Trematodes and cestodes of ruminants
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What types of life cycles do flukes and tapeworms have?
indirect involving intermediate hosts
What phylum and class are flukes and tapeworms part of?
phylum platyhelminthes
class trematode (fluke)
class cestoda (tapeworms)
What are the two types of liver fluke? What is the scientific name of rumen fluke?
fasciola hepatica (common liver fluke)
decrocoelium dendriticum (lancet/tea leaf fluke way less common)
rumen fluke is calicophoron daubneyi
What type of reproducer is the liver fluke?
hermaphrodite so clonal reproduction in intermediate host, a mud snail
25000 eggs a day
What is the lifecycle of the liver fluke?
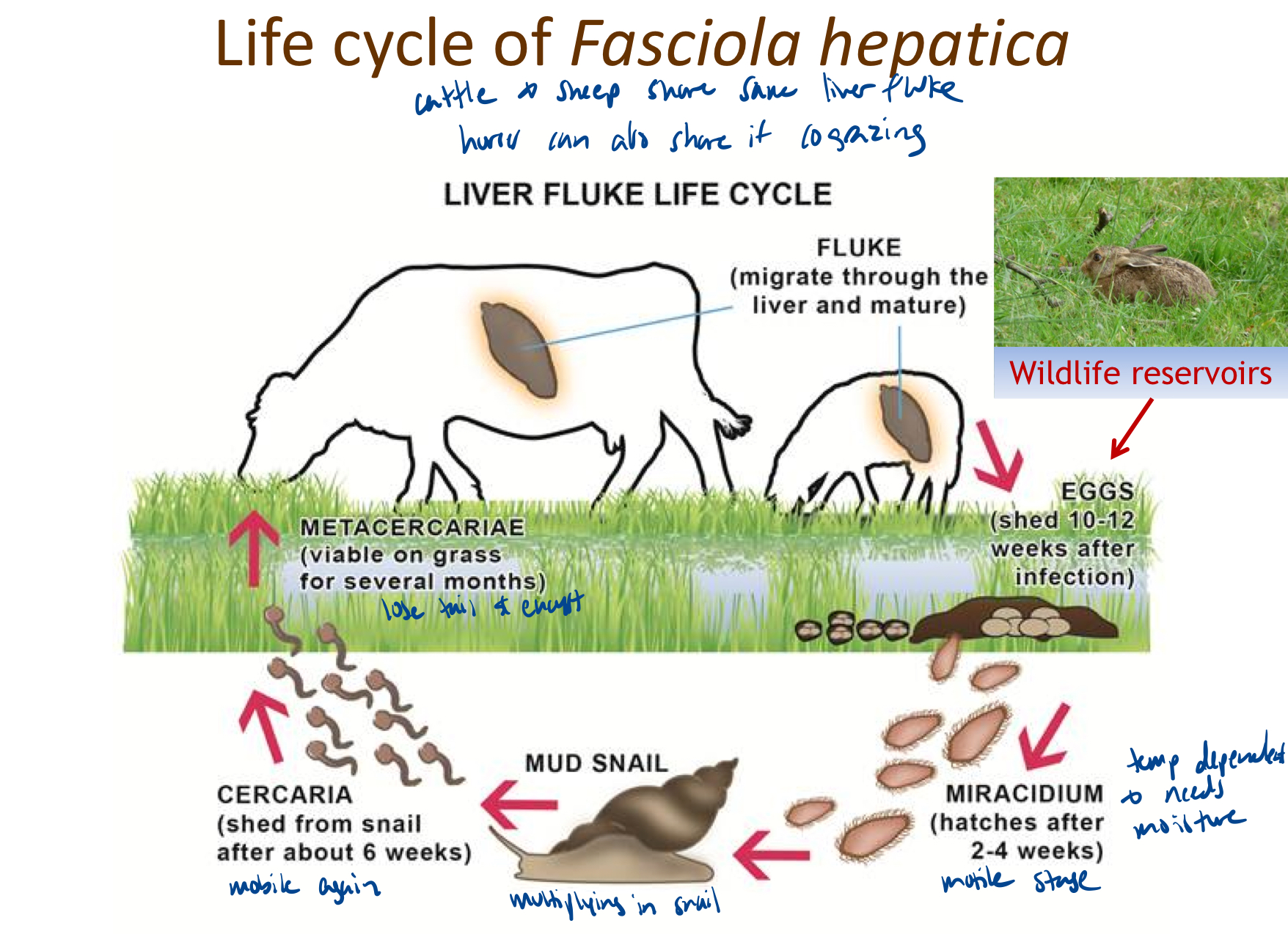
What is the temperature range that fluke eggs need to develop?
minimum 10 degrees to 25 degrees celsius
What is the temperature range that a cercarium needs to encyst in the pasture?
