Types of Tissues
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Areolar
Wraps and cushions organs; its phagocytes engulf bacteria; plays important role in inflammation; holds and conveys tissue fluid
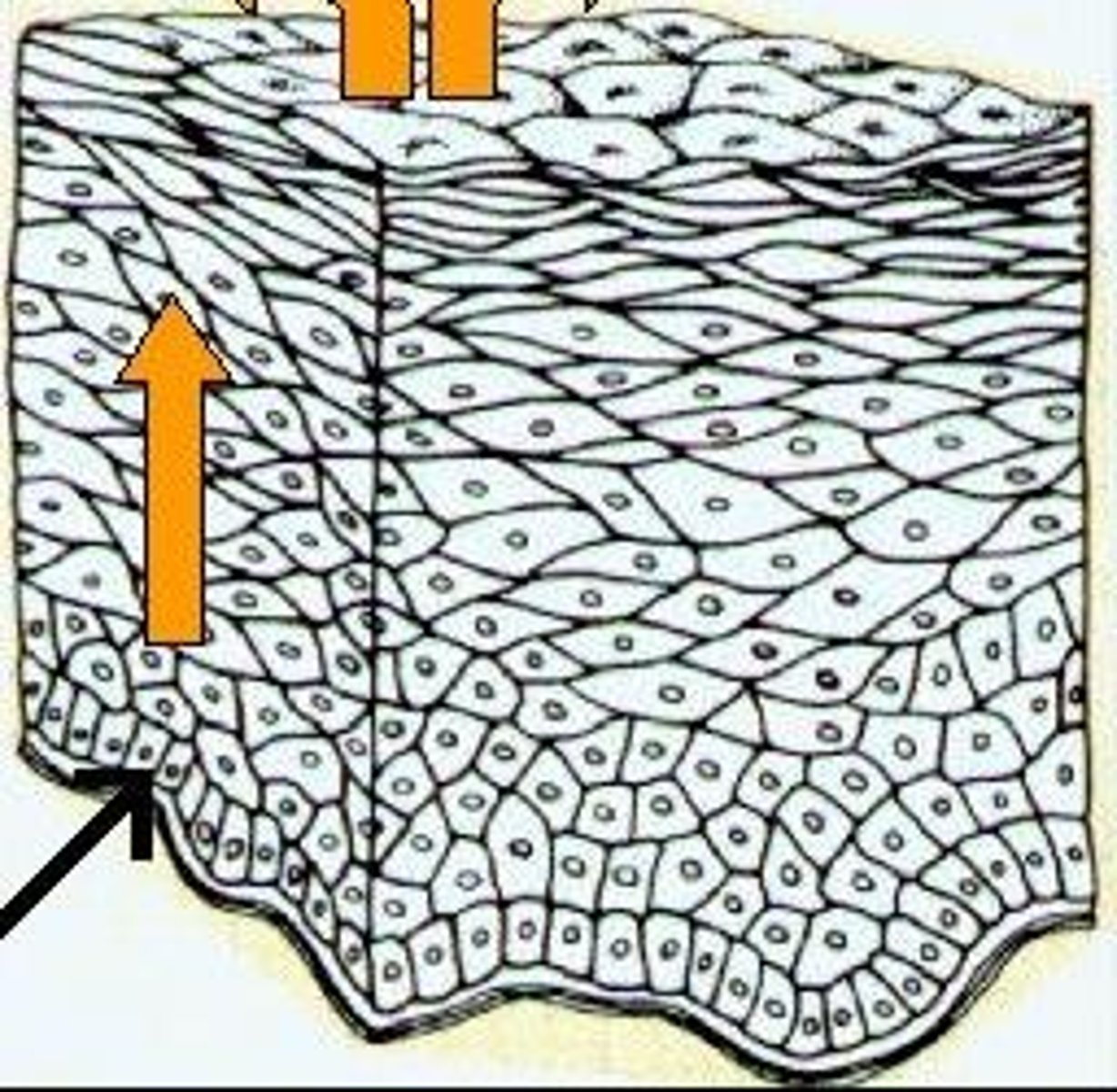
Stratified Squamous
