Cysa+ Full Set
1/321
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
322 Terms
/etc Directory
Linux Configuration
/Library/Preferences
Mac configuration files
C:\ProgramData\
Windows configuration files
East-West Traffic
Network traffic between systems located in the data center
North-South Traffic
Network traffic between systems in the data center and systems on the internet
Extranet
Intranet segments extended to business partners
Ad Hoc Network
Temporary networks that may bypass security controls
CASB
Enforces security policies in the cloud
Control Plane
Responsible for making routing and switching decisions
Data Plane
Responsible for carrying out the instructions of the control plane
SDN
Separates the control plane from the data plane— makes the network programmable
Password Vaulting
Stores administrative passwords
Monitoring
Logs administrative user activity
Command Proxying
Eliminates the need for direct server access
Credential Managment
Rotates passwords and access keys
On-Premises CASB
Intercepts network traffic headed to cloud services
Cloud-Based CASB
Uses APIs to interact with cloud services
CASB (Cloud Access Security Broker)
A security layer that sits between users and cloud services to monitor, control, and enforce policies on cloud usage.
Nmap
Free, open-source tool used to scan networks, discover devices, and find open ports and services
CASB benefits
Provides visibility into cloud use, offers DLP capabilities, and injects encryption into the cloud
Cryptography
The use of mathematical algorithms to transform information into an encrypted form that is not readable by unauthorized individuals
Cipher Suite
TLS depends upon pairings of encryption and hash functions known as cipher suites.
TLS