10-25 degrees celsius again
What is excystation?
“hatches" in the GI tract of the animal
What is peregrination?
the migration
they pass through the gut wall and enter the abdominal cavity
travel along inner surface of abdominal wall
reach diaphragm, against which lies the ventral lobe of the liver
juvenile fluke penetrate the diaphragmatic surface of the liver capsule
What does acute fasciolosis cause in sheep?
liver is easily damaged
high numbers of migratory juveniles cause parenchymal damage
hemorrhage within liver tissue
damage to larger blood vessels can cause catastrophic intra-abdominal hemorrhage
What is the timeline for acute fasciolosis?
week 1 to 8
At what point is it considered chronic and what are signs?
past the 12 week phase
cachexia
anemia
depression
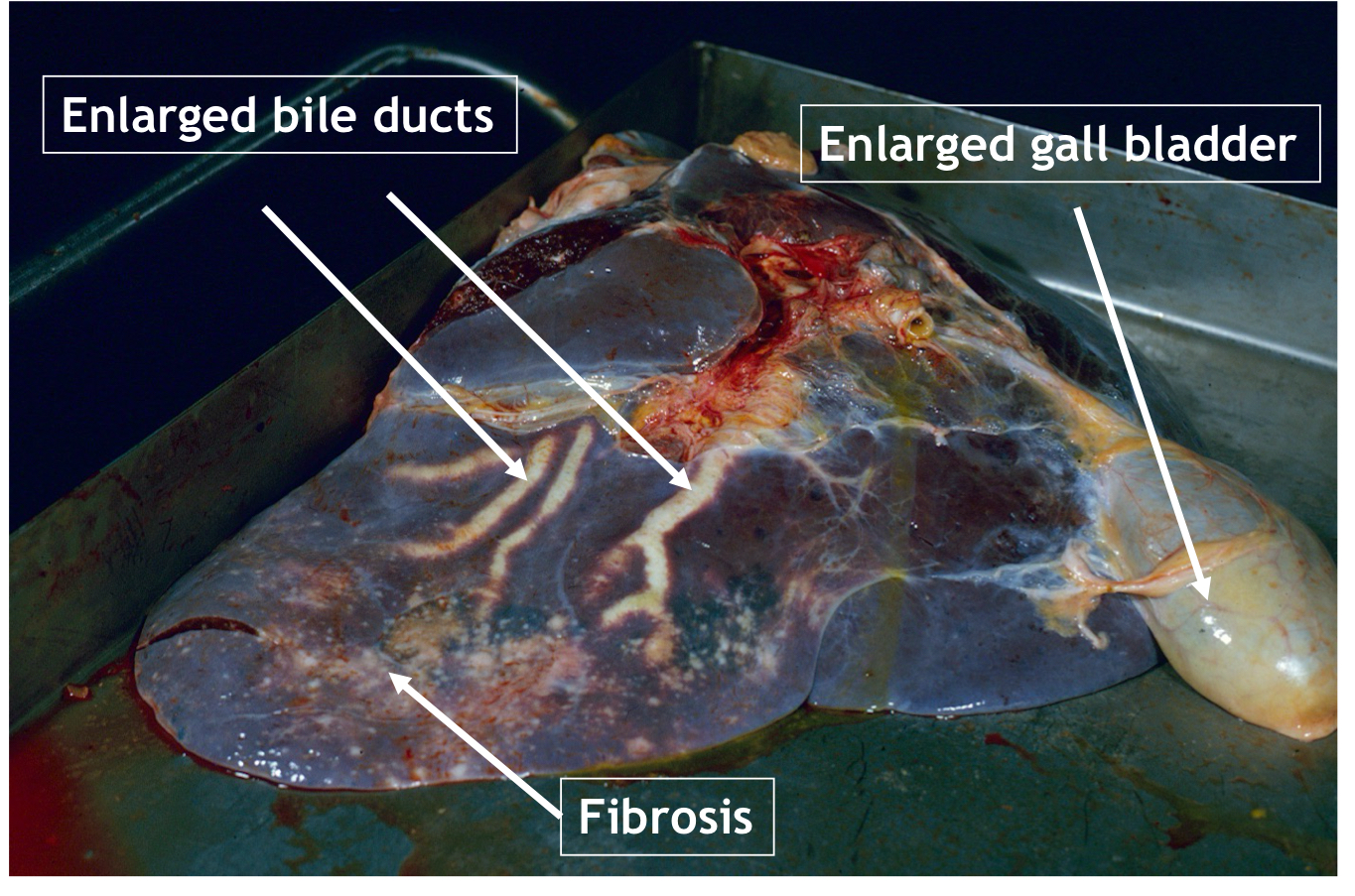
What does the gross pathology of chronic liver fluke in cattle look like?
