Lecture 21 & 22 Pharmacodynamics and Metabolite Kinetics
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1) Explain the relationship between pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. 2) Describe the concept of a therapeutic window, including the meaning of a narrow therapeutic window. 3) Compare graded and quantal drug effects. 4) Characterize and calculate intensity, onset, and duration of pharmacodynamic effects. • Describe the importance of studying metabolite kinetics. • Determine whether elimination of a metabolite is rate-limited by its formation. • Describe factors determining metabolite kinetics during constant infusion. • Describe factors determining metabolite kinetics after oral administration. • Describe the consequence of hepatic extraction on plasma metabolite concentration profile after oral administration.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is Pharmacodynamics?
a. It is the disposition of drug within, through, and out of the body.
b. Effect that the drug has on the body due to interaction at the target
b. Effect that the drug has on the body due to interaction at the target
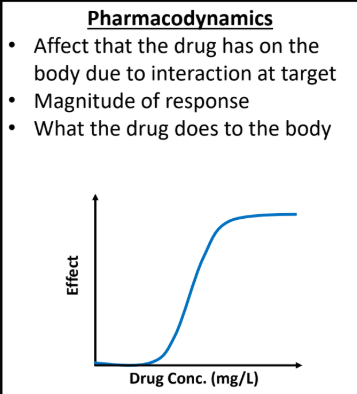
Example: good for plotting Phenytoin effects on patients with different drug conc.
Match the core pillars of pharmacodynamics to its definition:
Pharmacokinetics
a. an adequate drug conc. at the target site
b. mechanism of the drug interaction
c. nature of the biologic system the drug is altering
a. an adequate drug conc. at the target site
Match the core pillars of pharmacodynamics to its definition:
Pharmacology
a. an adequate drug conc. at the target site
b. mechanism of the drug interaction
c. nature of the biologic system the drug is altering
b. mechanism of the drug interaction
Match the core pillars of pharmacodynamics to its definition:
Physiology
a. an adequate drug conc. at the target site
b. mechanism of the drug interaction
c. nature of the biologic system the drug is altering
c. nature of the biologic system the drug is altering
What is a Therapeutic Window and is it better to have a narrow or large TW?
It is the concentrations where drug is expected to produce its desired effect without toxic side effects.
Better to have a LARGE therapeutic window

There are 2 type of drug effects, match the type to its definition (choose 2)
Quantal Response
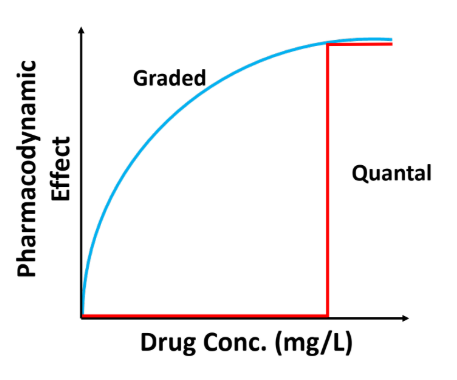
a. “All or none” response (discrete)
b. Continuous response
c. Adding increased dose does not help once desired response is achieved
d. Increased dose = increase effects
a. “All or none” response (discrete)
c. Adding increased dose does not help once desired response is achieved
Example: suppressing cardiac arrhythmia —> arrhythmia is either there or suppressed
There are 2 type of drug effects, match the type to its definition (choose 2)
Graded Response
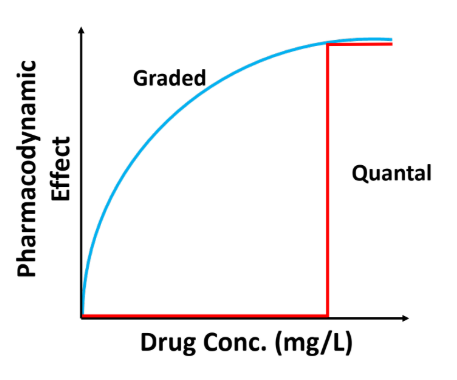
a. “All or none” response (discrete)
b. Continuous response
c. Adding increased dose does not help once desired response is achieved
b. Continuous response
d. Increased dose = increase effects
How is Intensity demonstrated when characterizing drug effects?
Emax Model is used: has semi-log plot (expands graph at lower concentrations, makes middle region 20-80% of effect) linear.
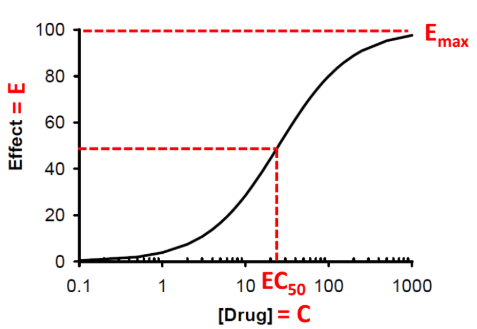
If the Emax is very steep (γ increases, steepness increases), what does the model suggest the type of drug effect is?
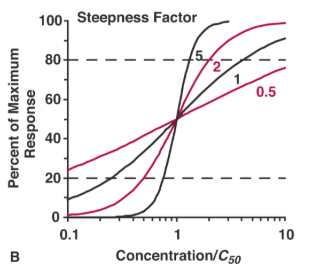
a. Quantal drug response
b. Graded drug response
a. Quantal drug response