Protects underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasion
Pseudostratified
Secretion, particularly of mucus; propulsion of mucus by ciliary action
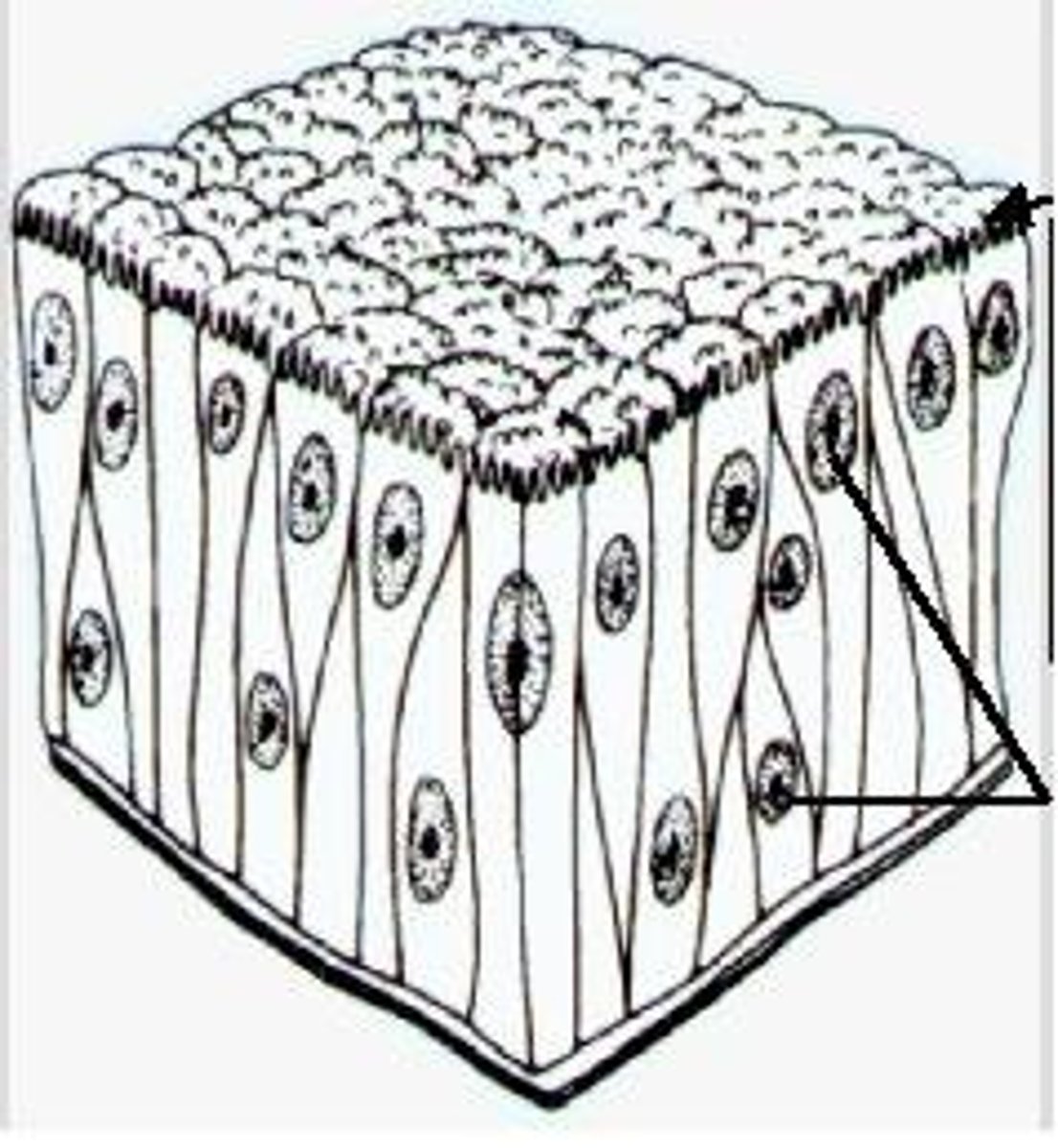
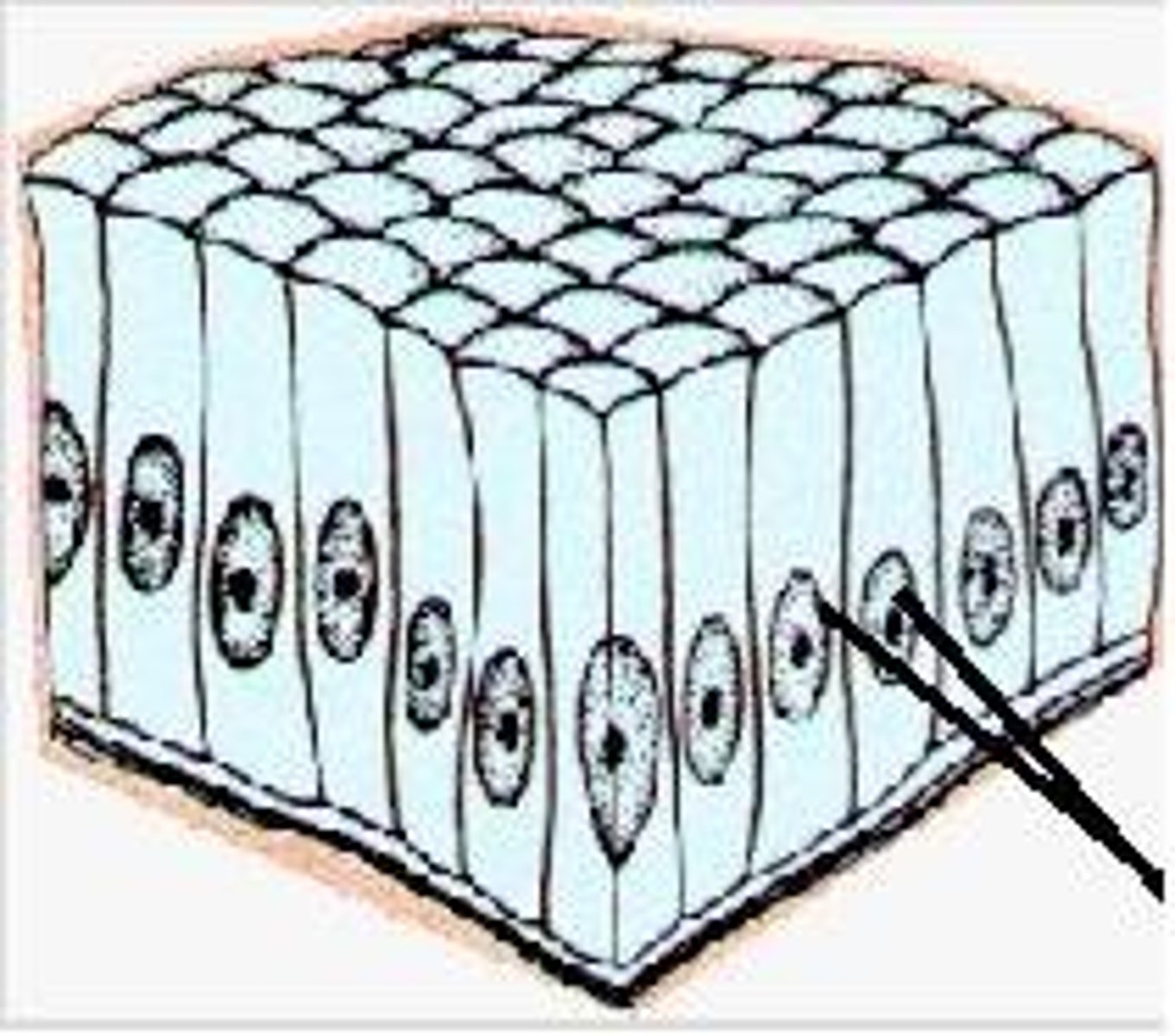
Simple Cuboidal
Secretion and absorption
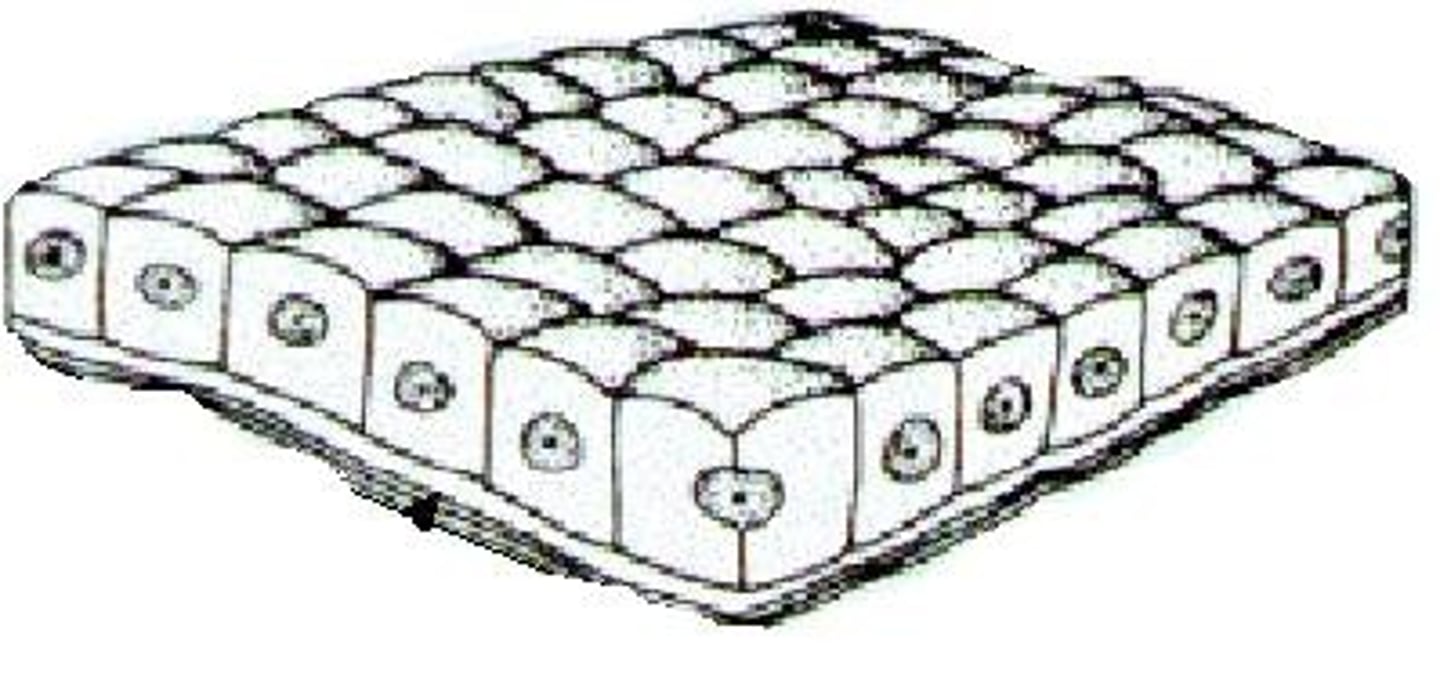
Transitional