What is the pathophysiology of liver fluke?
feeding of flukes- hemorrhage/anemia
anorexia- reduced food intake
liver damage and dysfunction- diverse effects
immunomodulation- bacterial co-infection, TB diagnostics (can get false positive and negatives if they have fluke as well)
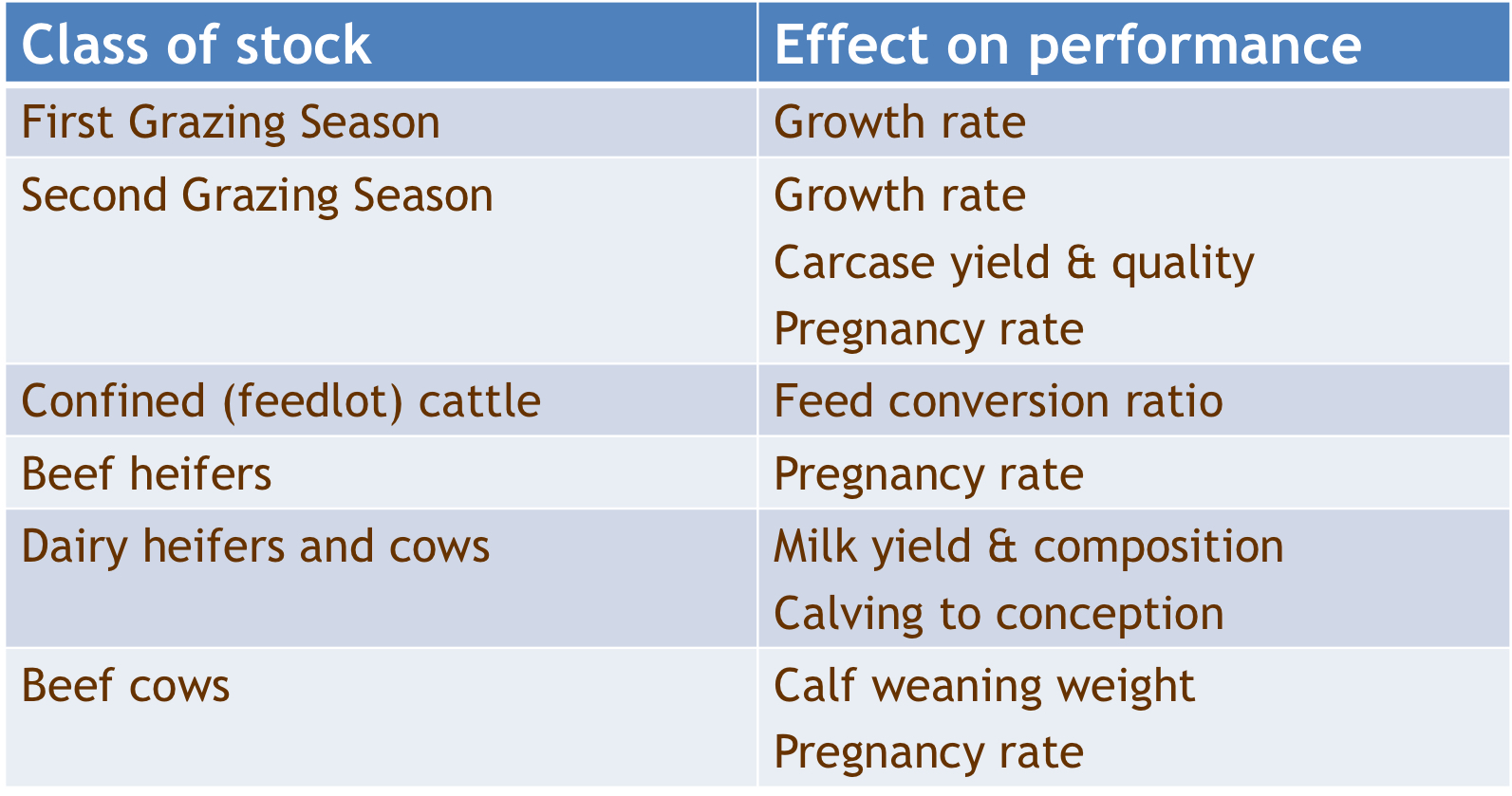
What are the major effect on performance of liver fluke at the different stages?
