all year 9 gcse bio content
1/315
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
316 Terms
What is the function of root hair cells?
To absorb water and mineral ions from the soil.
How are root hair cells adapted for water uptake?
They have thin cell walls and a large surface area for efficient osmosis.
What does xylem transport?
Water and mineral ions from roots to the rest of the plant.
Why are xylem walls strengthened by lignin?
To prevent the tubes from collapsing under pressure.
What does phloem transport?
Sugars (mainly sucrose) from the leaves to the rest of the plant.
What is the process of transporting sugars in plants called?
Translocation.
What is transpiration?
The loss of water vapour from the leaves through stomata.
How does light intensity affect transpiration rate?
It increases the rate of transpiration because stomata open in light.
How does humidity affect transpiration rate?
It decreases the rate because there is less evaporation when air is moist.
What is the role of guard cells?
To control the opening and closing of stomata, regulating gas exchange and water loss.
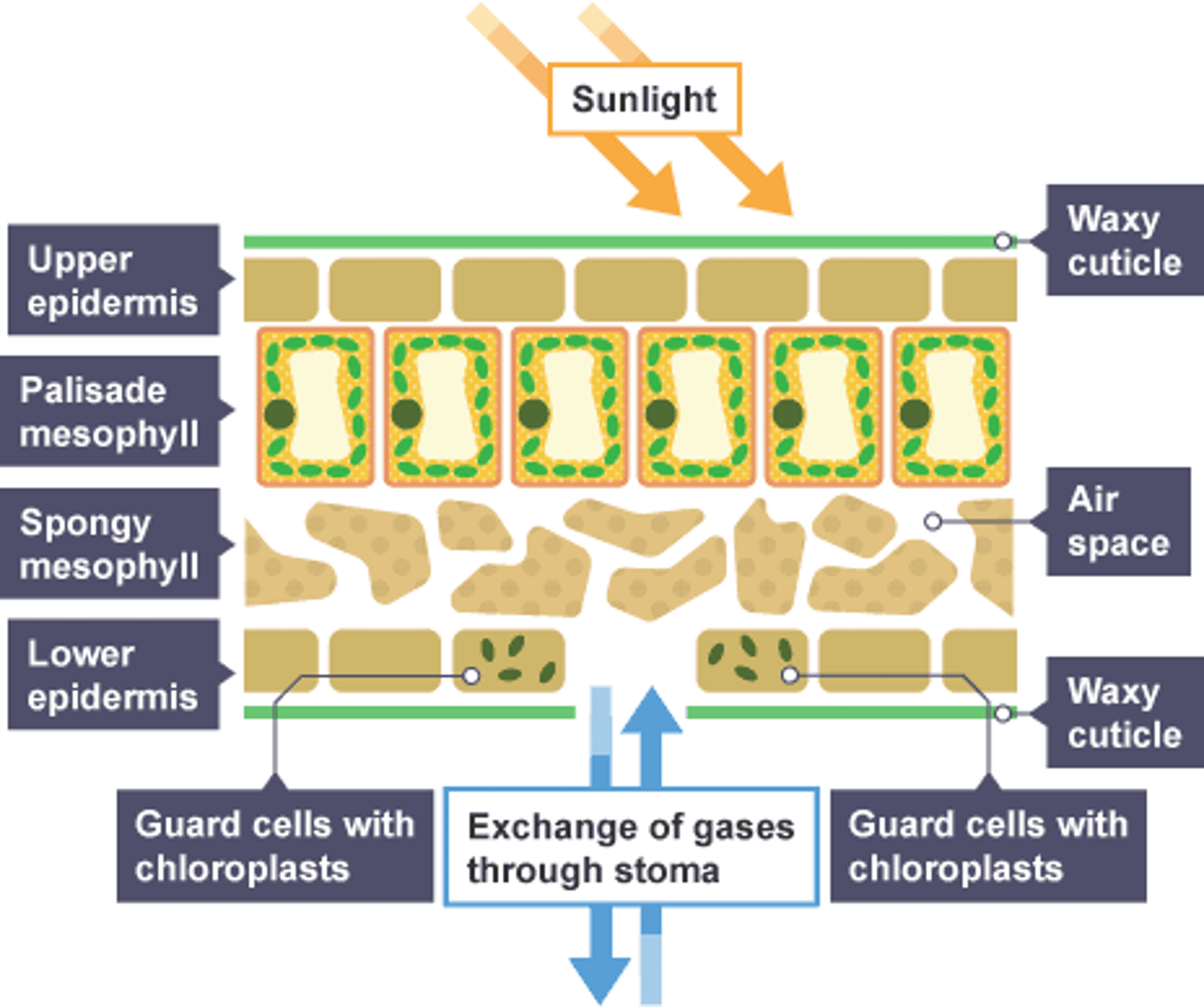
Epidermal tissue
-Covers the whole plant
-At the very top and bottom of the leaf
Upper epidermis
-At the very top of the leaf
-Transparent so that light can reach the chloroplast in the palisade layer, where photosynthesis takes place.
Waxy cuticle
-Covers epidermal tissue
-Reduces water loss via evaporation.
Palisade mesophyll tissue
-Below upper epidermis
-Has lots of chloroplasts for photosynthesis to take place.
Xylem
-Transports water and other nutrients(eg: dissolved mineral ions like magnesium-used to make chlorophyll) from the roots to the stem and the leaves.
-Some of this water is used for photosynthesis.
Phloem
-Transports dissolved sugars (glucose) produced by photosynthesis, from the leaves to the rest of the plant.
-Sugars can be used immediately: respiration/or stored as starch.
-(translocation)
Spongy mesophyll
-Below palisade mesophyll
-Lots of air gaps to increase rate of diffusion for carbon dioxide, being transferred to the palisade layer for photosynthesis, and oxygen going from the palisade to the stomata to be released.
