Principles of Marketing CLEP
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
What is marketing
Process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating and exchanging products and value with others. From a companies perspective, satisfying customers needs. The marketing concepts is understanding the needs and wants and satisfying customers and doing it better than the competition
Strengths of a SWOT analysis
Internal capabilities that may help a business be better than the competition.
Weakness of a SWOT analysis
Internal limitations that may interfere with a companies ability to achieve its objectives.
Opportunities of a SWOT analysis
External factors that the company could use to exploit to their advantage
Threats of a SWOT analysis
Current and emerging external factors that may challenge the companies performance
Environmental Scanning
Marketing environment includes all actors and forces outside the marketing department that affect managements ability to build and maintain successful relationships with customers.
Microenvironment
Consists of actors close to the company that affect its ability to serve customers. Suppliers, competitors etc.
Macroenvironment
Consists of larger societal forces that affect the microenvironment. Demographics, technology, societal factors etc.
Political and legal forces
Government and laws affect marketing at many levels. For example, laws against smoking may prohibit people from smoking in certain areas which could affect a company.
What is marketing research
Process that helps us understand factors such as the needs and wants of customers, what they value, etc. Consumer insights can provide a company a deeper understanding of their needs and wants.
Internal databases
Electronic collections of consumer and market information obtained from data sources within the company network
Marketing intelligence
The systemic collection and analysis of publicly available information about consumers, competitors and developments in the marketplace.
Why do companies do market research
To identify and define marketing opportunities and problems. Example, sales are down, but why? To generate, refine and evaluate marketing actions. Example: Should we add products? Also monitor marketing performance, and improve understanding of marketing
What are the steps in developing a research plan
1: Define the type of research and objectives
2: Develop the research plan for collecting information
3: Collecting and analyzing data
Exploratory Research
Your not sure what's happening. Define the problem and suggest a hypothesis (Why are sales going down?)
Descriptive Research
Describe factors: Market potential, demographics, attitudes etc
Casual Research
Test hypothesis on cause and effect. If we reduce price would sales go up?
Secondary data
Information that already exists, having been collected for a different purpose
Primary data
Information gathered for this specific research plan
Advantages of secondary data
Costs less. Less time to collect, could not get data otherwise
Disadvantages of secondary data
Is it current and relevant? (Markets change), Is it accurate? Who collected the data.
Internal and External sources are considered what type of data
Secondary data
Experiments, surveys, interviews and observations are considered what type of data
Primary data
In Stage 3: Collecting and analyzing data, what are good questions to ask yourself
How are we going to contact people? What's our research approach? What will the sampling plan be?
Observational Research
Involves gathering primary data by observing people. What are consumption patterns?
Ethnographic Research
Involves sending trained observers to watch and interact with consumers in their natural environment.
Survey Research
Usage of questionnaires and used for descriptive research.
Experimental Research
Best for cause and effect relationships. Gathering casual information
Cultural Factors on Consumer behavior
Cultures are meanings that are shared by most people in a social group. They can influence consumer behavior
Subcultures
Groups of people within the culture with shared value systems based on common life experiences
Social Factors on Consumer Behavior
Group membership influences an individuals purchase decisions and behavior
Norms
Values, attitudes, and behaviors that a group deems appropriate for its members. Example: You should not pick your nose
Status
The relative position of any individual member in a group. Roles define behavior that members of a group expects of individuals who hold certain positions
Reference Groups
Groups that serve as a direct or indirect point of comparison or reference in the forming of a persons behavior or attitude
Membership groups (A type of Reference group)
Primary groups: Family, friends neighbors and colleagues. The group you belong too
Might also be a secondary group: Religious, professional, class.
Aspirational Groups
Groups to which a person would like to belong
Opinion leaders
People within a reference group with special skills, knowledge, personality, or other characteristics that can exert social influences on others
Personal Factors on Consumer Behavior
Buyers decisions influenced by personal characteristics such as age and life cycle, occupation, economic situation, and self concept.
Real-self
Truly who you are. You and others should agree on descriptions of you
Self-Images
You have some idea of who you are, but others might not
Looking-glass self
How people believe others perceive them
Ideal self
Where you would like to be.
