Colonization of Land
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Characteristics of Fungi
Heterotrophs like animals - cannot carry out photosynthesis
Utilize external digestion and absorb materials in their hyphae
The above ground “parasol” is only a tiny part of the actual organism
Eukaryotic
Cell walls made of chitin
DO NOT store carbohydrates as starch
Reproduce sexually or asexually
Fungal Body
composed of hyphae - network of branched filaments adapted for absorption
essential for nutrient absorption, growth, reproduction, structure
Mycelium - hyphae woven into a mat-like structure
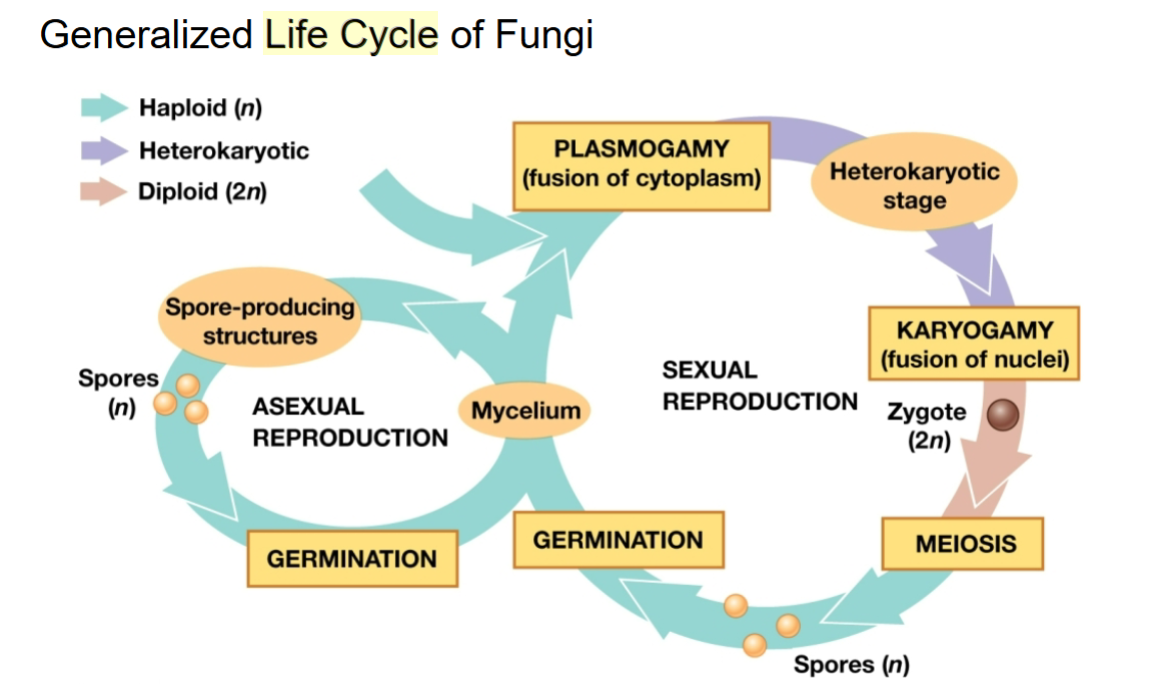
General Life Cycle of Fungi
Plasmogamy - union of cytoplasm from two different haploid mycelia, occurs first
Karyogamy - fusion of haploid nuclei to form diploid cells, occurs hours/days/or centuries later
Origin of Fungi
Microsporidia - unicellular parasites, identified as early diverging group of fungi (primitive fungi)
Groups of Fungi
Cryptomycetes - parasites of other fungi
Microsporidians - parasites with harpoon like spores
Chytrids - fungus attacking frogs and salamanders
Zoopagomycetes - parasites or symbionts of animals
