Specialist Modalities Applications
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Safety concerns of a Static Magnetic Field
Static Magnetic Field- projectile of metals/pulled force of metal, must remove metallic things (jewellery etc)
Need consent and safety forms
Safety concerns of Radiofrequency pulse
Radiofrequency Pulse can:
Produce heat and create burns if there is a closed circuit in the body
Produce Peripheral Nerve Stimulation
Safety concerns of Gradient Coils
They vibrate loud so can damage hearing
Patients require earplugs
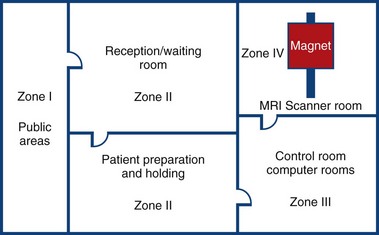
MRI Zone 4
Zone 4: Magnet Room
Authorised access only
The scan room door is always locked when unattended
Metal is removed
Danger signs
When the scan room door is opened, the MRI Safety barrier must be implemented at all times by MRI personnel
Forms for safety and consent

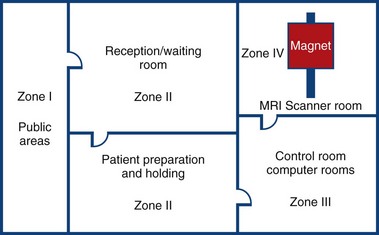
MRI Zone 3
Zone 3: Control Room
All metal removed
Locks on doors
Caution signs
Authorised access only

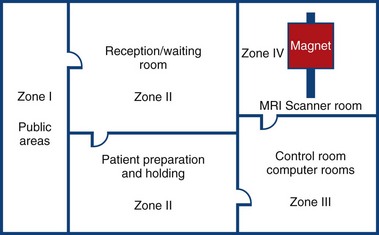
MRI Zone 2
Zone 2: Patient Screening and Prep
Patients and families undergo screening and are cleared to enter the magnetic area

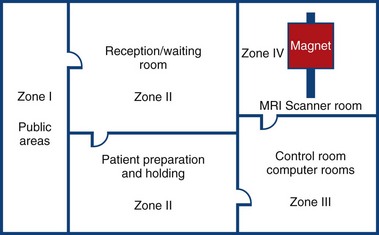
MRI Zone 1
Zone 1: Unrestricted area (public walkway)

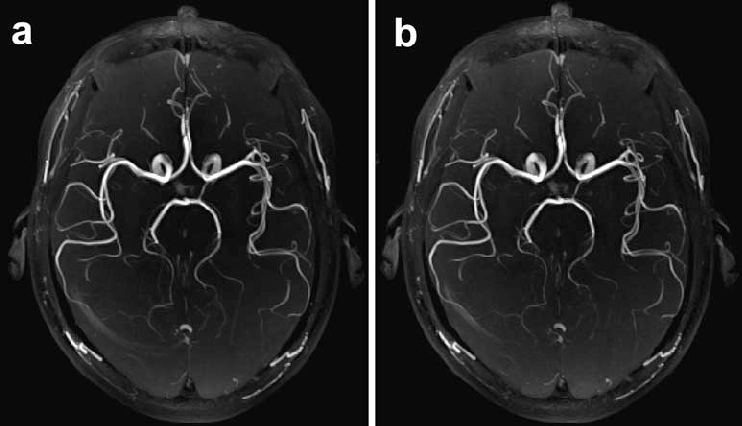
Time of Flight (TOF) applications
A specialised imaging technique of visualising blood vessels without contrast
Applications:
TOF MRA is commonly used to diagnose conditions like intracranial occlusions, aneurysms, and arteriovenous malformations
In plane Imaging
In-Plane Imaging is where the MRI is parallel to the flow direction allowing the image to be bright.
This is because we are still in the FoV so get signal
Applications:
In plane imaging offers the potential for assessing vessel patency, and both volume flow rate and flow velocity
Through plane Imaging
Through Plane Imaging is where the imaging is perpendicular to the flow direction making the image dark.
