3.6.1 Government Intervention
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Define the Competition and Markets Authority.
The main competition regulator in the UK. They investigate when competition is weak and take action when necessary. They explore the costs and benefits of mergers and takeovers
What are the 5 benefits of promoting competiton?
Lower prices
Higher quality
Higher choice
Greater welfare
Increased efficiency for firms
How do governments intervene to control mergers?
The competition and markets authority investigate potential mergers between two large firms, if they would dominate the market by merginf ( have above 25% market share)
What is one example of governments blocking a merger?
European commission blocked the merger of Ryanair and Aerlingus in 2010 as they would control more than 80% of al Europe flights from Ireland
What are the 4 ways governments intervene to control monopolies?
Price regulation
Profit regulation
Quality standards
Performance targets
How does price regulation control monopolies?
Regulators can force monopolists to charge a price below the profit max price
✔ Yes, the cap in RPI - X is the maximum price increase allowed.
✔ It protects consumers and forces monopolies to be efficient.
✔ If the firm manages to cut costs even more than X, it can keep the extra profits — win-win (in theory!).
What are the two formulas businesses may use?
RPI-X represents expected efficiency gains of the firms, pass these gains onto consumers in the form of lower prices
RPI-X+K represents the level of investment
RPI = retail price index
What does RPI, X and K all stand for?
Term | Meaning | Purpose |
|---|
RPI | Retail Price Index (inflation) | Measures general price increases |
X | Efficiency savings expected | Forces firm to be efficient |
K | Capital investment allowance | Lets firm raise prices slightly more to invest |
RPI - X | Price can rise less than inflation | Encourages cost-cutting & efficiency |
RPI - X + K | Adds investment allowance | Supports long-term improvements |
What is the difficulty of using these formulas to regulate prices?
Where do we set X? Rapid improvements in technology. This is assymetric information as the government does not jnow where efficiency gains could happen
Draw a monopoly diagram where the government has set the regulated price at the allocatively efficient level of output
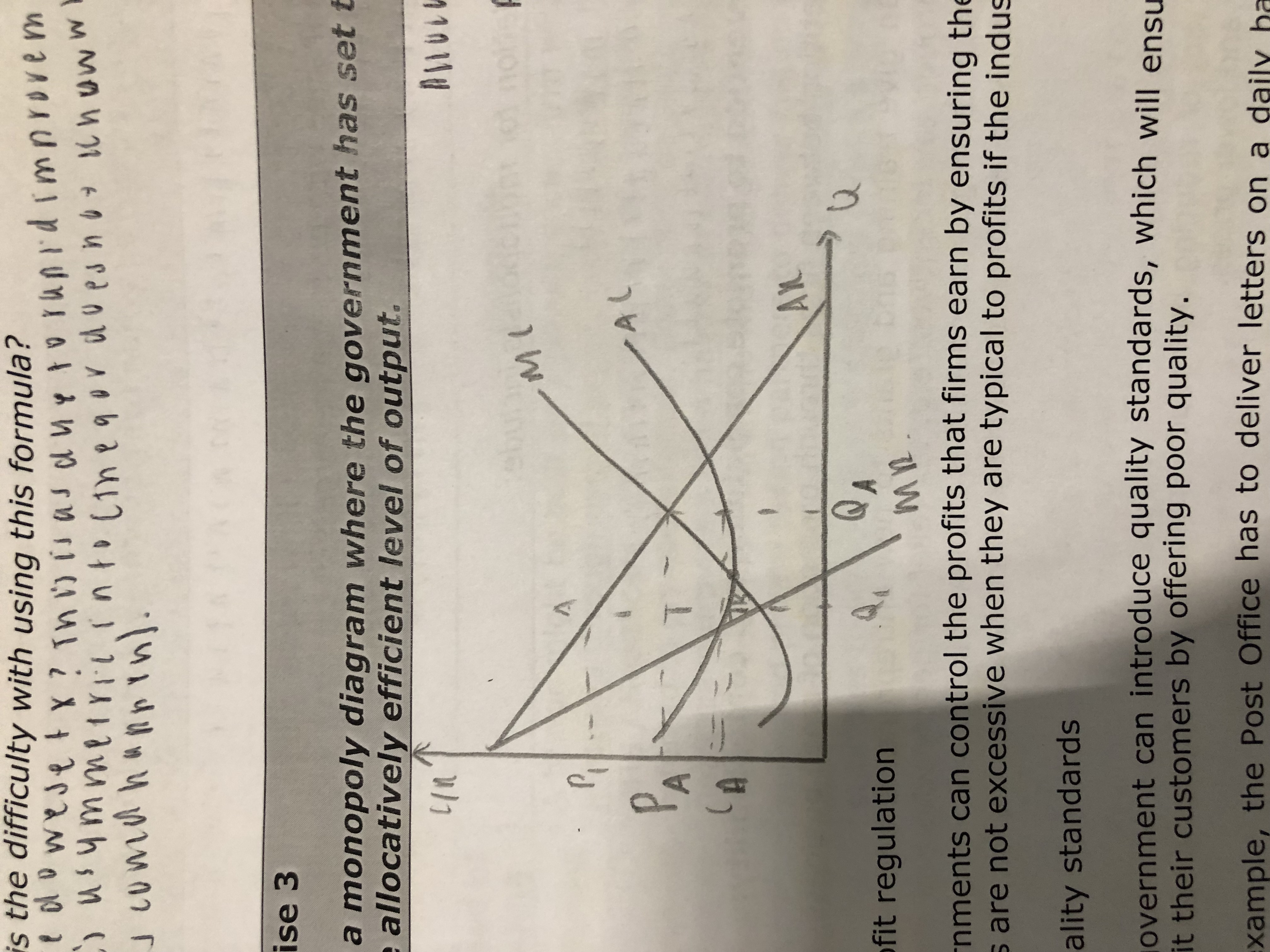
How do governments can control mergers through profit regulation?
