Thigh and Knee Region
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
Superior and inferior gluteal arteries are branches of which artery?
Internal iliac artery
Through which structure does the superior gluteal artery enter the gluteal region?
Greater sciatic foramen
Landmark used for gluteal nerves?
Piriformis
The _______ and ______ gluteal nerves pass _____ the piriformis
Superior, inferior, above
Which artery is the major blood supply for the gluteus maximus?
Inferior gluteal artery
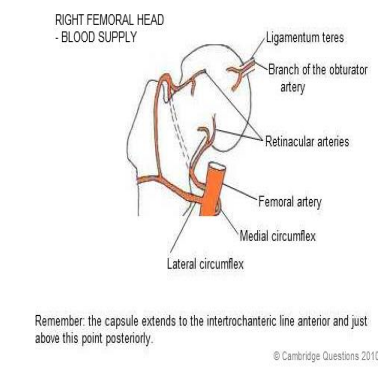
What structure is the MAIN blood supply to the head of the femur?
Trochanteric anastomosis
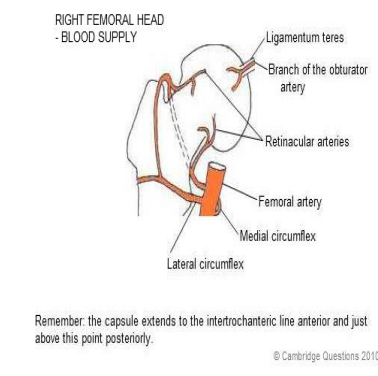
What are the arteries that supplies in the trochanteric anastomosis:
Superior and inferior gluteal, medial and lateral femoral circumflex, branch from obturator arteries
The Cruciate anastomosis is situated at the level of the ________ ________ of the femur
lesser trochanter
Cruciate anastomosis together with trochanteric provides aconnection between the ________ ______ and ________ arteries?
internal iliac, femoral
Name all artery involved in the cruciate anastomosis.
Profunda, first perforating, inferior gluteal, lateral and medial femoral circumflex arteries
Which artery passes through the greater sciatic foramen beneath the piriformis?
Inferior gluteal artery
The function of the _______ are to stabilize the ______ and prevent its ______ at the _________ joint by the weight of the vertebral column