This is because the atom we gave the signal to has now left/gone past the fov
Applications:
Used for quantitative flow measurements, such as volume flow rate and velocity
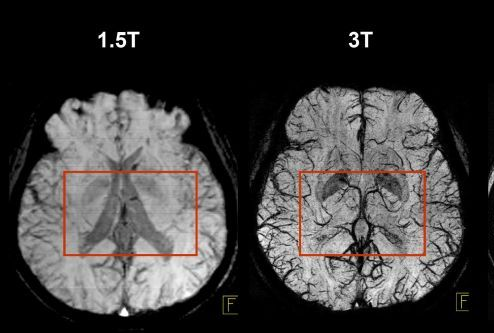
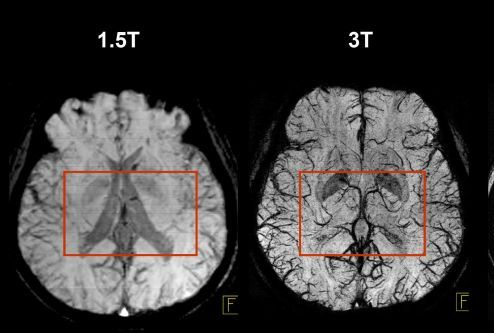
1.5 Tesla Imaging Method
1.5 T imaging uses a magnetic field strength of 1.5 Tesla. It is used for routine, whole-body imaging and is found in public hospitals:
Pros
is more tolerable for sick patients
less movement artefacts
safer
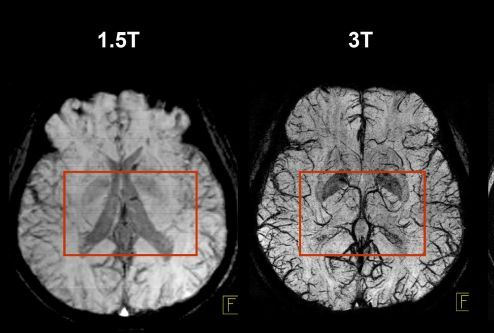
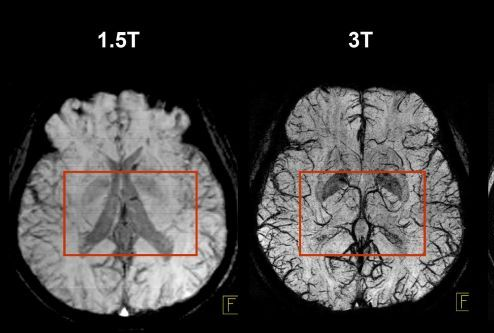
3 Tesla Imaging Method
3 T Imaging uses a magnetic field strength of 3 Tesla and is high resolution imaging.
Pros
has more signal
decreased scan time
Cons
More chance of burns and projectiles
Harder for patients to thermoregulate so increased movement
T1 Weighted Imaging
T1 is typically used as an informal anatomy scan.
