4 - Delirium
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
What is delirium
1. Develops suddenly (over hours to days)
2. Disturbance in attention and awareness
3. Disturbance in cognition
4. Change from baseline
5. Fluctuates
6. Evidence that the disturbance is caused by a medical condition, substance intoxication or withdrawal, or medication side effect
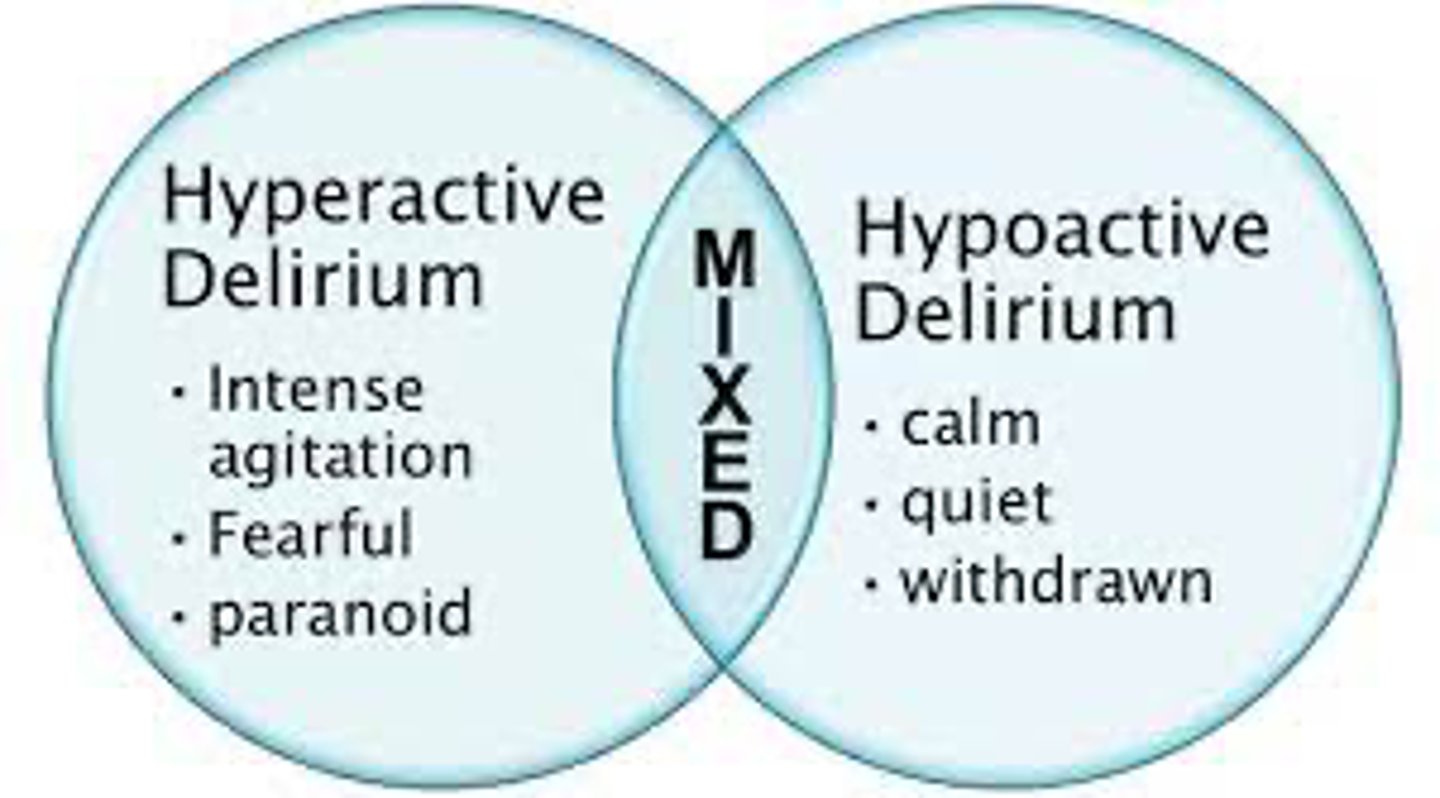
What are the two types of delirium?
Hyperdelirium
Hypodelirium
(can also be a mixture of both)
What are the risk factors for delirium?
- Increasing age (over 65yrs)
- Severe illness
- Underlying brain disease (eg. dementia, IPD)
- Previous delirium
What are the causes of delirium?
PINCH ME acronym
Pain
Infection
Nutrition (lack of)
Constipation
Hydration (lack of)
Meds (opioids, anticholinergics)
Electrolytes/environment
How to assess a patient with suspected delirium?
Collateral history is key!
- Can be obtained from anyone who knows the person well (family, friends, carers etc)
- Get an idea of the persons baseline cognition and function
HPC
- Onset of confusion
- Any infective symptoms?