Lower epidermis
-At the very bottom of the leaf, below spongy mesophyll
-Contains pores called stomata, which let CO2 diffuse into the leaf, and let oxygen and water vapour out.
Guard cells
-In lower epidermis
-Control opening and closing of stomata in response to environmental conditions.
Meristem tissue
-Found at growing tips of roots and shoots, able to differentiate into different specialised cells allowing the plant to grow. (stem cells)
overall strcuture-image explain
what IS cancer?
the result of changes in cells that lead to uncontrolled growth and division.
What causes cancer?
uncontrolled cell growth and division
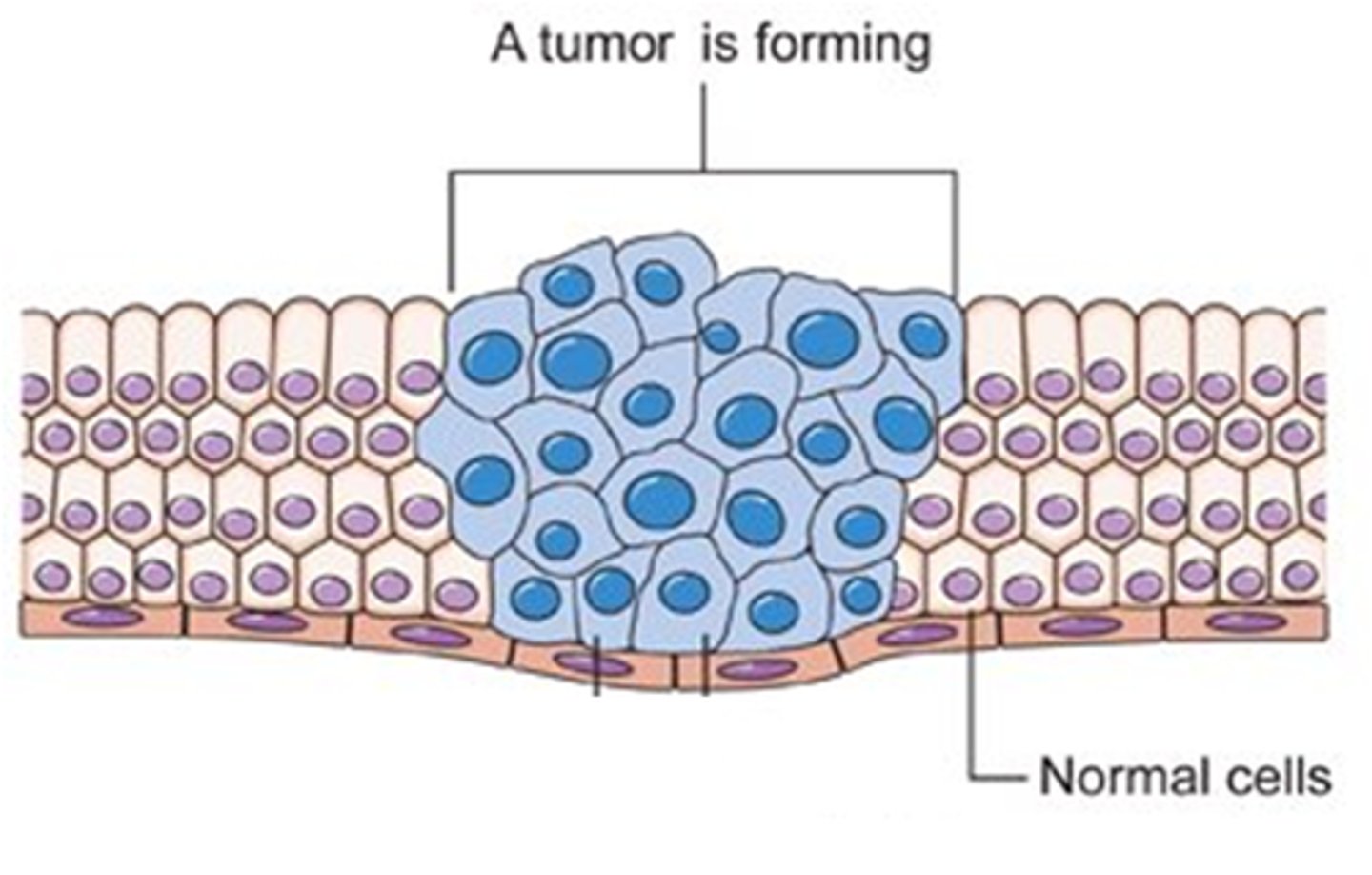
What do we call the growth of unwanted cells ?