Stretches readily and permits distension of urinary organ by contained urine
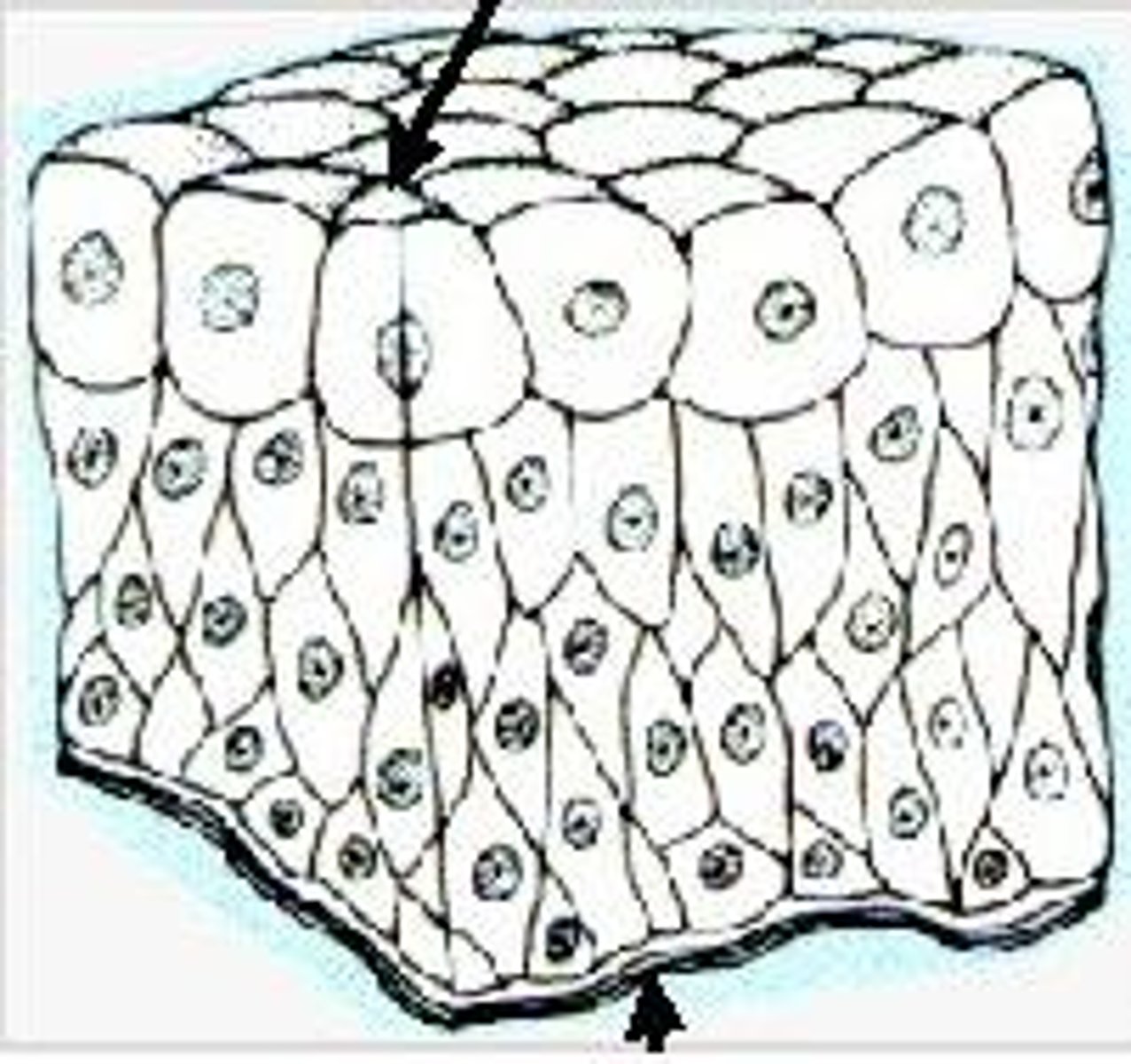
Simple Columnar
Absorption; secretion of mucus, enzymes, and other substances; ciliated type propels mucus by ciliary action
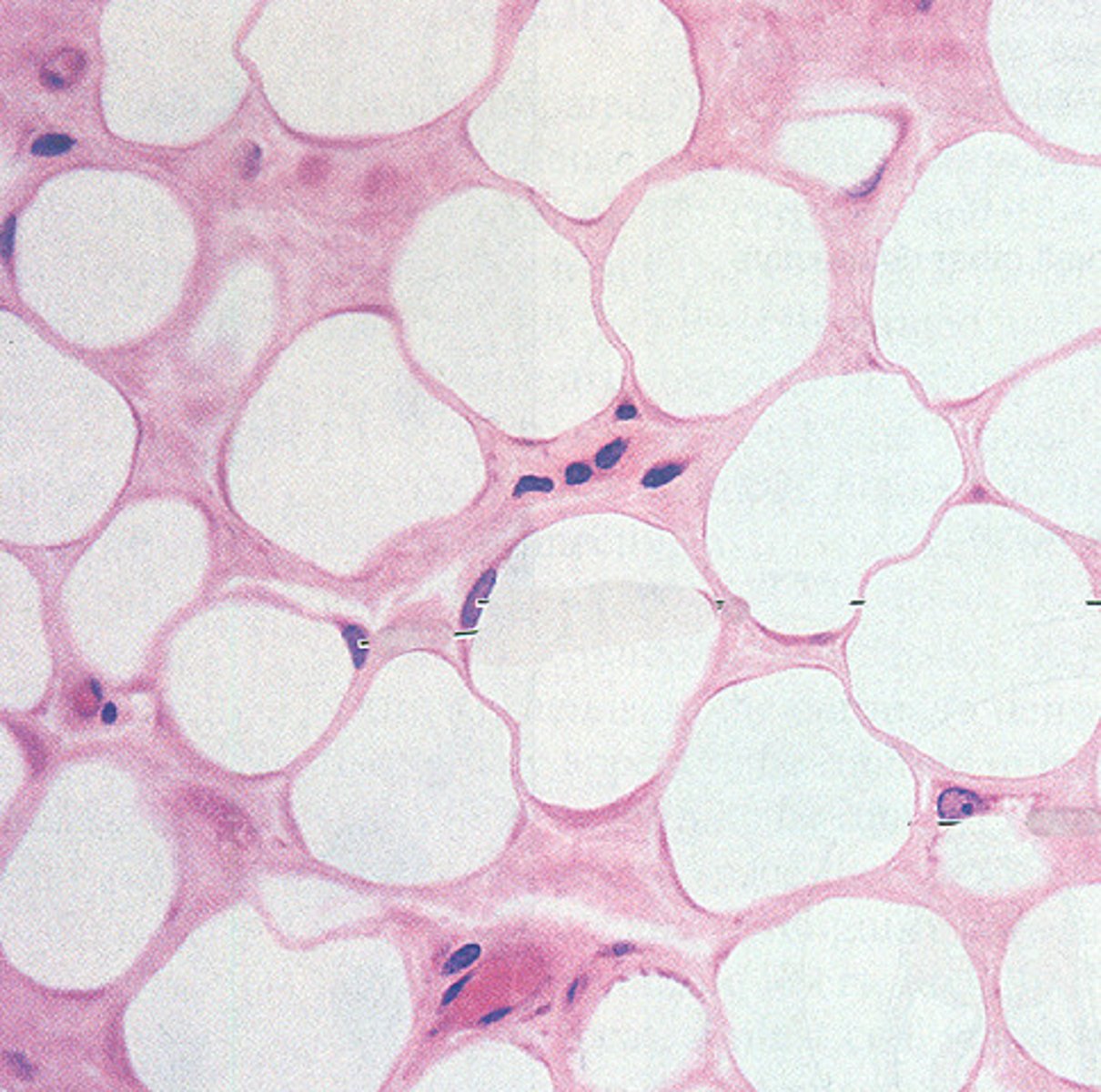
Adipose
