Natural Clones in Plants
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is vegetative propagation?
Natural cloning/asexual reproduction in plants
What are the vegetative organs of plants?
- Root and shoot tips
- Axillary buds
- Vascular cambium
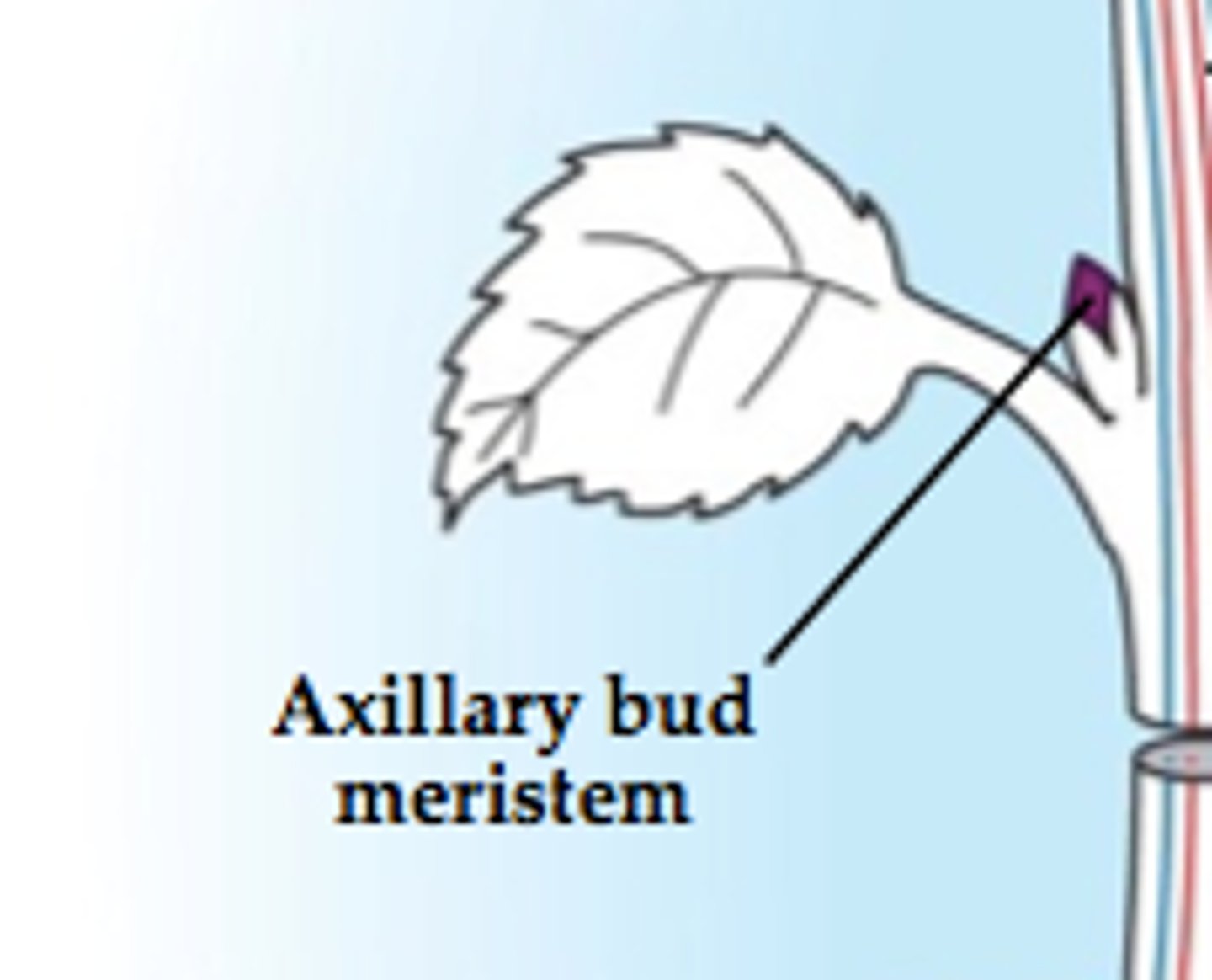
Where are axillary buds?