the formation of a tumour
What is a tumour
mass of cells
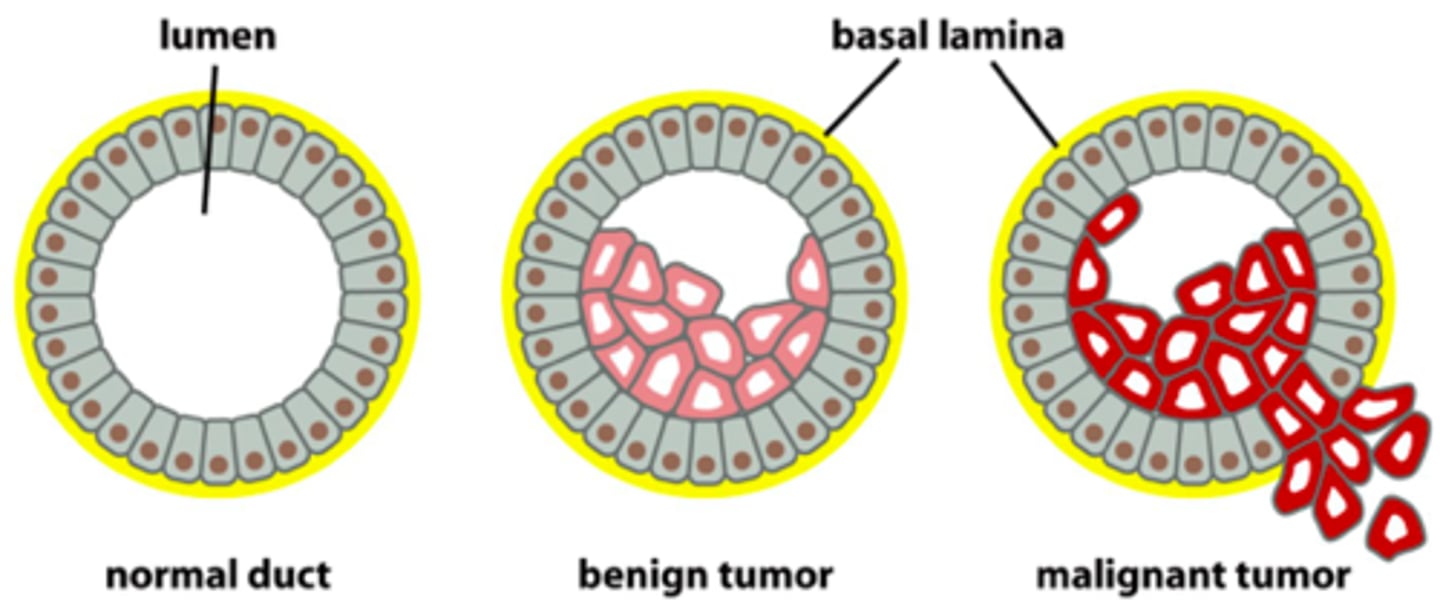
What is a benign tumor?
Growths of abnormal cells which are contained in one area, usually within a membrane. They do not invade other parts of the body.
Where are benign tumours usually contained
within the membrane
Are benign tumors cancerous
No
What is a malignant tumor?
cancerous tumor that can spread
What do malignant tumours form
secondary tumours
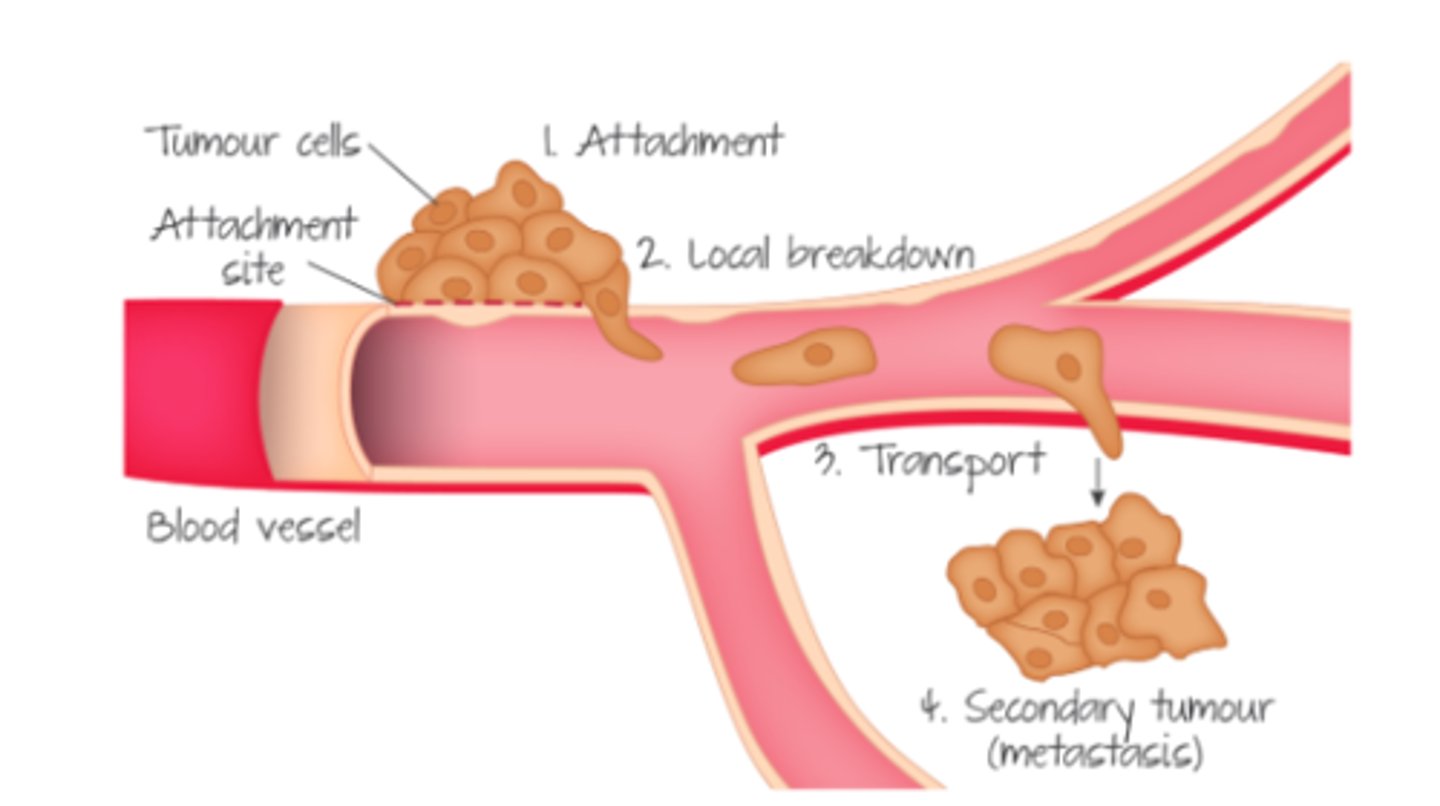
Cells can break off and travel through....
the bloodstream
Are malignant tumours cancerous
Yes, they can be fatal
Why have cancer survival rates increased?