A cryptographic protocol that secures data as it moves between two systems over a network
Session Keys are known as
Ephemeral Keys
Pipe
Sends output to another command
Output redirection
Sends output to a file
Grep
Searched files for patterns
Regular expressions
Allow pattern matching
Window of Vulnerability
The time between the discovery of a zero-day vulnerability and the release of a security update
End-of-Sale
Product will no longer be offered for purchase, but the vendor will support existing customers
End-of-Support
The vendor will reduce or eliminate support for existing users of the product
End-of-Life
The vendor will no longer provide any support or updates for the product
CybOX - Cyber Observable eXpression
A format to describe individual events on a system (What happened)
STIX - Structured Threat Information eXpression
A standardized language to describe cyber threats (What the threat is)
TAXII - Trusted Automated eXchange of Indicator Information
A delivery system to share STIX info between tools/orgs (How it’s shared securely)
Data Enrichment
Automatically supplements incident data
Darknets
Unused but monitored IP address space
Webhooks
Sends signals between services
Network Mapping
Scans networks to search for systems that have open ports and are accepting connections from remote systems
Nmap - Host Discovery Flags
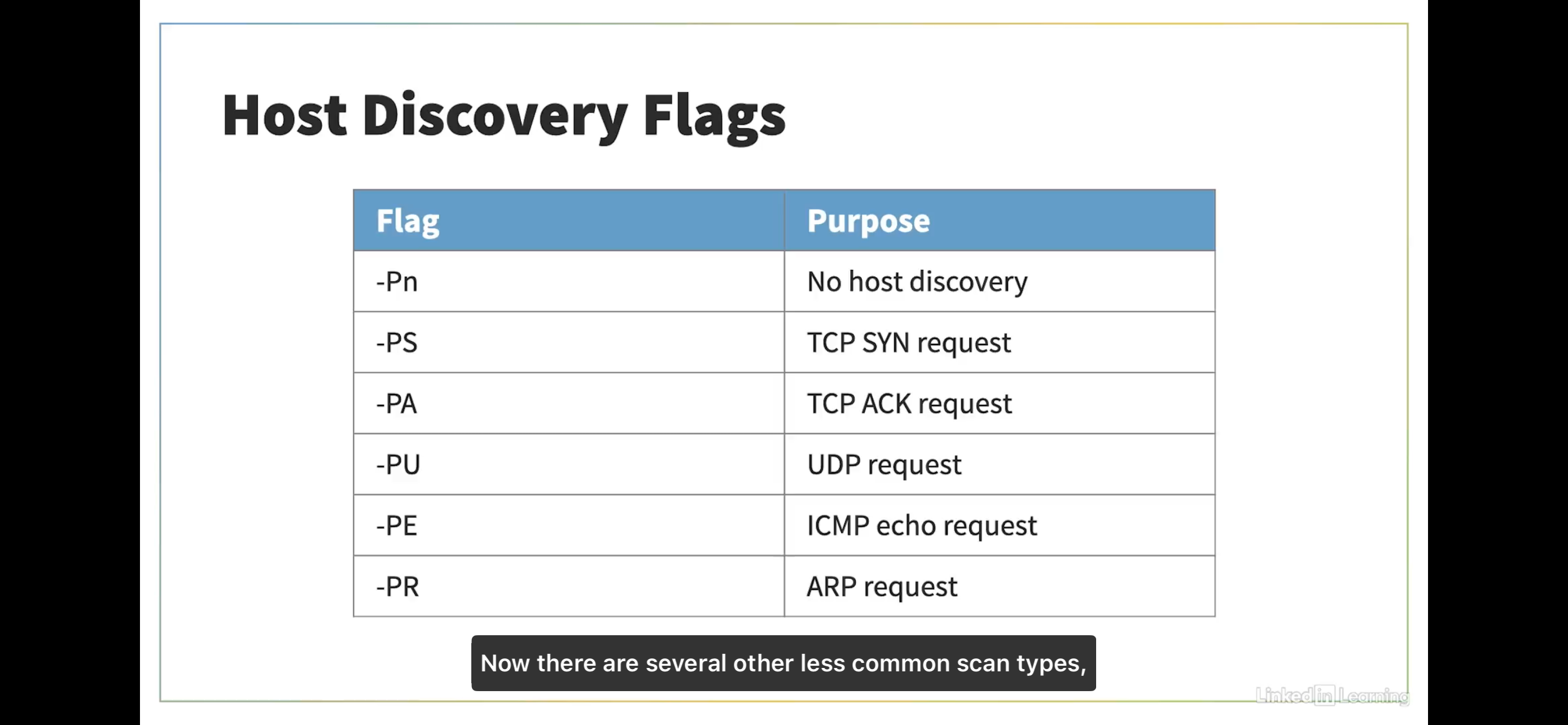
Service Version Detection
Guesses the service versions running on an open port
Agent-Based Scanning
Installs software on each target device
Credential Scanning
Uses passwords to log into systems
Scan Engine Updates
Software updates to the scanner itself that fix bugs and add new features
Plug-In Updates
Vulnerability feed updates that provide the scanner with information about current vulnerabilities