Brand personality
Set of traits people attribute to a product as if it were a person. Nike has an athletic personality for example
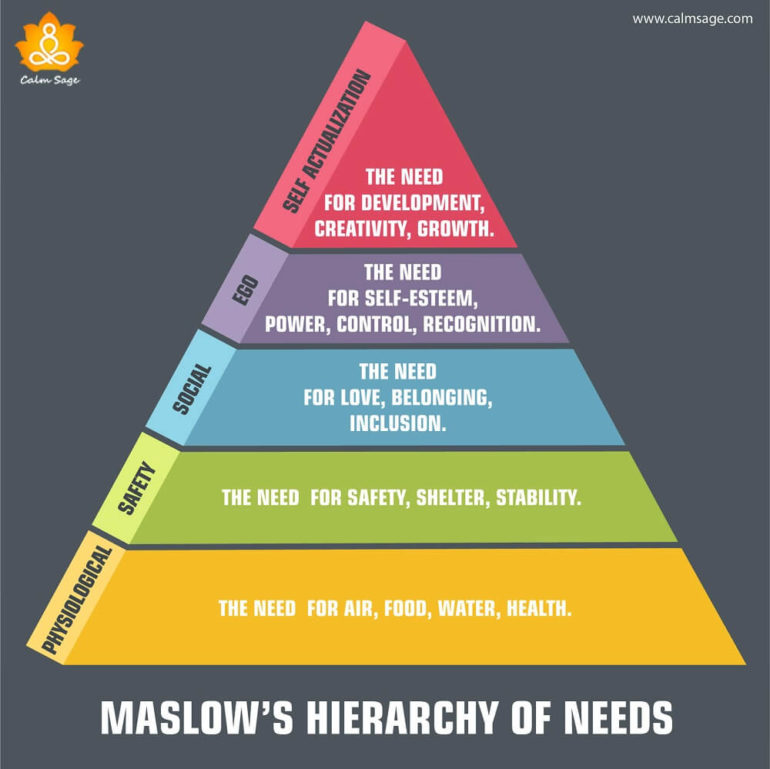
Maslow's hierarchy of needs. What are the two types of needs
Psychogenic and Biogenic
Diagram for Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Says that you cannot reach the upper levels without achieving the lower levels
Selective attention
People pay attention to SOME information but not others.
Selective distortion
People interpret information in a way that they want to be true. Paying more attention to stuff that fits your wants of beliefs
Selective retention
Remember good points about competing brands. Example: I’m a loyal customer to Toyota, and I listen to what's good about them
Continue with 2.1.3
Product
Anything that can be offered for attention, acquisition, use or consumption to satisfy needs or wants
Service
Any activity or benefit that can be offered that is intangible and does not result in ownership of anything (A type of product)
Experiences
What buying the product or service will do for the customer's experience. Example: Disney, American Girl or a Cruise. (A type of product)
Core Customer Value
Why your buying a product
Actual Product
Refers to the product itself. Design, brand name, quality etc.
Augmented Product
Additional services or benefits that come from a product. After sale service
Durable products
Don’t expire. Television for example
Non durable product
Expires eventually. Food for example.
Convenience Products
Bought with little time and effort. Milk, bread, chocolate bar. (A consumer product)
Shopping products
Extensive comparison is the norm. Cars, furniture, clothes for example. (A consumer product)
Specialty Products
Strong brand preference. Rolex, gucci, etc. Consumers goes into lots of effort (A consumer product)
Unsought Products
Unknown to the consumer, or if known, undesired. Might have a negative association. Flu shots, insurance, blood donations.
Marketers make product decisions are 3 levels. What are they
Individual product decisions
Product line decisions
Product mix decisions
There are sub levels to each decision
Product attributes sub stage of individual product decisions
What benefits does the product offer? Quality, style, image. Core value of the product.
Branding sub stage of individual product decisions
A brand is a name, term, symbol, or special design. It gives you association with the product
Brand equity
The differential effect that the brand name has on customer response to the product and its marketing.
Packaging sub stage of individual product decisions
Involves designing and producing the container or wrapper for a product. Packaging can send different messages to the consumer
Labeling sub stage of individual product decisions
Labels identify the product or brand, describe attributes, and provide promotion. How do I identify the product? Its ketchup because it says so. The fact that its red associates it with tomatoes.
Product support services sub stage of individual product decisions
What kind of service does the company give at the end of the purchase? What if you have issues? How do you give feedback for the product?
