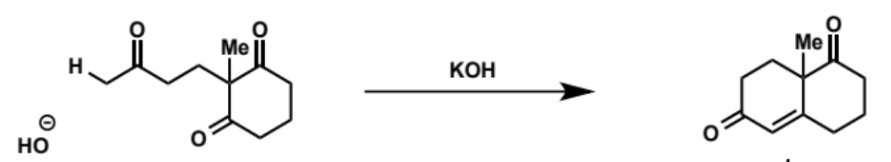
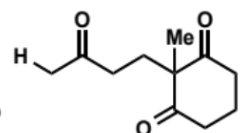
first stage of intramolecular aldol (basic conditions)
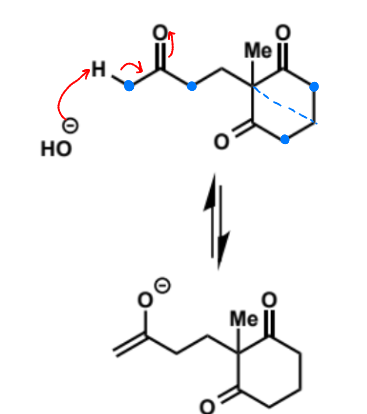
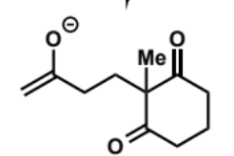
next stage of intramolecular aldol (basic conditions)
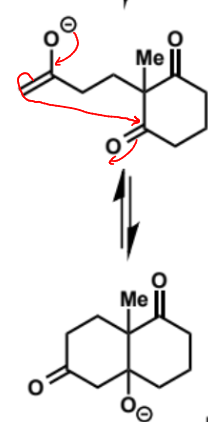
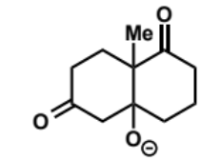
next stage of intramolecular aldol (basic conditions)

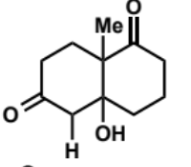
