3.3 Revenues, costs, and profits
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Revise this BEFORE 3.3 Business objectives
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
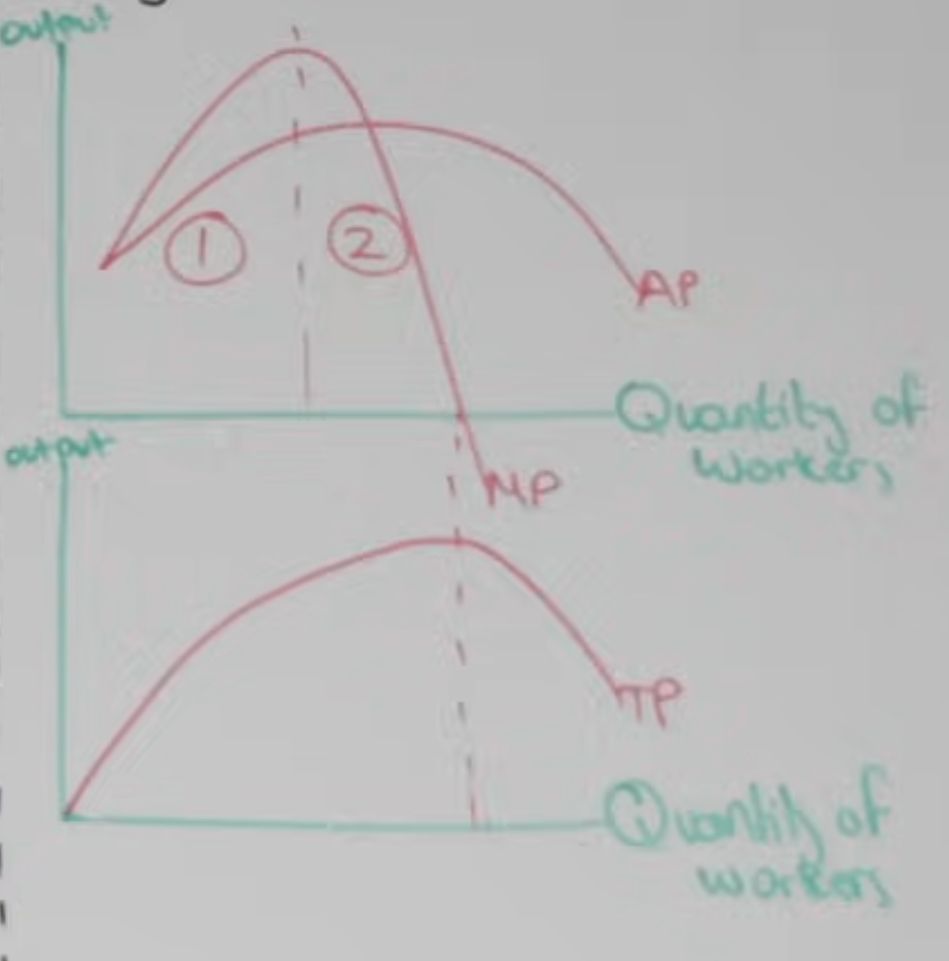
Law of diminishing marginal returns
In the SR when variable factors of production(labour) are added to a stock of fixed factors of production, total/ marginal product (output) will initially rise and then fall.
Rises at first due to specialisation+underutilisation of FoP→higher labour productivity→more output
Falls afterwards due to limited land + capital(FoP) which become a constrain on production→lower productivity→less output
Total revenue
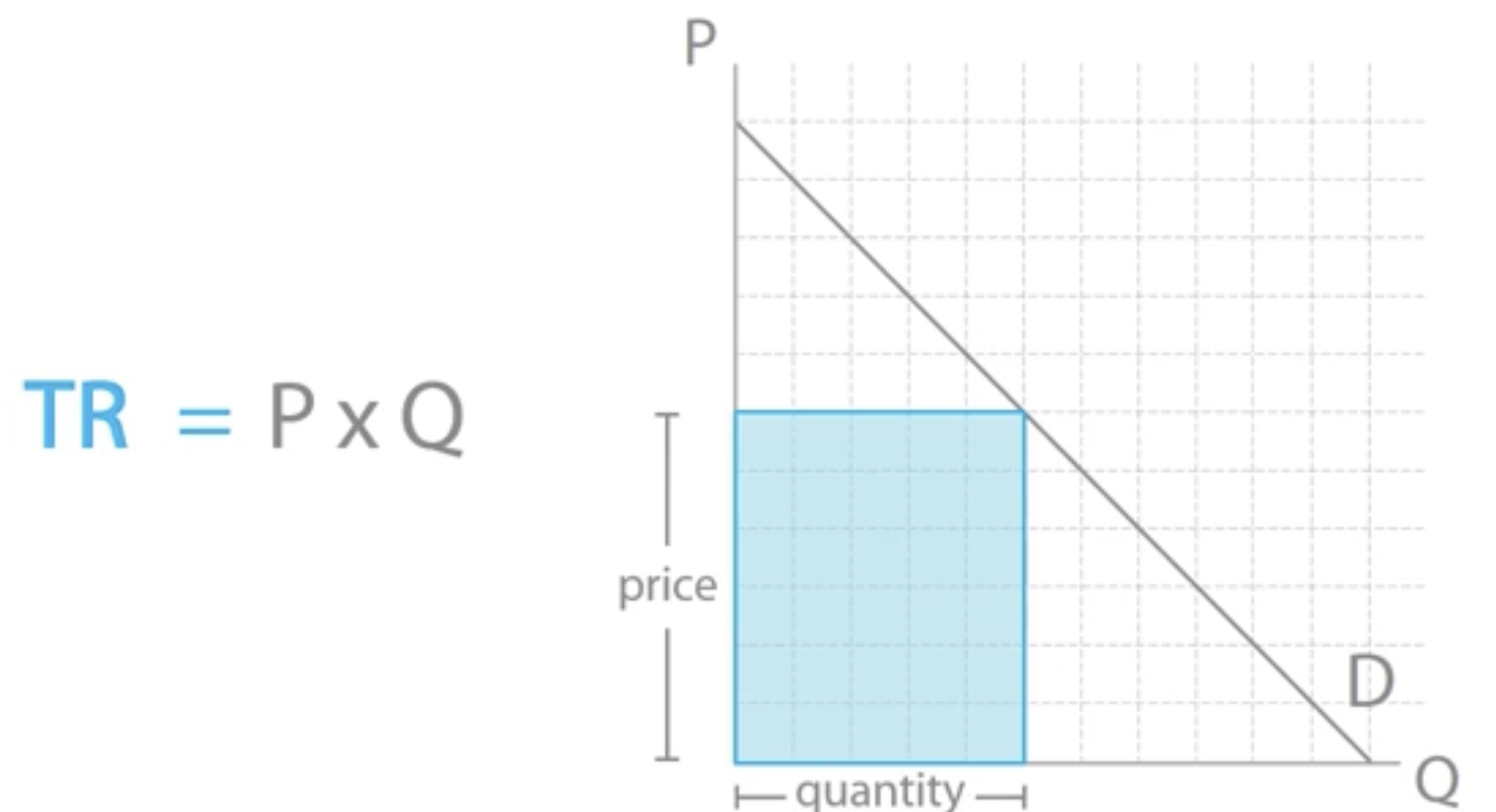
Total money made by sales by a business.