Fat is Bright (quickly realigns its longitudinal magnetisation with B0)
Water is Dark (has much slower longitudinal magnetisation realignment after an RF pulse and therefore, has less transverse magnetisation)
Applications:
T1 focuses on highlighting anatomy
Useful to detect contrast
As contrast media goes to areas of high blood supply it can detect infections
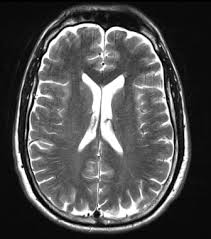
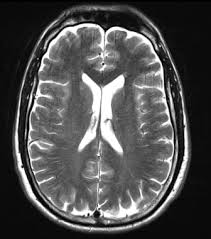
T2 Weighted Imaging
T2 is good for detecting pathologies such as cysts
Water is bright
Fat is grey
Applications:
T2 focuses on pathology, making fluids bright, which is ideal for visualizing inflammation, edema, and certain lesions
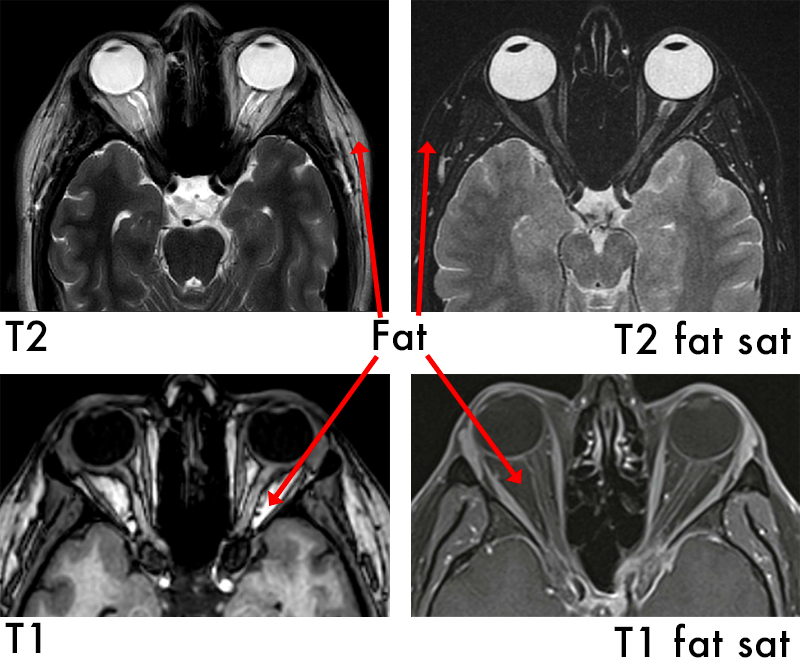
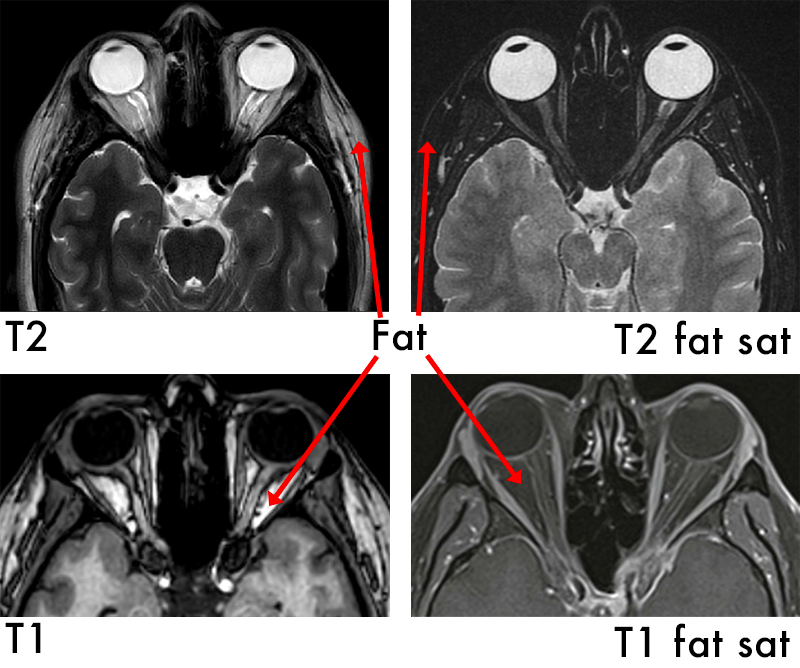
T2 Fat Saturation
T2 Fat Saturation is used to see inflammation. This technique “turns off” or removes any fat from the image so now:
Fluid is bright
Bone is dark
Fat is dark
Applications:
Enhance the visualization of specific tissues or structures by suppressing the signal from fat
Advantages of Ultrasound
Advantages
Readily available
Relatively cost effective
Does not use ionising radiation
No contraindications
Shorter scan and wait times compared to MRI
Can be dynamic and interventional
Scan can be easily extended to assess other areas
Non-invasive
Minimal patient prep
Mobile
Dynamic info
Excellent solid vs cystic info
Ultrasound Disadvantages
Disadvantages
Operator Dependence - training of sonographer and experience may yield varying results
Artefact misinterpretation
Thermal/mechanical injury (fetus most at risk- no known effects)
Limitations: bone, air or unfavourable body habitus
User injury
Little physiological info
Reproducibility between scans
Benign vs Malignant cross-over appearances
Complex Cyst Appearances
Thick walled
Internal echoes
Septations
Internal Flow
Irregular Outline
solid and cystic