Where leaves and the stem meet
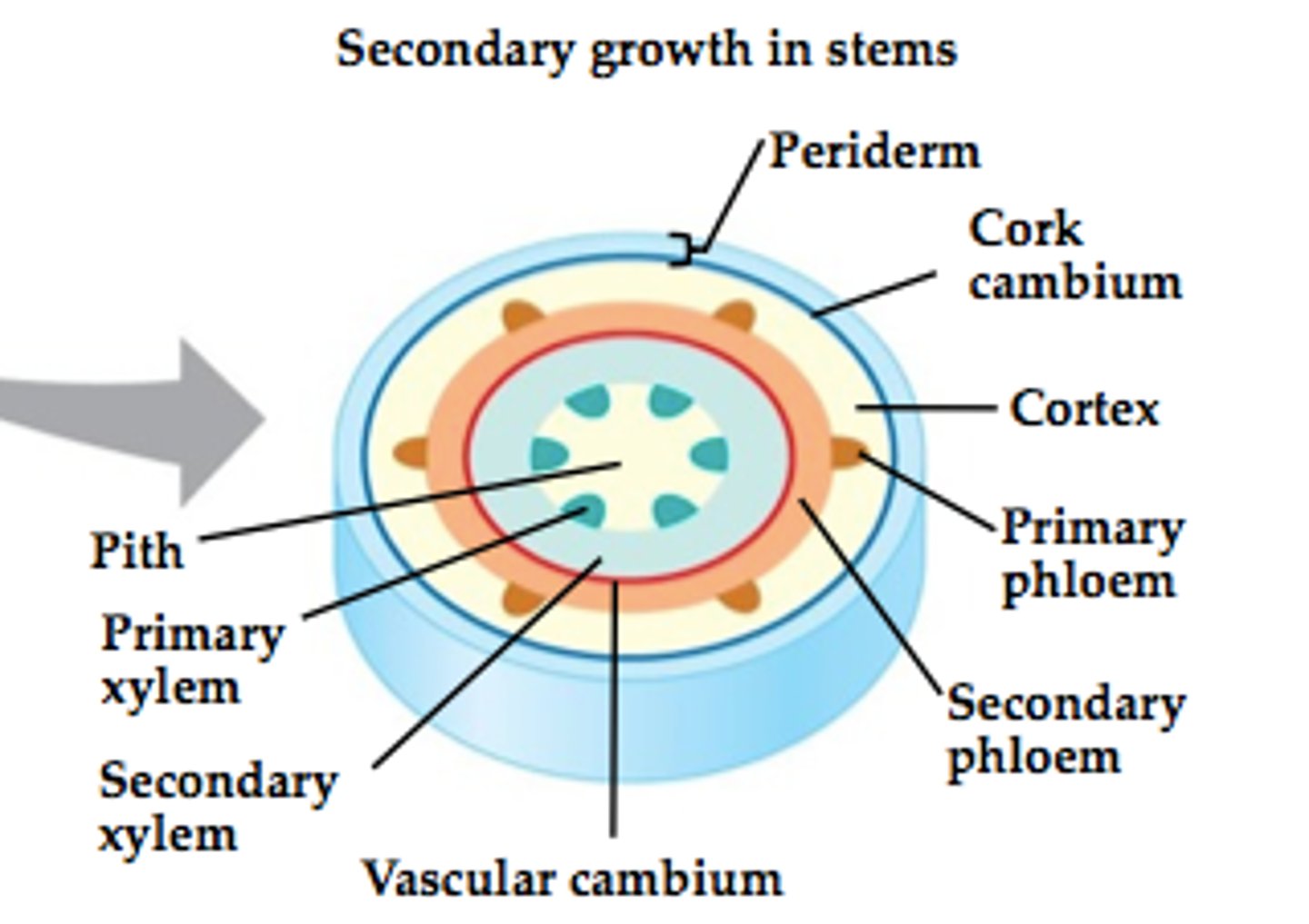
Where is vascular cambium?
Between xylem and phloem
1) Vegetative Reproduction
Over time, a plantlet forms at the vegetative organs and remains attached to its parent plant
2) Vegetative Reproduction
These plantlets are clones of their parents as no other DNA has been introduced
3) Vegetative Reproduction
At maturity, the plantlet becomes detached from its parent and can live independently, when it is capable of photosynthesising by itself
4) Vegetative Reproduction
The new plants all have the same phenotype, so are uniform
What are runners/stolons?