When does the peak challenge from fluke occur?
autumn from the metacercariae
What are the different methods of fluke diagnostics?
parasite, immunity, pathophysiology, pathology
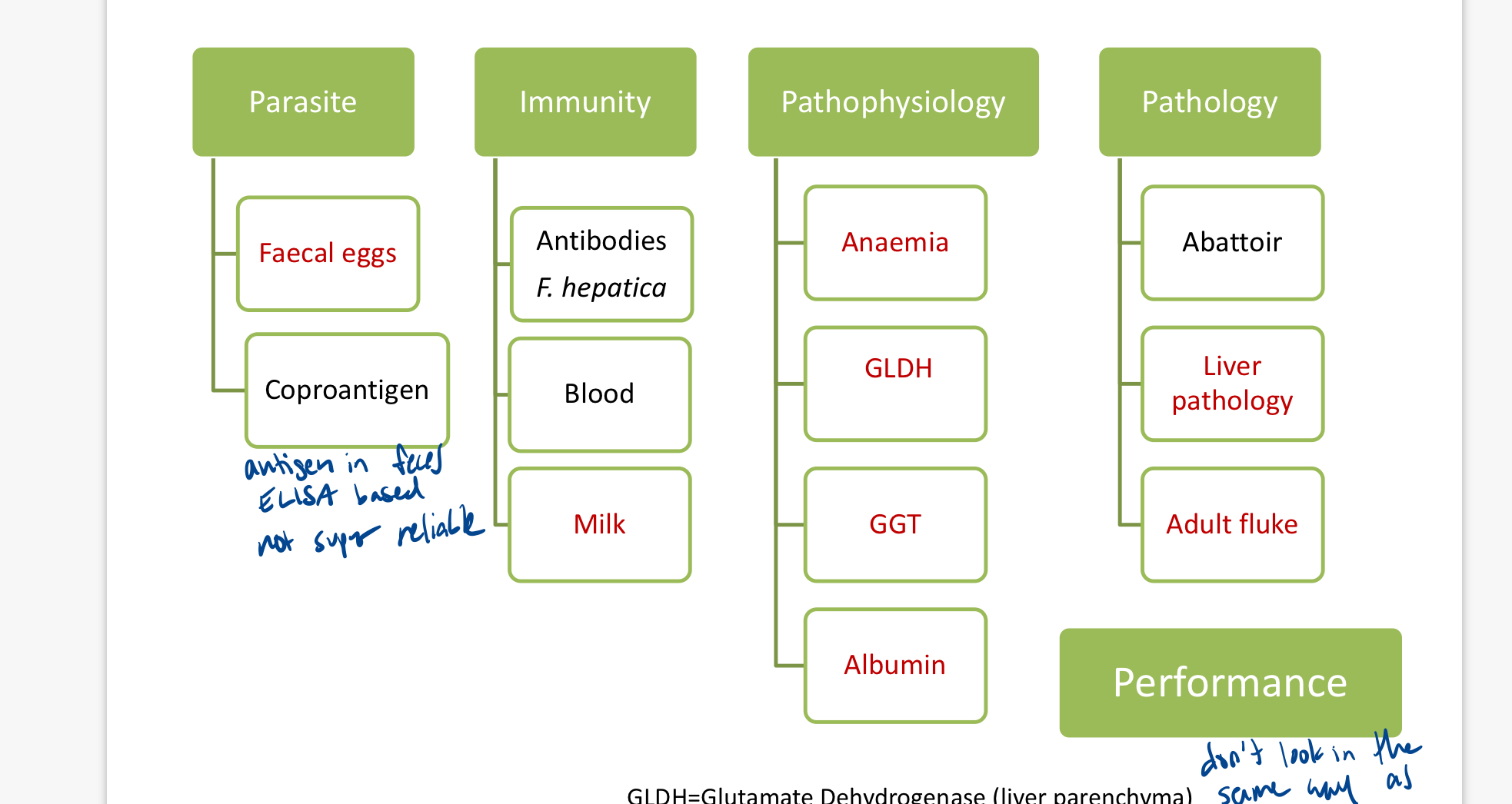
What animals do the new lateral flow testing kits aim to test?