Provides reserve food fuel; insulates against heat loss; supports and protects organs
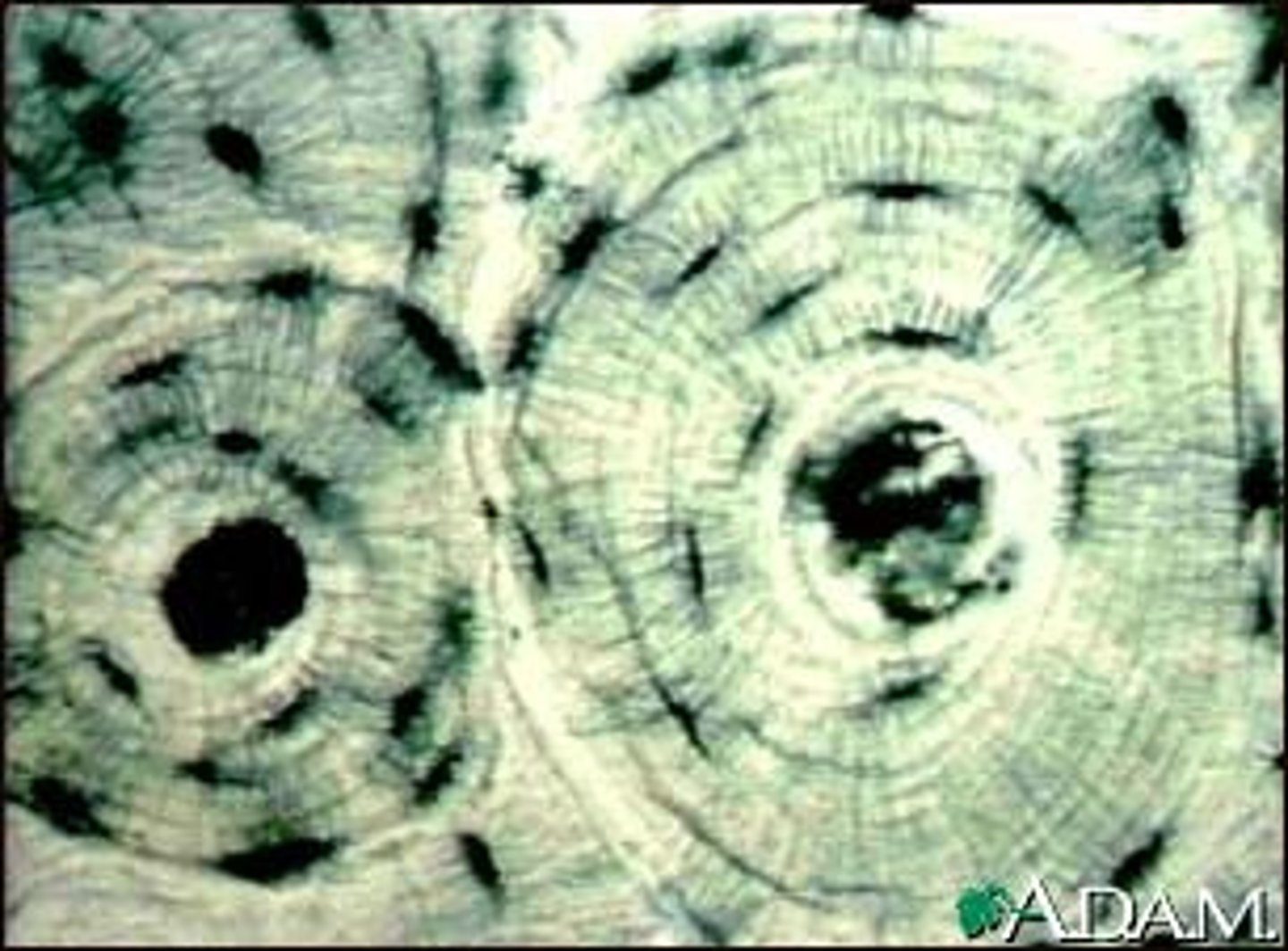
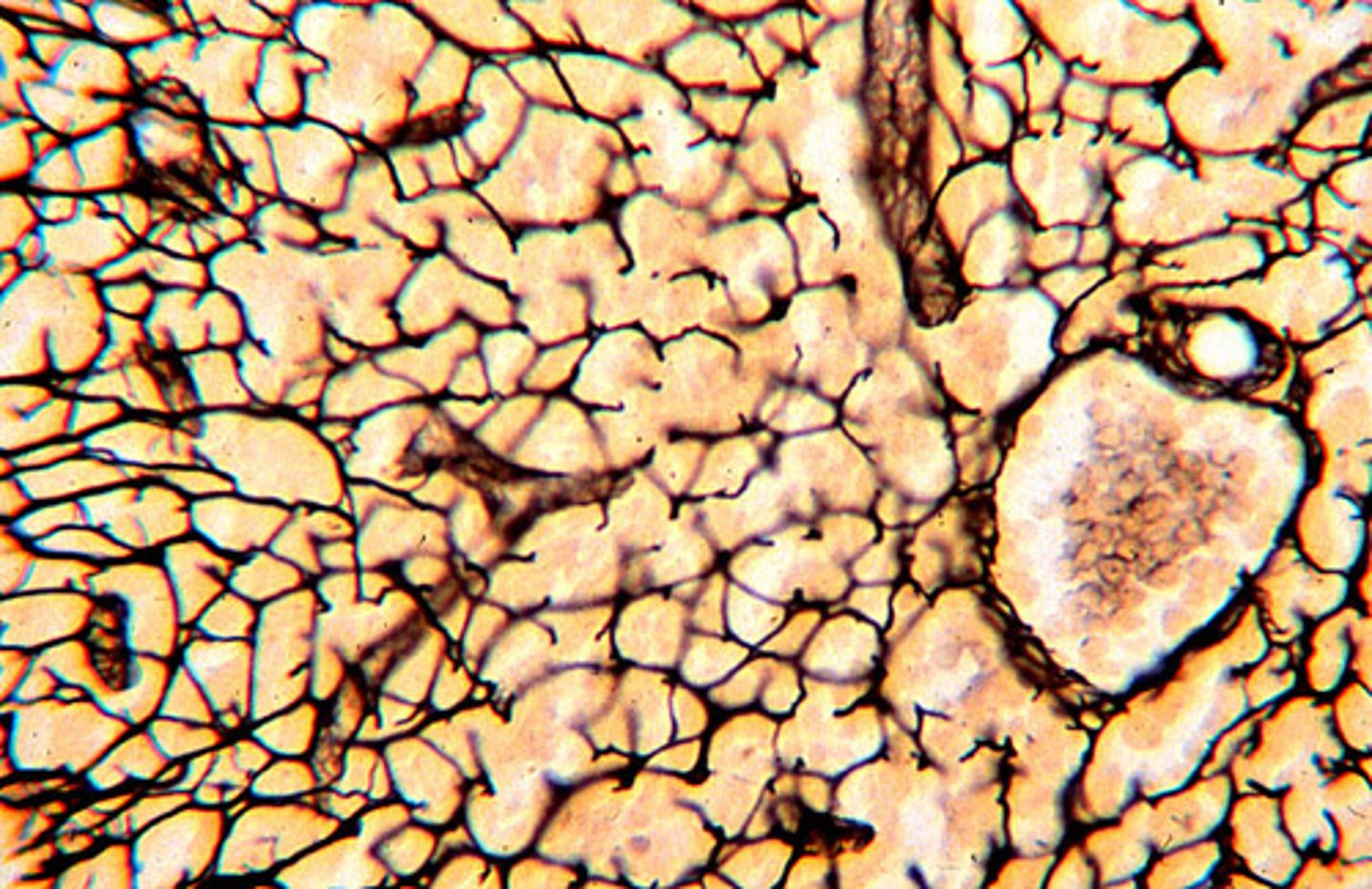
Reticular
fibers form soft internal skeleton (stroma) that supports other cell types
Four Types Of Tissue
Connective, Muscular, Epithelial, Nervous