>Medical advances such as improved treatment.
>Being able to diagnose cancer earlier
>Increased screening for the disease.
What is a risk factor?
anything that increases the likelihood of injury, disease, or other health problems
What are four lifestyle risk factors for cancer
Smoking: lung cancer
Obesity:Bowel,liver,kidney
UV exposure:Skin cancer
Viral infection:Hepatitis C/B-Liver cancer
Risks factors can also be associated with
Genetics

What are risk factors linked to?
an increased rate of a disease
Risk factors can be...
1- aspects of a person's lifestyle
2- substances in the person's body or environment
State a risk factor of type 2 diabetes
Obesity
Diet has not been proven to be a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. True or false?
False

Name two organs thought to be affected by alcohol
liver and brain
Smoking is a risk factor for two diseases; state them.
lung disease and lung cancer
State a risk factor of cancer
Carcinogens, including ionising radiation

Unborn babies are negatively impacted when the mother drinks alcohol and smokes. True or false?
True
Diseases are always caused by a single factor. True or False?
False, they are caused by an interaction of factors
what is the difference between health and disease?
health is the state of physical and mental well-being
diseases are major causes of ill health.
what are some risk factors for disease? (like in general)
- food we eat
- alcohol intake
- amount of exercise
- stress
- air pollution
- age
- smoking
-family medical history
- working environment
- UV light
What is CVD (Cardiovascular Disease)?
a general term for conditions affecting the heart or blood vessels
what are some risk factors that can increase your chance of getting CVD? and explain each one a little.
age - older people are more at risk
high blood pressure - increases the risk of heat disease
gender - men are more likely to develop heart disease
genes - if your parents have heart disease, you're at a greater risk.
smoking - can double the risk of heart disease
diet - affects weight and cholesterol levels
using examples describe how different types of diseases may interact [3 marks]
having one disease might put you more at risk of developing another disease. [1 mark]
for example: [2 marks for the examples]
- a defective immune system increasing your risk of infectious disease
-severe physical ill health can lead to mental illness.
What builds up inside the coronary arteries in coronary heart disease?
Fatty material.
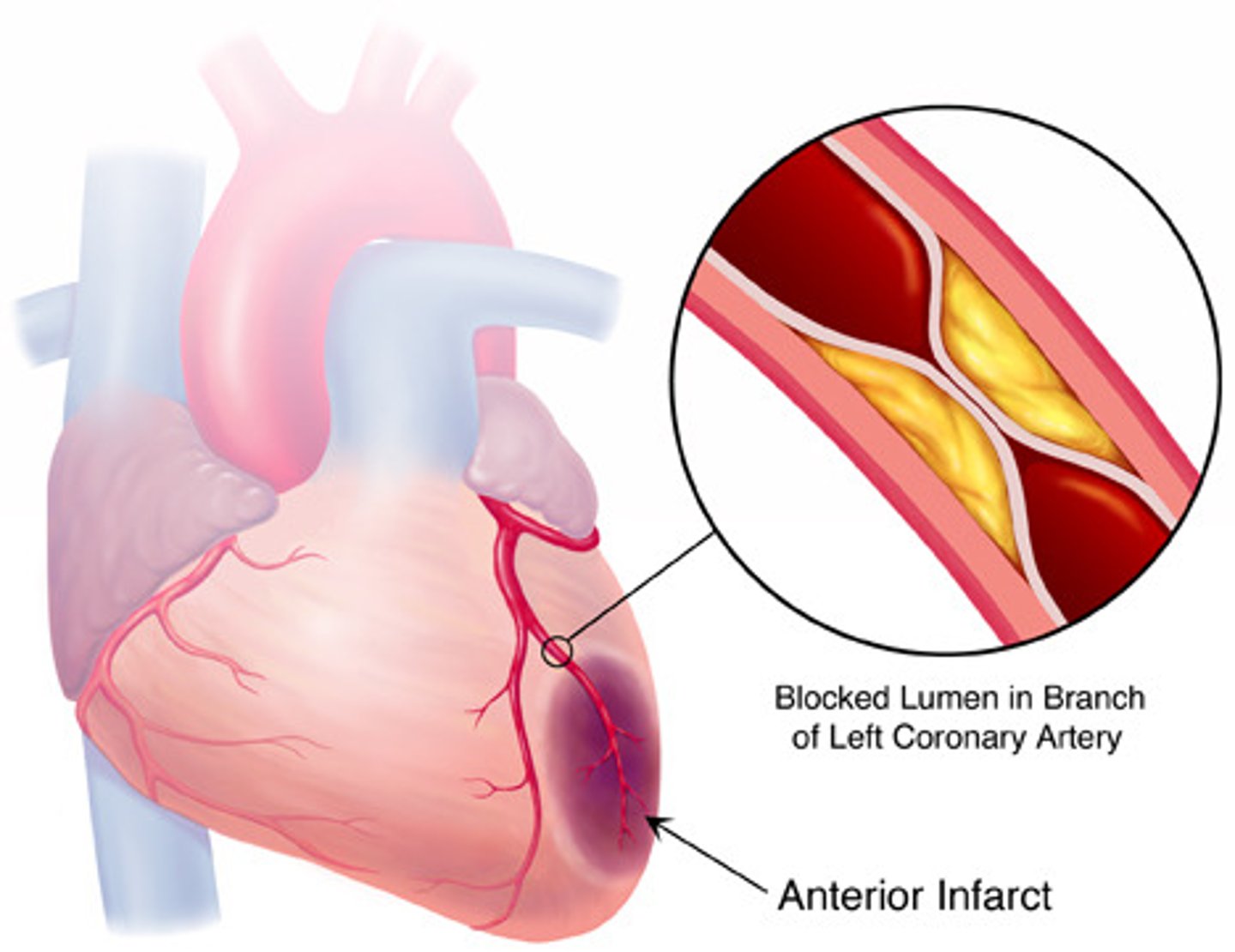
What is the cause of fatty material build up inside coronary arteries?