Mucuromycetes - molds implicated in food storage
Ascomycetes - sac fungi which produce ascocarps
Basidiomycetes - club fungi; decomposers and mushrooms
Seedless Plants
adapted to life on land
Plants on land needed structural support and protection from drying out
Carbon dioxide more available
Fewer things to eat plants at first
First plants colonized high humidity areas
New Plant Structures for Land
Alternation of generations
Diploid Sporophyte (2n) to produce haploid spores
Haploid Gametophyte (n) to produce haploid gametes
Apical meristem in shoots and roots
Waxy cuticle protects leaves from drying out
Cell walls with lignin to strengthen them
Gymnosperms
No flowers or fruits
“Naked” seeds that are not enclosed in chambers
Often bear cones for seed production
Primarily wind pollinated
Less sophisticated vascular system than angiosperms
Smaller, more ancient
Angiosperms
Enclosed seeds, protected within a fruit which develops from the ovary of a flower
Flowers/fruits
Diverse pollination methods, wind/water/insect
More sophisticated vascular system
Largest and most diverse group of plants
Cluster of flowers called an inflorescence
Double fertilization to give endosperm
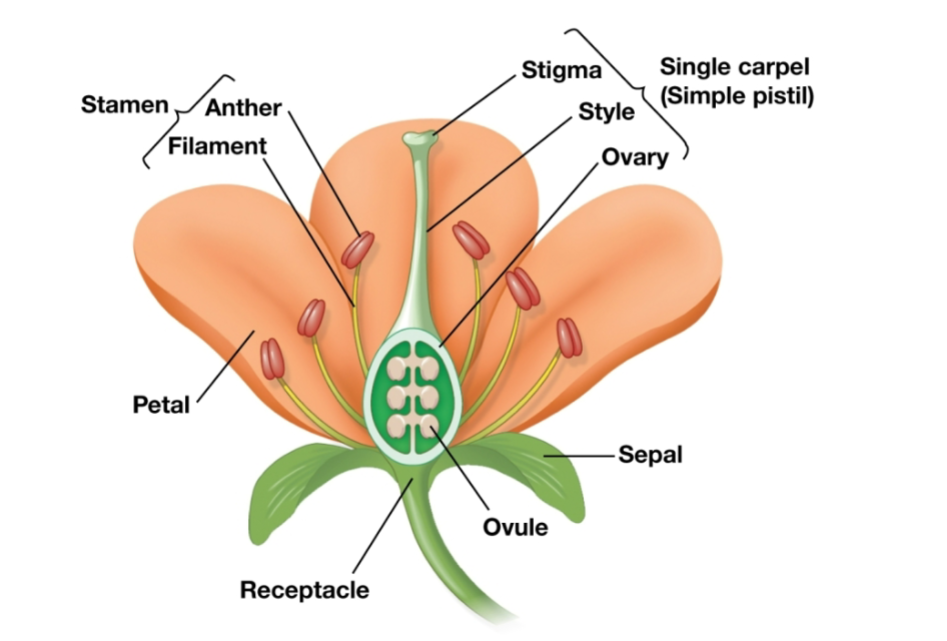