Modified stems that grow horizontally above ground. The buds on these stems produce roots and shoots
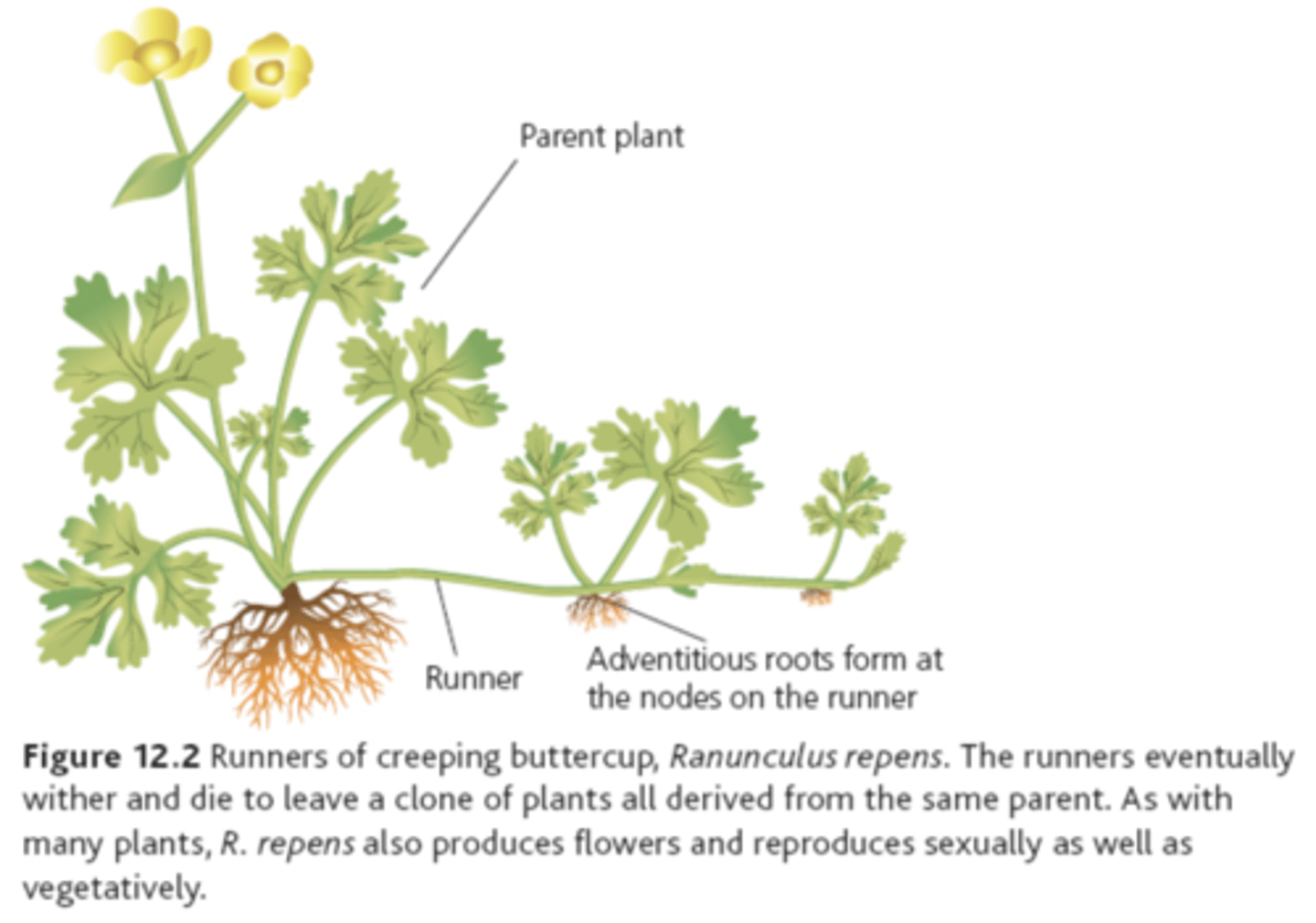
What are roots that form under the nodes of runner called?
Adventitious Roots
Will the plantlet be okay when the runner dies?
The plantlet is self sustaining so yh
What is propagation?
The reproduction of organisms (like plants) through methods like cuttings
Why don't methods of propagation require seeds?
It is asexual reproduction
A well as runners/stolons, how else can plants can propagate asexually?