The narrowing of the arteries.
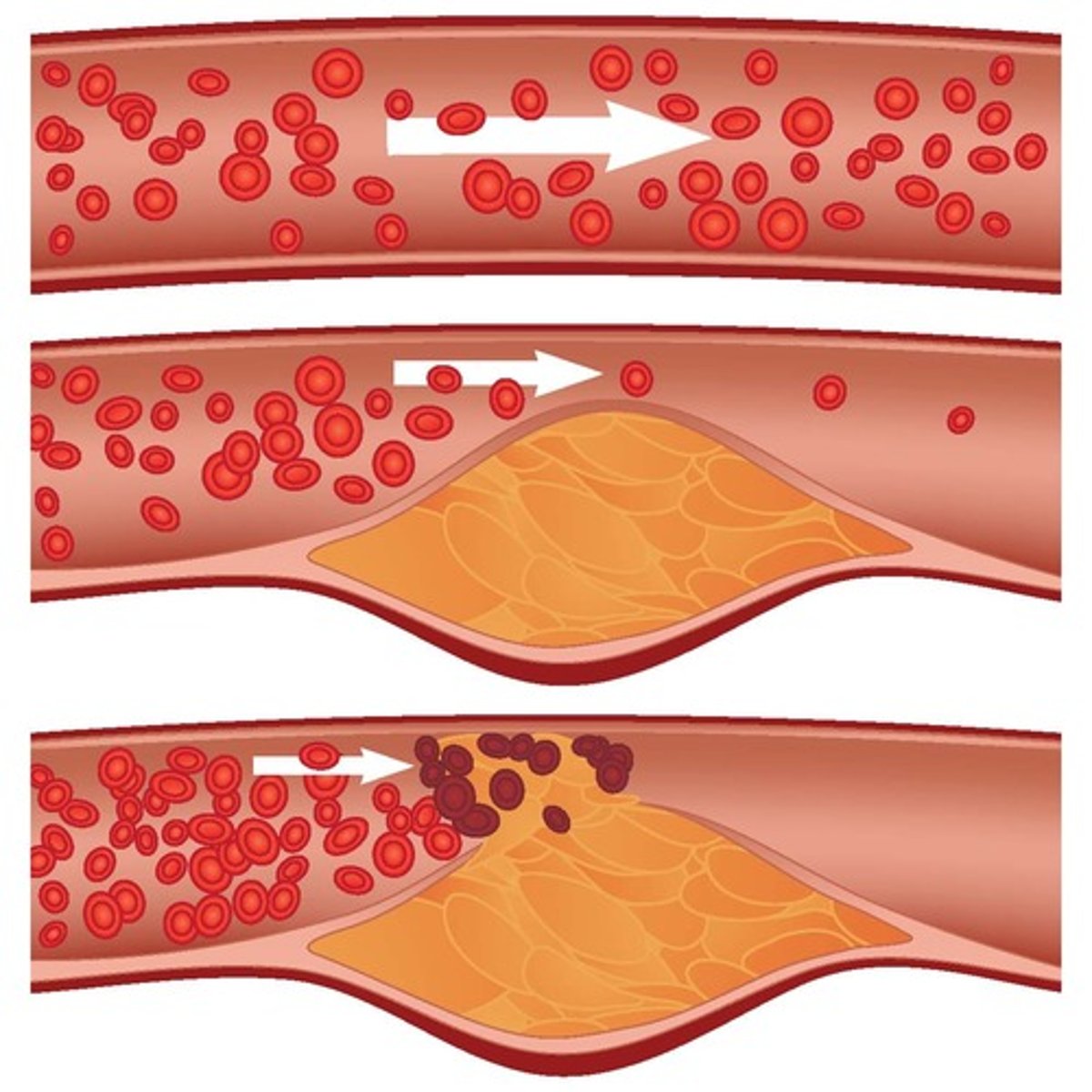
Why is the narrowing of coronary arteries bad?
It reduces the flow of blood resulting in a lack of oxygen for the heart muscle.