profit regulation helps prevent monopolies from taking advantage of their market power by ensuring that their profits are reasonable and not excessive. It can help protect consumers and encourage competition, but it can also have drawbacks in terms of economic efficiency and innovation.
Rate of Return Regulation: rate of return regulation rewards firms for capital investment by allowing them to earn profits that reflect the value and costs of their capital improvements, which helps them maintain operations and cover production costs.
How can governments control monopolies using quality standards?
The government can introduce quality standards which will ensure that firms do not exploit their consumers by offering poor quality
imposition of quality standards or specialist organisation for regular monitoring, such as ofsted and education, increases quality of goods which increases welfare
How do performance targets control monopolies?
Government employs performance to ensure that firms do not exploit consumers with high prices, low quality, low choice
Governments can impose yardstick competition, targets on prices cost of production quality choice, firms don’t wanna be fined or have a bad rep so they improve their g/s
EVAL. firms try to game the system as to meet targets without increasing costs. uk rail travel, firms given targets for punctuality and so change the whole timetable lol thats acc smart tho
What other issues arise with performance targets?
Windfall taxes
Breaking up the monopolist
Self regulation such as having codes of conduct as it is cheaper for the government
What are windfall taxes?
A windfall tax is a tax levied by governments against certain industriesd when economic conditions allow those industries to experienfe above average profits
The Energy Profits Levy (EPL) was introduced in May 2022 after companies recorded skyrocketing profits due to a sharp rise in energy prices.
It was increased in the most recent UK government budget last year and means oil and gas producers are paying a headline tax rate of 78%
What are the 4 ways the government can intervene to promote competiton and contestability?
Enhancing competiton brtween firms through promotion of small business
Deregulation
Competitive tendering for government contracts
Privatisation
How does enhancing competition between firms through promotion of small business promote competition?
The fovernment can give trianing and grants to new entrepreneurs and encourage small businesses through tax incentives ( eg tax reflief for people who buy shares in small companies to help then grow) or subsidies. This will increase competiton since there will be more firms in the market resulting in increase innovation and increased efficiency
How does deregulation promote competiton and contestability?
Deregulation is the act of reducing how much an industry is regulated resulting in increased efficiency and lower prices
What is a downside of deregulation to promote competition?
Deregulation can have some negative effects, leading to poor business behaviour. Some have argued that the deregulation of financial markets was a major contributor to the financial crisis of 2008
How does competitive tendering for government contracts promote competiton?
Competiting for government contracts leads to firms being extremely innovative and efficienct as only the best proposals are selected for government contracts, this drives down prices while increasing quality
Define public private sector partnership
Where the government involves the private sector in public sector projects
What was the private finance initiative?
The private finance initiative was launched in 1992. It was a way of trying to increase the involvement of the private sector in the provision of public services by the conservative government and expanded further by the labour government from 1997-2010. By the end of 2011 almost one thousand public projects has been built including hospitals schools and prisons
How do public private sector partnerships work?
The public sector states what it needs eg a new bridge or school
Private sector firms bid for the contract
The firm eith a mixture of the lowest prices ajd the highest quality win the contract
What are the two methods of funding?
Self funded
Government purchasing private sector services
What is one example of a self funded partnership?
A bridge might be built by a private sector firm with the cost recouped through user chargers such as a toll
What are two examples of government purchasing private sector services?
NHS, when waiting lists are hugh patients get referred to private hospitals
The national tutoring programme provide 70% subsidies to schools to hire private tutors
What are the 3 advantages of public private partnerships?
Imrpves efficiency
Improved quality and innovative design
More funding for projects
What are the 3 didadvantages of public private sector partnerships?