Dense Connective
Attaches muscles to bones or muscles; attaches bones to bones; withstands great ensile stress when pulling forces is applied in one direction
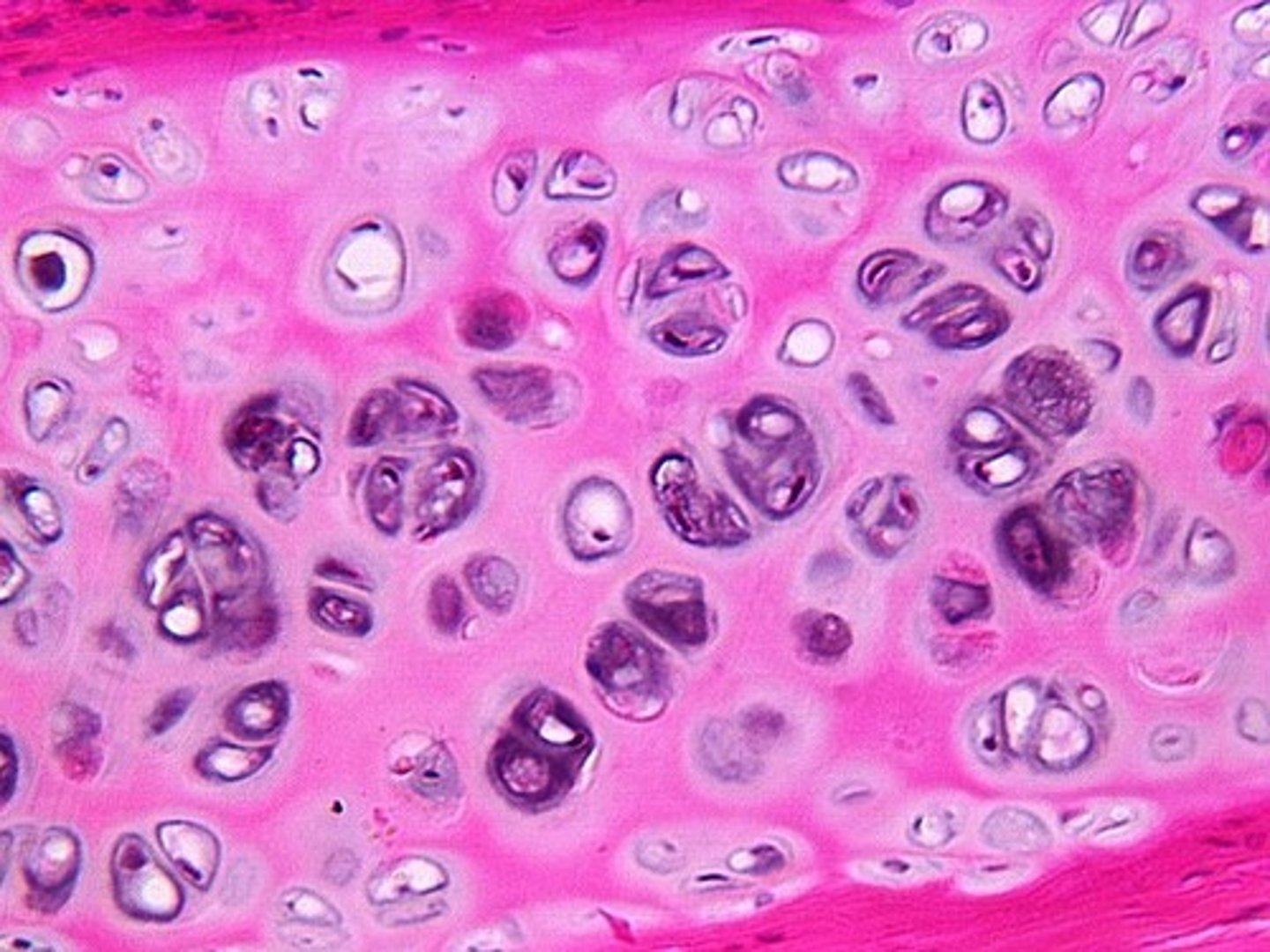
Hyaline Cartilage
Supports and reinforces; has cushioning properties; resists compression