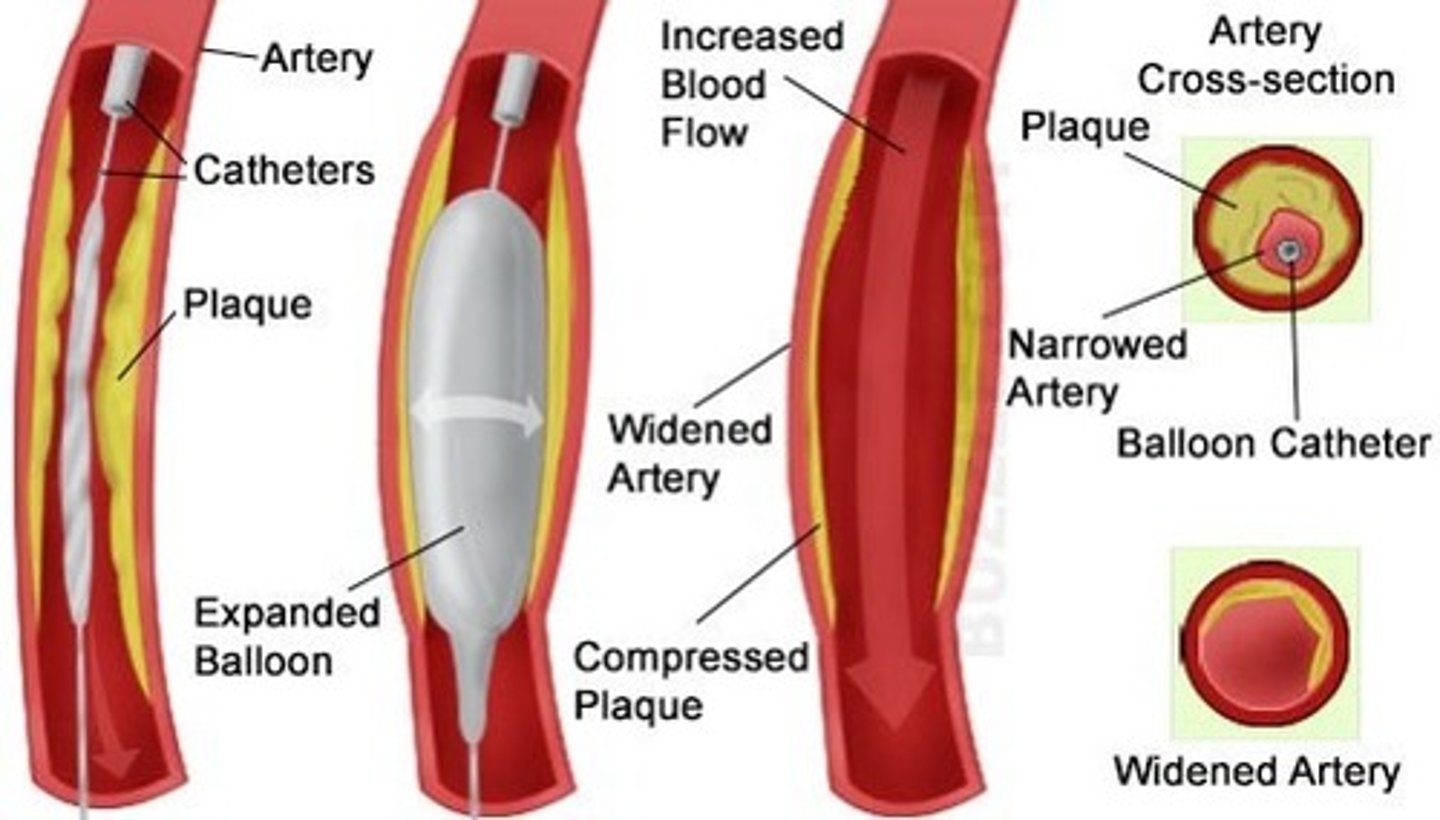
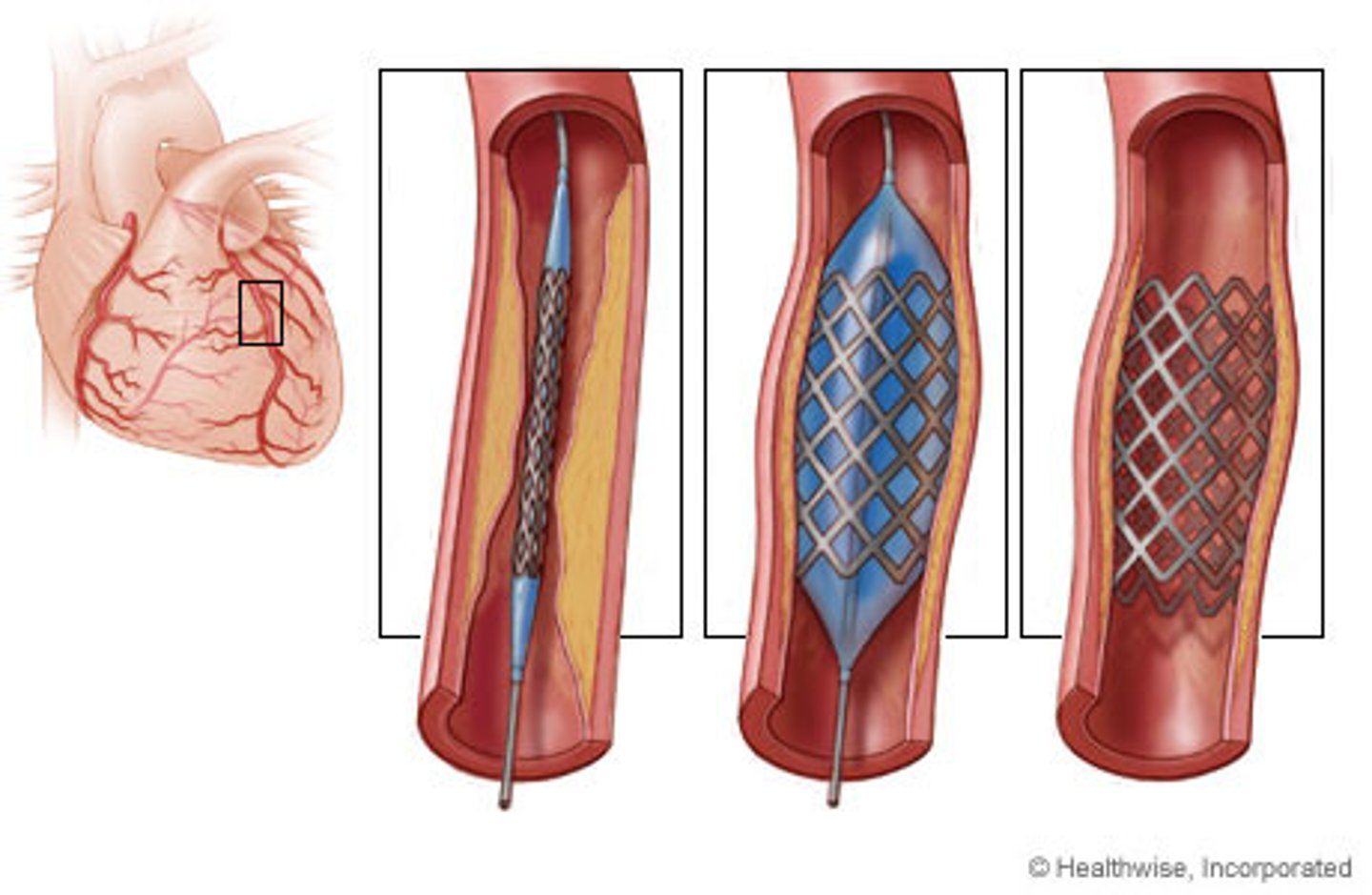
Name a mechanical device that treats coronary heart disease.
