Ch. 26 Reproductive System
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
The Y chromosome contains a region for male sex determination that is known as the _ gene
SRY
What are the functions of gonads?
Produces gametes and secrete sex hormones
How do the products of gonadal function differ in males and females?
Female gonadal hormones: estrogen, progesterone, androgens, and inhibin
Male gonadal hormones: androgens and inhibin
Name all structures the gametes pass through on there journey.
Seminiferous tubule
Epididymis
Ductus deferents
Ejaculatory duct
Urethra
Uterine cavity
Cervix
Vagina
T/F all testosterone is produced in the testes
False. Some are produced in the adrenal glands of both sexes.
T/F Only males make androgens and only females make estrogens.
False. Both sexes produce both hormones.
T/F High levels of estrogen in the late follicular phase help prepare the uterus for menstruations
True
T/F Progesterone is the dominant hormone of the luteal phase of the ovarian cycle.
False. High levels of late follicular estrogen help prepare the uterus for implantation.
What are the main components of semen?
True.
Where is semen produced?
TESTICLES
What is semen?
A sperm fluid mixture made mostly by the accessory glands.
Why are X-linked traits exhibited more frequently by males than females?
Since males only have one X chromosome they have a higher chance to receive a recessive trait. Unlike females who have double X chromosomes and if one is dominant will control the phenotype.
AMH
Absence allows the formation of females and with it allows formation of males
DHT
DHT promotes prostate growth, sebaceous gland activity, male pattern baldness, and body, facial, and pubic hair growth.
Interstitial cells
Cells that form part of the connective tissue (interstitium) between other tissues,
Mullerian cells
Becomes fallopian tube, uterus, cervix, and upper half of vagina
Sertoli cells
Are somatic cells in the testes that are essential for sperm production in men
Wolffish ducts
Forms epididymis, vas deferens, and seminal vesicles.
Male vs Female FSH
Stimulates gamete production in both sexes
Male vs Female inhibin
Inhibits FSH secretion
Male vs Female activin
Stimulates FSH secretion
Male vs female GnRH
Stimulates release of FSH and LH
Male vs Female LH
Stimulates gonadal sex hormone production; in females, also necessary for gamete maturation
Male vs Female DHT
testosterone metabolite responsible for fetal development of male genitalia
Male vs Female estrogen
Present in both sexes but dominant in females
Male vs Female Testosterone
Present in both sexes but dominant in males
Male vs Female Progesterone
Females only, helps prepare the uterus for pregnancy
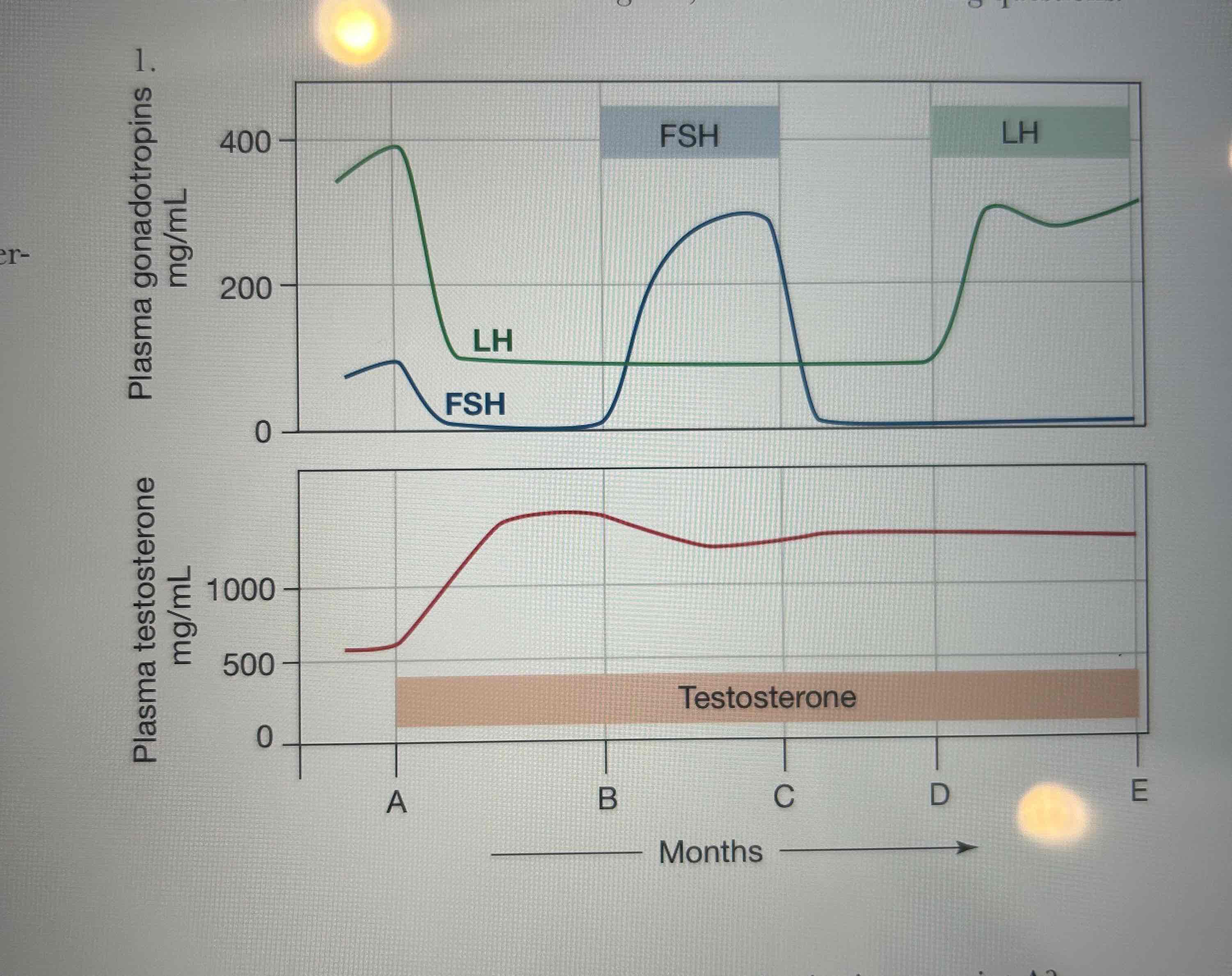
A) was administered to all subjects
B) negative feedback by testosterone
C) sperm production decreased A-B because FSH and LH decreased.
It increased toward the end of the B-C because FSH allowed sperm production to resume.
Sperm production did not increase significantly during the D-E interval.
Which organ produces Anti-Muellerian Hormone (AMH)?
The testis
The vas deferens
The pituitary gland
The hypothalamus
The testis
Which hormone causes the differentiation of the Wolffian duct into the internal structures of the male reproductive system?
Testosterone
In the male reproductive system Androgen-binding protein
Is produced by the Sertoli cells.
Is produced by the Leydig cells.
Serves to bind testosterone and concentrate it in the seminiferous tubules.
Both a and c
Both b and c
Both a and c
During the early to mid-follicular phase of the ovarian cycle what produce Anti-Muellerian Hormone (AMH)?
The thecal cells
The granulosa cells
The pituitary gland
The Leydig cells
B. Granulosa cells
Which hormones does the corpus luteum produce during the early to mid-luteal phase of the ovarian cycle??
Estrogens
Progesterone
Inhibin
All of the above
Only a and b
All the above
Which hormone causes a 0.3-0.5° C spike in body temperature during the early to mid-luteal phase of the ovarian cycle?
Progesterone
Estrogen
Inhibin
FSH
LH
Progesterone