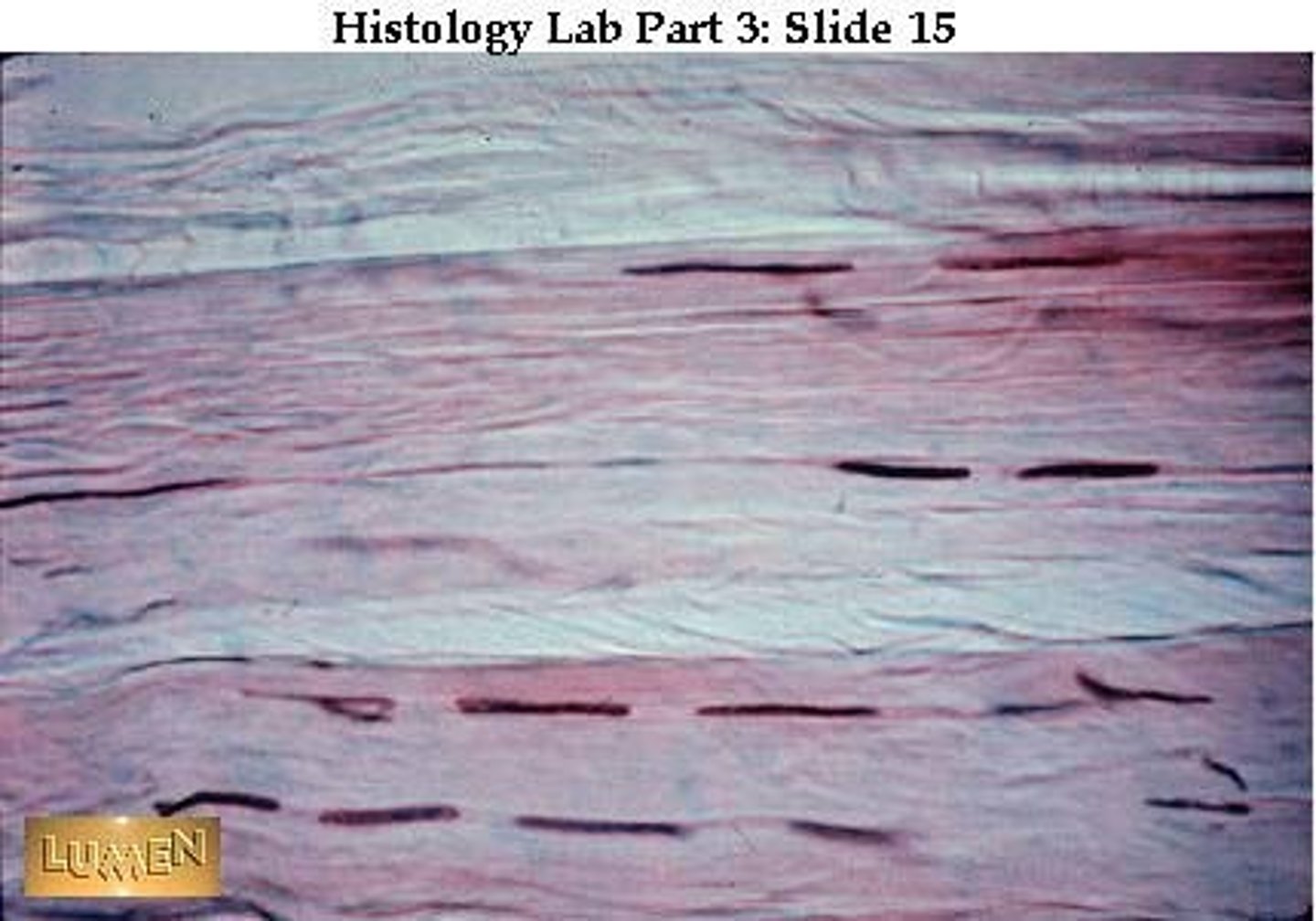
Skeletal
Voluntary movement; has striations
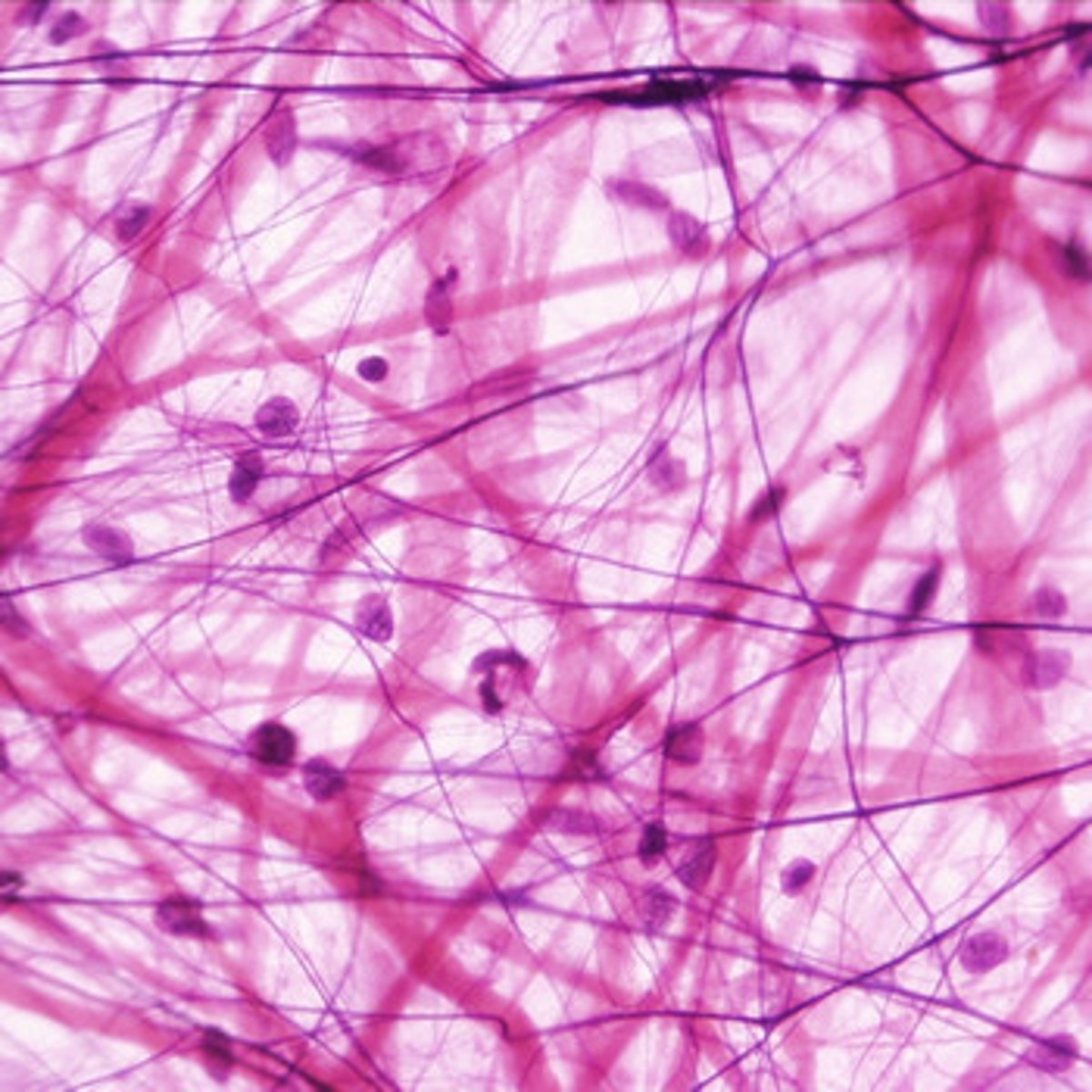
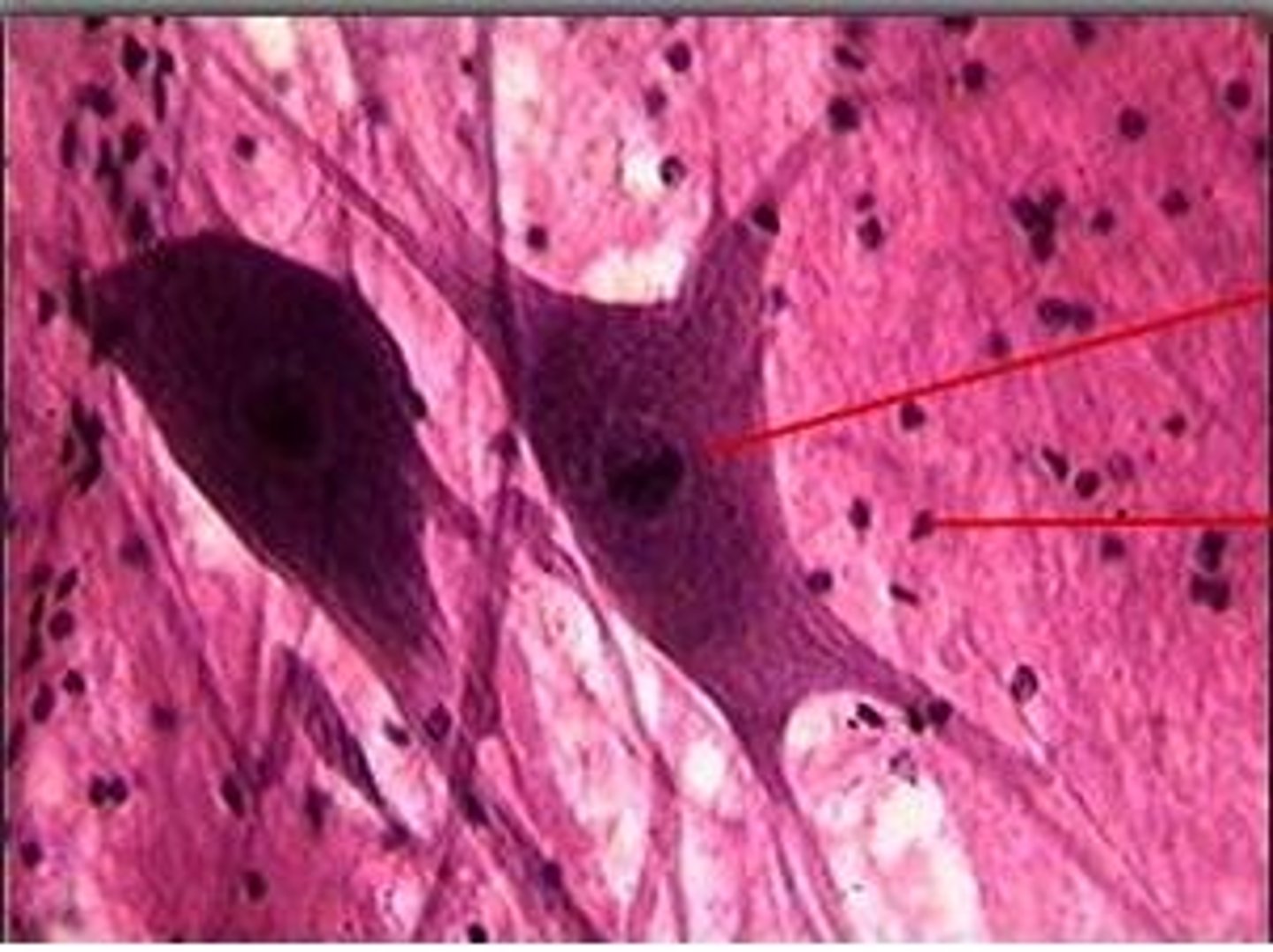
Nervous
Transmits electrical signals from sensory receptors and to effectors (muscle and glands) which control the activity