Ligaments, sacrum, rotation, sacroillac
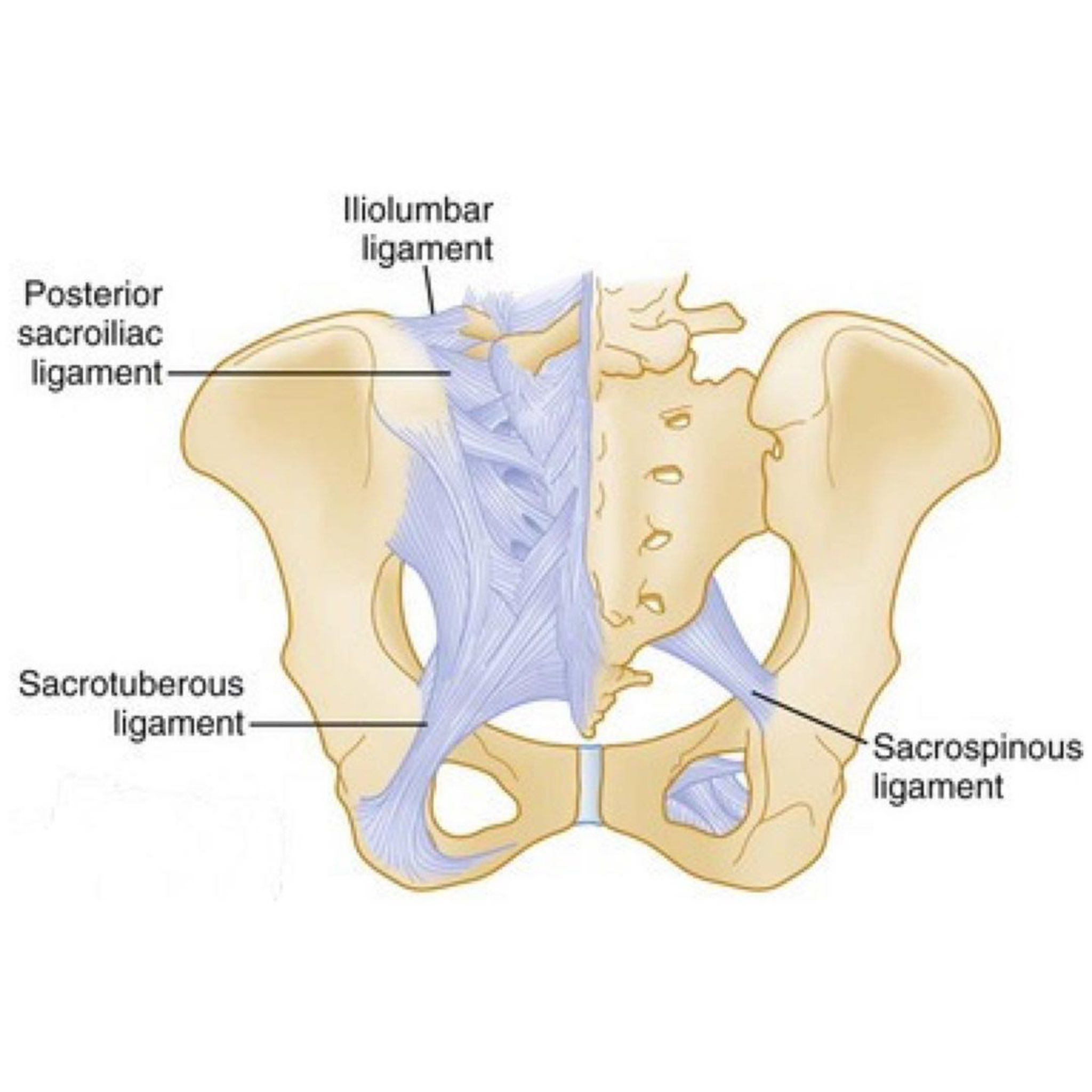
The _______ lig. connects the back of the ______ to the ________ _______
Sacrospinous, sacrum, ischial spine
The _______ lig. connects the back of the ______ to the ________ _______
Sacrotuberous, sacrum, ischial tuberosity
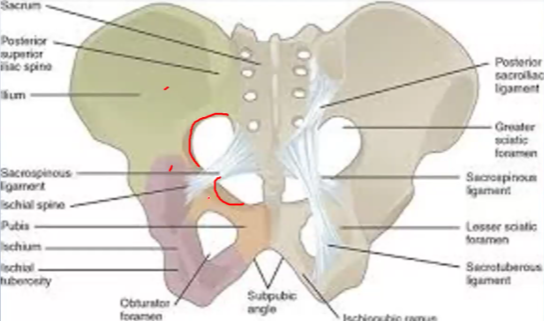
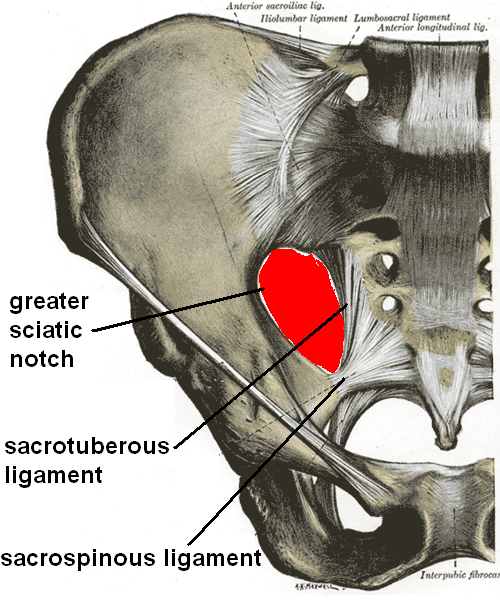
From which 2 bones does the Greater sciatic notch come from?…
Ilium, ischium
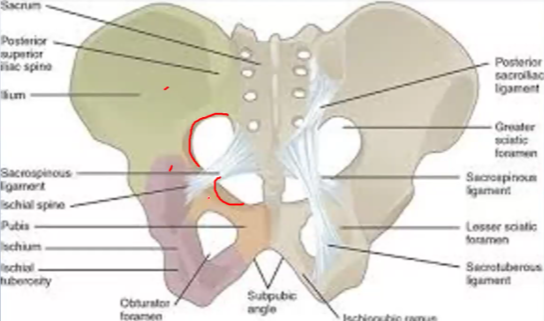
From which bone does the Lesser sciatic notch come from?…
Ischium
The Greater sciatic notch provides an ____ for the _____ plexus from the pelvis into the _____ region
Exit, lumbrosacral, gluteal
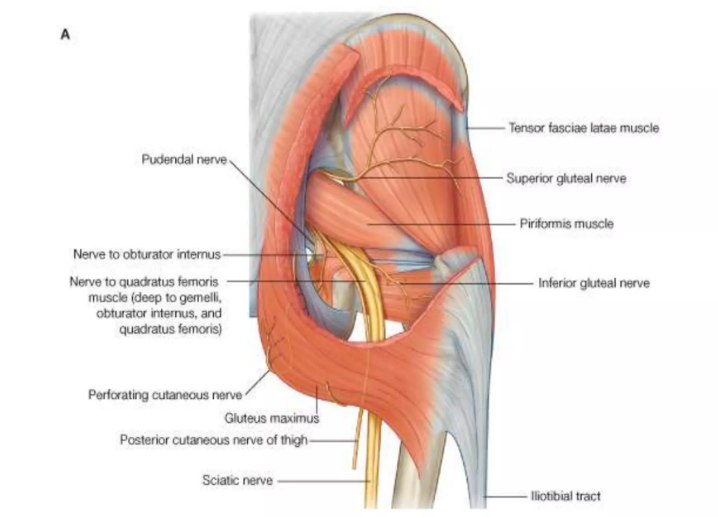
The contents of the Greater sciatic notch… (PS PS PS NI)
Piriformis, Sciatic nerve, Posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh, Superior and inferior gluteal nerves, Pudendal nerve, Superior and inferior gluteal arteries and veins, Nerves to obturator internus and quadratus femoris, Internal pudendal artery and vein
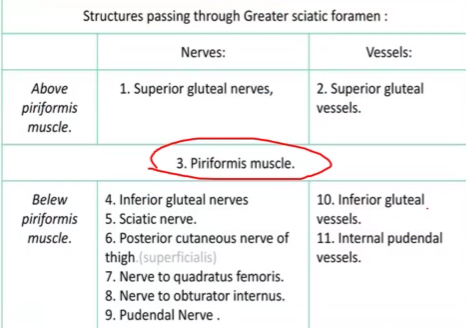
Above and below piriformis muscle (Type 1)
1
What structure provides entrance into the perineum from the gluteal region?
Lesser sciatic foramen
The Lesser sciatic foramen enables passage for structures leaving the pelvis through which foramen?
Greater sciatic foramen
Tendons | Nerves | Vessels |
1. _____ | 2._____ | 4.____ |
Lesser Sciatic foramen contents…