Increased costs
Delays due to disagreements or assymetric information
Private sector may pay less attention to health and safety concerns and use cheap materials instead
What are methods of government intervention to protect suppliers and employees?
Restrictions on monopsony power
Restrictions on monopoly power
Workers rights
Nationalisation
Illustrate how governments can restrict monopsony power.
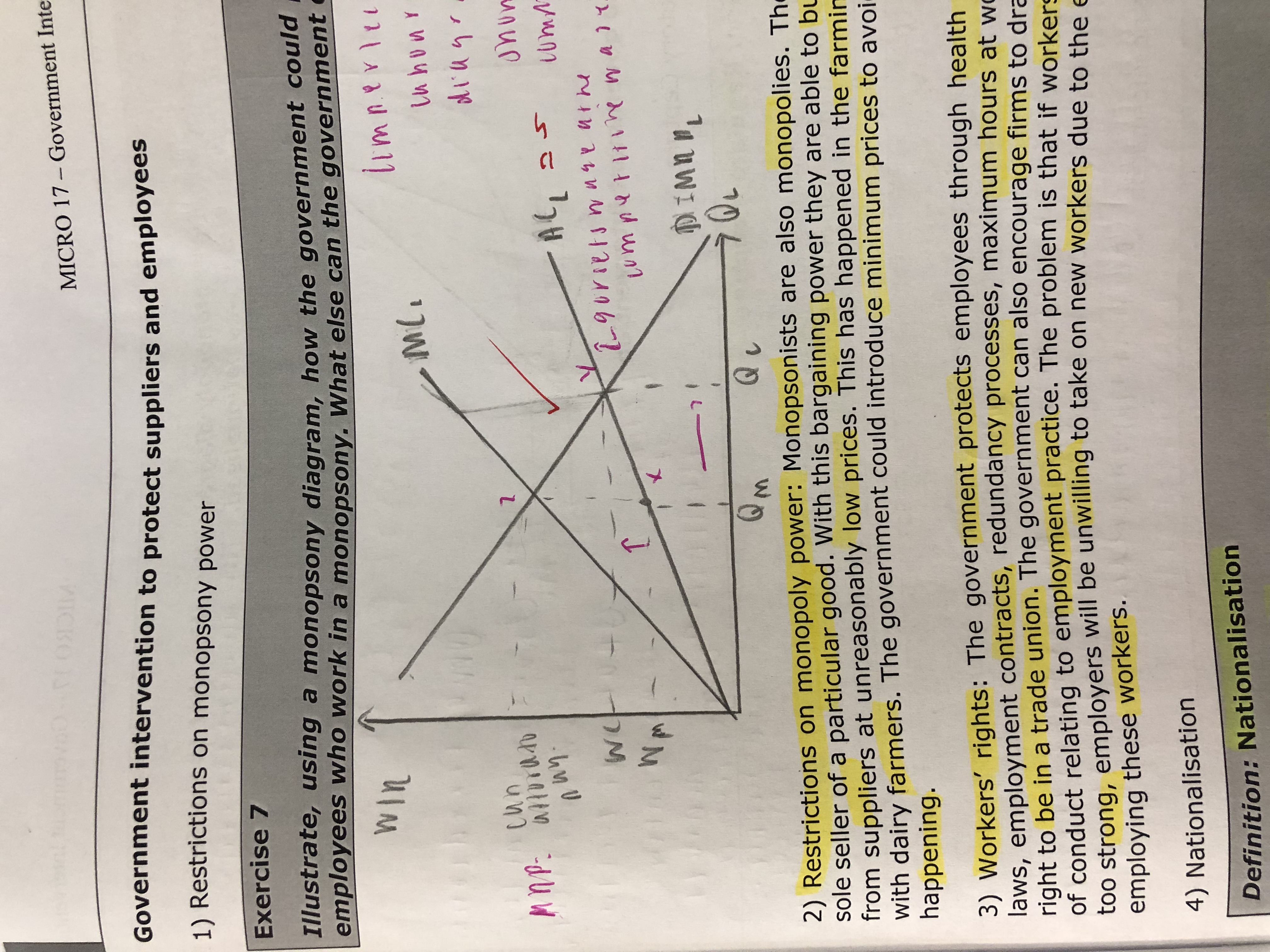
How do restrictions on monopoly power protect suppliers and employees?
Monopsonists are also monopolies. They are a sole seller of a particular good. With this bargaining power they are able to buy frim suppliers are unreasonable low prices. This has happened beforr in the farming industry with dairy farmers. The government could introduce minimum prices to avoid this from happening
How to workers’ rights protect suppliers and employees?
The government protects employees through health and safety laws, employement contracts, redundancy processed maximum hours at work and the right to be in a trade union.