price x quantity sold
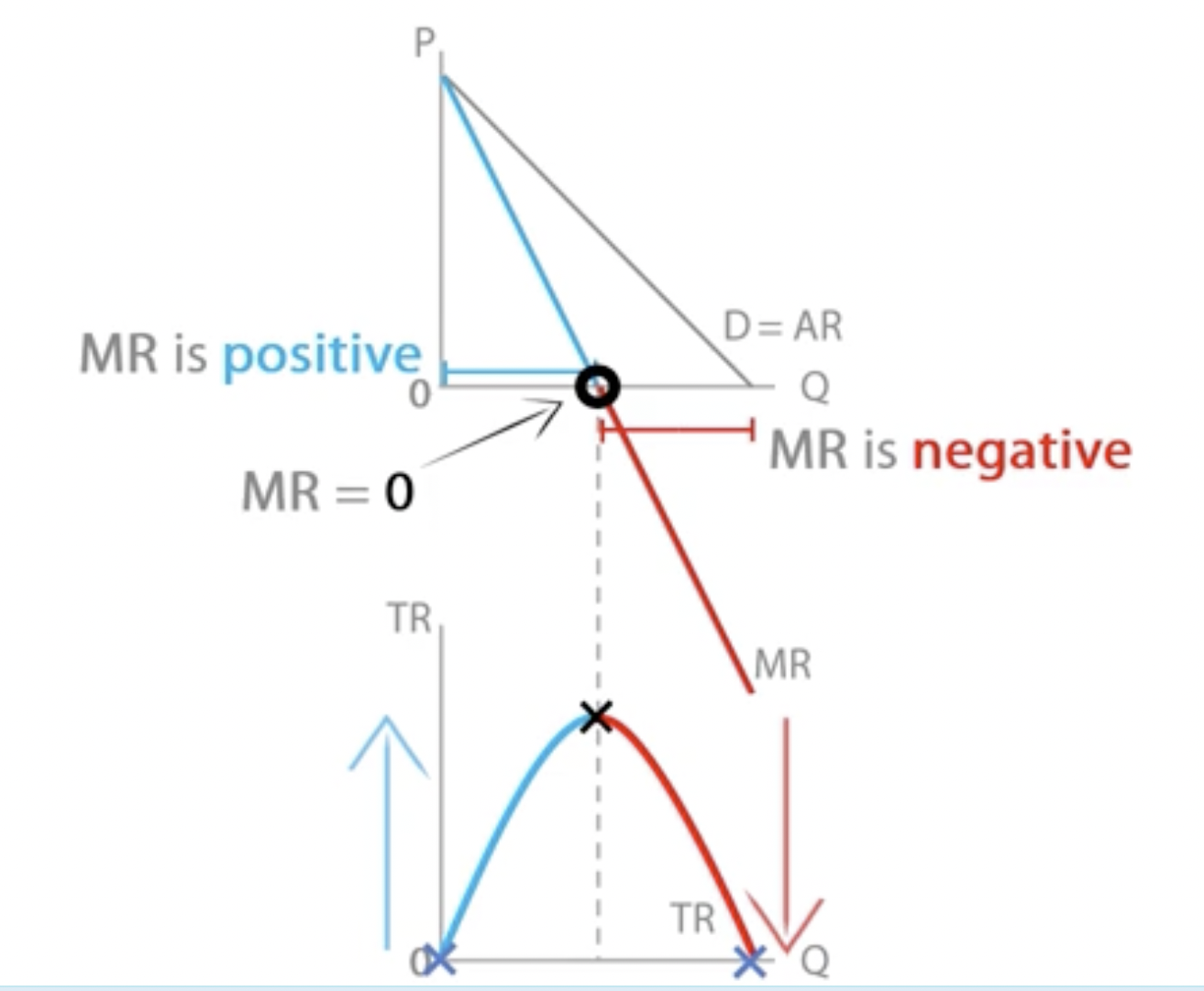
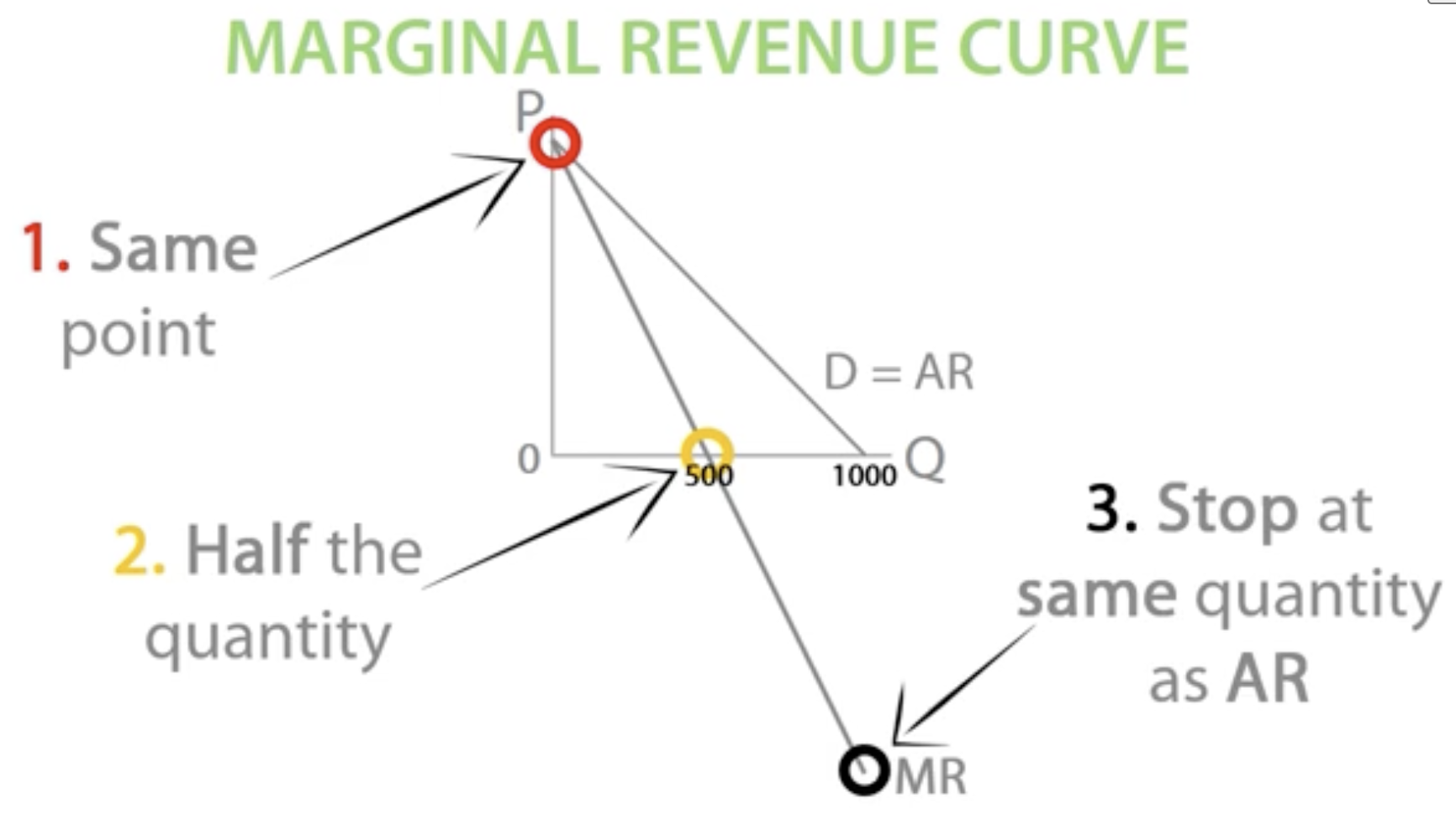
TR reaches its peak when MR = 0.