Mural Nodules
Right Upper Quadrant Pain (Biliary Stones) Symptoms
Complaining of RUQ pain (sometimes colicky)
Onset of pain after fatty food
Nausea/vomiting
Bloating
Murphys positive
Jaundice
RUQ Pain Differentials
Hepatitis or other liver disease
Pancreatitis
Cholecystitis
Choledocolithiasis
Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction
Vascular Compromise- eg portal vein thrombosis (patient usually is unstable)
X-ray use for US
An erect cxr is used to rule out plural causes or abdominal air
Abdoment xr to rule out obstruction - occasionally a large biliary stone can be found
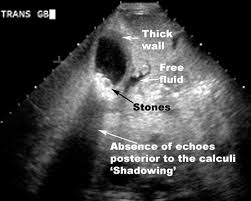
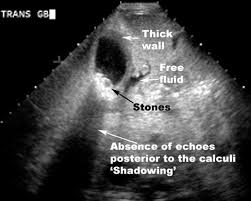
Cholecystitis on US
Thick Gallbladder walls
Oedematous wall (swollen)
Vascular wall
Murphys positive (hand pressed on gallbladder area produces pain on inspiration)
Fluid surrounding Gallbladder
Stones in Gallbladder
Contracted gallbladder
Wall Echo Sound sign (contracted gall bladder filled with stones)
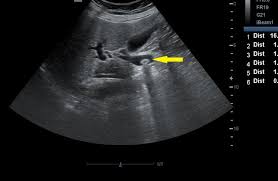
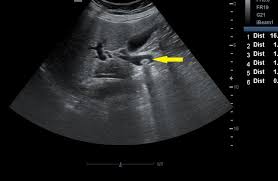
Choledocholithiasis on Ultrasound
Choledocholithiasis
Bile duct >6mm
Intrahepatic duct dilatation
Distended Gallbladder
+/- pancreatic duct dilation
Stones in gallbladder
Ultrasound vs ERCP Advantages
US Advantages
Non-invasive
Assessment of organs/complications or other causes of pain - assess Gallbladder as well as the Bile Duct and mobility of stones in the gall bladder
Readily available, cost effective etc
May lead to surgical intervention earlier for:
Cholecystitis (to OT for Lap Chole)
Choledocholithiasis (if confirmed on US then to ERCP, if not confirmed on US then to MRCP)
No stones seen but ductal dilatation intra and extrahepatic (to CT for ?mass or MRCP)
US vs ERCP Disadvantages
US Disadvantages
Limitations due to gas, habitus and (sometimes) pain - can see distal obstruction signs but not the cause