sentinel animals
ie in autumn for that year’s lambs or calves
What are different control measures?
grazing management: avoid grazing high risk pastures, selective grazing in endemic regions
snails: drainage, fencing
flukicides: strategic (pasture contamination), therapeutic (animal welfare and performance)
What is the spectrum of activity for each flukicide?
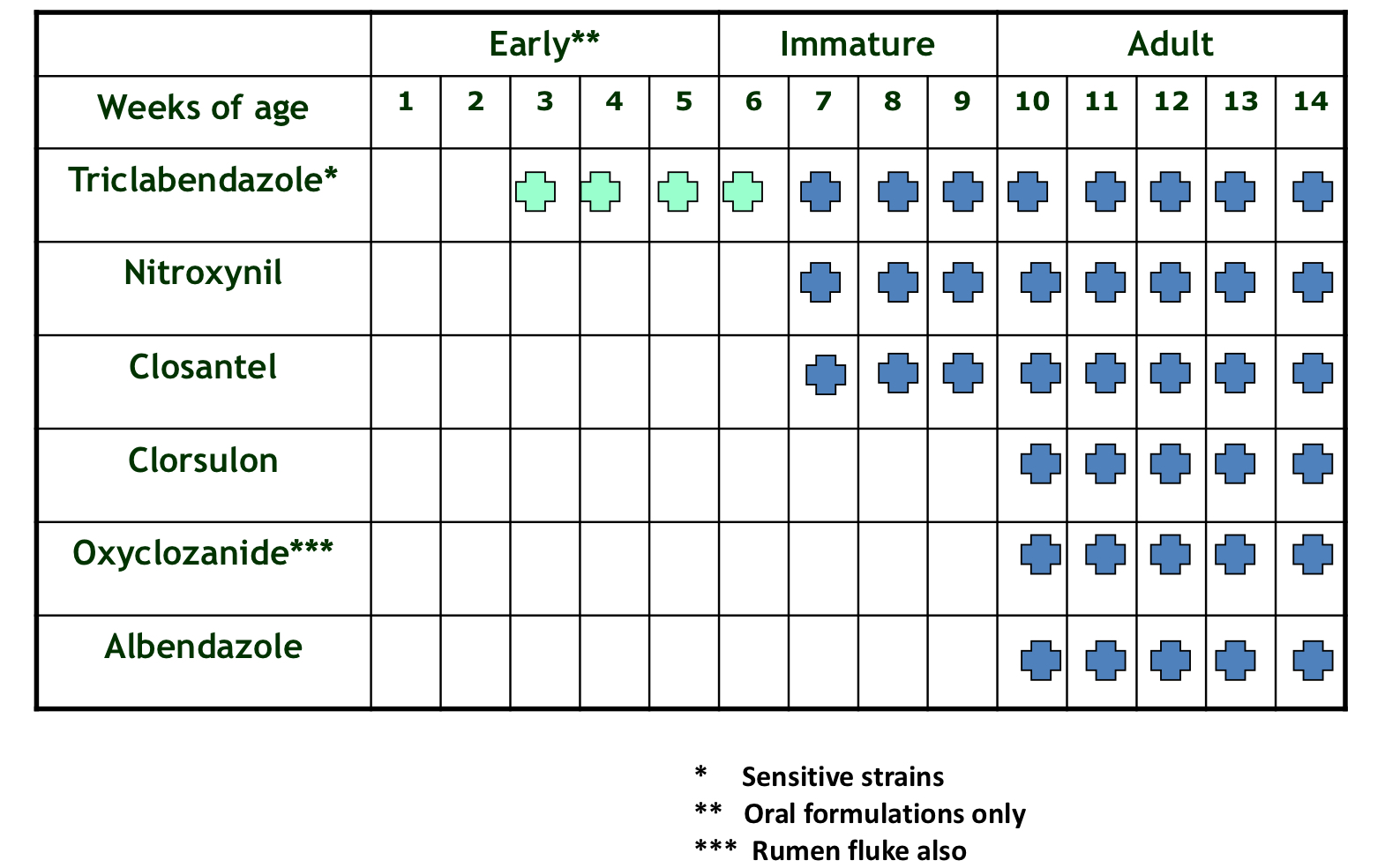
What is the rationale for using flukicides therapeutically?