The government can also encourage firms to draw up codes of conduct relating to employment practice. The problem is that workers rights are too strong employers will be unwilling to take on new workers due to the extra cost of employing these workers
Define nationalisation
The act of taking industries out to private ownership and placing them in the hands of the government
What is an argument for taking Thames Water into public ownership?
They are a profit macimising company. They make more profit than paying fines than actually incesting and preventing sewage in the water
Illustrate the price the government would set if thames water was nationalised?
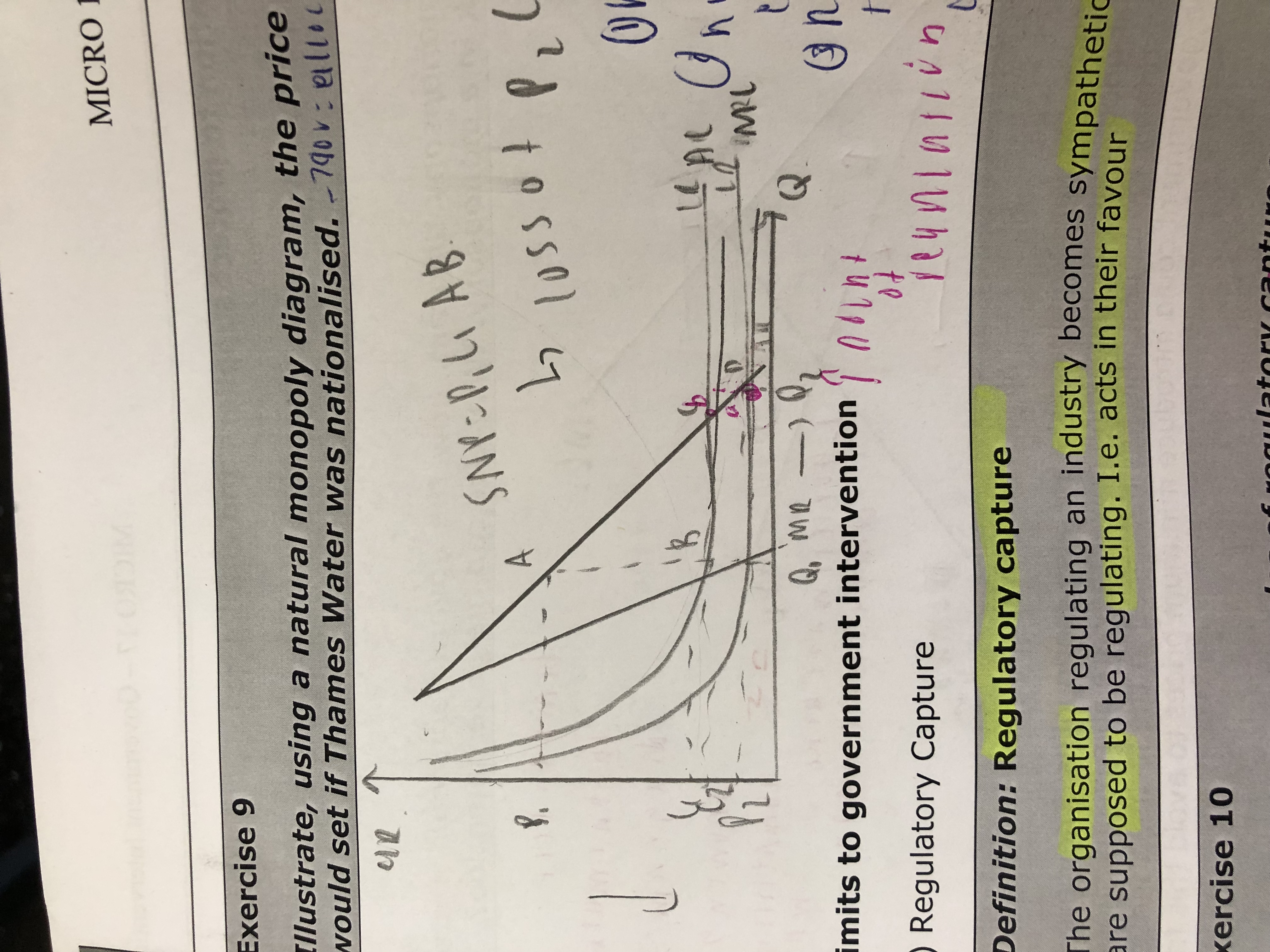
What are the 2 limits to government intervention?
Regulatory capture
Asymmetric information
Define regulatory capture.
The organisation regulating an industry becomes sympathetic to the businesses they are supposed to be regulating ie acts in their favour
Define asymmetric information.
A situation where one party in a transaction has more information than the other party
What is an example of regulatory capture?
Oil and gas drilling in the US. Minerals management service was responsible for offshore drilling in the US and made it easier to drill in offshore areas