Operator Dependent
No Intervention available at the time of scan
ERCP vs US Advantages
ERCP Advantages
Higher sensitivity for Choledocholithiasis
Interventions available at time
Sphincterotome can be performed for further stones to come through
Avoids full anaesthetic in comparison to IOC/Lap Chole
ERCP vs US Disadvantages
ERCP Disadvantages
Invasive
Ionising Radiation
Sedation required
Risk of perforation
Risk of pancreatitis
Painful
Reduced Pt compliance/consent
US vs MRCP Advantages
US Advantages
Non-invasive
Assessment of organs/complications or other causes of pain - assess Gallbladder as well as the Bile Duct and mobility of stones in the gall bladder
Readily available, cost effective etc
May lead to surgical intervention earlier for:
Cholecystitis (to OT for Lap Chole)
Cholecystitis and Common Bile Duct Dilatation may have Intra Operative Cholangiography and Lap chole
Choledocholithiasis (if confirmed on US then to ERCP, if not confirmed on US then to MRCP)
No stones seen but ductal dilatation intra and extrahepatic (to CT for ?mass or MRCP)
US vs MRCP Disadvantages
US Disadvantages
Limitations due to gas, habitus and (sometimes) pain - can see distal obstruction signs but not the cause
Operator Dependent
No Intervention available at the time of scan
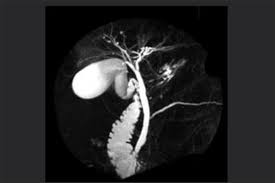
MRCP vs US Advantages
MRCP Advantages
Detailed anatomy - can detect head of pancreas mass and for cholecystitis
Higher sensitivity for Choledocholithiasis
Not limited by gas, bone or most habitus
No ionising radiation
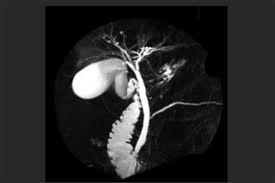
MRCP vs US Disadvantages
MRCP Disadvantages
Expensive
High demand modality - long wait times
Claustrophobia - reduced patient compliance
Does not assess mobility of gallbladder stones
Non-interventional
Advantages of US vs CT for Right Right Iliac Pain
US Advantages
US is non-ionising