Using tubers, bulbs, suckers
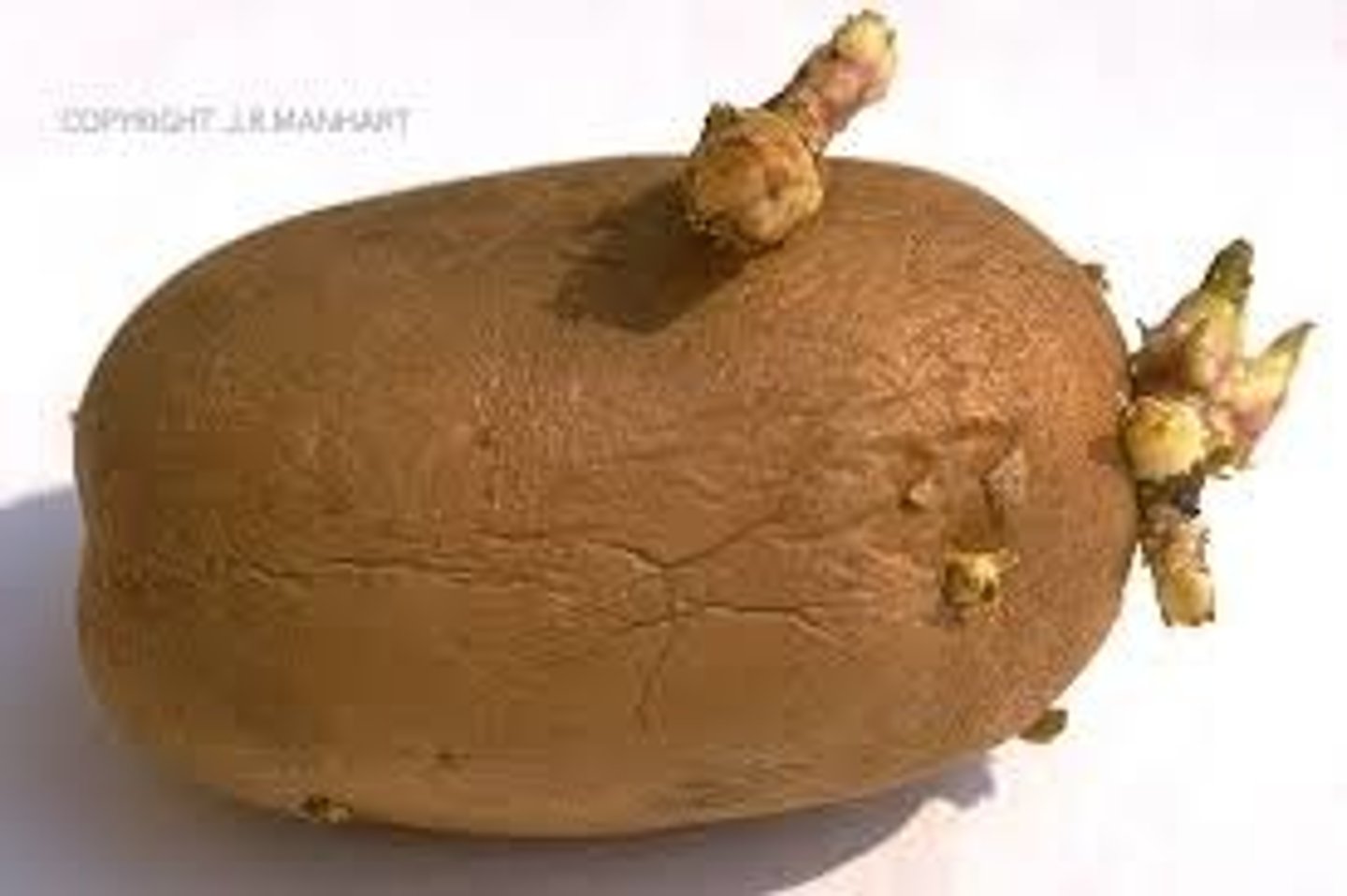
What is a stem tuber?
The tip of an underground stem becomes swollen with stored food to form a tuber or storage organ. Buds on the storage organ develop to produce new shoots (like eyes on a potato)

What is a stolon?
What is a bulb?