Obturator internus tendon, nerve to obturator internus, pudendal nerve, internal pudendal artery and vein
What is the area between the hip and knee called?
Thigh
What are the two divisions of thigh fascia?
Superficial and deep
Which fascia layer contains a fatty and membranous layer?
Superficial
The fatty layer of the thigh extends on _________ to _______?
Anterior abdominal wall, thigh
The membranous layer of the thigh attaches to _______?
Fascia lata
The _______ ____ is like spandex and its upper end is attached to _____ and _______ lig, while the lateral end is attached to _______ _____
Fascia lata, pelvis, inguinal, iliotibial band
What is the deep fascia of the thigh called when it thickens laterally?
Iliotibial tract
_____ is the gap in the _____ fascia of the thigh that transmits the ____ _______ vein, ______ artery, _____ vessels
Saphenous opening, deep, great saphenous, femoral, lymph
_______ is the _____ _____ _______ of the saphenous opening…
Falciform margin, lower lateral border
What tissue covers the saphenous opening?
Cribriform fascia
Which nerve (L2-3) supplies the lateral aspect of the thigh and knee?
Lateral cutaneous nerve
Which nerve (L1-2) supplies the anterior area below the inguinal ligament?
Genitofemoral nerve
Which nerve (L1) supplies the penis, scrotum, or clitoris/labia majora?
Ilioinguinal nerve
Which branch of the femoral nerve (L2,3,4) supplies the medial aspect of the thigh?
Medial cutaneous nerve
Which nerve (branch of obturator nerve) supplies the anterior thigh?