Average revenue
What a business receives on average from each sale it makes.
AR = total revenue / quantity
AR = price
AR curve = demand curve
Marginal revenue
Additional revenue a firm makes selling one extra unit of output.
change in TR / change in quantity
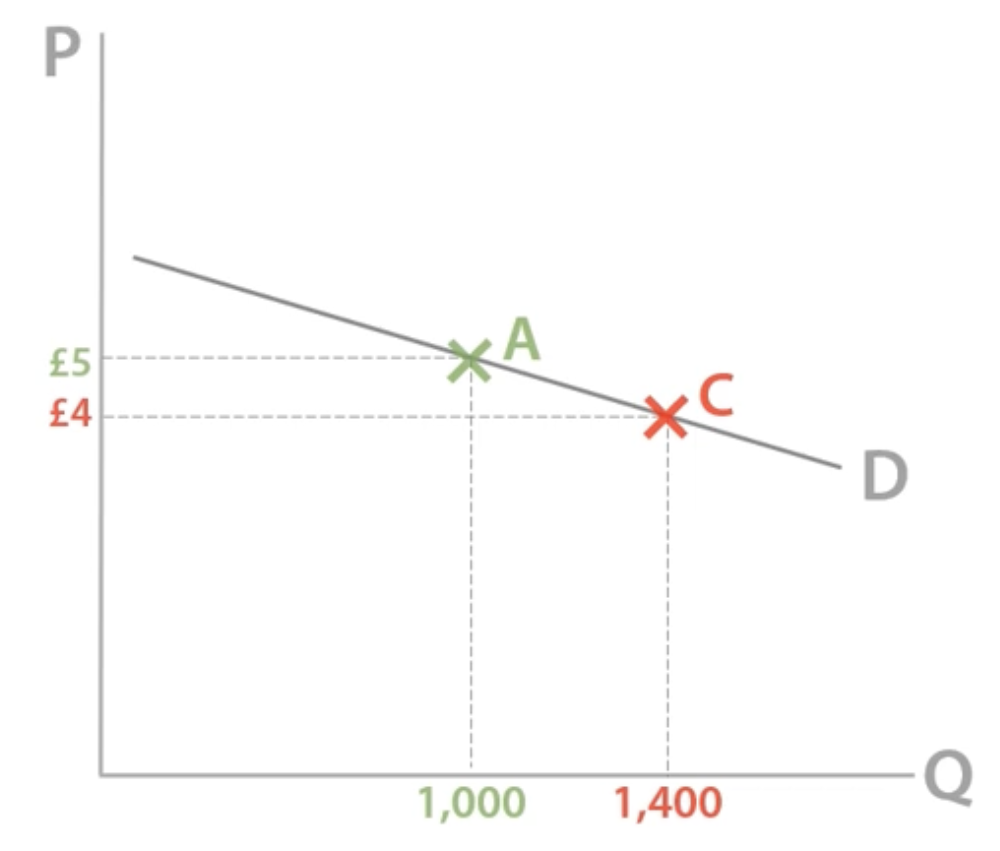
TR and price elasticity of demand
When price ↓ by a small %, quantity demanded ↑ by a larger %, increasing TR overall.
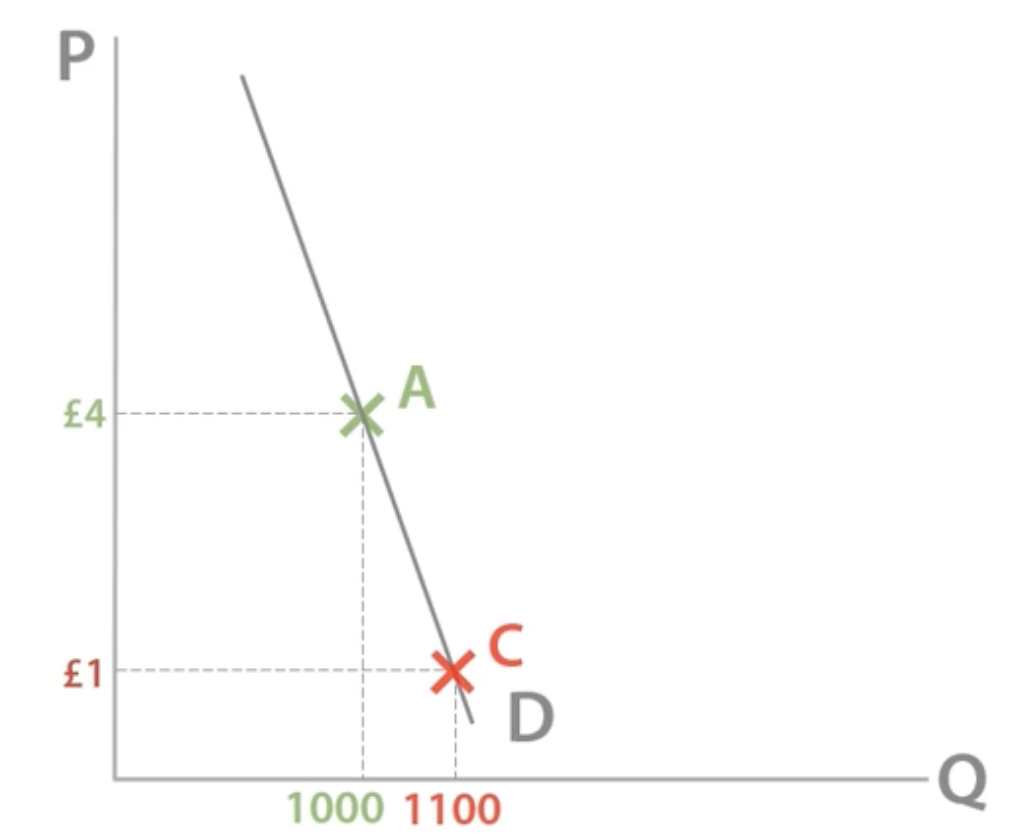
TR and price inelasticity of demand
When price ↓ by a larger %, quantity demanded ↑ by a small %, decreasing TR.