remove adult fluke to limit damage to host
no need to use triclabendazole for a case like this
What is the rationale for using flukicides strategically?
remove adult fluke at key times to limit pasture contamination with fluke eggs
mainly beef because it’s difficult in adult dairy except spring-calving herds
How do you monitor fluke outbreaks?
bulk fecal eggs
What are the different options for winter treatments if housed? There are two options for different drugs.
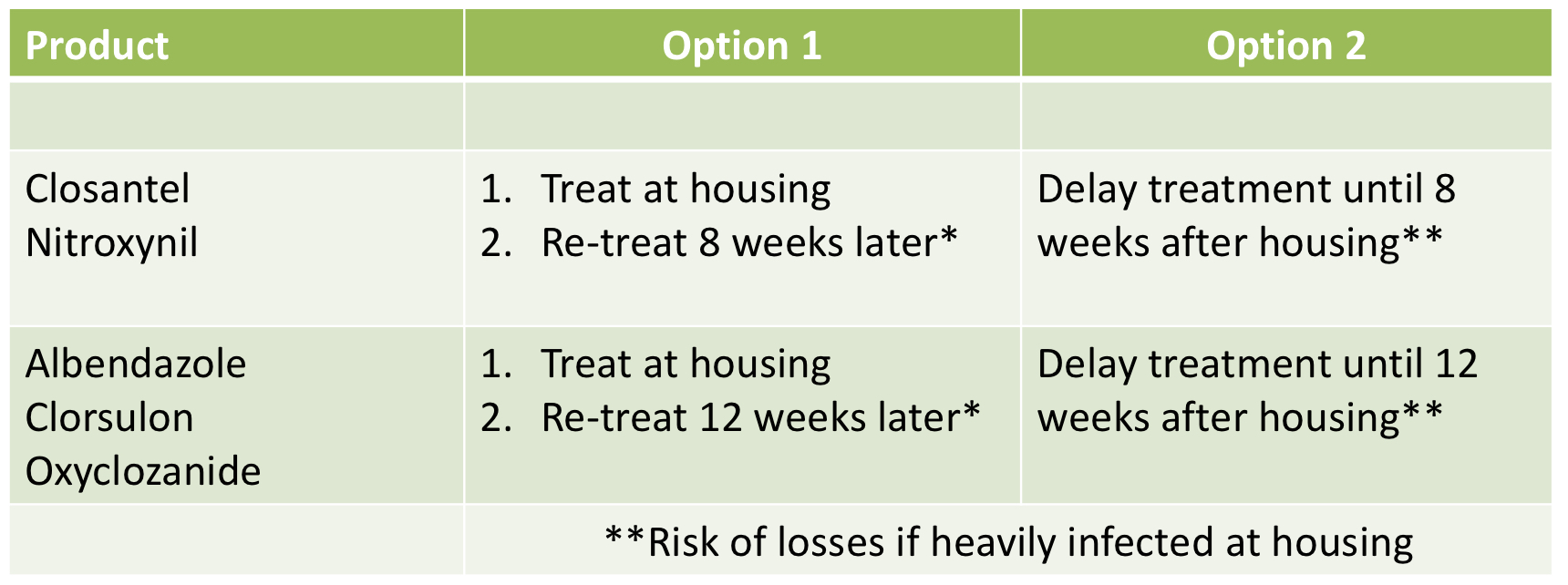
When should flukicide treatment be given if the cattle is housed over winter? What about if out-wintered?
should be given about 8 weeks after turnout
out-wintered: flukicide treatment should be given about 8 weeks after the previous treatment
What flukicides can be used in milking cows?
oxyclozanide
albendazole
What are the obstacles to fluke control?
no natural immunity
practical limitations on ‘environmental’ control
flukicides- limited product range for juvenile fluke, withdrawal periods restrictive, limited options for rumen fluke
treatment recommendations- limited evidence base, co-infections, limited diagnostics
What is the treatment for dicrocoeliosis in sheep?