Intermediate cutaneous nerve
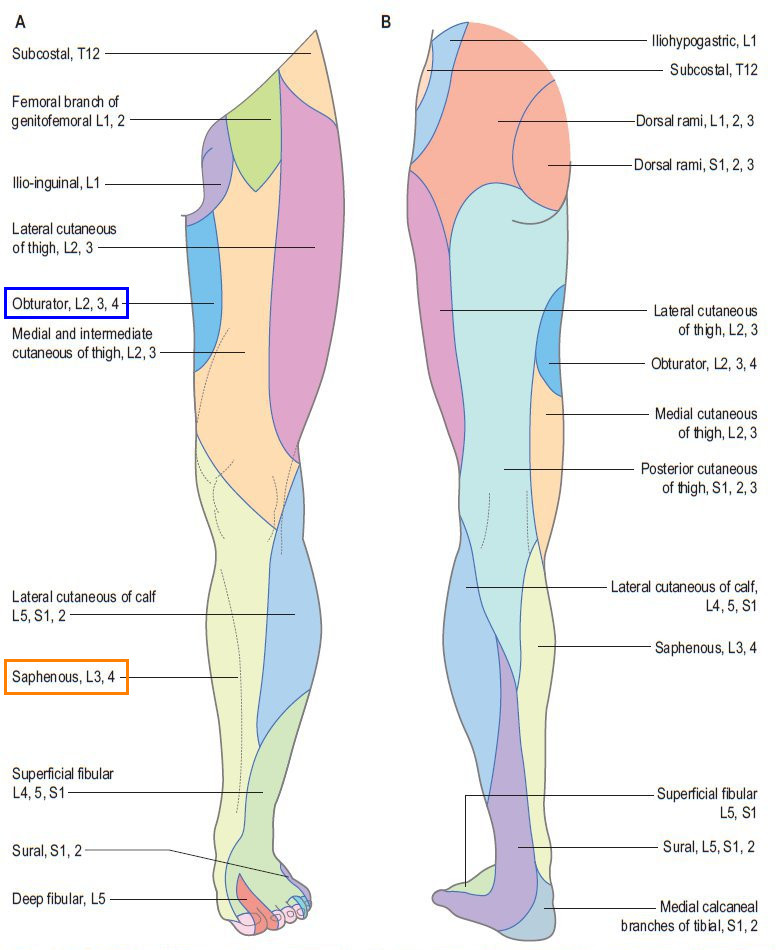
All the cutaneous supply of the thigh:
1. _______
2._______
3._______
4._______
5._______
6._______
Ilioinguinal, Genitofemoral, Lateral cutaneous, Medial cutaneous , Intermediate cutaneous, Posterior cutaneous
What are the two groups of superficial inguinal lymph nodes?
Horizontal and vertical
Which group of superficial inguinal nodes receives lymph vessels from anterior abdominal wall below level of umbilicus and perineum
Horizontal group
Which group of superficial inguinal nodes has the terminal part of great saphenous vein and receives majority of superficial vessels of lower limb
Vertical group
______ inguinal nodes pass femoral canal…
Deep
Name all muscles in the ANTERIOR fascial compartment…
Sartorious, iliacus, psoas, pectineus, quadriceps femoris
What is the blood and nerve supply for the ANTERIOR fascial compartment?
Femoral
What is the LARGEST branch of the lumbar plexus?…
Femoral
What muscles does the femoral nerve supply (according to the lumbar plexus)
Sartorious, pectineus, rectus femoris, vastus medialis, lateralis and intermedius
What are the 2 sensory branches of the femoral nerve?…
Medial cutaneous, saphenous
True or False: The saphenous nerve is more proximal in the thigh
False
What is the Longest muscle in the body?..
Sartorius
