Chapter 19, Lesson 4: Electrical and Contractile Activity of the Heart
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 19, Lesson 4 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Tenth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Heart cycles
Done through contraction and relaxation
Systole
The contraction of the heart
Diastole
The relaxation of the heart
Sinus rhythm
Normal heartbeat by the SA node, around 70-80 per minute
Ectopic focus
A region of spontaneous firing other than the SA node, may govern rhythm if damaged
Nodal rhythm (junctional rhythm)
A type of ectopic focus where the AV node sets the heart rate
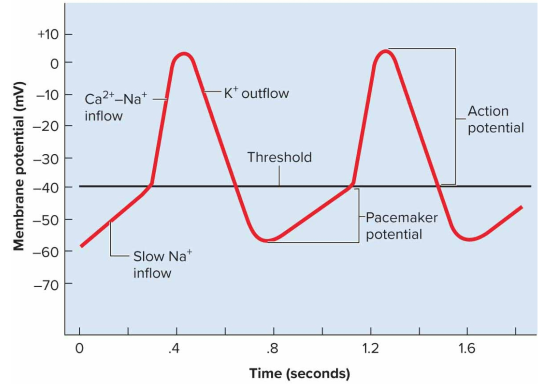
SA node firing (Sinuatrial node firing)
Done through depolarization and repolarization to set off heartbeat, usually every 0.8 seconds
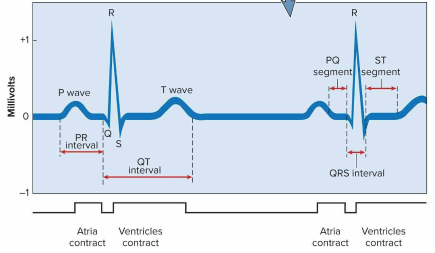
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
A composite of all action potentials of nodal and myocardial cells detected as a result of firing and signals; comprises of letters PQRST for marking
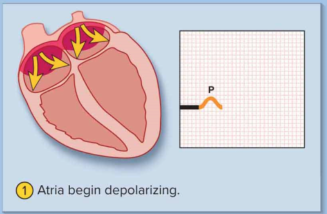
P wave
The intial depolarization of the atria to trigger an atrial systole
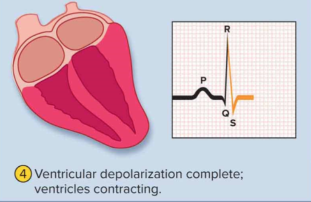
QRS complex
Depolarization of the ventricles, where ventricular systole begins shortly after
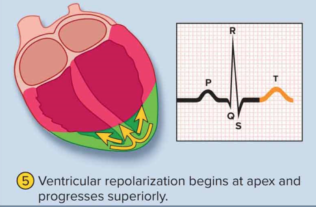
T wave
Repolarization of the ventricles immediately prior to diastole
Ventricular fibrillation
Random signals result in no pumping action, can result in myocardial infarction and fatality
Atrial fibrillation (AFib)
Weak rippling contraction in atria due to chaotic signals; atria fail to stimulate ventricles
Heart block
Failure of part of conduction system; includes bundle branch block and total heart block
Myocardial infarction
Commonly known as a heart attack; heart stops pumping action