Behavioral Genetics Lec 3- DNA, Genes, Chromosomes
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Chromosome nondisjunction is an example of what?
Meiotic drive→ the biased transmission of specific alleles from heterozygous parents to offspring
This is itself a case of intragenomic conflict→ an evolutionary phenomenon where specific genetic elements within a single organism's genome act to increase their own transmission or replication at the expense of other genes or the overall fitness of the host organism (selfish gene theory)
What is the result of spermatogenesis and oogenesis? Explain this observation.
Spermatogenesis: 1×2N→ 4×1N
Oogenesis: 1×2N→1N
Oogenesis produces less because 2 polar bodies are released (have less cytoplasm)→ eggs are much larger and contain much more cytoplasm than sperm cells (only transfer DNA material)
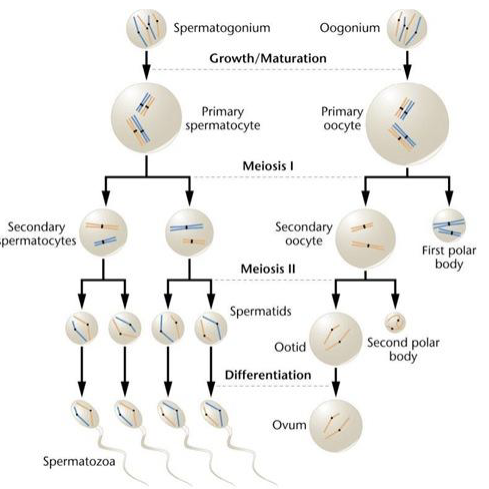
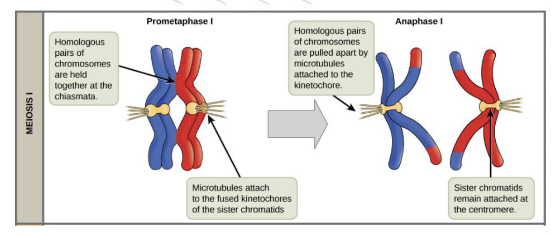
There is competition between homologous chromosomes to end up in the egg. Explain how chromosomes are “selected” to be in the egg versus being released in a polar body.
The centromeres are under selection to attach more strongly to spindles→ strongly attached centromeres end up in the egg and “win” while the more weakly attached centromeres “lose” and kill the embryo via aneuploidy (few exceptions)
What are the sources of genetic variation in sexual reproduction?
Independent Assortment
Random Fertilization
Crossing-over (recombination)
De Novo Mutations
Sources of Genetic Variation: Independent Assortment
Random distribution of homologous chromosomes to daughter cells -
Number of all unique gametes? 2(n) = 223 = over 8 million
Sources of Genetic Variation: Random Fertilization
Any two unique gametes can make a fertilized egg
Number of all unique fertilized eggs? (223)2 = over 64 trillion
Sources of Genetic Variation: Crossing-over (recombination)
Exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes
Sources of Genetic Variation: De Novo Mutations
Not present in either parent (not inherited), but occur during meiosis→ (~ 60 in every human) (more via older fathers)
When do egg cells divide relative to the age of the future mother? How does this differ from sperm cells?
Egg cells divide before the future mother is born→ every individual is produced from an egg cell made in their maternal grandmother’s body (meiosis is arrested in prophase 1 prior to puberty)
Sperm is produced continuously and accumulate mutations as the age increases
Define transcription, translation, and expression.
Transcription→ Encoding of RNA by DNA
Translation→ Encoding of protein by mRNA
Expression→ A gene is transcribed and translated
All cells in a person have the same DNA, but the identity of every type of cell is due to its expression profile (e.g. neuron vs kidney cells, or different types of neurons)
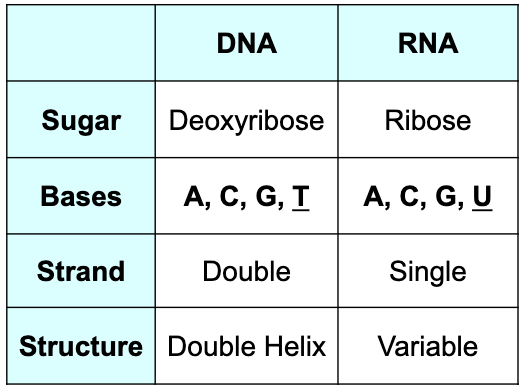
What is RNA? How does RNA differ from DNA?