General Structure of a Flower
Sepals (sterile) - enclose the unopened flower
Petals (sterile) - attract pollinators with bright colors
Stamens (fertile) - produce pollen
Carpels (fertile) - produce ovules, term pistil refers to single or two or more fused carpels
Seed Plants
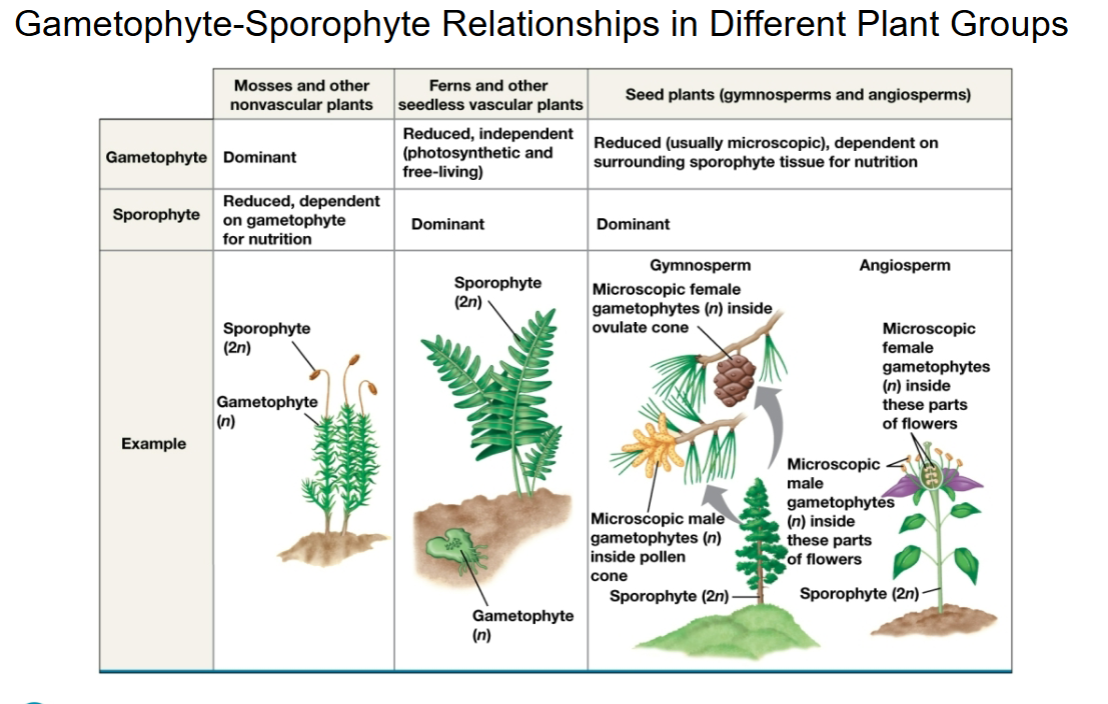
Always see the sporophyte form. Only non-vascular plants have the haploid gametophyte as the most important form.
Heterosporus Plants
Produce two kinds of spores
Megasporangia
Produce megaspores which produce female gametophytes
Microsporangia
Produce microspores which produce male gametophytes
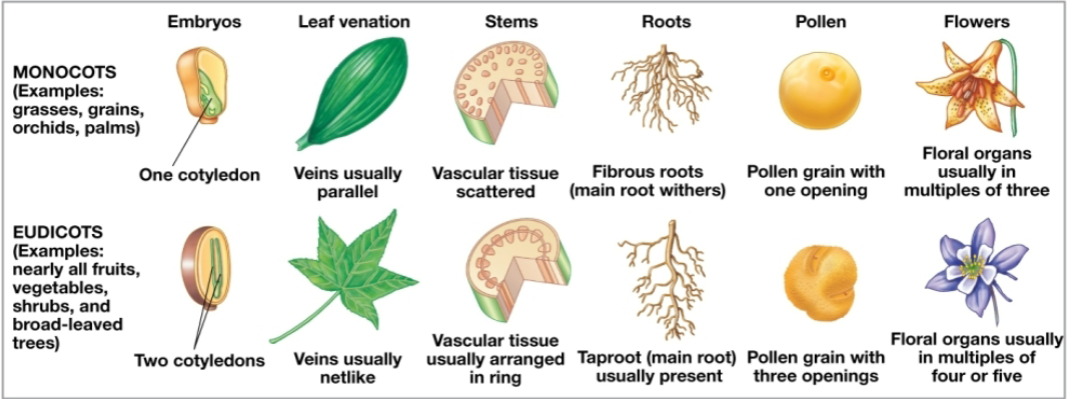
Monocots vs Dicots
Gymnosperms_
came first
naked seeds on scales on cones
ovule but no ovaries
never fruits or flowers
Male and Female cones
Microsporocyte (male)
Megasporocyte (female)
ex. Cycads, ginkgophytes, Gnetophytes, conifers
Conifers
Cone bearing
Male and female cones
Needle-like leaves
No fruits or flowers
ex. Pine tree, Douglas Fir
Cycads
Resemble palms but have cones
Large compound leaves
ex. Sago Palm
Ginkgophytes
High resistance to pollution
Male and female trees
ex. Ginkgo Baloba
Gametophyte - Sporophyte Relationships