ECE 244: Electrostatics Unit
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
The magnitude of E(r, t) is
the strength of an electric field at a given point in space and time, typically measured in volts per meter (V/m).
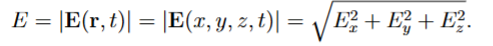
electric flux density
a measure of the electric field strength per unit area, representing the flow of electric field lines through a given area.
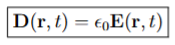
Units for D
C/m²
Electric Field from a Single Point Charge: Coulomb’s Law
The electric field produced by a single point charge, calculated using Coulomb's Law, which states that the field strength is directly proportional to the charge and inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the charge.
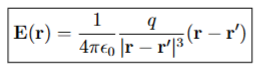
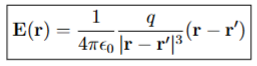
r
the distance from the charge to the point where the electric field is measured.
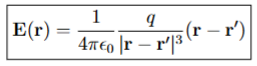
r’
vector pointing from the origin to the point charge
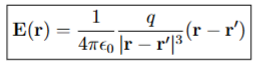
|r - r’|
the distance from the point charge t the observation point
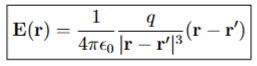
q
the magnitude of the source charge (units C)
Electric Field from a System of N Point Charges
The vector sum of the electric fields produced by each point charge at a given point in space, calculated using Coulomb's law.
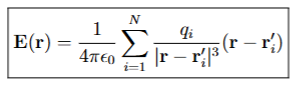
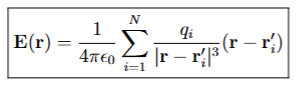
ri’
represents the position vector of the i-th point charge in a system of point charges.
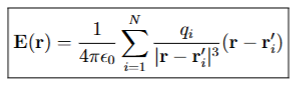
qi
represents the magnitude of the i-th point charge in a system of point charges, measured in coulombs (C).
Electric Field from a Continuous Volume Charge Distribution
The electric field sources are ____________ distributions rather than discrete point charges
continuous volume charge
The electric field sources are continuous volume charge distributions rather than __________
discrete point charges
The electric field sources are continuous volume charge distributions rather than discrete point charges characterized by the _________
volume charge density pv(r)
Standard units of pv(r)
coulombs per cubic meter (C/m³)
For a continuous charge distribution with density ⇢ v (r), the total charge enclosed in
any volume V can be calculated as
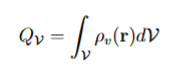
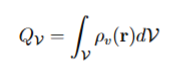
pv(r)dV’
the charge in a differential volume dV at r
The electric field at an observation point P due to a volume charge distribution with
density ⇢v (r) within a volume V 0 is
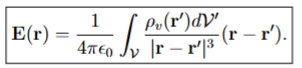
Charge from Electric Field: Gauss’ Law
Obtain the electric field E(r) due to a given volume source charge density ⇢ v (r)
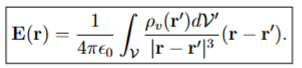
Obtain the source charge density ⇢ v (r) from the electric field E(r)
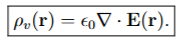
Obtain the source charge density ⇢ v (r) from the electric field E(r)
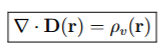
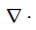
What does this operator denote?
The divergence operator
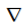
This is the “vector differential” (or “del”) operator, defined in Cartesian coordinates
as:
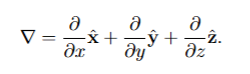
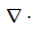
What does this transform about a field?
A vector field into a scalar field
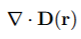
This is defined as:
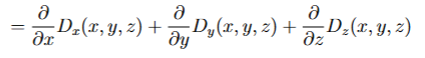
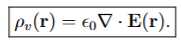
By the differential form of Gauss’ Law, the volume charge density at any point r is
related to the (spatial rate of change of) the electric field about that point as:
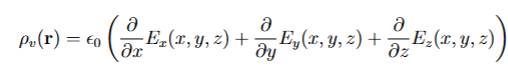
The divergance of E(r) is the measure of the extent to which?
To which the “electric field lines” diverge from the point r
The divergence of E(r) is positive when the field lines point _____ and diverge from the point r.
away
The divergence of E(r) is negative when the field lines point _____ and coverge to the point r.
towards
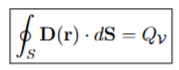
The integral form of Gauss’ Law
By Guass’ Law (integral form), the total charge enclosed in a volume V is related to the integral of the electric field on the surface S enclosing that volume as:
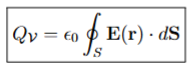
The point of the integral form of Gauss's Law is
to relate the total electric flux through a closed surface to the enclosed charge
Integral form of Guass Law
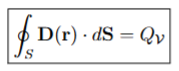
The charge enclosed in volume V, given del * D(r) for pv(r)
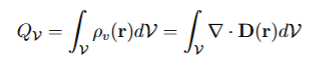
The net electric flux through surface S enclosing C:
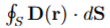
Note that the net charge Q V enclosed in V is positive if the net electric flux through S points ____ of V
out
Note that the net charge Q V enclosed in V is negative if the net electric flux through S points ____ of V
in
From the differntial and integral form of Guass’ Law, Del*D(r) = 0 at some point r…
when the electric field is neither diverging from nor converging to that point
From the differntial and integral form of Guass’ Law, Del*D(r) = 0 at some point r when the electric field is neither diverging from nor converging to that point, so therefore pv(r) =
0
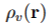
Volume charge density
From the differntial and integral form of Guass’ Law, Del*D(r) = 0 everywhere within some volume V…
Because the electric field is divergence free within that volume
The effect of the static electric field is exertion of a _____ on an electrically charged body.