RNA:
Type of nucleic acid (like DNA)
Both coding (mRNA) and noncoding types (ncRNA)
Every protein-coding gene in DNA encodes an mRNA
Contains ribose as sugar
Uracil instead of Thymine
Single-stranded
Can noncoding DNA be considered genes?
It depends→ yes if the ncRNA it codes for has a function
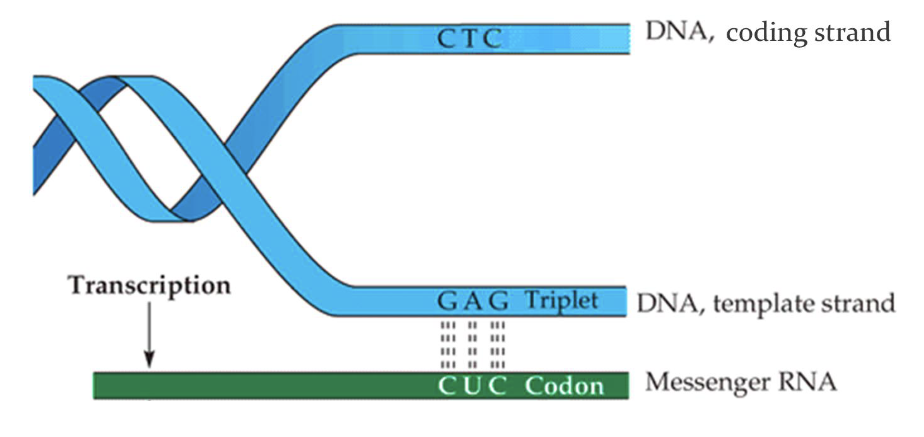
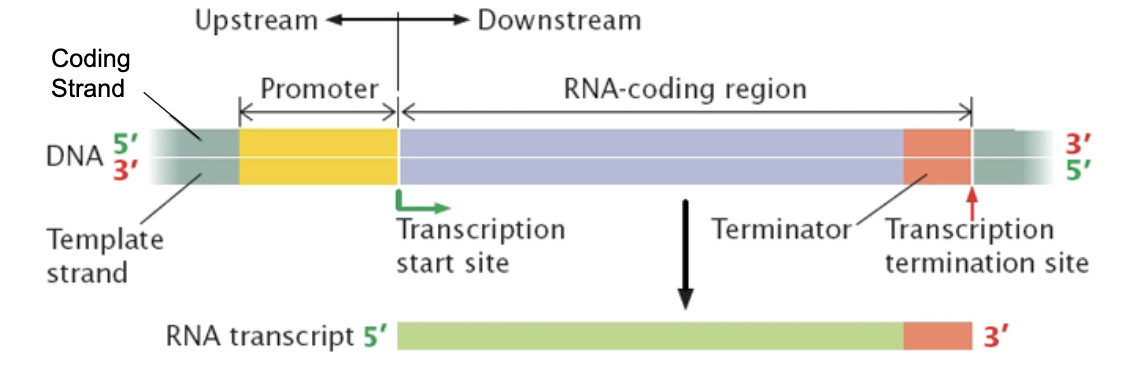
Define template strand and coding strand in transcription.
Template strand→ Used for transcription
Coding strand→ Complementary to the template, identical to RNA
What are the components of a gene?
Genic sequences→ Exons (coding sequences), Introns, 5’ UTR, 3’ UTR (untranslated regions)
Regulatory sequences→ Promoter, enhancers, Silencers, etc.