When you are “Indian sitting” what muscle do you utilize?…
Sartorius
What is the BIGGEST muscle in the body?…
Gluteus maximus
True or False: The psoas is innervated by the femoral nerve
False
Common insertion of your Quadriceps muscles…
Quadriceps tendon into patella, then via ligamentum patellae into tuberosity of tibia
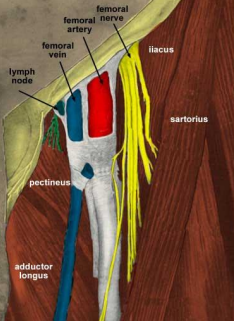
What is included in the femoral sheath?…
Femoral vein, artery, lymph nodes, canal
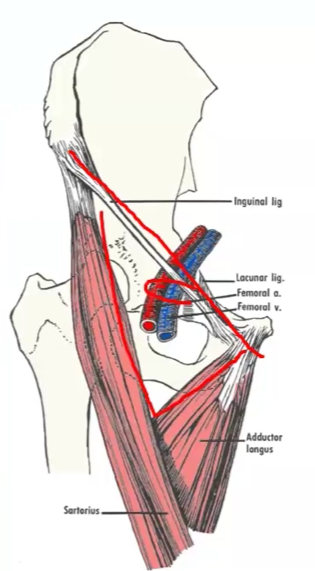
What is included in the femoral triangle?…
Femoral vein, artery, nerve, lymph nodes, sheath
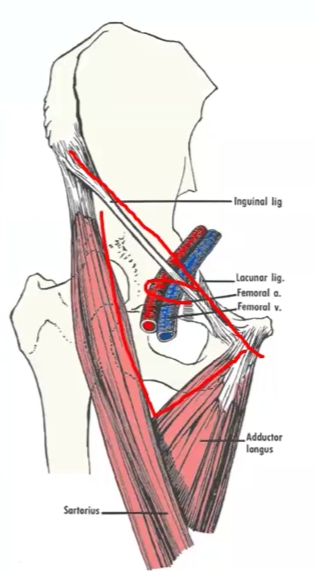
The femoral ______ is an depressed area that is situated in the ________ third of the ______ _______ part of the thigh
triangle, upper, anterior, medial
Name the boundaries of the femoral triangle:
Laterally - _________
Medially - _________
Superior - _________
Floor - _________
Roof - _________
M. border sartorious, M. border adductor longus, inguinal lig., fascia lata, iliopsoas, pectineus and adductor longus
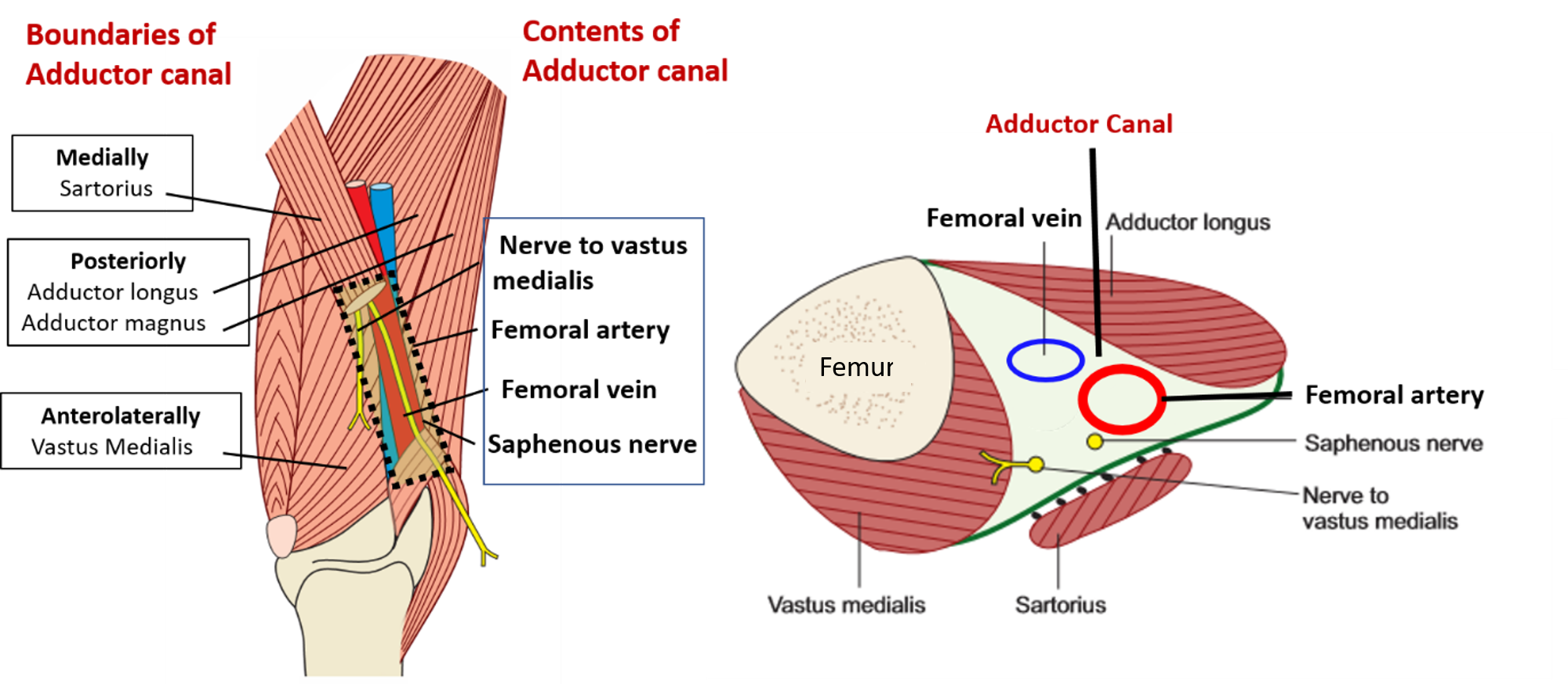
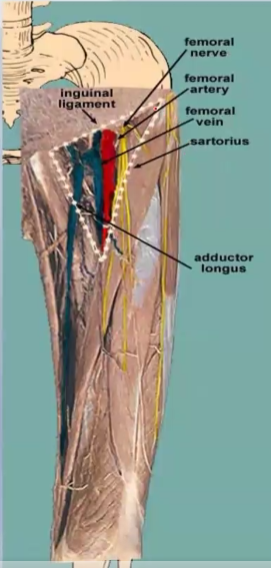
Name the walls of the adductor canal:
Anteromedial wall – __________
Posterior wall – _______
Lateral wall – _________
Sartorius, adductor longus and magnus, vastus medialis
What are the muscles of the MEDIAL compartment of the thigh?