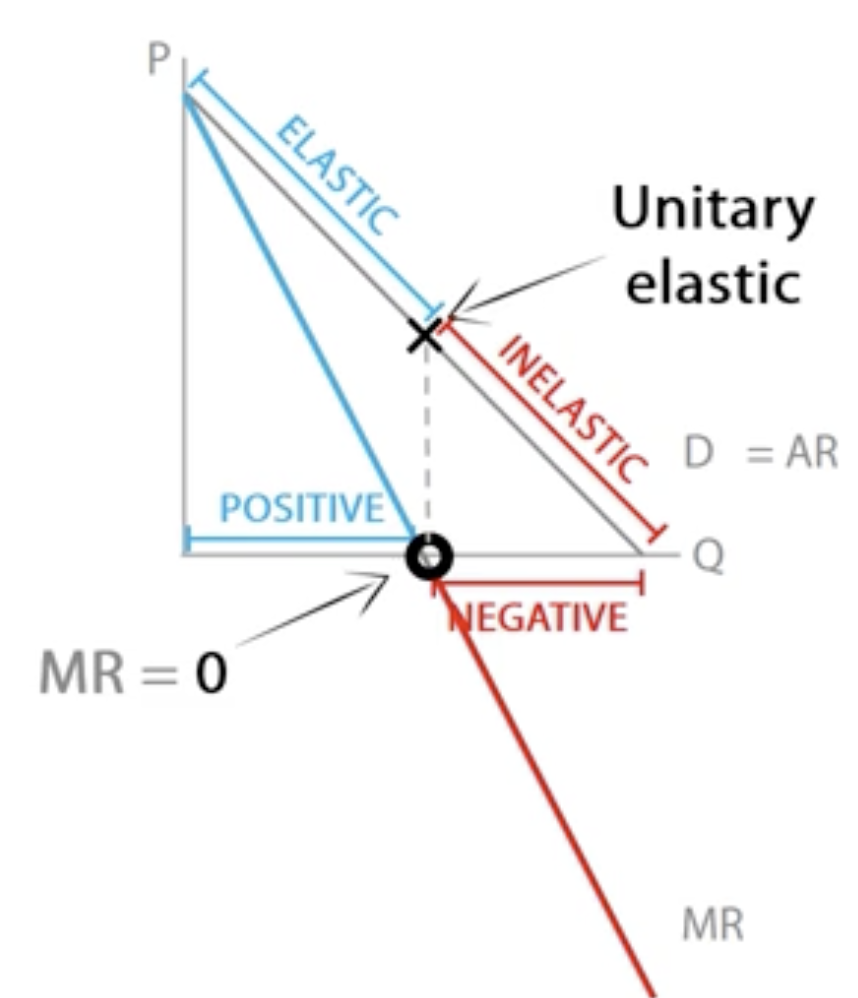
How does PED change along the demand curve
When price is low, a % change in price will have a small effect, so consumers will be unresponsive and demand will be inelastic.
Fixed + variable costs
Variable costs: costs vary with output
e.g. wages, raw material costs, utility bills
Fixed costs: costs that don’t vary with output
e.g. salaries, rent, interest on loans
In the LR, all factors become variable, so there are only variable costs.
In the SR, one factor must be fixed, so there are only fixed costs.
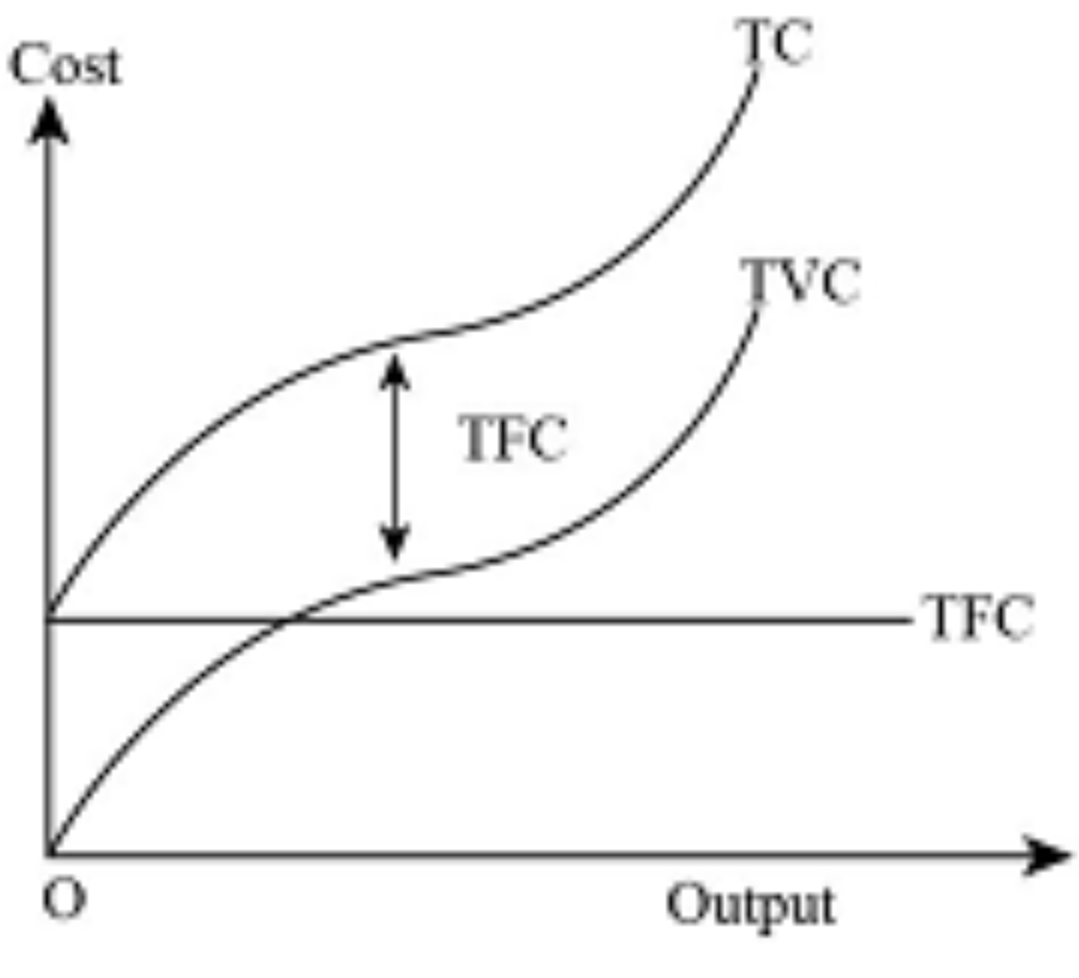
Total fixed cost (TFC)
TC-TVC or AFC x Q
Have nothing to do with law of diminishing marginal returns.
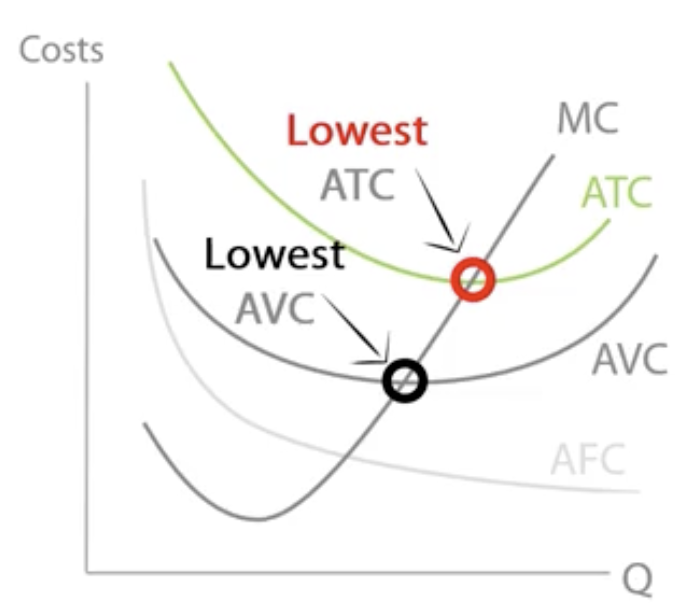
Average fixed cost (AFC)
TFC/ Q or AC-AVC
Decreases as TFC stays same while Q increases.
Have nothing to do with law of diminishing marginal returns.