General-Purpose
Nessus and OpenVAS are general-purpose vulnerability scanners.
Open-Source Scanners
Arachni and Nikto are open-source web application vulnerability scanners.
Active Scanning
Probes systems for issues
Active Scanning Drawbacks
Can be detected by administrators, May accidentally exploit vulnerabilities, Will miss some vulnerabilities due to firewall settings, network segmentation, and IPS deployments
Passive Scanning
Observes network traffic
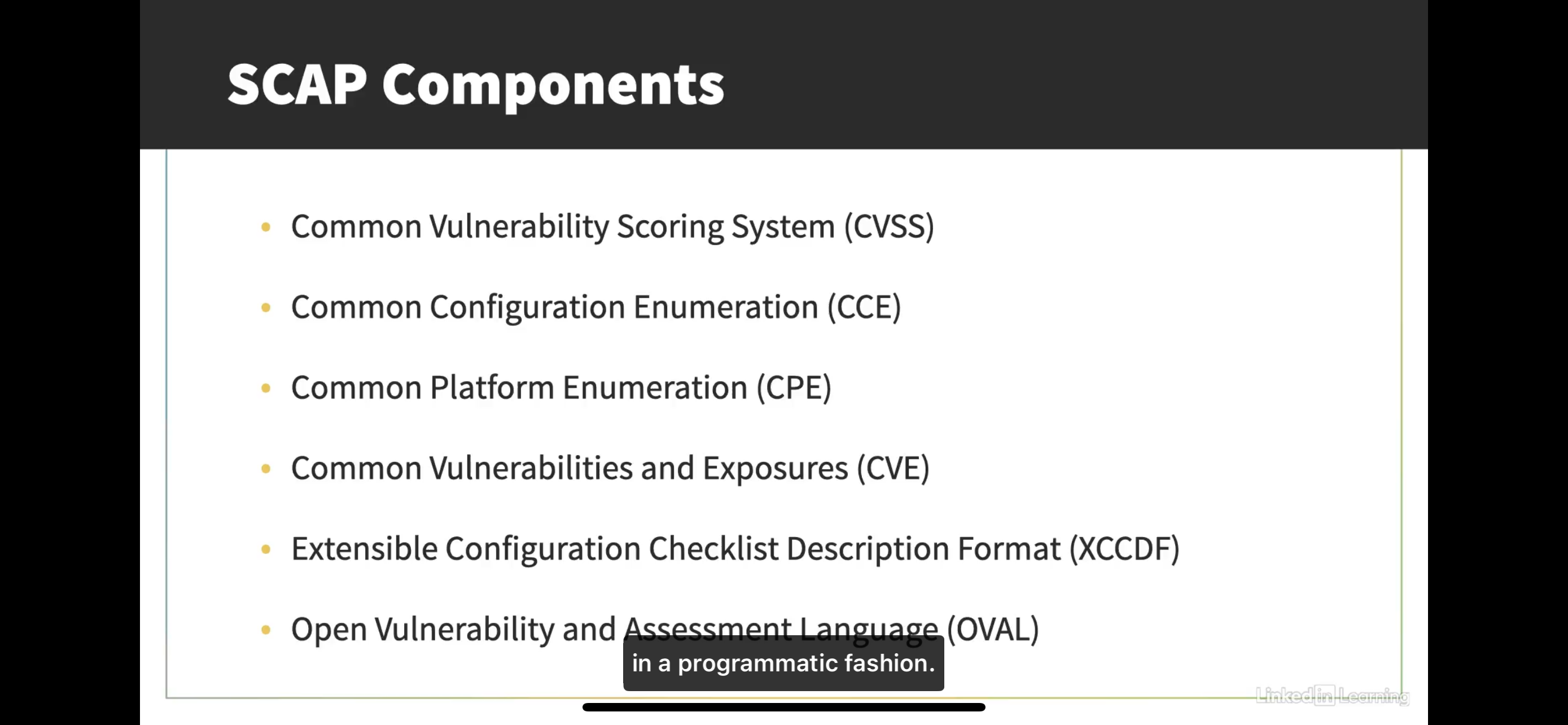
SCAP Components
CVSS
Scores vulnerabilities on a 10-point scale
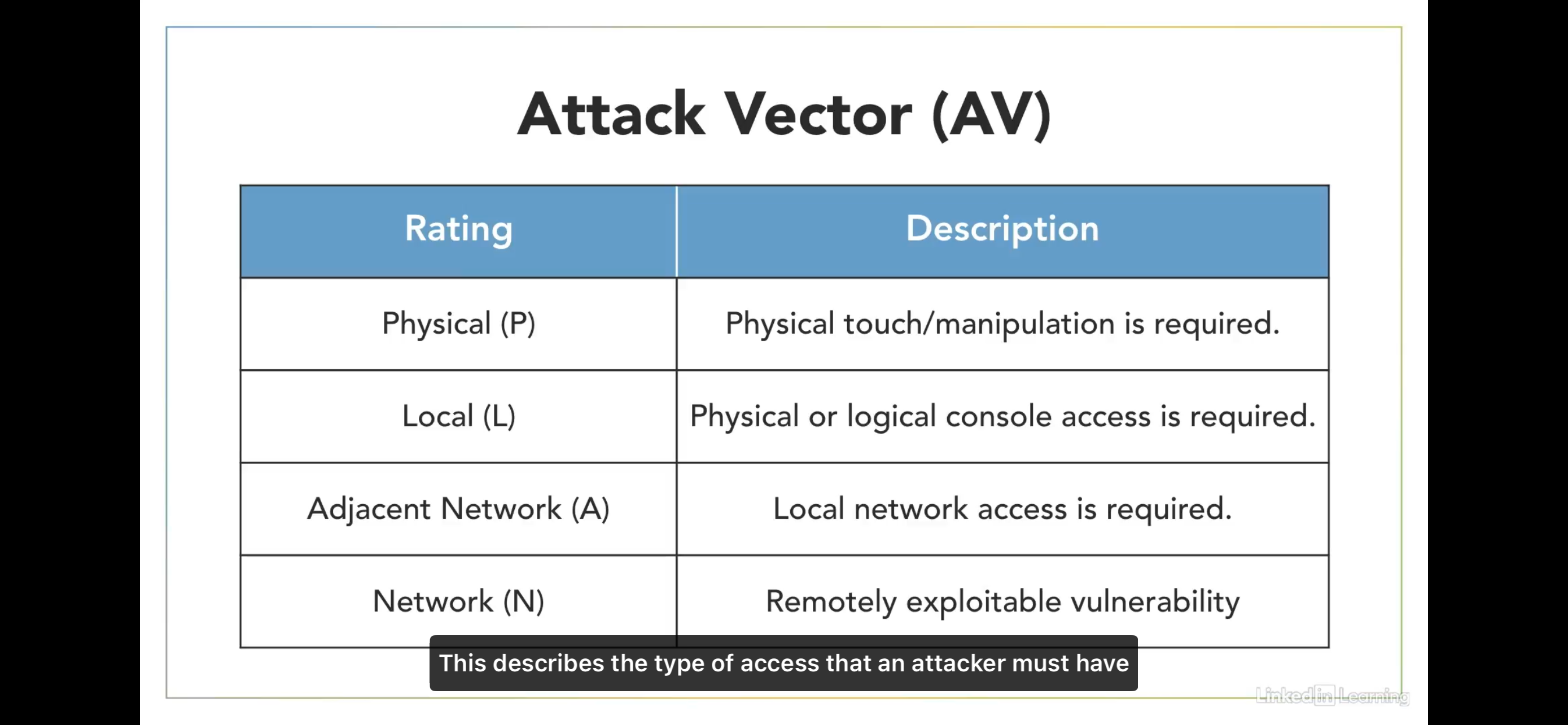
Attack Vector
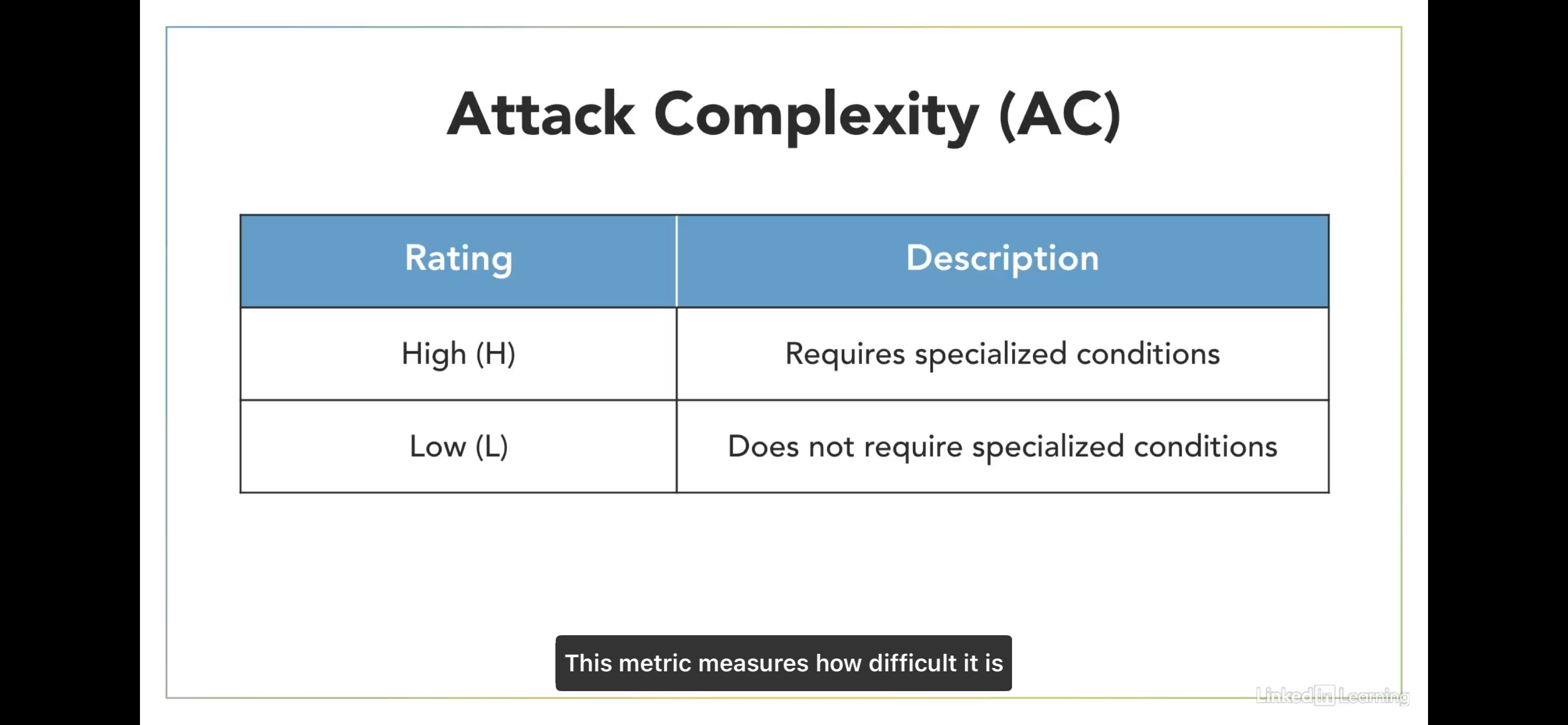
Attack Complexity
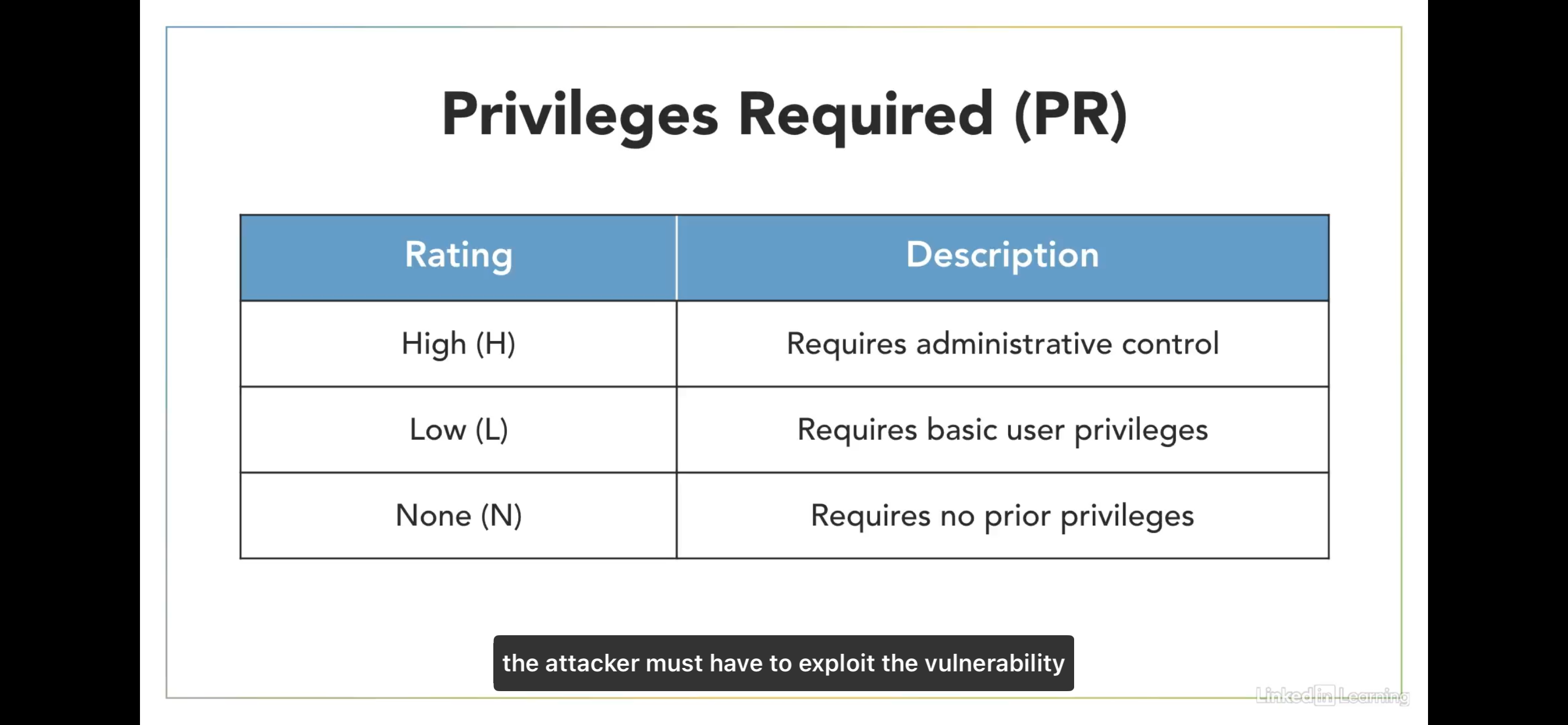
Privileges Required
Stored / Persistent XSS
The attack is stored on a remote server, waiting for a victim to discover it.