Gracilis, adductor longus, brevis, magnus, obturator externus
What is the nerve supply of the MEDIAL compartment of the thigh?…
Obturator nerve
True or False: The pectineus muscle is partly innervated by the obturator nerve
True
What muscles does the obturator nerve supply?…
Gracilis, adductor longus, brevis, magnus, partly pectineus, obturator externus
What are the muscles in the POSTERIOR compartment of the thigh?.
Biceps femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranosus, adductor magnus
What structure does the semimembranosus insertion form to reinforce the back (capsule) of the knee joint?
Oblique popliteal ligament
The oblique popliteal ligament comes from which muscle?…
semimembranosus
3 muscles that insert into the medial surface of the shaft of the tibia (Pes anserine)
Sartorius, gracilis, Semitendinosus
True or False: All POSTERIOR muscles flex/cross the knee
False
What are the roots of the Sciatic nerve?
L4-5, S1-3
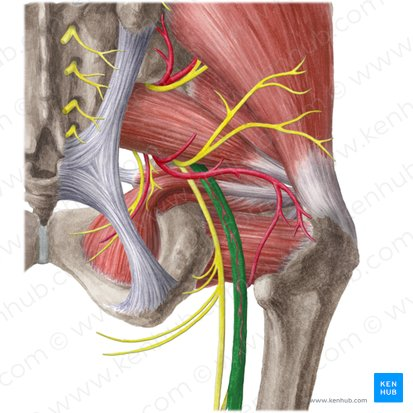
The ______ nerve lies in the ________ aspect of the ________ _______ muscle…
Sciatic, posterior, adductor magnus
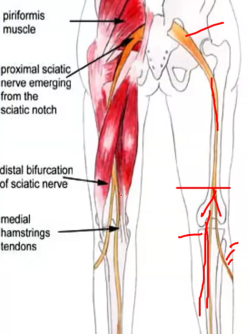
The Sciatic nerve branches into the ______ nerve and ________ (fibular) nerve
Tibial, common peroneal
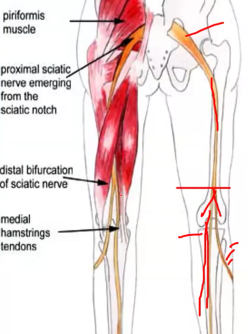
True or False: The tibial portion of the sciatic nerve is found laterally in the leg
False
What is the largest joint in the body?…
Knee joint
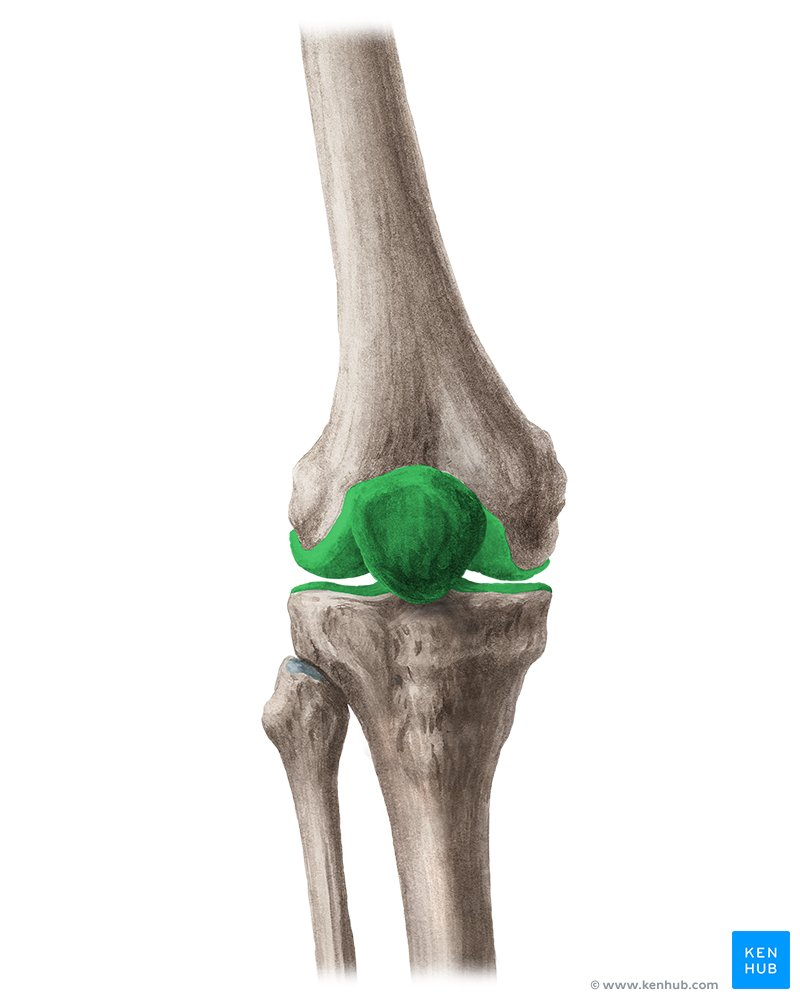
What type of joint is the tibio-femoral joint?