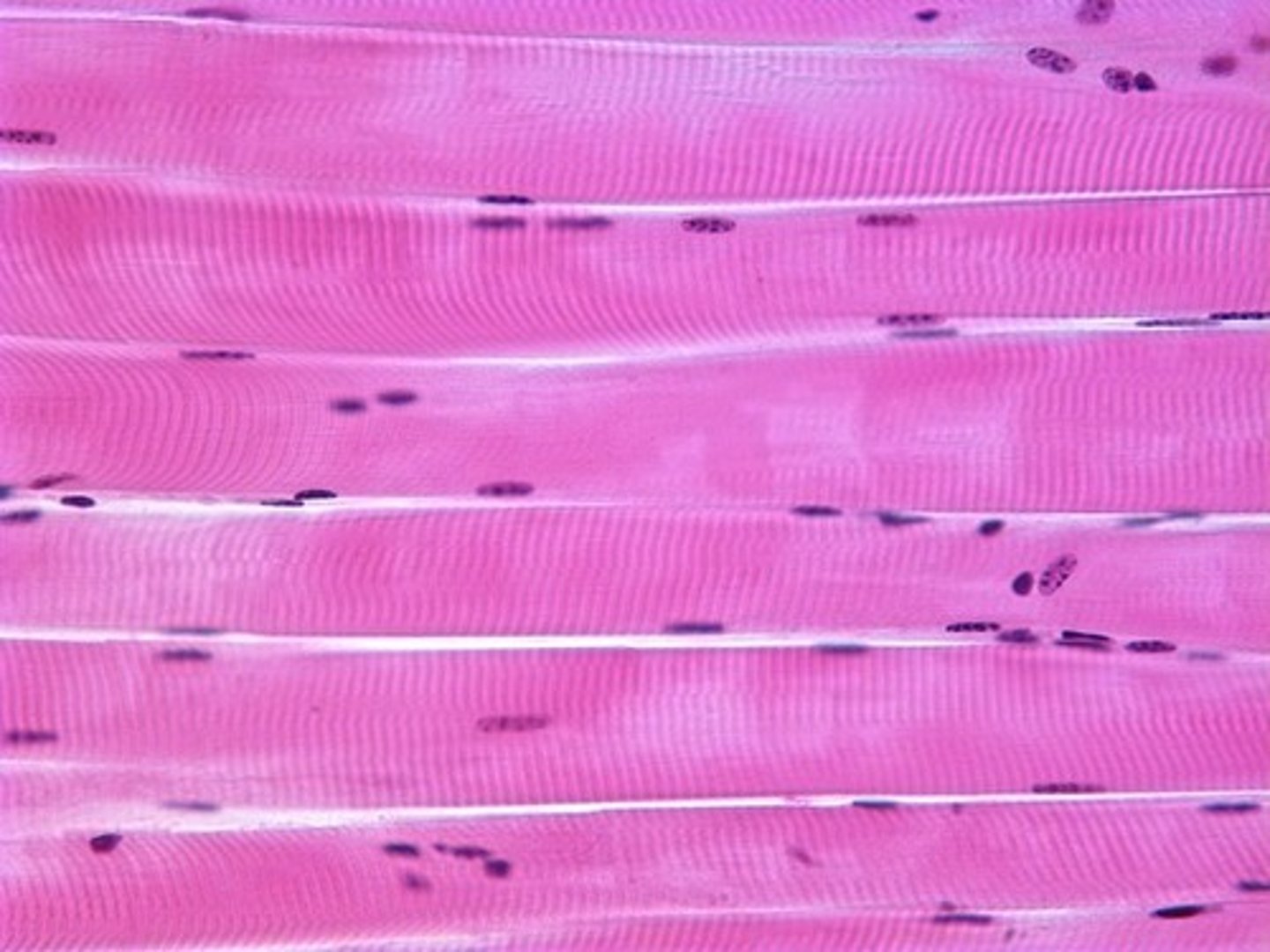
Smooth
Involuntary; no striations
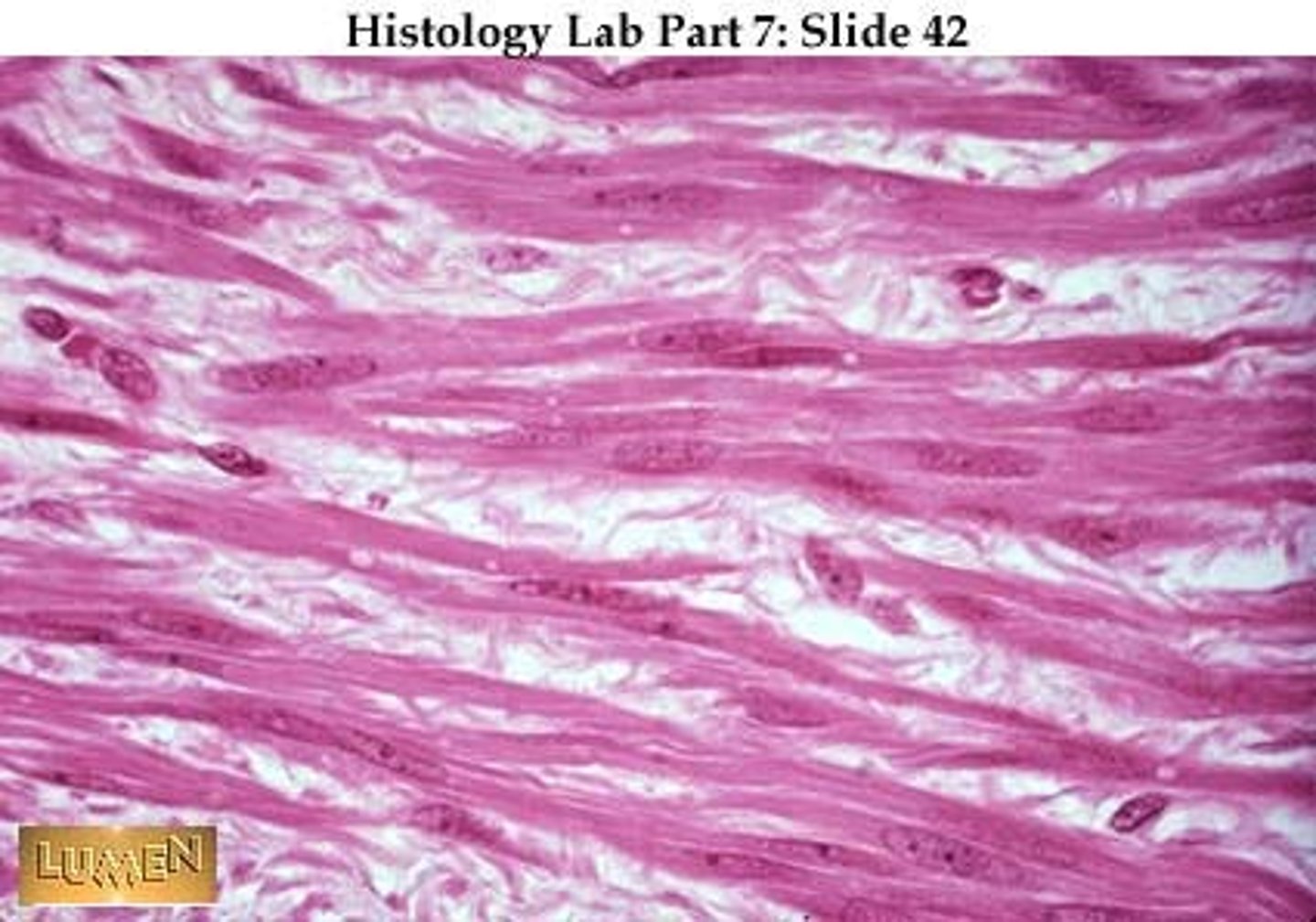
Cardiac
Involuntary movement; has striations and intercalated discs
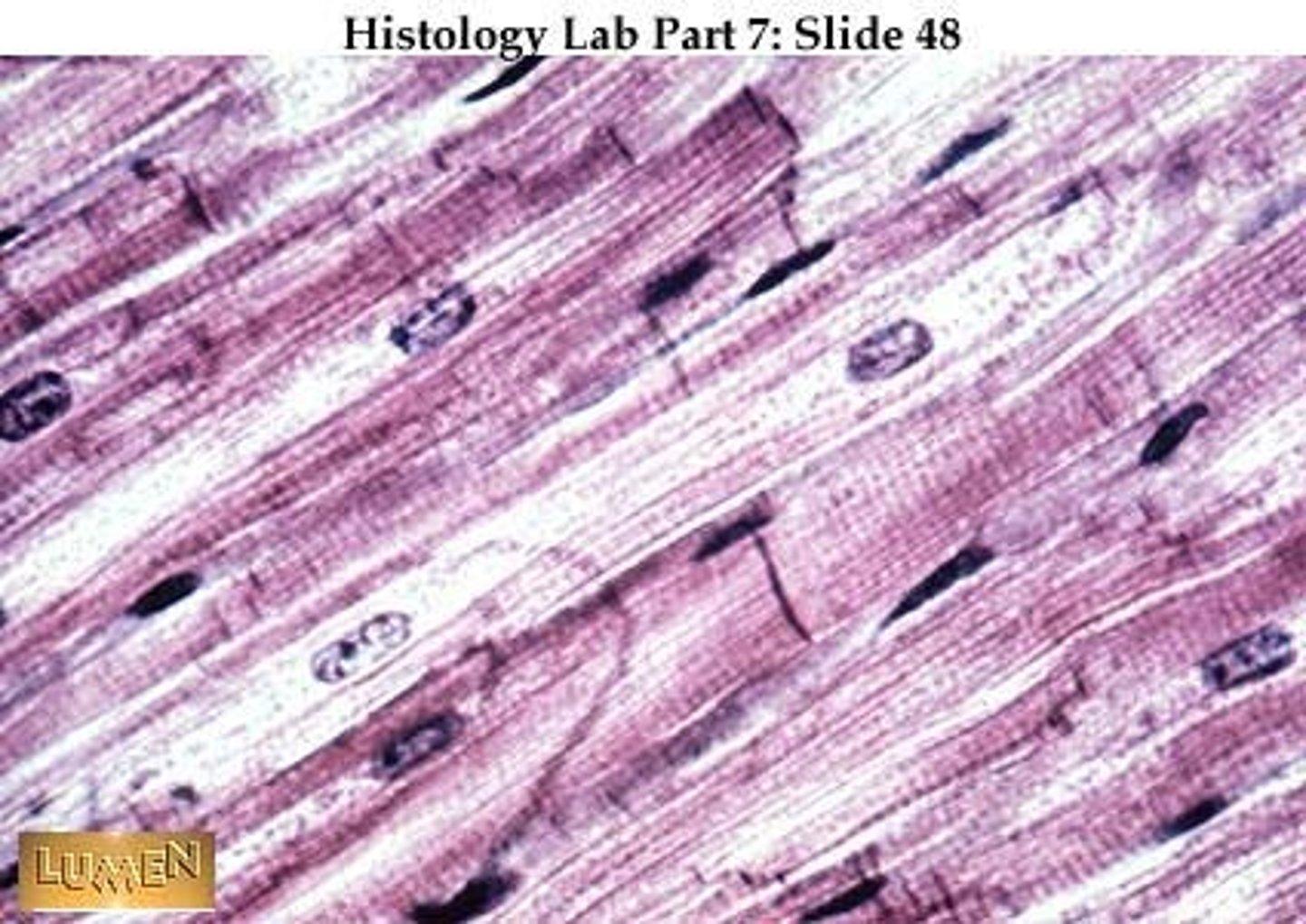
Simple Squamous
Allows passage of materials by diffusion and filtration in sites where protection