Dynamic assessment
Readily available
Female - rule out ovary involvement
Male - may proceed to CT sooner
Disadvantages of US vs CT for Right Iliac Fossa pain
Disadvantages of US
US limitation of gas and mid ureter
Sonographer may not be onsite (overnight)
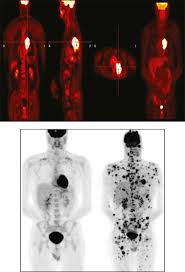
Functional Imaging Nuc Med
Functional Imaging= uses radioactive tracers (radiopharmaceuticals) to visualize and assess the physiological functions of organs and tissues
Visualises physiological activity such as
blood flow
metabolism
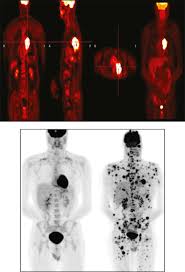
Anatomical Imaging Nuc Med
Anatomical Imaging= uses various techniques to visualize the internal structures of the body
Provides structural detail
Key difference: function vs structure
Components of Gamma Camera
Components
Collimator
Scintillation Crystal
Detector Heads
CT
Radiation Safety Principles
TDS: Time, Distance, Shielding
ALARA: As Low as Reasonably Achievable
Limitations: cannot use lead gowns when the pt is in the source
Inverse square law: doubling distance reduces exposure by a factor of 4
Units of Measurement and Timing
Becquerel (Bq): Decays per second
Half life considerations: impacts image timing, shorter in PET vs traditional Nuc Med
R(t) is the decay rate at time t
R0 is the initial decay rate at time 0
e is the base of the Naperian logarithms
λ is the decay constant of the radioactive isotope
Quantification in Imaging
Allows assessment of tracer uptake
Both Dose and time are very important
Important in MAG3, thyroid scans and more
Functional Imaging Pros and Cons
Functional Imaging Pros
Detects early functional changes
High sensitivity (true positive ratio)
Cons
Poor anatomical detail
Low specificity (true negative ratio)
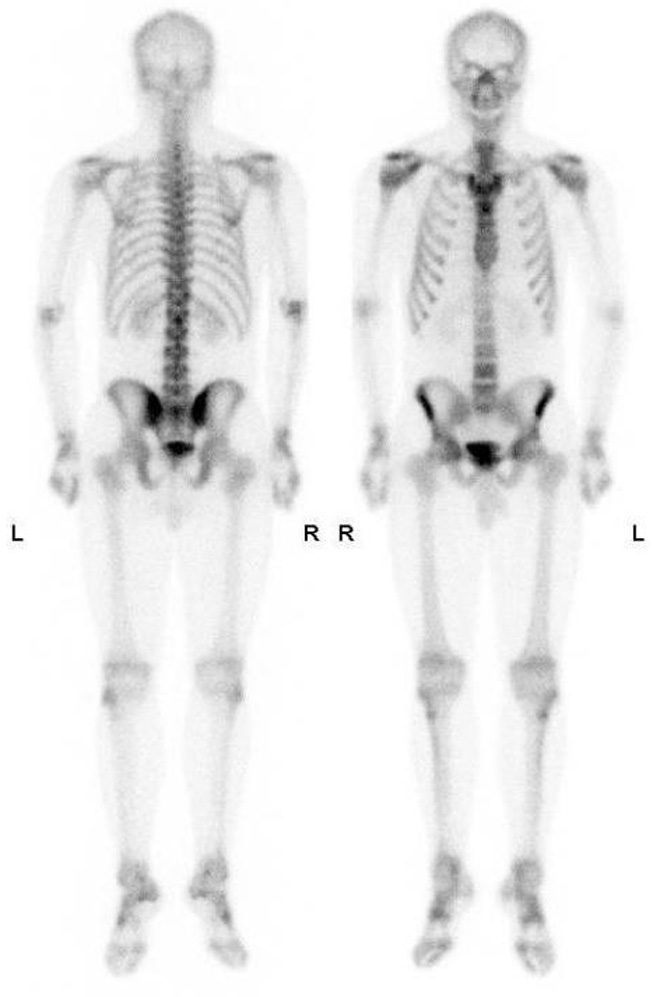
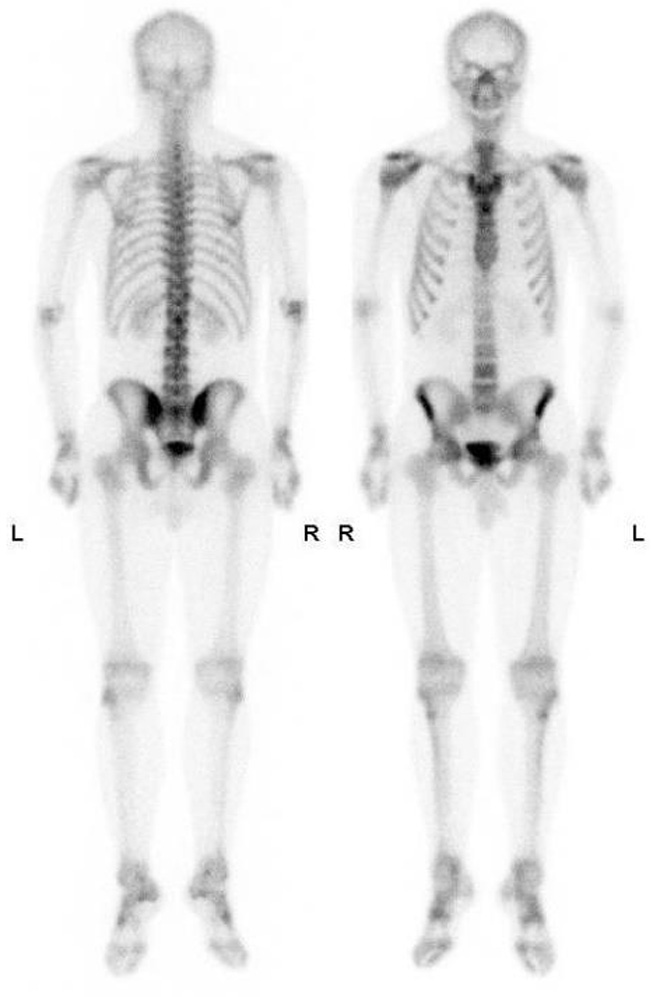
Bone Scans
Advantages of Bone scans over Conventional Imaging:
Early detection of bone metabolism changes, whole body screening
3 Phase Bone Scan: blood flow, blood pool, delayed.
Used for: osteomyelitis, prosthesis infection
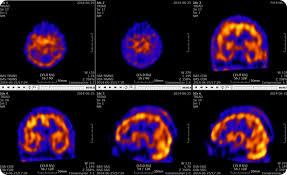
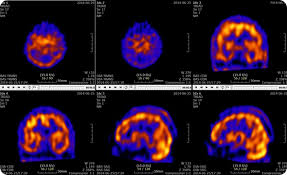
SPECT/CT Benefits
SPECT: a nuclear medicine imaging technique that creates detailed, 3D images of organs, tissues, and bones by detecting the gamma rays emitted by radioactive tracers injected into the body
Benefits:
Combines function and structure so improved localisation
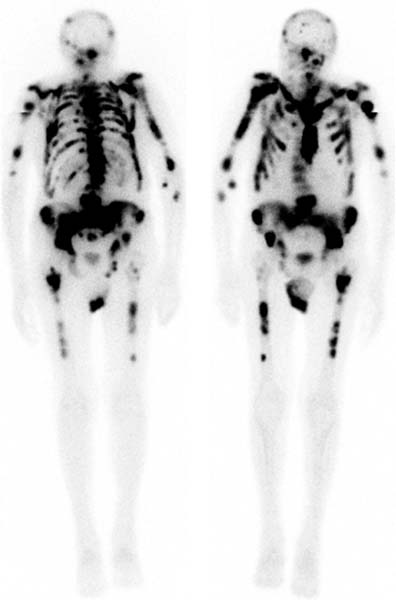
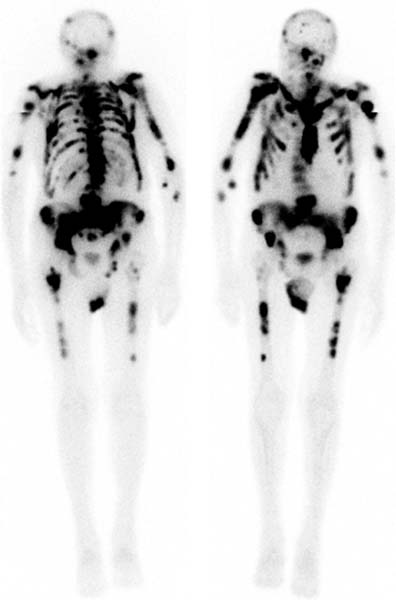
Superscan
Intense skeletal uptake with reduced renal/ST activity (eg: metastatic disease)
Common Indications:
? bony mets
Infection
Trauma
Arthritis
Thyroid Imaging Nuc Med
Dose Quantification: determines % uptake, guides diagnosis and therapy
Anatomical Localisation: using landmarks (eg sternal notch)
Iodine and CT contrast: contrast saturates thyroid. Wait 4-6 weeks post CT
Thyroid Imaging - Goitre
Goitre:
Multinodular= heterogeneous
Thyroid Imaging - Graves
Graves= diffuse increased uptake
Lung Ventilation Perfusion (V/Q) Scan indications Nuc Med
