AP Psychology - Personal Focus Areas
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
What does Acetylcholine do?
Memory, arousal, learning, & involuntary muscle movement
What does GABA do?
Inhibitory transmitter, calms nervous system
What does Glutamate do?
Major excitatory, crucial role in synaptic transmission
What does norepinephrine do?
Involved in stress response as well as sleep cycle, mood, and memory
What does the Hypothalamus do?
fleeing, fighting, fornication, feeding
Which four structures belong to the limbic system? (HACH)
Hippocampus, hypothalamus, cerebellum, Amygdala
What is the limbic system responsible for?
Process and regulate emotion and memory as well as sexual stimulation and learning.
Which four structures are part of the brainstem?
Pons, Reticular Formation, Medulla, Thalamus
Which structures are a part of the Cerebral Cortex? (WTF BCOP)
Wernicke’s area, Temporal lobe, Frontal Lobe, Broca’s area, Corpus Callosum, Occipital Lobe, Parietal Lobe
What is the Parietal lobe’s function?
Sensory perception and integration
What is the Temporal lobe’s function?
Memory, production/perception, and emotion association.
What is the Frontal lobe’s function?
Thinking, emotions/personality, muscle control, memory storage
What is a CAT scan?
Provides information about the density and shape of different brain structures w/ x-rays
What is a PET scan?
It shows the metabolic processes happening in the brain by detecting levels of glucose uptake w/ radioactive tracers
What does the Pituitary gland do?
Releases hormones
What does the Adrenal gland do?
Produces hormones involving stress, metabolism, and blood pressure
What does the Thyroid gland do?
Controls hormones involved in metabolism, growth, etc
What are Beta waves?
Normal waking conscience and heightened level of alertness
What are Alpha waves?
The relatively slow brain waves of a relaxed, awake state
What are Delta waves?
Delta waves are the slowest type of brain wave, typically occurring during deep sleep or meditation
What is Weber’s Law?
States that the perceived magnitude increases just as the intensity of the stimulus increases. (Higher intensity, more change needed to notice)
What is Signal Detection Theory?
Measures a person’s ability to differentiate between meaningful information (signal) and random background noise (noise) in decision-making.
What does the pupil do?
Adjustable opening in the center of the eye that controls the amount of light entering the eye
What does the lens do?
Focuses incoming light rays into an image on the retina by changing its curvature (accommodation)
What does the retina do?
Innermost layer of the eye that contains photoreceptors which detect light
What does the eardrum do?
It vibrates when sound waves strike it, initiating the hearing process.
What does the middle ear (hammer, anvil, stirrup) do?
Bones work together to amplify and transmit vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear, allowing us to perceive sound
What does the cochlea do?
Converts sound vibrations into electrical signals that the brain can interpret. Has hair follicles that bend
What does the Basilar membrane do?
Responsible for transforming sound waves into electrical impulses, which are then transmitted to the brain.
What is Phi Phenomenon?
Makes us believe that fixed images are moving. It is created by presenting two stimuli rapidly, causing the mind to perceive nonexistent motion
What is acquistion?
First stage of condition when a response is first established and gradually strengthened.
What is the over justification effect?
Someone is rewarded for doing something they already enjoy, and suddenly they become less interested in doing it just for fun
What is the age and definition of sensorimotor stage?
0 → 2 years. Infants learn about their environment through exploring through looking, listening, touching, and tasting4.
What is the age and definition of preoperational stage?
2 → 7 years. Children can think symbolically and engage in make-believe play, but their thinking is still egocentric and lacks logic
What is the age and definition of Concrete stage?
7 → 11 years. Children develop organized and rational thinking.
What is the age and definition of Formal Operational stage?
12 years → onwards. Children's thinking becomes much more sophisticated and advanced, allowing them to think abstractly and manipulate ideas in their head
What is conservation?
Understanding that certain properties of an object, such as quantity, volume, or mass, remain the same even when their appearance changes
What was the strange situation designed to do?
Designed to observe the child's response to separation from and reunion with the caregiver in a controlled but play-like setting.
What is fluid intelligence?
Fluid intelligence is the capacity to think speedily and reason flexibly to solve new problems without relying on past experience and accumulated knowledge. Decreases w/ age
What is Crystallized Intelligence?
Intelligence refers to the ability to use skills, knowledge, and experience to solve problems and adapt to new situations. It is based on facts and rooted in experiences
What is reaction formation?
Unconsciously replaces an unwanted or anxiety-provoking impulse with its opposite,
What are the Big Five (OCEAN)?
Openness, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Agreeableness, and Neuroticism
What is reciprocal determinism?
Suggests a person's behavior is influenced by and influences both individual factors and the environment.
What is self-efficacy?
Self-efficacy is defined as an individual's belief in their capacity to execute behaviors necessary to produce specific performance outcomes.
What is Excoriation?
Characterized by repetitive and compulsive skin picking, often resulting in physical damage and emotional distress.
What is somatoform?
Mental illness that causes one or more bodily symptoms, including pain.
What is catatonia?
Involves a lack of movement and communication, and also can include agitation, confusion, and restlessness.
What is Stupor?
Stupor is defined as a condition of greatly dulled or completely suspended sense or sensibility
What is Rational-Emotive Therapy?
Psychotherapy that aims to resolve emotional and behavioral problems by helping individuals understand the power of their emotions and challenge irrational beliefs and thoughts.
Which ideas are a part of psychoanalytic perspective?
Id, Ego, Supergo, Defense Mechanisms, Projective tests
Which ideas are a part of trait perspective?
The big five (OCEAN), Myers-Briggs (MMPI)
Which ideas are a part of Socio-Cognitive perspective?
Reciprocal determinism, self-efficacy, internal/external locus of control, learned helplessness
What is the Diathesis-Stress model?
While a person may have a genetic vulnerability to a disorder, it is the presence of stressors that triggers the onset of the disorder.
What is the working model of memory?
The working memory model is an explanation for how short-term memory works. The model shows that short-term memory can be sub-divided into distinct components
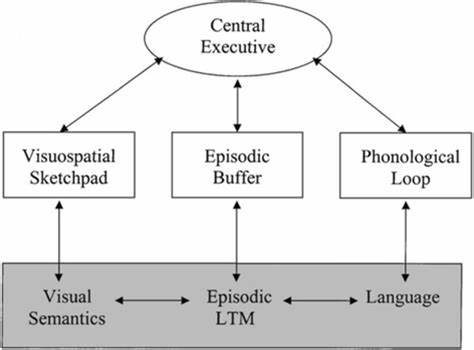
What is discontinuous stage view?
People develop in distinct stages throughout their lifespan
What is continuous stage view?
People develop over their entire lifespan gradually and continuously.
What are the monocular depth cues?
Texture gradient, relative size, and linear perspective
What is texture gradient?
Monocular depth cues in which objects appear further away as their texture becomes less clear and distinct
What is linear perspective?
Monocular depth cues in which objects converge on two parallel lines, determining distance
What is relative size?
Monocular depth cues in which objects that appear smaller are perceived as being further away
What is Yerkes-Dodson Law?
Describes relationship between arousal and performence
What is the law of effect?
Behaviors followed by positive consequences are more likely to be repeated, whereas behaviors followed by negative consequences are more likely to stop
Actor-Observor bias
Behavior in which a person attributes their own actions to external factors and the actions of others to internal factors
Self-serving bias
Attributing one’s own successes to internal factors and qualities and our failures to external factors and others.
What is declarative memory?
Type of memory that involves conscious recall of facts and events, divided into semantic and episodic