Reflected XSS
The attack is unintentionally sent to the server by the victim and then returned in the resulting webpage.
Same Attack
Cross-site request forgery, CSRF, XSRF, and
"sea surf" all refer to the same attack.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
attacks occur when an attacker embeds malicious scripts in a third-party website that are later run by innocent visitors to that site.
Cross-Site Request Forgery
Attacks leverage the fact that users are often logged into multiple sites at the same time and use one site to trick the browser into sending malicious requests to another site without the user's knowledge.
Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF)
Request forgery attack that targets servers, rather than users, by manipulating servers into retrieving malicious data from what it believes to be a trusted source
Directory Traversal Attacks
When an attacker uses directory navigation references to search for unsecured files on a server
Confidentiality
Ensures that unauthorized individuals are not able to gain access to sensitive information
Integrity
Ensures that there are no unauthorized modifications to information or systems, whether intentionally or unintentionally.
Availability
Ensures that information and systems are ready to meet the needs of legitimate users at the time they request them
Privacy
focuses on the ways an organization can use and share information collected about individuals
Vulnerability
A weakness in a device, system, application, or process that might allow an attack to take place. Vulnerabilities are internal factors that cybersecurity professionals can control (e.g., upgrading outdated software).
Threat
An outside force that may exploit a vulnerability. Threats can be malicious (e.g., a hacker) or nonmalicious (e.g., an earthquake
Risk
The combination of a threat and a corresponding vulnerability
Adversarial Threat
Individuals, groups, or organizations deliberately attempting to undermine security (e.g., nation-states, trusted insiders, competitors).
Accidental Threat
Individuals mistakenly performing an action that undermines security during routine work (e.g., a system administrator accidentally deleting a critical disk volume).
Structural Threat
Equipment, software, or environmental controls failing due to resource exhaustion, exceeding operational capability (extreme heat), or age.
Environmental Threat
Natural or human-made disasters outside organizational control (e.g., fires, severe storms, power failures).
Technical controls
Systems, devices, software, and settings that enforce CIA requirements (e.g., secure network building, endpoint security).
Operational controls
Practices and procedures that bolster cybersecurity (e.g., conducting penetration testing, using reverse engineering).
Network Access Control (NAC)
Limiting network access to authorized individuals & Ensuring that systems accessing the network meet basic security requirements.
Triple-homed Firewalls
connect to three different networks: the Internet, the internal network, and a special network known as the demilitarized zone (DMZ) or screened subnet
DMZ
A network zone designed to house systems that receive outside connections (e.g., web and email servers). Placing these systems here isolates them, so if they are compromised, they pose little threat to the internal network.
Rule Base/ACL
Firewalls evaluate connection requests against a rule base, which is an access control list (ACL).
Default Deny Principle
If there is no rule explicitly allowing a connection, the firewall will deny that connection
Port 20,21
FTP
Port 22
SSH
Port 23
Telnet
Port 25
SMTP
Port 53
DNS
Port 80
HTTP
Port 443
HTTPS
Packet filtering firewalls
checking only packet characteristics against rules; often found in routers.
Stateful inspection firewalls
Maintain information about the state of each connection; the most basic standalone firewall products
Next-generation firewalls (NGFWs)
Incorporate contextual information about users, applications, and business processes; current state-of-the-art.
Web application firewalls (WAFs)
Specialized firewalls designed to protect against web application attacks (e.g., SQL injection, cross-site scripting).
Jump Box
A server placed in a screened subnet to act as a secure transition point between networks, providing a trusted path.
Honeypots
Systems designed by experts to falsely appear vulnerable and lucrative to attackers. They simulate a successful attack and monitor activity to learn attacker intentions
DNS Sinkholes
Feed false information to malicious software.
Hardening
involves making configurations as attack-resistant as possible.
Compensating Controls
Alternate means
Mandatory Access Control (MAC)
administrators set all security permissions, and end users cannot modify them
Discretionary Access Control (DAC)
the file owner controls the permissions