What is Onset Effect?
The time to reach pharmacodynamic response.
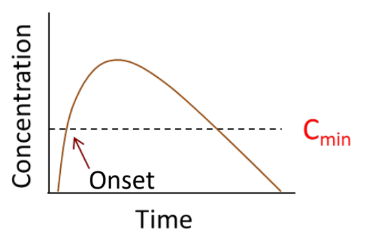
What is the Minimum Effective Concentration (Cmin)?
When the onset will occur when the drug exceeds a critical concentration at the site of action.

What is the Minimum Amount in Body (Amin)?
Least amount of drug in the body (not concentration) that is needed to produce a response
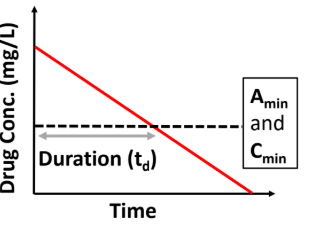
What is Duration of Effect?

The effect will last as long as concentrations are above Cmin and Amin (Amin = Cmin * Vd)
The half-life of Drug X is 3 hours. After a dose of 50 mg, its effect lasted for 5 hours. What is the expected duration from a 100 mg dose?
A. 2 hrs
B. 4 hrs
C. 5 hrs
D. 8 hrs
E. 10 hrs
F. 20 hrs
D. 8 hrs
If you give a dose
that is 2x the minimum amount
necessary to achieve a therapeutic
effect (Amin), then the duration of
the response will be 1 half-life.
Which of the following is NOT a contribution of metabolites in PK?
a. displacement
b. induction
c. replacement
d. inhibition
e. toxicity
f. action
c. replacement
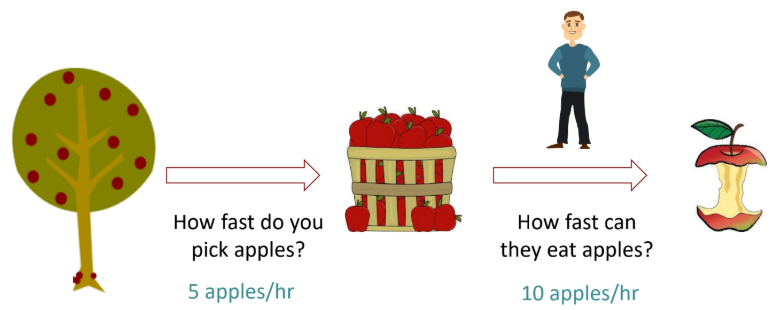

5 apples/hr —> _____ rate (slower rate)
10 apples/hr —> _____rate
Apparent, True
The apparent elimination rate of metabolite
is determined by the metabolite formation rate
(= parent drug disappearance rate, if fe=0).
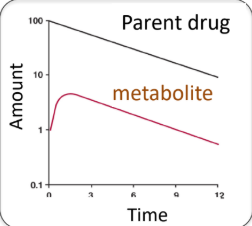
Metabolite formation rate < Metabolite elimination rate
What defines the PK profile of a metabolite?
Rate-limiting step (slowest step)
a. Metabolite formation rate < Metabolite elimination rate
b. Metabolite formation rate > Metabolite elimination rate
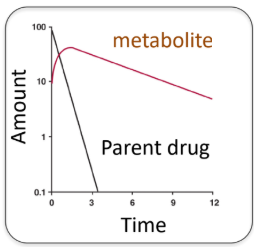
b. Metabolite formation rate > Metabolite elimination rate
The apparent elimination of metabolite is
determined by true metabolite elimination
rate.