Components of genes: other image
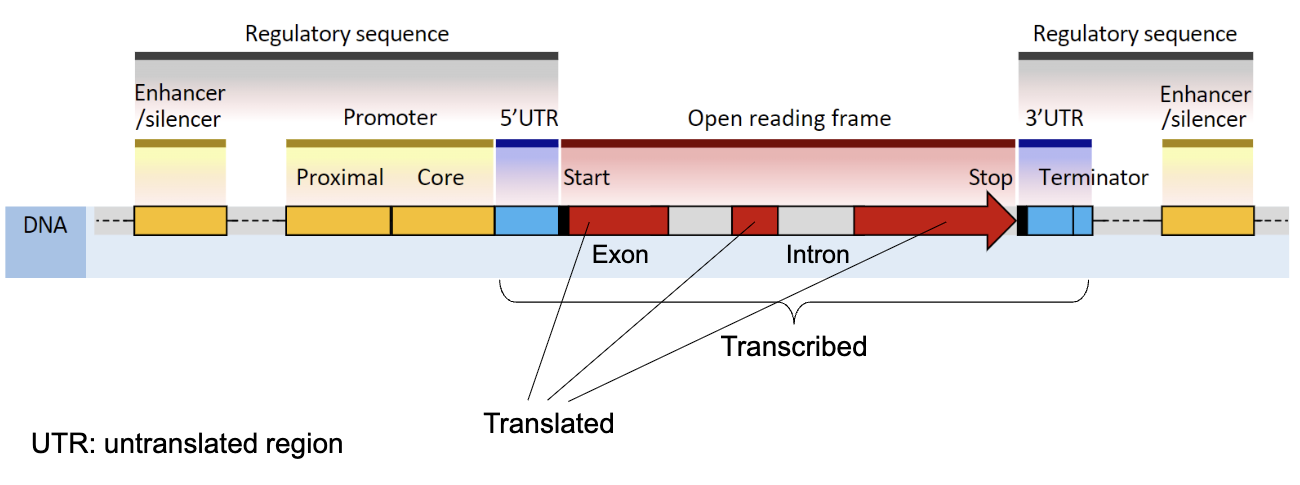
What differentiates Pre-mRNA and Mature RNA?
Pre-mRNA: Exons + Introns→ Mature RNA: Exons
Introns are spliced out and are not translated
5’ cap and Poly-A tail are added→ present in mature RNA and are necessary for translation
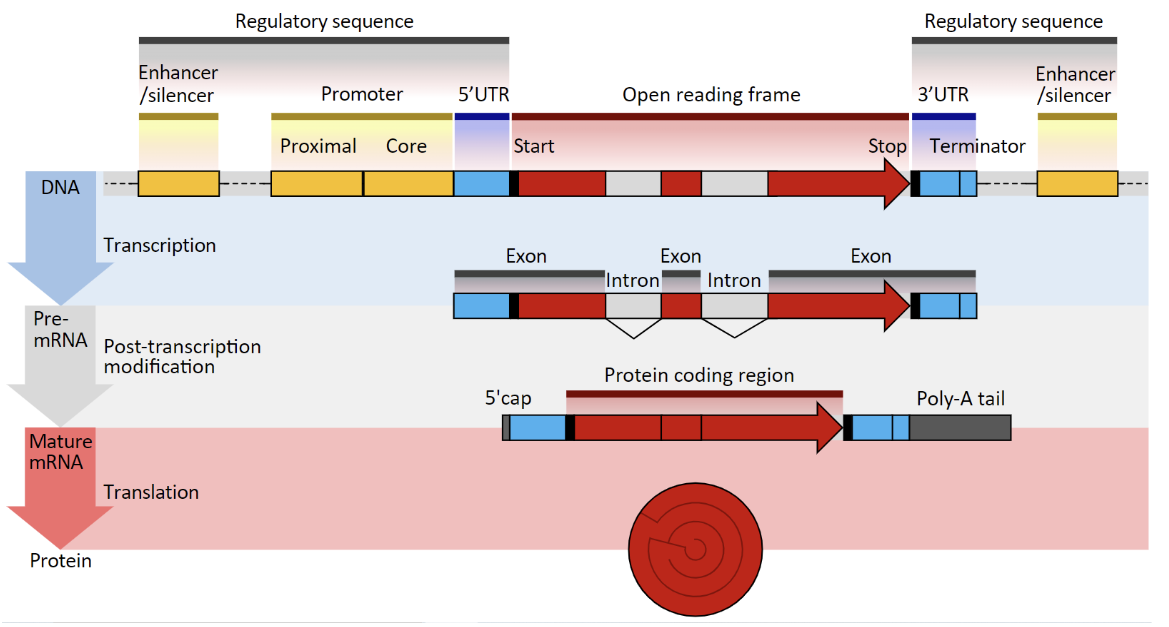
What does “Cis Regulatory Elements (CREs) refer to?