next stage of intramolecular aldol (basic conditions)
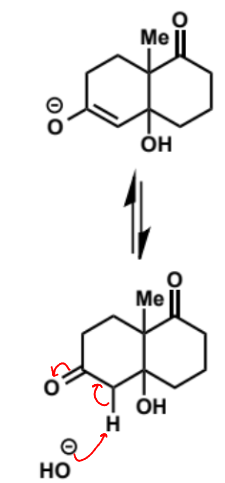
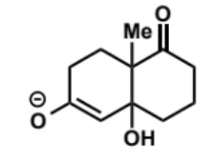
next stage of intramolecular aldol (basic conditions)
name of step
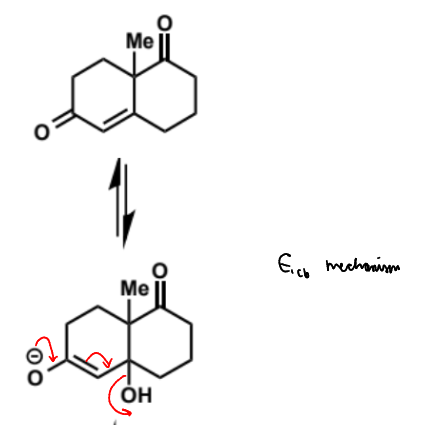
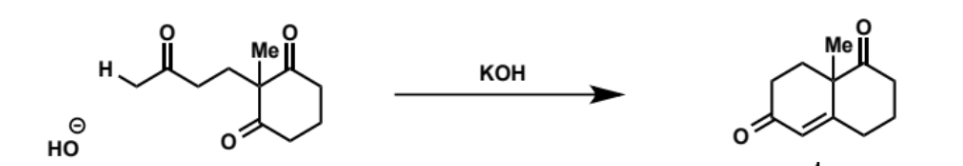
show mechanism
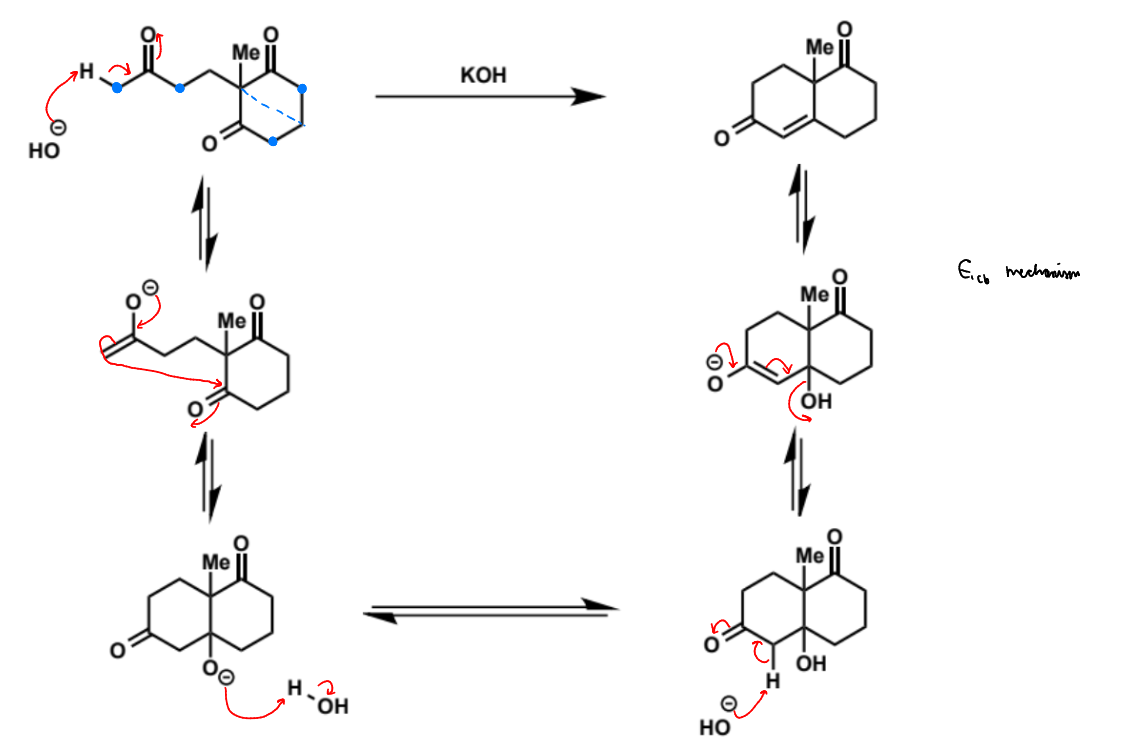
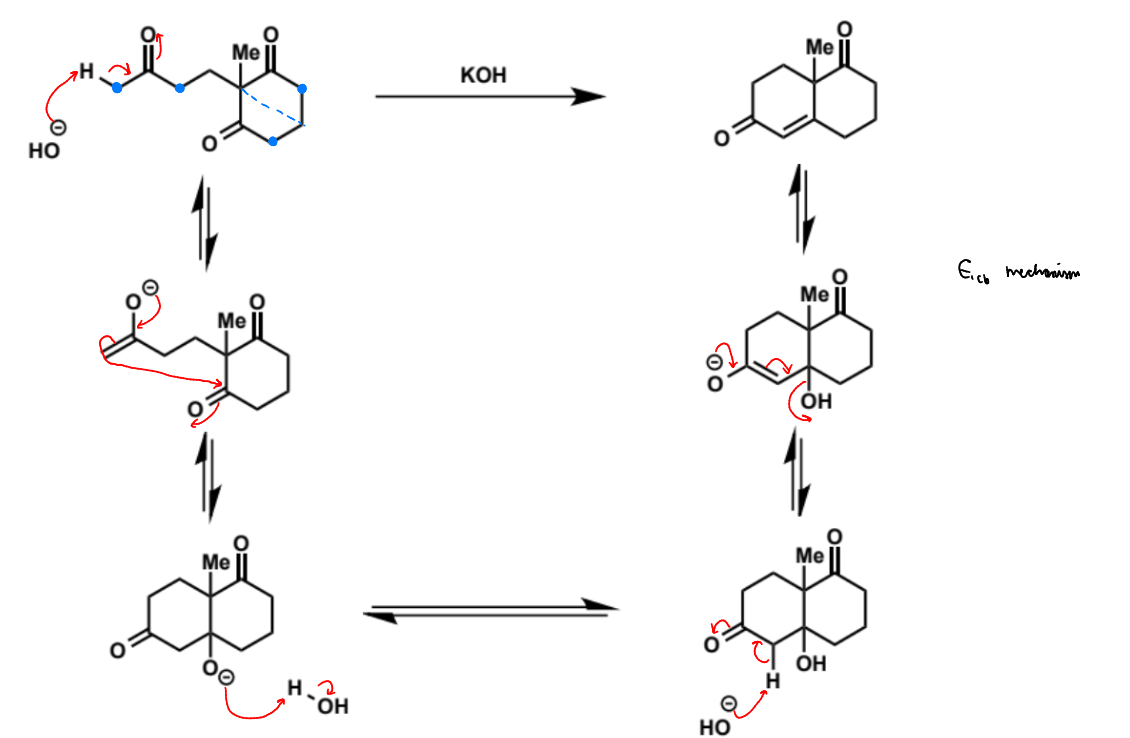
possible other products of this mechanism and why the reaction is selective