Average variable cost (AVC)
TVC/ Q or AC-AFC
As you employ more workers, productivity increases, ↓AVC, then decreases as output decreases, ↑ AVC.
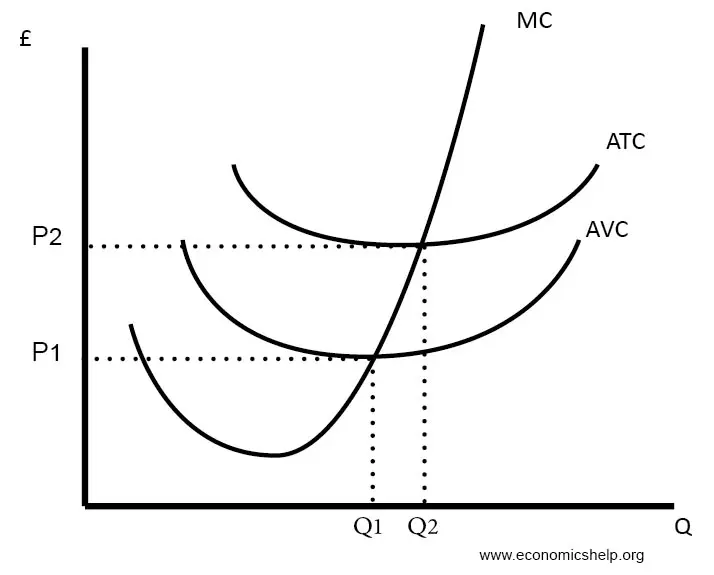
Marginal cost (MC)
∆TC/ ∆Q
The extra cost of producing one more unit of output.
-as labour productivity ↑, MP ↑, MC ↓ due to the higher productivity.
-as labour productivity ↓, MP ↓ and MC ↑ due to the lower productivity.
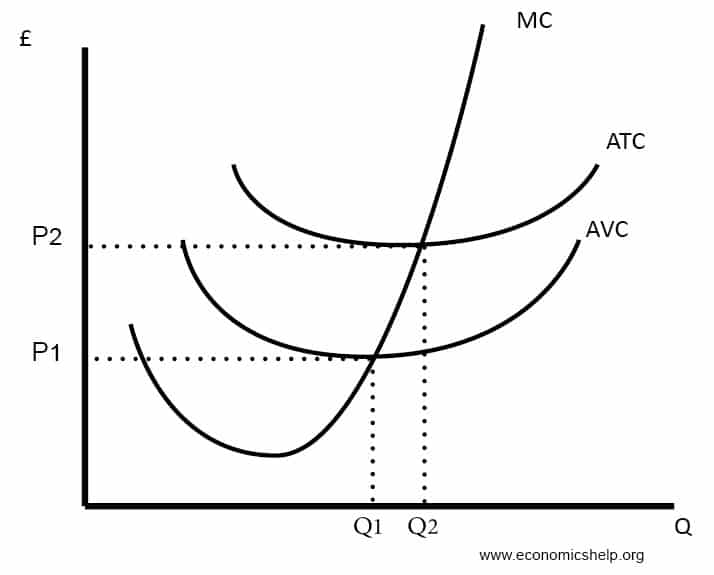
Average total cost/ average cost
TC / Q or AVC + AFC
TC,TVC,TFC diagram