A thickened, underground stem with fleshy storage leaves attached at the base
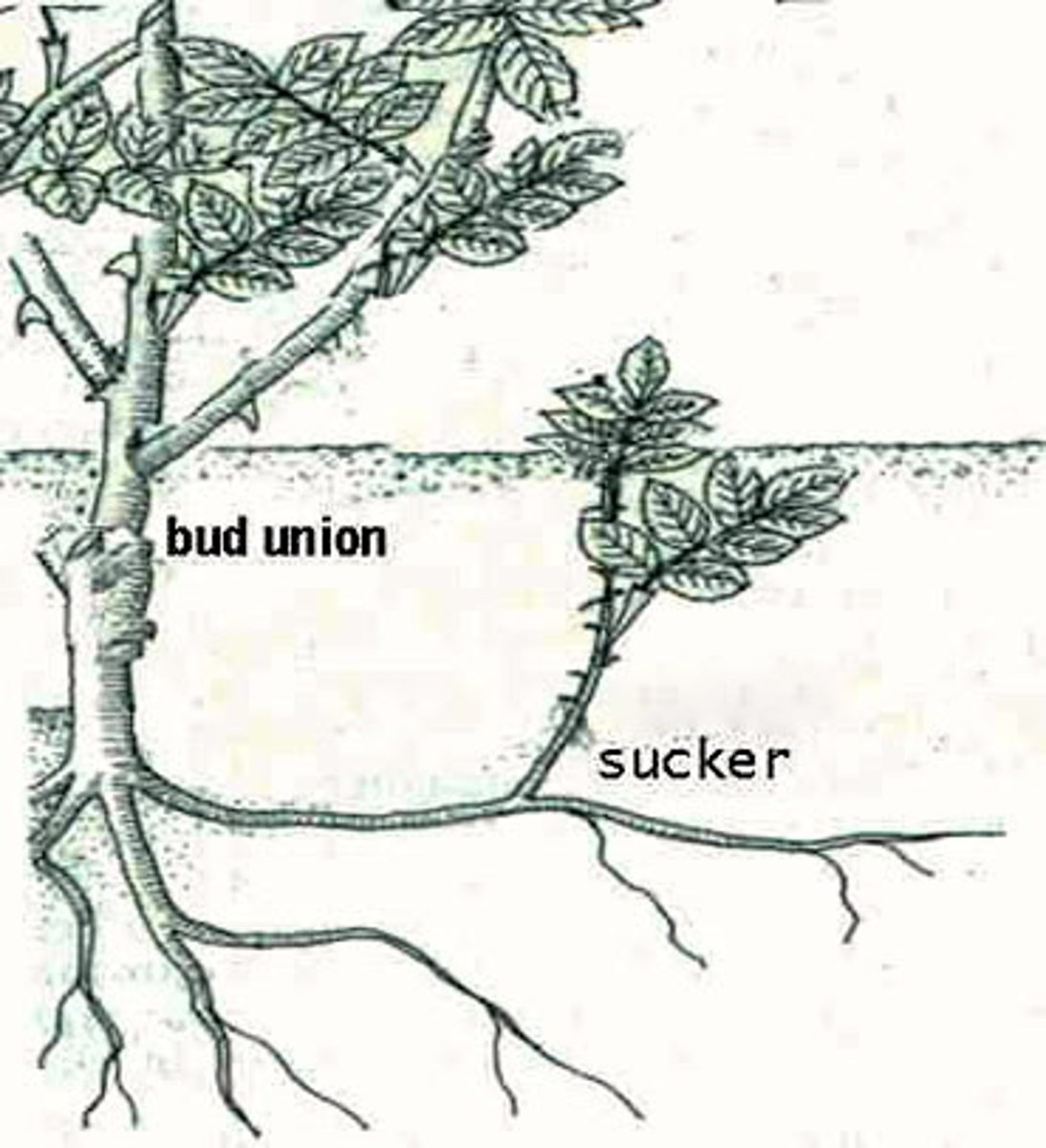
What are suckers?
Plant stems that arise from buds on the roots
What do onions and garlic produce?
- Bulbs
- Bulbs can grow adventitious roots underground and leafy shoots above ground
How the production of natural clones is exploited in horticulture.
- To propagate desirable species asexually, effectively, and at a lower cost than utilising sexual reproduction techniques.
- Splitting up bulbs, removing young plants from runners, and cutting up rhizomes all increase plant numbers cheaply, and the new plants have exactly the same genetic characteristics as their parents.