- Any history of falls with head injury?
- Any issues with bowels/passing urine?
- Any issues with eating and drinking?
PMH
- Any underlying brain disease?
- Previous history of delirium?
DH
- Review of new and current drugs that may contribute to confusion
SH
- How are they managing at home?
- Any alcohol excess?
- Any illicit drug use?
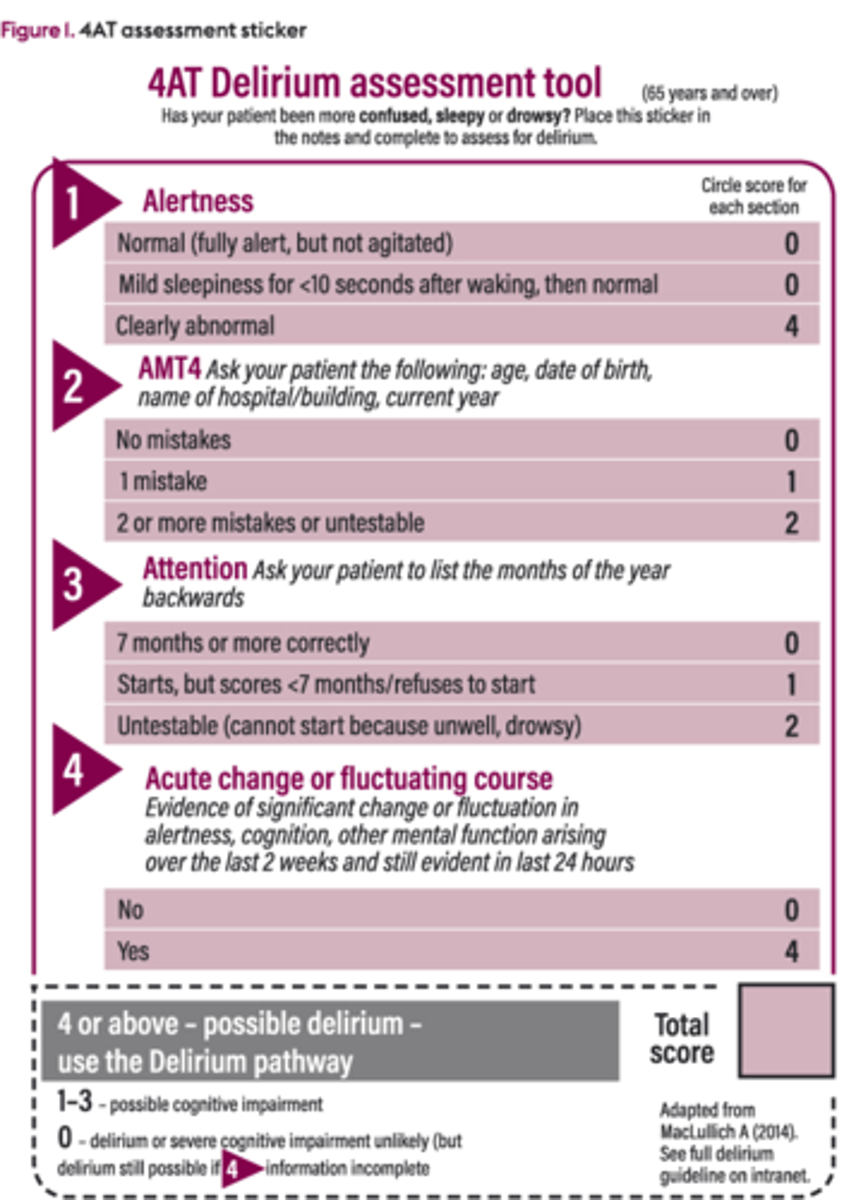
How is delirium screened for?
4AT assessment test for delirium and cognitive impairment
How is delirium managed?
- Treat the underlying cause/s
- Supportive medical care
-> “this is me" document
-> encourage eating and drinking
-> hearing aids, glasses
-> bowel care
-> sleep!
- Medications (eg. sedation, anti-psychotics) not routinely used
-> limited evidence, side-effects
-> consider if a person is in significant distress or poses a risk to self/others
What side effects do anticholinergics (eg. oxybutinin) cause?
- Can't see (dry eyes)
- Can't pee (urinary retention)
- Can't spit (dry mouth)
- Cant shit (constipation)
Anticholinergics are not preferred in geriatrics due to the likelihood of delirium
What is the difference between delirium and dementia?
Delirium:
- Sudden onset
- Tends to fluctuate
- Variation in conscious level (hypoactive vs hyperactive)
Dementia:
- Gradual onset
- Progressive decline
- (usually) conscious level not impaired
What is the recovery from delirium?
- Most people with delirium improve once the underlying problem is treated and they are back to their usual environment
- It can take days to weeks to resolve
- In some cases, can take months, and may uncover underlying cognitive impairment