TVC rises due to wages paid to workers being employed, slows down as they specialise in their roles so output increases greater than cost, then increases again due to law of diminishing returns.
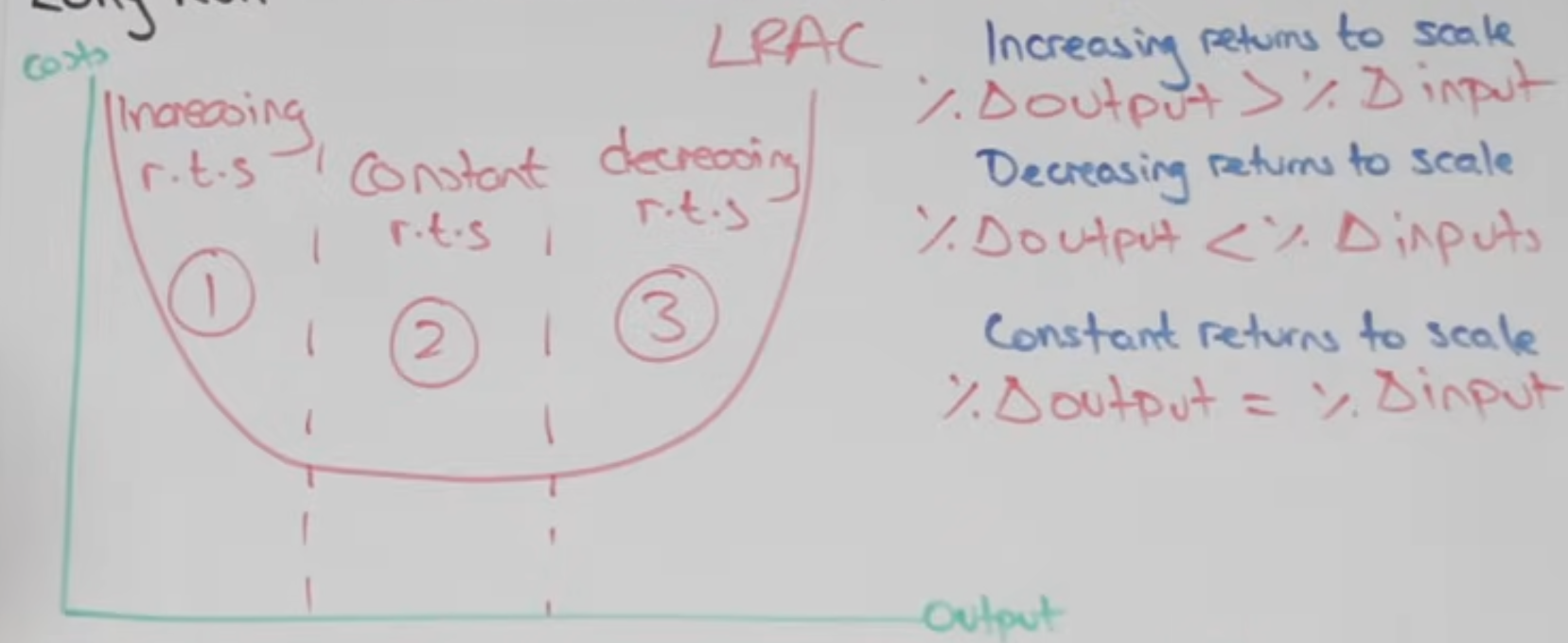
Long run average cost (LRAC) curve
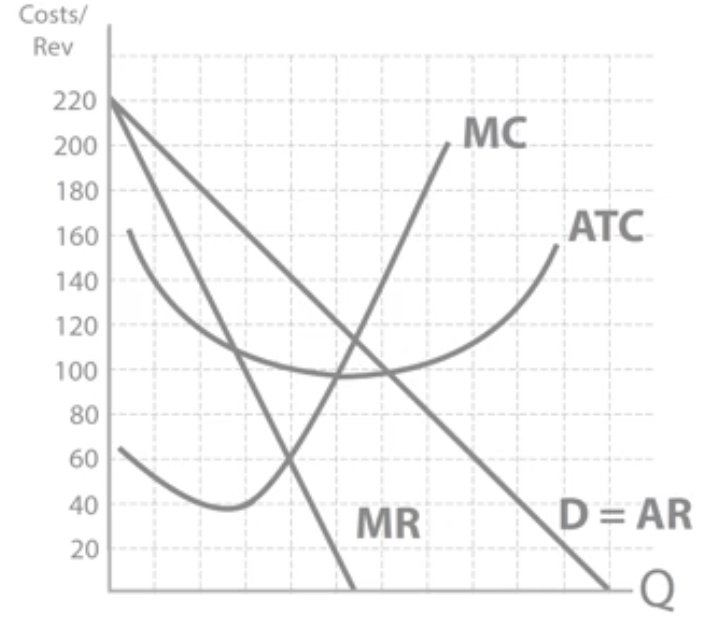
Costs + revenues diagram
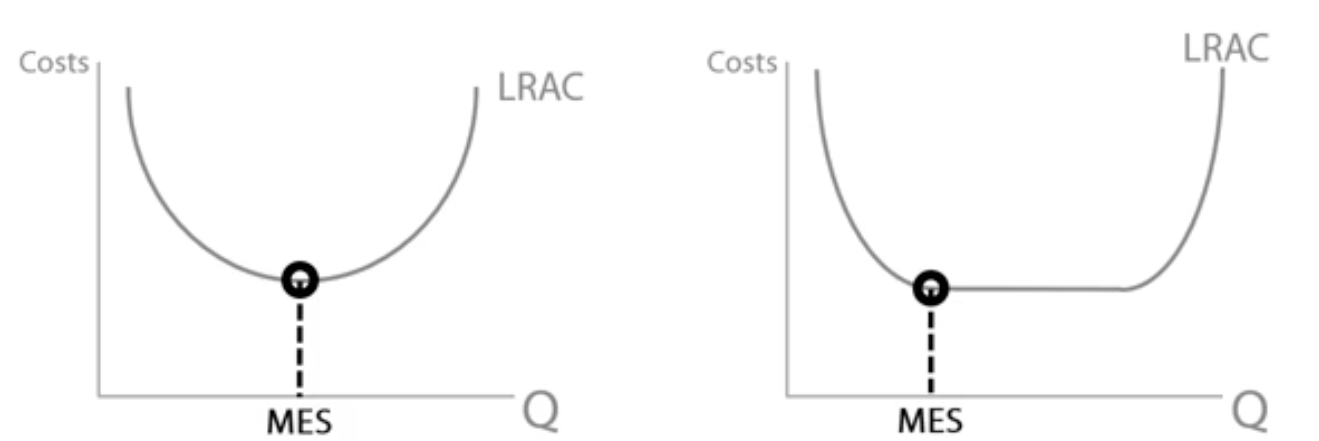
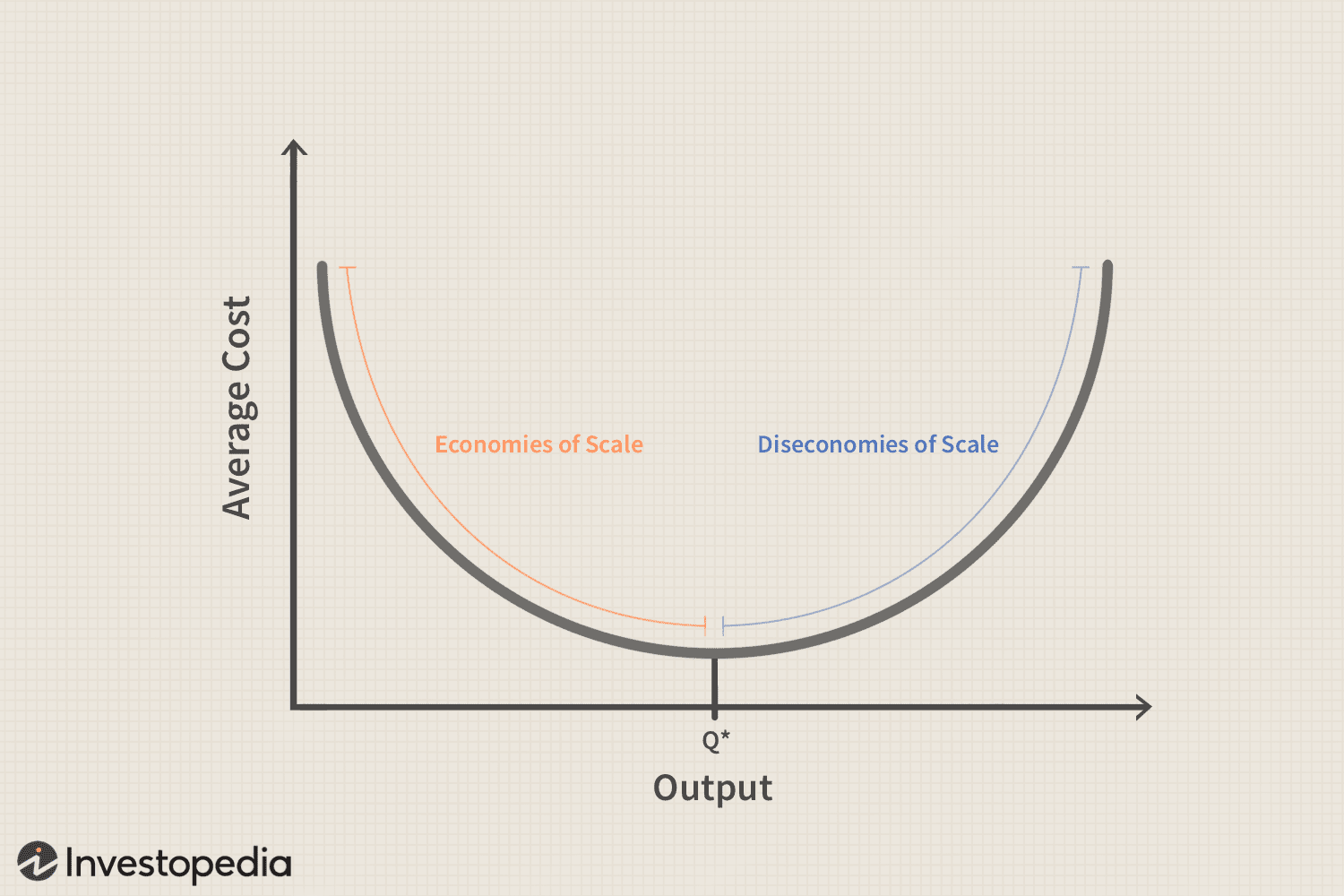
Minimum efficient scale (MES)
The lowest level of output required to fully exploit economies of scale.