is not important; may secrete lubrication substances
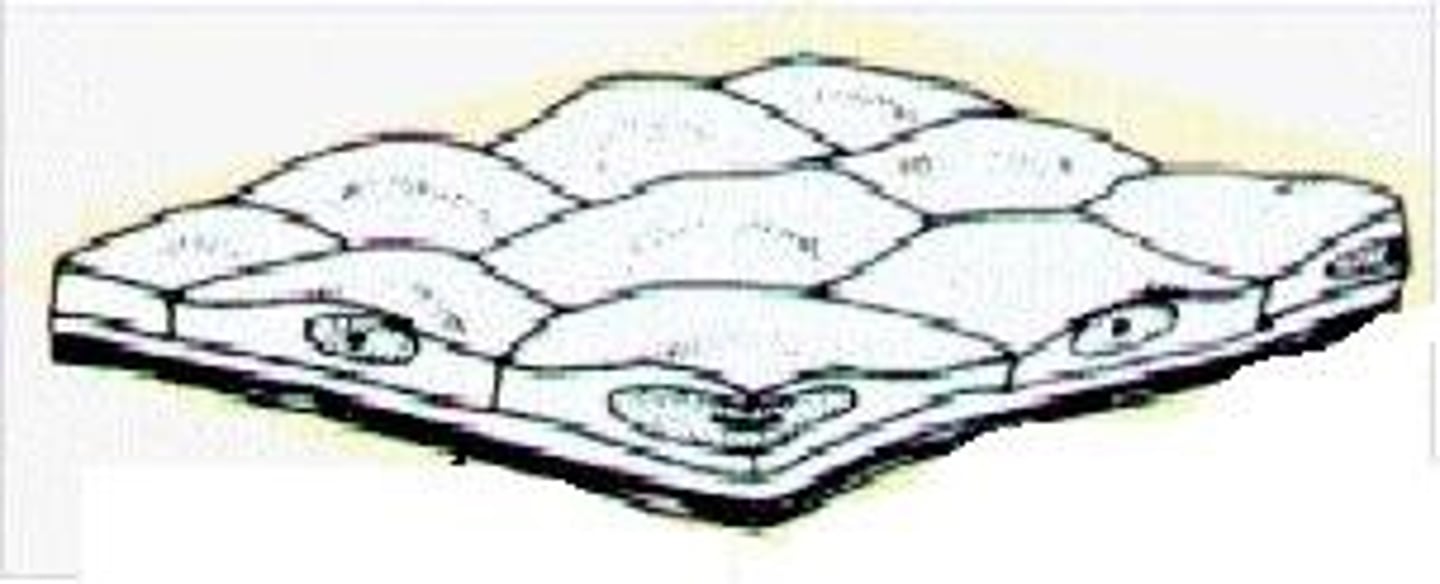
Bone (Osseous Tissue)
Supports and protects; provides levers for the muscles to act on; stores calcium and other minerals and fat; marrow inside bones is the site for blood cell formation (hematopoiesis)