Typically considered more important
Proximal Elements→ Promoter (necessary for transcription, most important part of regulatory sequences, immediately adjacent to transcription start site)
Distal Elements→ Enhancers, Silencers
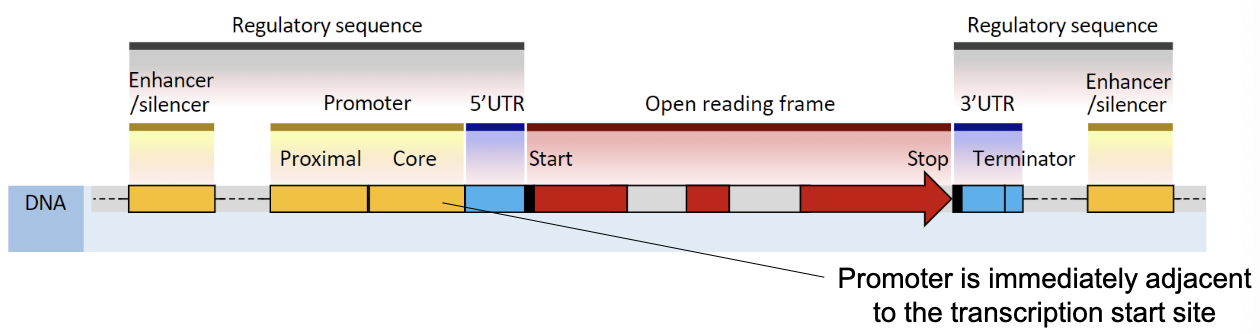
What is the function of transcription factors and mediator proteins?
Transcription factors bind to the promoter to initiate transcription
Mediator proteins bind to regulatory (distal) sites to aid in regulation
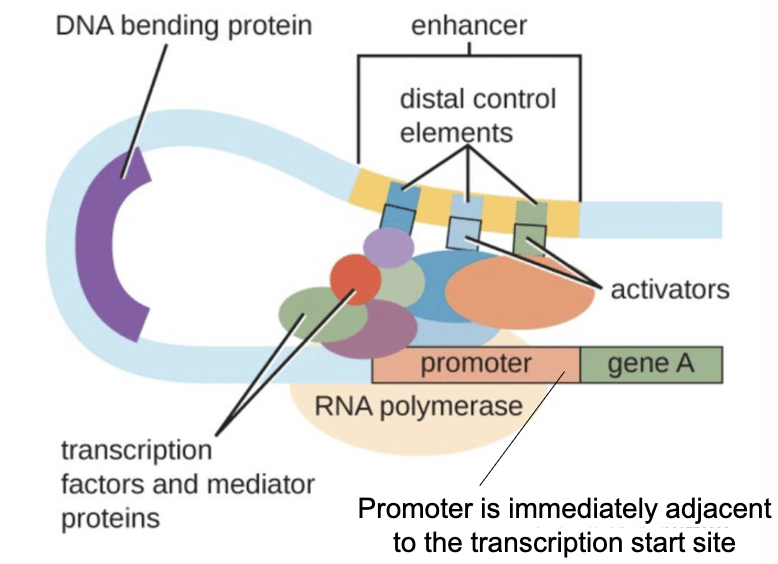
What are Trans Regulatory Elements (TREs)?
Genes encoding Transcription Factors (TFs)→ TFs are proteins that bind to a specific DNA sequence (a regulatory element) and controls the rate of transcription (up or down)
Located at a completely different site on genome→ could be on another chromosome
Define Alternative Splicing.