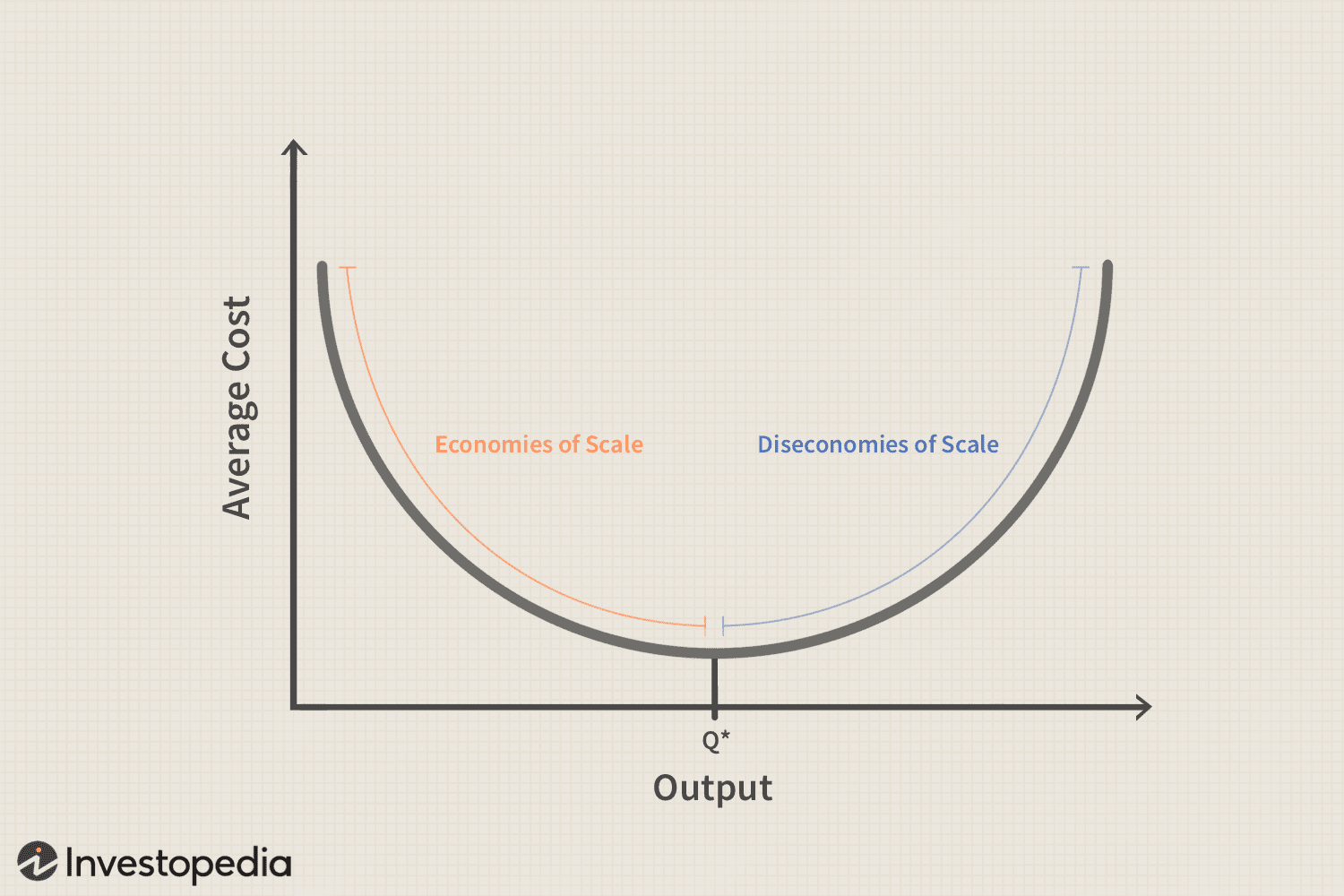
Economies of scale
Internal economies of scale
AC = TC↑/ Q↑↑↑
A reduction in LRAC as output increases.
Within a businesses control to reduce LRAC as their output increases.
TYPES:
Risk-bearing
Managerial
Financial
Purchasing
Technical
Marketing
Richard’s Mum Flies Past The Moon
Risk-bearing economies
Firm gets larger→spread risk of failure (opportunity cost) over larger range of output→ cost per unit of output decreases.
Managerial economies
Firm gets larger→employ specialist managers with specialist skills→boost productivity of workers→increases quantity + therefore output
Financial economies
Firm gets larger→negotiate lower rates of interest from bank as they are profitable + have proven success (lower risk)→ reducing costs
Purchasing economies
Firm gets larger→able to buy raw materials in bulk by negotiating unit discounts→lower AC per unit
Technical economies
Firm gets larger→invest in specialist machinery→boost efficiency + productivity→more output
Marketing economies
Bigger firms→bulk buy advertisements e.g. billboards by negotiating lower unit costs→spread advertising costs over larger output→reduces AC per unit
External economies of scale
As entire industry grows, average cost for business decreases due to larger factors occurring outside the business.
Better transport infrastructure: e.g. new roads, airports, →reduces TC for firm as it’s cheaper to transport + access raw materials→reduces AC
Component suppliers move closer: large firm→in their interest to move closer to firm→reduce transport costs + TC
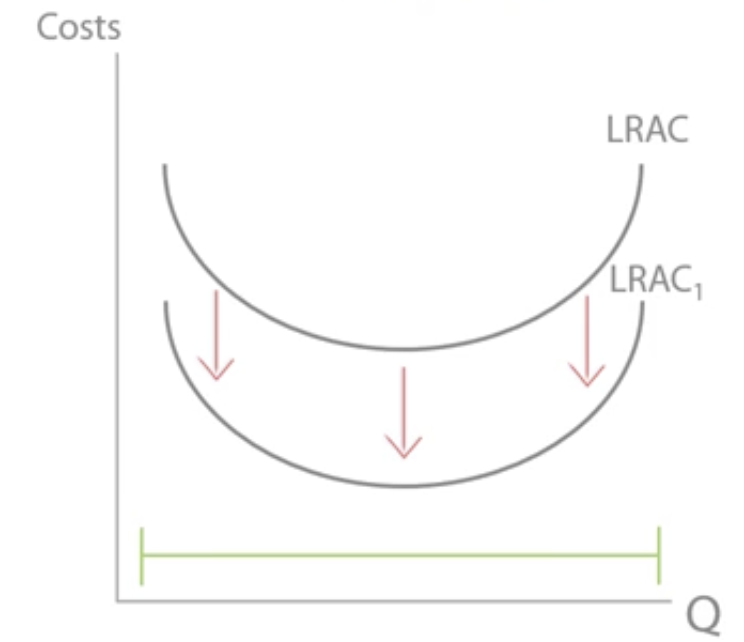
Diseconomies of scale
AC = TC↑↑↑/ Q↑
An increase in LRAC as output increases.
3 C’s and an M
Control: Firm grows→ harder to control workforce→workers slack off→productivity decreases
Communication: Firms grows→harder+slower to communicate + send messages between CEO’S + workers→reduce productivity
Coordination: Firm grows→difficult for different departments to coordinate + working in same way→decreases productivity
Motivation: Firm grows→workers feel like they’re not value→demotivated to work→productivity decreases.