Product Line
A group of products that are closely related because they function in a similar manner, are sold to the same customer groups, are marketed through the same types of outlets, or fall within given price ranges.
Product Mix
Set of all product lines
Width: Number of product lines. Coke: Coke zero, vanilla coke, etc.
Length: Number of items within the product line
Depth: The number of versions of each item carried. (Cherry coke with lemon, with lime etc)
Consistency: How closely related the product lines are.
Services are products too. What are the parts of a service
Intangibility
Variability
Inseparability
Perishability
Intangibility of a service
Services cannot be seen, tasted, felt, heard or smelled.
Inseparability of a service
Services cannot be separated from their providers. Consumer identifies the service given with the company
Variability of a service
Service is only as good as the person who provides it. Depends on who provides them and when, where, how.
Perishability of a service
Services cannot be stored for later sale or use.
How does a company know when to extend products, develop new ones, or invest into existing ones?
Use the BCG
Use a product/market expansion grid
BCG
Looks at two components: Relative Market Share (Relative to competition) and Industry growth rate. If both are high, invest more funds into that product. If both are low, consider withdrawing. If relative market share is high and industry growth is low, then keep doing what you’re doing. If relative market share is low and industry growth is high, either invest more funds or consider disinvesting.
Product/Market expansion grid
Market Penetration: Increase the usage of my product within the target market.
Product development: Offer new products to existing markets
Market Development: A product that is already manufactured is put into new markets
Diversification: Riskiest strategy. Appeals to new markets by developing new products
Brand (Promise)
The company’s promise to deliver a specific set of features, benefits, services, and experiences. consumer can’t identify certain products over others without a brand.
Why would a company NOT brand
Can’t build up the brand or promote it.
The quality of the brand is not consistent or high
The products are not easily differntiated.
When making a brand, what stages should a company consider
Brand positioning
Brand name selection
Brand sponsorship
Brand development
Brand positioning
We want to look at the attributes, benefits and values.
Branding name selection
What name do we give our product? Suggest something about the products benefits for example. Should be easy to pronounce, remember, and recognize. Ability to be translated into other languages
Brand sponsorship
Who owns the brand. Might be a private store or the manufacturers brands. There may be licensing which allows companies to co own parts of it
Brand Development
Uses line extensions: Using existing brand names to make new forms, colors, sizes, ingredients etc. diet coke, cherry coke, classic coke etc.
What is a risk with brand extension or development
Extension not consistent with the current image can hurt the original product.
Whats considered a new product
A product never offered by the company before. The target market may not’ve gotten that product before aswell.
What are the stages of New product development
Idea generation
Idea screening
Concept development and testing
Marketing strategy development
Business analysis
Product development
Test marketing
And commercialization
Idea generation (new product development stage)
When the company knows they want new products but are unsure of which ones. There are sources of new product ideas that can be internal or external. External could be competitors, distributors, and outside firms etc.
Idea screening (new products development stage)
Tries to reduce the number of ideas to a few good ones
Concept Development and testing (new products development stage)
Product concept, and images are developed. Product Concepts are detailed versions of the idea. Product image is the way consumers will perceive an actual or potential product
Marketing Strategy Development (New products development testing)
(Still don’t have a product). Refers to the initial marketing strategy to introduce the product to the market. We want to know the description of the target market. Product positioning, sales, market share and profit goals. Price, distribution, budget. Long term sales, and marketing mix strategy.
Business Analysis (New products development testing)
Involves a review of the sales, costs, and profit projections to find out whether they satisfy the company’s objectives. What does it cost to make the product
Product development (New products development testing)
Involves the creation and testing of one or more versions by engineering departments. Requires increase in investment
Test marketing (new products development testing)
The stage where the product and marketing program are introduced into more realistic marketing settings. This is before the products full introduction
Commercialization (New products development testing)
Introducing the new products into the market.
Product Life Cycle (PLC)
The course that a products sales and profits take over its lifetime. Stages include
Product development
Introduction
Growth (increase in sales but no profit)
Maturity (increase in profits)
Decline
Market Modifying Strategy
When a company tries to increase consumption of the current product
“Special” Product Life Cycle
Has very strong increase in growth. No “introduction” might fluctuate in maturity.
Companies can often put a higher price on a product than what its actually worth and still profit. Why is this
Because consumers associate the product with a higher value