Hinge
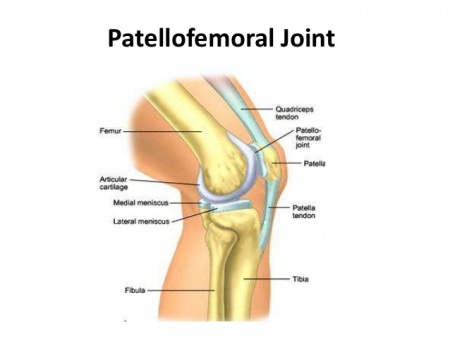
What type of joint is the patella-femoral joint?
Plane
Stability of the joint depends on: _____ and _______of the surrounding muscles & ligaments that connect the _____ and ______
Strength, actions, femur, tibia
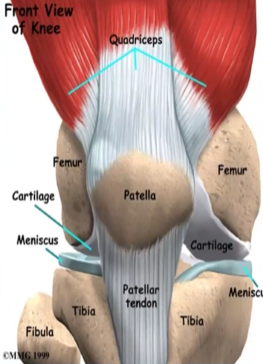
Movement of the Knee joint: Which muscle performs knee flexion, and what limits it?
Hamstring, contact of calf and thigh
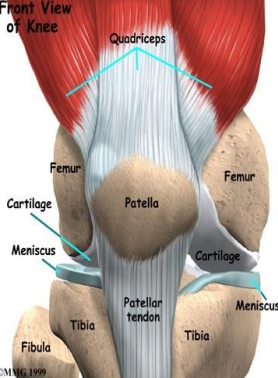
Which muscles perform MEDIAL rotation of the knee, and which ligament checks it?
Popliteus, semitendinosus, semimembranosus, cruciate ligament
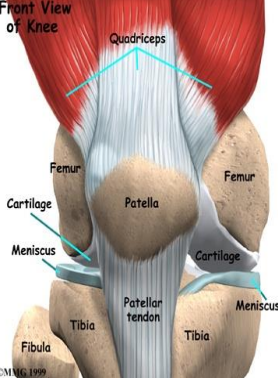
Which muscle performs LATERAL rotation of the knee, and which ligament checks it?
Biceps femoris, collateral ligament
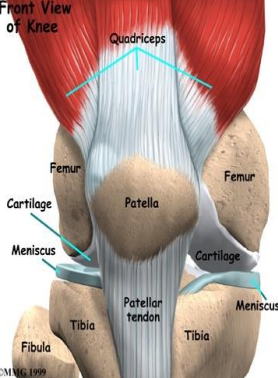
Which muscle performs knee extension, and what limits it?
Quadriceps, cruciate and collateral ligaments
True or False: The capsule of the knee joint is found to the margin of the articular surfaces and sides and anterior of joint
False
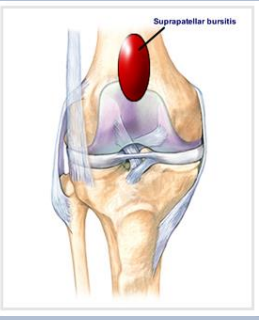
What structure forms a pouch beneath the quadriceps tendon?
Suprapatellar bursa
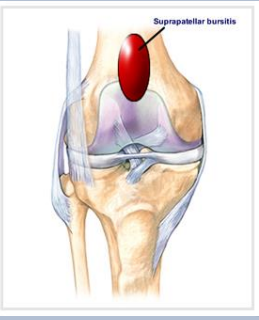
_______ is held in position by the attachment of a small potion of the vastus ______ muscle, called the _________ _______ muscle.