Alternative Splicing→ introns are spliced out, sometimes with some exons
one gene→ multiple mRNA variants→ multiple protein isoforms
contributes to complexity of expression due to different ways of splicing→ different exons can be removed or none at all
>100,000 proteins, 20,000 genes
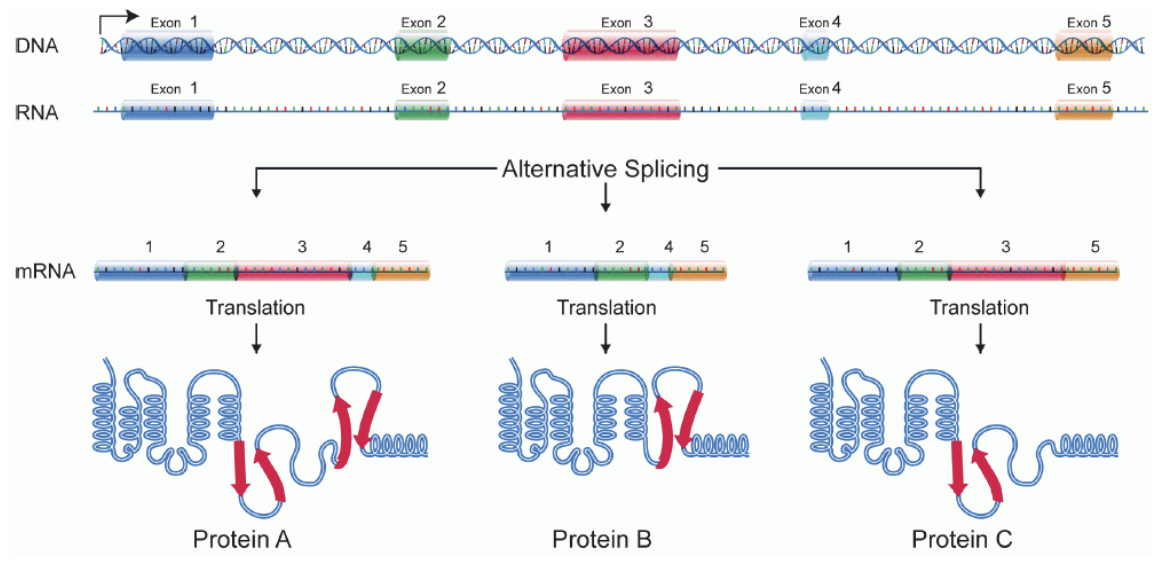
What does translation do? What is involved?
RNA→ proteins
Protein building blocks→ amino acids (20 types)
AA’s differ in their R group
Sequence of amino acids (peptide chain) corresponds to a sequence of nucleotides (NTs) in mRNA
RNA: 5’→3’
Peptide: N terminus→C terminus
What are codons?
Codons→ 3-NT codes (order matters, repetition allowed)
4 NTs→ 20 AAs
43=64 codons
64 codons→ 20 AAs: Codon degeneracy/redundancy→ robustness (back up options b/c different codons can code for same AA)
What are the other two types of RNA involved in translation?
tRNA (transfer RNA):
Binding site for codon (mRNA): Anticodon
Binding site for specific AA
rRNA (ribosomal RNA):
Part of ribosome
Large RNA-protein complex
3D structure facilitates mechanical function
What are the steps of translation?
tRNA brings AAs to ribosome (start codon: AUG: Met)
Anticodon on tRNA and codon on mRNA bind
AA is added to the peptide chain and tRNA is released
Ribosome moves along mRNA until reaches a stop codon (stop codons: UAA, UAG, UGA)
What are point mutations and what types are there?
Change in one nucleotide (one base pair) → different consequences:
Silent mutation: new codon → same amino acid
Missense mutation: new codon → different amino acid
Nonsense mutation: new codon = stop codon → no further translation
Frameshift mutation: insertion/deletion of one NT→ change in reading frame unless insertion/deletion is in multiples of three NTs