Stents.
Name a drug that treats coronary heart disease.
Statins.

What do stents do?
Keep arteries open.
What do statins do?
Reduce blood cholesterol levels which slows down the rate of fatty material deposit.
What happens in the case of heart failure?
A donor heart can be transplanted.
When are artificial hearts used?
To keep patients alive whilst waiting for a heart transplant, or to allow the heart to rest as an aid to recovery.
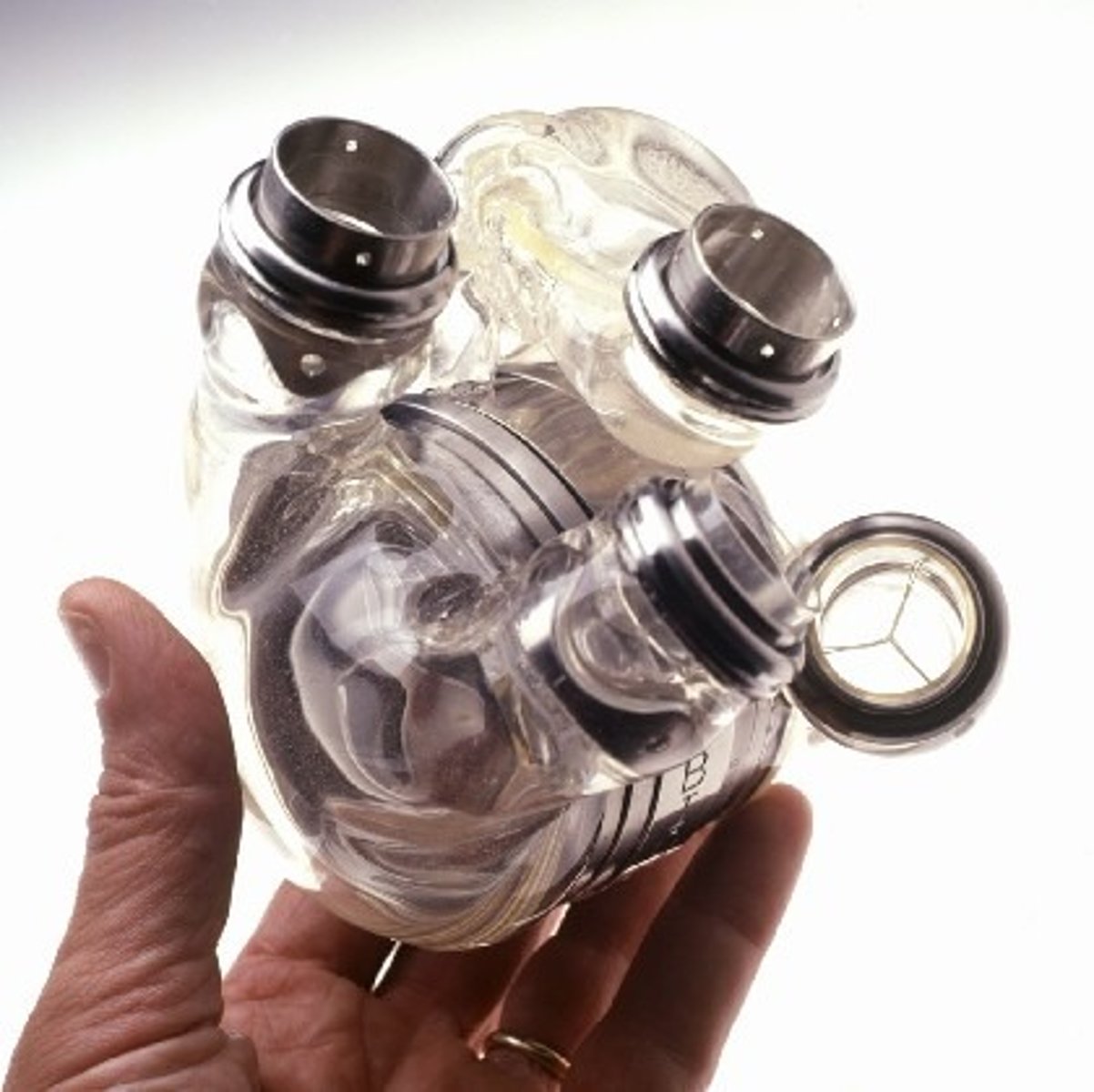
Give advantages of using drugs to treat heart diseases.
Often cheap to buy, and do not require surgery.
Give disadvantages of using drugs to treat heart diseases.
May have side effects, and the patient has to remember to take them.
what is the purpose of the coronary arteries?
provide oxygen to the muscle cells of the heart.
consequences of faulty valves?
less blood being pumped to the body, causing symptoms like tiredness and breathlessness because of reduced oxygen.
advantages and disadvantages of stents?