Suprapatellar bursa, intermedius, articularis genus
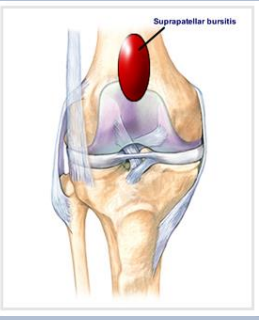
Which tendons reinforce the lateral and medial sides of the suprapatellar bursa?
Vastus lateralis and medialis
What is the distal part of the quadriceps tendon called?
Patellar ligament
Which ligament prevents excessive adduction of the knee?
Lateral collateral ligament
Which ligament prevents excessive abduction of the knee?
Medial collateral ligament
What part of the Medial (tibial) collateral ligament is attached to the medial meniscus?
Deep part
Which ligament strengthens the fibrous capsule of the knee posteriorly?
Oblique popliteal ligament
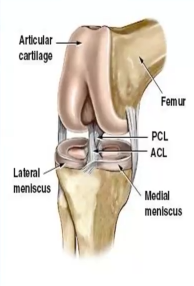
Where are the cruciate ligaments located, and what do they provide to the knee joint?
Center, stability
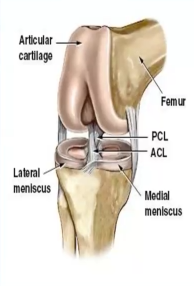
Which cruciate ligament is weaker and has poor blood supply?
Anterior cruciate ligament
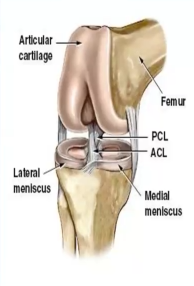
The ACL prevents ______ displacement of the femur and ________ displacement of the ________ and ________ of the knee
Posterior, anterior, tibia, hyperextension
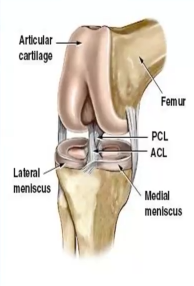
The ACL is ____ when slacked, while _____ when taut
Flexed, extended
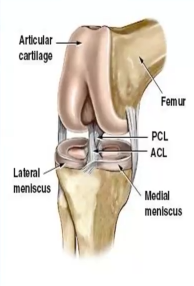
The PCL is ____ when slacked, while _____ when taut
Extended, flexed
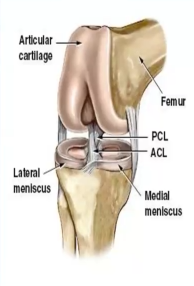
The PCL prevents ______ displacement of the femur on tibia and ________ displacement of the ________ and ________ of the knee
Anterior, posterior, tibia on femur, hyperextension
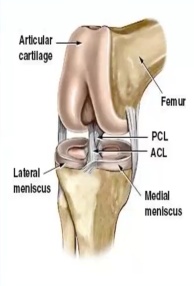
What ligament is utilized during weight-bearing exercises?…
PCL
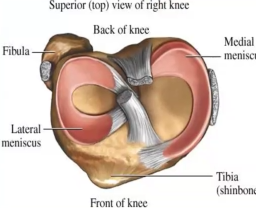
Which meniscus is circular, smaller, and more freely movable?
Lateral meniscus
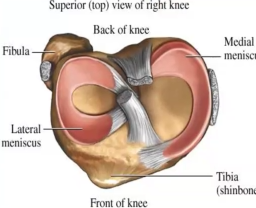
Which meniscus is C-shaped and broader?
Medial meniscus
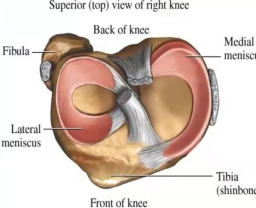
Where is the anterior end of the medial meniscus attached?
Anterior intercondylar area of tibia
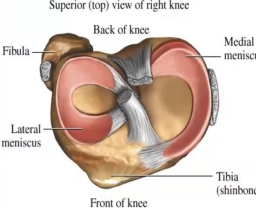
Where is the posterior end of the medial meniscus attached?
Posterior intercondylar area of tibia
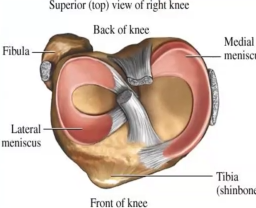
Which ligament is the medial meniscus firmly attached to?
Tibial collateral ligament