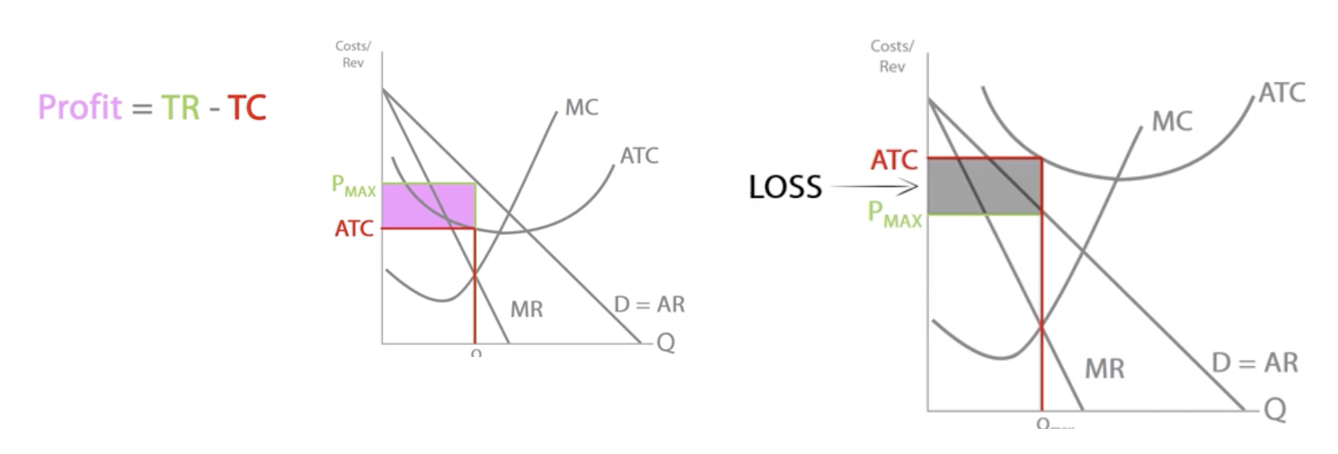
Profit
Economic profit = TR - TC
TC: Physical costs (TFC, TVC) + Opportunity costs
Normal profit, supernormal profit, subnormal profit
Normal profit: The minimum level of profit required to keep FoP in their current use + cover TC. Economic profit = 0
AR = AC
Supernormal profit: Any profit made above normal profit.
AR>AC
Economic loss: Any profit made below normal profit. Profit made is not enough to cover the opportunity cost of production.
AR<AC
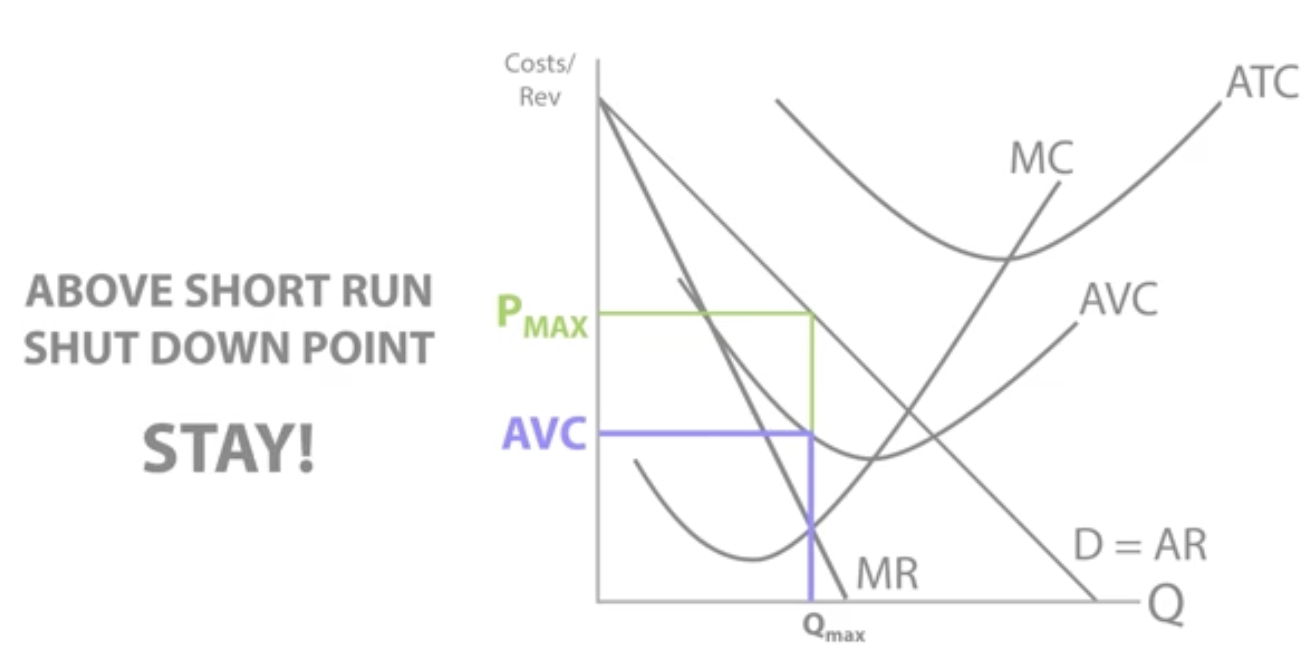
Short run shut down point
Price(AR) = AVC
If price(AR) > AVC, firms will stay in the market(not shut down), as any revenue generated above the firms AVC can be used to pay off fixed costs.
Still gaining money on each unit sold
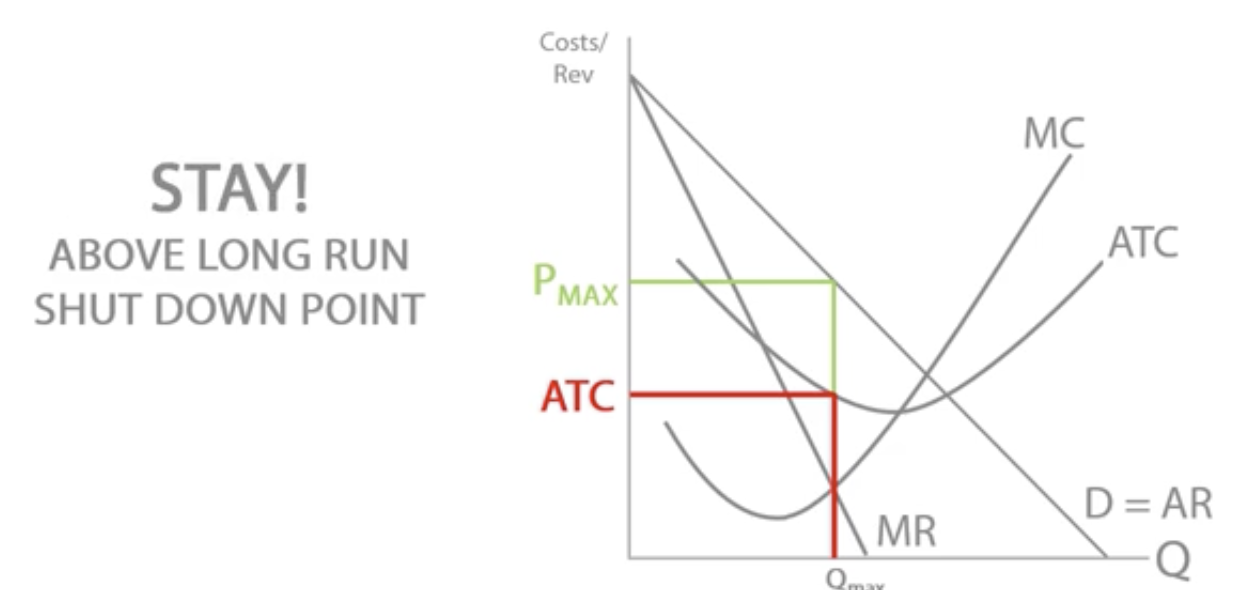
Long run shut down point
Price(AR) = ATC
as there are no fixed costs in the long run as all factors of production are variable.
If price(AR) > ATC, firm will stay in market as it’s still making profit on each unit sold.