nothing registered, but albendazole at 15-20 mg/kg
How does the clinical disease of rumen fluke manifest?
typically affected animal showing diarrhea, dehydration, and poor condition
What would you find on necropsy on rumen fluke?
duodenum showing marked reddening with immature flukes (resembling bubbles) on the mucosa
immature rumen fluke in the duodenal lumen showing the acetabulum (oral sucker) surrounding a plug of duodenal mucosa
How do you control rumen fluke?
epidemiological overlap with liver fluke- snail habitats, sheep and cattle
treatment (off-label): oxyclozanide
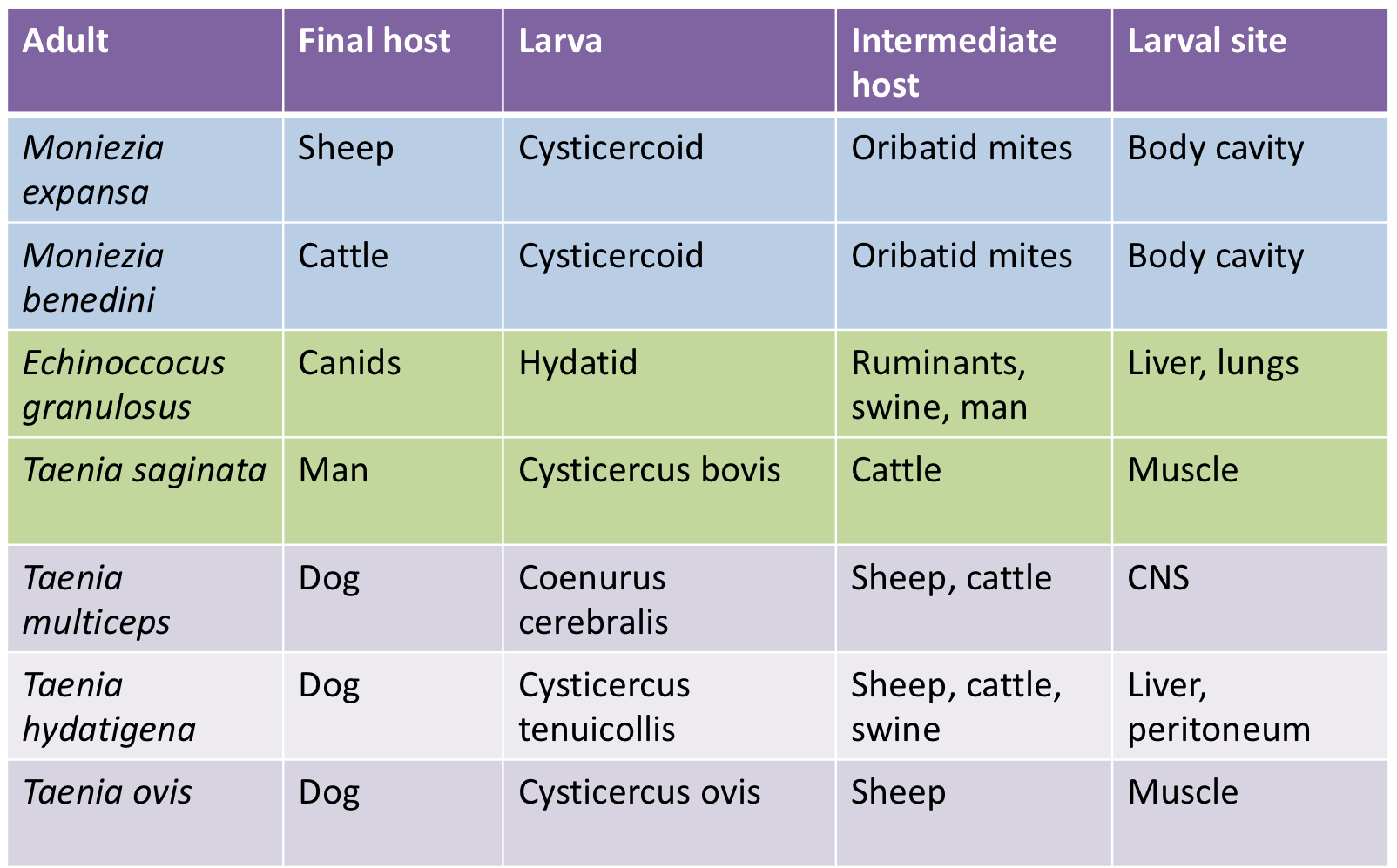
Here’s a chart with all the ruminant cestodes
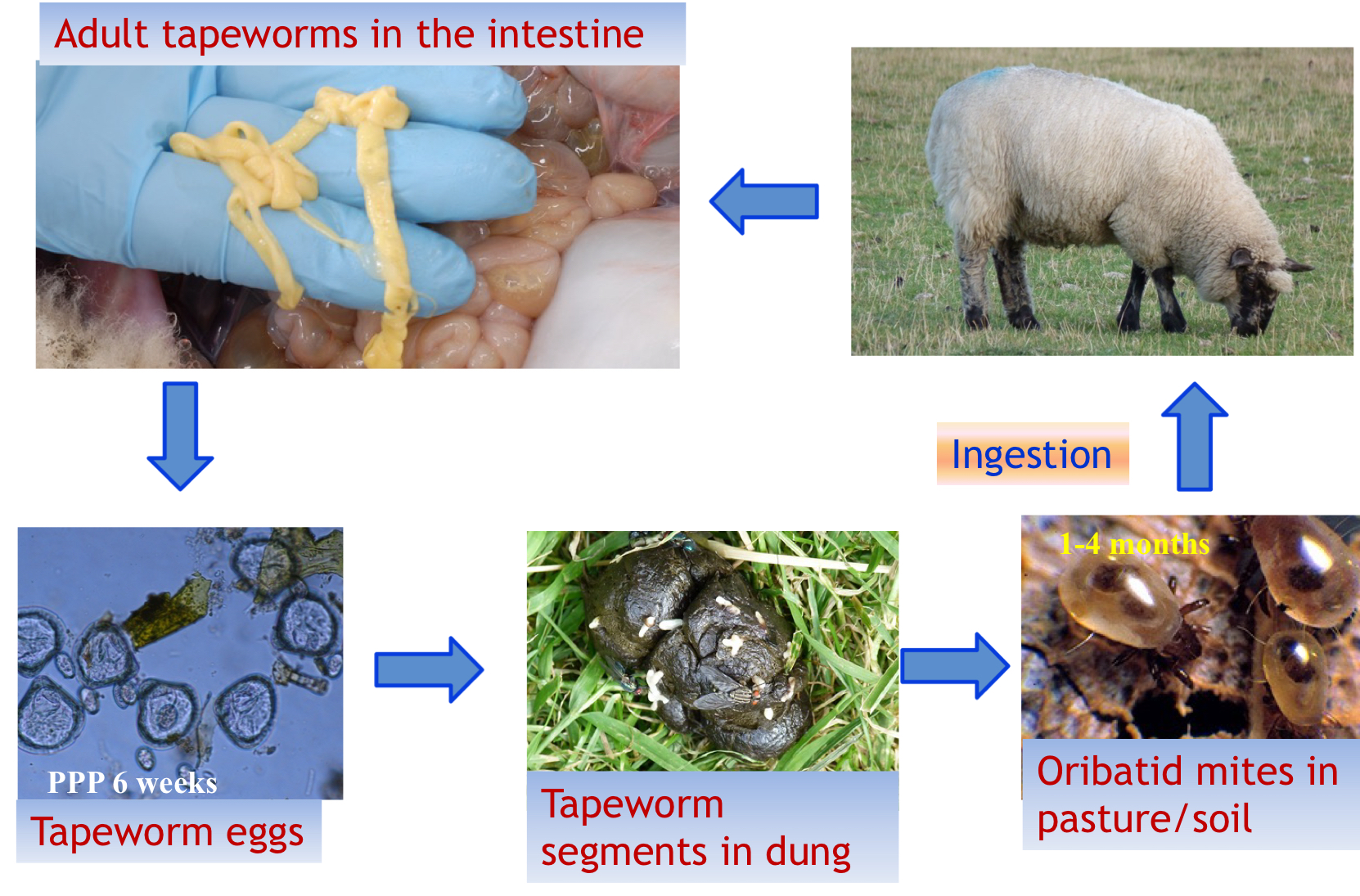
What is the life cycle for monieza expansa?
one intermediate host
How do you control tapeworms?
ruminants: albendazole, fenbendazole, ricobendazole, praziquantel + levamisole
dogs: praziquantel produces, exclude dogs from fields with sheep or cattle