Indication: Pulmonary Embolism
Lung Ventilation Perfusion scan Nuc Med vs CTPA
Lung (V/Q) Advantages:
Contrast allergy
Less ionising for pregnant patients
Can image those with renal impairments
Pharmaceuticals used in Lung (V/Q) scans
Ventilation= 99mTc Technegas
Perfusion= 99mTc MAA
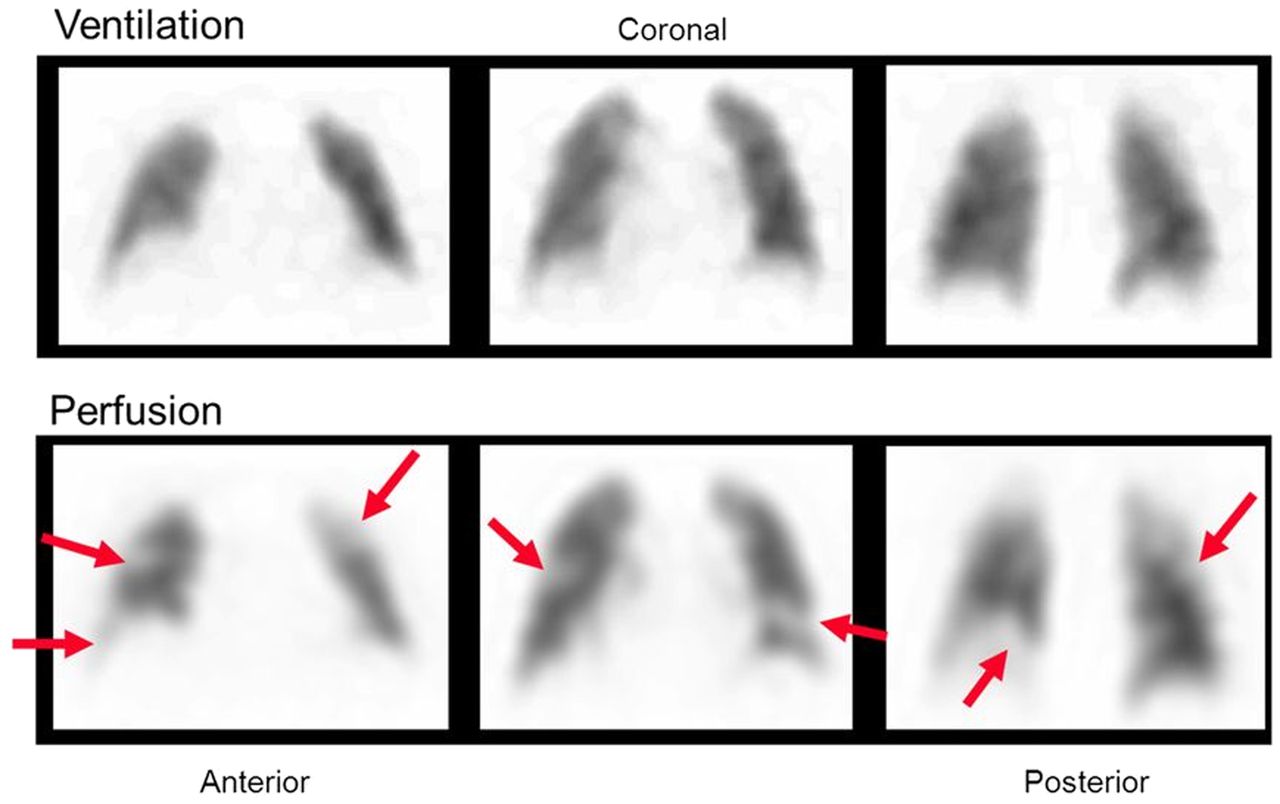
PE Appearance in Lung (V/Q) scan
Normal ventilation, perfusion defect (mismatch)
Poor image quality causes for Lung V/Q scan
COPD= poor ventilation distribution
Renal Imaging MAG3
A MAG3 renal scan uses radiopharmaceuticals and a gamma camera to highlight and take pictures of your urinary system
MAG 3 Indications
Indications:
PUJ/VUJ obstruction
Transplant work up
Renal Imaging DMSA
A DMSA renal scan is a diagnostic imaging exam that evaluates the function, size, shape, and position of the kidneys and detects scarring caused by frequent infections
PET/CT Nuc Med
PET Advantages:
Better resolution
Sensitivity than gamma camera
Patient Prep: fast, no exercise, keep warm to reduce brown fat uptake
Fluorodeoxyglucose Tracer: mimics glucose uptake, used in cancer and inflammation