Advantages:
- last a long time
Disadvantages:
- risk of damage to blood vessel during surgery.
advantages and disadvantages of statins?
advantages:
- reduces the levels of "bad" cholesterol (LDL) in the blood which reduces the risk of fatty deposits building up- this reduces the risk of CHD
disadvantages:
- need to be takes regularly and long-term, otherwise they are not as effective.
evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of treating cardiovascular diseases with drugs, mechanical devices or transplants.
Drugs -----
Advantages:
- Reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke by lowering cholesterol levels.
- Can be cost-effective and widely available.
Disadvantages:
- Require long-term or lifelong commitment.
- Can have side effects like headaches, joint pain, or kidney problems.
- Are not suitable for everyone, such as those with liver disease .
- Do not take effect immediately.
Mechanical devices -----
Advantages:
- Artificial devices are not rejected by the immune system like biological transplants.
- Mechanical heart valves have a higher survival rate and don't need replacing as often as some biological valves.
Disadvantages:
- Require a power supply.
- Can wear out and need to be replaced.
- Mechanical valves carry a higher risk of blood clots, requiring lifelong anti-clotting medication, which can cause excessive bleeding.
- Surgery to implant them is invasive and involves long hospital stays.
Transplants: -----
Advantages:
- Can be a life-saving procedure.
- Can significantly improve the patient's quality of life.
Disadvantages:
- The body's immune system may reject the new organ.
- Requires a long recovery period.
- Involves a complex and expensive operation and aftercare.
- The patient must take anti-rejection drugs for life, which have their own side effects.
Where are the pacemaker cells found what do they do?
Found: right atrium
Function: set the natural rhythm of contraction of the heart
How does the structure of an artery related to its function?
Structure: narrow lumen, thick layer of muscle and elastic fibres
Function: take oxygenated blood at high pressure away from the heart
How does the structure of a vein relate to its function?
Structure: widest lumen and contains valves
Function: take deoxygenated blood at very low pressure towards the heart
How does the structure of a capillary relate to its function?
Structure: walls one cell thick and permeable
Function: exchanges materials between blood of medium to low pressure and tissues
Explain gaseous exchange.
- oxygen moves into red blood cells by diffusion
- carbon dioxide moves out of blood plasma by diffusion
How have alveoli adapted to their function?
- large surface area
- large concentration gradient
- short diffusion distance
Explain the circulatory system?
- Deoxygenated blood enters the heart via the vena cava, emptying into the right atrium.
- Blood flows down through a set of valves into the right ventricle
- When the ventricles contract, blood travels up through the pulmonary artery to the nearby lungs where gas exchange occurs (and the blood becomes oxygenated)
- Oxygenated blood returns to the heart via the pulmonary vein, emptying into the left atrium
- Blood flows down through a set of valves into the left ventricle
- When the ventricles contract, blood travels up through the aorta, and to the rest of the body
What are artificial pacemakers?
Electrical devices used to correct irregularities in the heart rate
what does blood consist of?
plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets
what is blood plasma?
A yellow liquid within blood that transports all of your blood cells around the body.
what do red blood cells do?
They carry oxygen from the lungs to all the cells in the body
what does bile do?
emulsifies fat
where is bile made?
in the liver
bile _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ the _ _ _ _ released from the _ _ _ _ _ _ _
bile NEUTRALISES the ACID released from the STOMACH
Name the three parts of the human digestive system that produce amylase. (pss)
salivary gland, pancreas, small intestine
what do arteries do?
these carry blood AWAY from the heart
what do capillaries do?
connect arteries and veins
what do veins do?
these carry blood TOWARDS the heart
Explain how amylase breaks down starch. Answer in terms of the ‘lock and key theory’.
Amylase breaks down starch by fitting into its specific structure, like a key in a lock. This fitting allows amylase to catalyze the reaction that splits starch into simpler sugars such as maltose.
what are enzymes?
enzymes are large protein molecules, made up of amino acids. they are biological catalysts that speed up reactions.
- a protein that speeds up chemical reactions
what is a polymer?
a long chain molecule made up of many individual molecules
what is the active site?
The active site is the place on the enzyme where the substrate binds.
what is a substrate?
A substance on which enzymes act.
what is it called when the active site shape is damaged?
denatured
what does the GLANDULAR TISSUE in the stomach do?
produces digestive juices that break down food
what does the EPITHELIAL TISSUE in the stomach do?
helps to protect the stomach lining from the harsh acidic environment
what does the MUSCULAR TISSUE in the stomach do?
Moves the stomach wall to churn the food
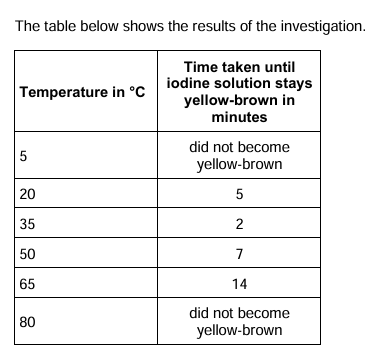
explain the results at 5 C and 80C (amylase practical)
at 5 °C amylase / starch / molecules have low (kinetic) energy (therefore) there are fewer (enzyme-substrate) collisions.
At 80 °C, amylase becomes denatured. this causes the shape of the active site to change so the starch can no longer fit.
what is the pancreas (gland) purpose?
- makes hormones to control blood sugar
- makes enzymes to digest
what is the livers purpose?
bile is produced here
what is the small intestines purpose?
digests and absorbs food
what is the stomachs purpose?
the digestion of proteins occur here
what is the large intestines purpose?
absorbs water from undigested food, producing feces.