force
The force on a point charge that results from an electric field:
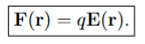
Consider a point charge q located at position r within an electric field E(r). The force F(r) experienced by the charge is given by the equation F(r) = qE(r).
Which of the following statements is correct regarding the direction of the force F(r) relative to the direction of the electric field E(r)?
A) The force is along the direction of E(r) regardless of the sign of q.
B) The force is along the direction of E(r) if q is positive and opposite if q is negative.
C) The force is opposite the direction of E(r) regardless of the sign of q.
D) The force is opposite the direction of E(r) if q is positive and along if q is negative.
B) The force is along the direction of E(r) if q is positive and opposite if q is negative.
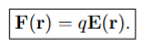
Units
Joules per meter, or Newtons
Electrostatic potential
how much work you'd have to do to move a tiny positive charge to that point in the electric field, without speeding it up or slowing it down
Electrostatic potential units
V
Static electric field E(r) derived from a scalar potential field (electrostatic potential)
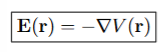
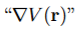
Denotes
denotes the gradient of V (r)
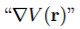
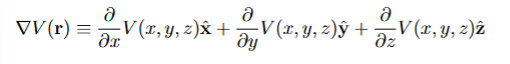
Direction: rV (r) points along the direction of maximum spatial rate of change of the scalar field V (r) at r, specifically in the direction of maximum ______ of V (r) at r.
increase
Magnitude: The magnitude of rV (r) is the _______ spatial rate of change (spatial
derivative) of the scalar field V (r) at r.
maximum
at every point r, the electric field E(r) points _______ the electrostatic potential gra-
dient
opposite
Writing the electric field as E(r) = rV (r) yields
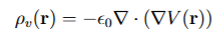
When to use Poissons Equation
To determine the volume charge distribution from electrostatic potential
Poisson’s Equation
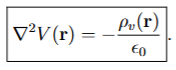
Given that the electric force F(r) on a point charge q is related to the electric field E(r) at its location by the equation F(r) = qE(r), what does this equation imply about how the electric force depends on the charge q and the electric field E(r)?
A) The force is independent of the charge.
B) The force is directly proportional to the charge and the electric field.
C) The force is inversely proportional to the charge and directly proportional to the electric field.
D) The force is directly proportional to the charge and inversely proportional to the electric field.
B) The force is directly proportional to the charge and the electric field.
What is the relationship between electric force on a point charge q and the electric field?
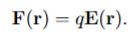
What is the electric field defined in terms of the electric potential
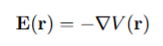
What is the relationship between electric force and electrostatic potential?
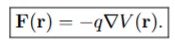
the force on a particle at some point r in a potential energy field U (r) is
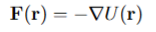
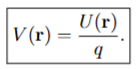
The electrostatic potential V(r) is defined in terms of the potential energy field U(r) and charge q by the equation.
What does this equation imply about the relationship between the electrostatic potential, the potential energy, and the charge?
A) Electrostatic potential is the potential energy per unit charge.
B) Electrostatic potential is the product of potential energy and charge.
C) Electrostatic potential is independent of the potential energy but depends on the charge.
D) Electrostatic potential decreases as potential energy increases, for a constant charge.
A) Electrostatic potential is the potential energy per unit charge.A
The relationship between the potential energy U(r), electrostatic potential V(r), and the electric force F(r) on a point charge q in an electric field E(r) is given by the equations:
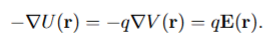
Faraday’s Law
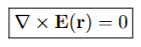

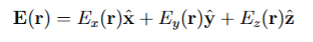
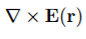
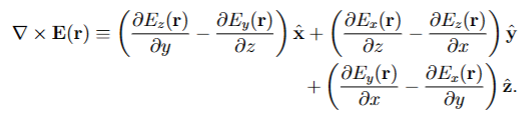
Faraday’s Law states that the curl of E(r) always vanishes
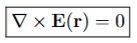
Static Electric Field
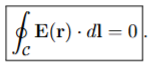
Stoke’s Theorem
Stokes’ Theorem, says that, for any open surface S bounded by a closed contour C,
the surface integral of the curl of a vector field over S is equal to the line integral over
C.