Metabolite elimination is _______ rate-limited.
True tt/2 of metabolite is ____ than t1/2 of parent drug
Apparent t1/2 of metabolite is similar to t1/2 of parent drug
formation
shorter
This is a typical pattern for most drugs
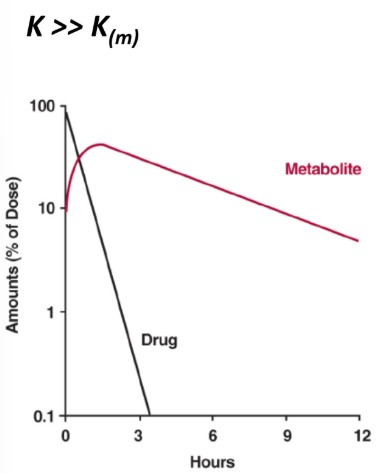
Apparent metabolite is _________ rate-limited.
Both the apparent and true t1/2 of metabolite is ____ than t1/2 of parent drug
metabolite elimination
longer
Typical pattern for prodrugs
For formation-limited drugs, the time to reach SS for metabolite is ____ as that of the parent drug.
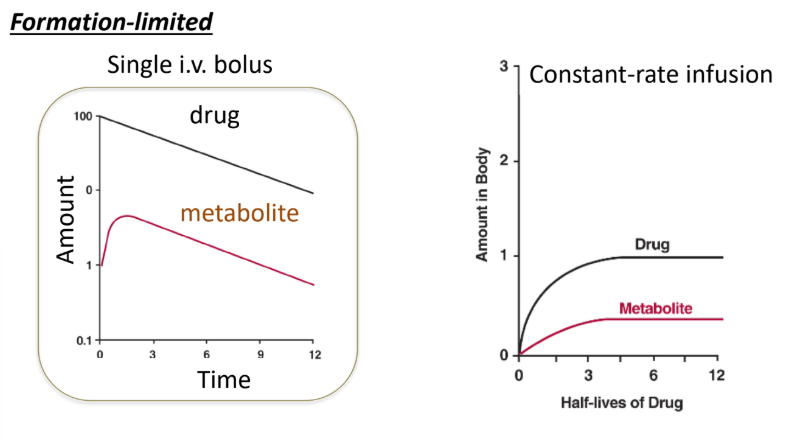
same
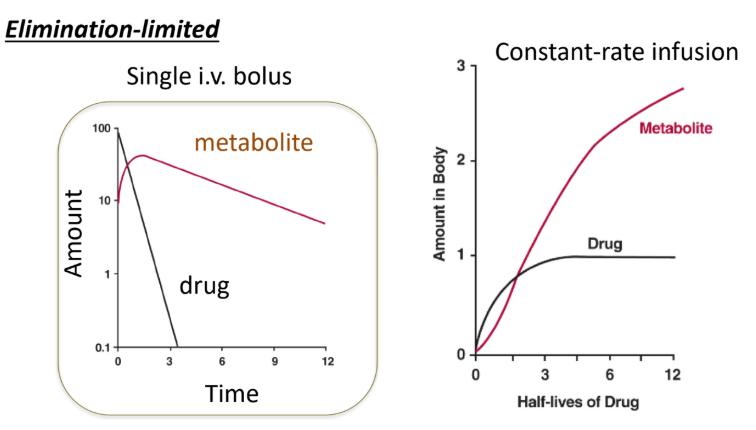
For elimination-limited drugs, the time to reach steady state for metabolite is ____ than that of the parent drug.
longer
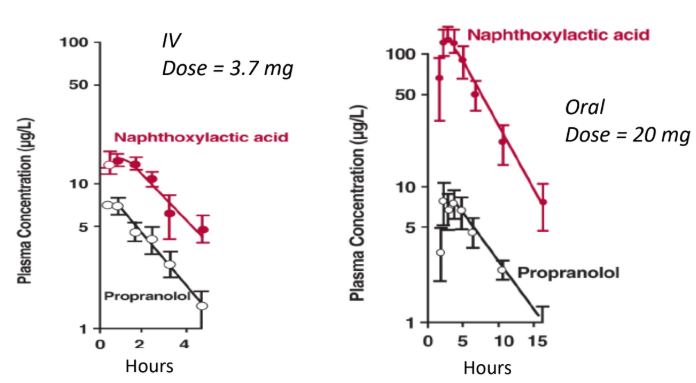
Drugs that experience significant first pass
effect (high EH) show _____ metabolite-to-
parent drug concentration ratio after oral
administration as compared to IV.
high
True or false: Low F of prodrug does not mean a poor therapeutic effect following oral administration.
True!
A shorter onset and a more intense response may occur after oral administration than iv
TRUE OR FALSE: Tolbutamide metabolite PK is “formation rate-limited.” Then, the true t1/2 of hydroxytolbutamide (t1/2 obtained after administration of hydroxytolbutamide) would be shorter than t1/2 of tolbutamide.
TRUE!!
TRUE OR FALSE: Drugs of high EH are associated with low F. A prodrug that has a high EH would exhibit minimal pharmacological activity after oral dosing.
FALSE!!