GEOG 202 EXAM ONE
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
What does Geography mean?
Writing the earth
Define the two types of geography
Physical Geography: Climate, landforms, soils, vegetation, hydrology
Human Geography: An examination of economic, cultural, and social systems across space and scale
What is a formal region
A contiguous, bounded territory that shares similarities (economic, political, cultural, environmental, population, settlement, and physical geography)
What is the concept of political economy and what is North America’s
The Relationship between markets and the state, and how those relationships impact society and the environment
Capitalism is the political economy of North America
How could capitalism be defined in four bullet points
Capitalism: large scale realization of profit by producing goods and services for more than was paid to produce them
Property in the form of the mean of production is privatized
Means of production is publicly held and the goal of the corporation is to make profit for shareholders
those without means of production work for those who have the means of production
How could North America be defined
Regional Boundaries between Mexico, Central America, and the Caribbean
Resource rich with costs to its environments
Wealthy region with wealth inequality
How is capitalism a world system?
Capitalism is the primary way that economies work all over the world and it the economic driver of globalization
Within the capitalistic system, no on is in charge, with individuals and corporations making independent decisions based on their own interests
Markets are the mechanism by which exchanges are made, no one is in charge of the markets
Markets are able to determine winners based on efficiency
Government regulate markets to varying degrees (tariffs or currency valuation)
What is the role of labor in capitalism
Labor takes the form of wage labor. People work for wages instead of product
Labor must be efficient and is defined by its productivity
Efficiency: maximum effort of labor for the lowest wage, and minimum wastage of resources
Corporations and individuals businesses that produce most efficiently increase their market share
What is division of labor
Break productive labor down into its smallest components to increase productivity
through the division of labor, skill level is lowered so their wages could be reduced as well
Deskilled laborers tend to not be invested in what they are producing
What is a major feature of life in North America
Mass consumption: the production of large amounts of goods to be consumed by a large amount of people
Consumer culture: A society in which patterns of consumption are key basis for status differentiation, personal identities, and pleasure
How does lecture define Sub-Saharan Africa and what are the challenges the region faces
African states south of the Sahara desert (49 states and territory)
Shared History of colonization
No uniting religion, language, philosophy, or political system
North Africa is excluded due to its ties to the Arab world
Fast-growing, generally poorer, more rural and younger
Largest landmass straddling the equator
Environmental obstacles to development
Poor soils
Widespread disease
Drought Vulnerability
What are the challenges that face Sub-Saharan Africa
Challenges
Environmental Degradation
Climate Change
Poverty
Disease
Violence and Refugees
How do geographers reference a specific point on the globe
Latitude: Measures the North and South of the equator
Longitude: Measures the West and East of the Prime Meridian
What are map projections
Due to the globe being a circle, a 2D drawing would never to representative of landmass size, each projection tries to be as accurate as possible
Mercator projection is the most used, good for navigation, but N/S latitudes are disportionately and not used anymore
Robinson projection is the one used in the textbook, makes size more balanced, but distorts shape
Map projections often have to sacrifice what two things
Relative location and size of the continents
What are regions and the definitions associated with regions.
Region: Contiguous bounded territory with common traits
Formal Regions: Defined by physical and/or cultural features
Functional Region: Defined by activities
Why is the Sahel important to Sub-Saharan Africa
The Sahel is a zone of transition between the Sahara and the more humid regions of Africa (south Africa)
Currently, the Sahel is increasing due to desertification
Some argue that the desert ebs and flows, and that this is just natural changes
What is the overall climate of Sub-Saharan Africa
Depends due to the distance to the equator, with majority being some type of Tropical
What are some of Africa’s environmental issues
Sahel and desertification
Sahel ecological zone
balance of limited rain, drought resistance crops, and transhumance
Desertification due to expansion of agriculture and overgrazing
How is climate change affecting Sub-Saharan Africa?
Sub-Saharan Africa emits the least amount of CO2, but has the greatest vulnerability
Extreme risk for poverty, drought, and heavy dependence on rainfall
Arid and semi-arid regions are most vulnerable
Impacts vary by subregion
Famine widely affects many countries due to this
Food and Water insecurity is quite common
All good maps have
Title
Relative Fraction
North Indicator
Legend
Credit or attribution
Purpose
What are the types of maps
Thematic Maps: Display data in a visually appealing way
Dot map: Each dot has a value, usually depending on the size
Choropleth map: Shows information in a color-organized manner
Reference Maps: Show locations of features
Every map must have a legend to interpret the map
Define small and large scale representative fractions
Small Scale: Large area showing small details
Large Scale: Small area showing large details
What is remote sensing
Aerial photographs taken by airplane, balloon, drones, or satellite
Electromagnetic images from aircraft and satellities
Light wavelengths and resolutions tell what is one the ground
Usually colored by geographer to indicate features
What is GIS
Geography information systems
Computerized data from many sources
Spatial databased used to analyze a wide range of issues
Central to geographic problem solving in many areas
Discuss the causes of desertification in the Sahel
Overplanting and overuse by farmers
Overgrazing by livestock
Overcutting (deforestation for firewood and biofuels)
Overpopulation due to the growing population in Sub-Saharan Africa
What are some possible solutions in the Sahel
Crop Rotation to prevent the overtilling of soil
Terracing to prevent rain from washing soil away
Tree Belts to help soil down wind erosion and to hold the soil in place
What are the types of grassland in Sub-Saharan Africa
Steppe: Semi-Arid Grasslands
Savannah: Tropical Wet/Dry Grasslands
Why are some species endangered in Sub-Saharan Africa
Habitat loss due to human usage and desertification
Illegal hunting of protected animals (poaching for ivory and rhino horns)
What are some possible solutions in protecting endangered species in Sub-Saharan Africa
Ecotourism: making the natural habitat of animals profitable in order to help protect them
Stiff penalties for poaching
How would one describe Latin America
Shared colonial history
Racially diverse
Extensive natural resources for development
Majority of population is low to middle income
600 Million People
In all of the 17 states, more than 50% live in cities
Describe the colonial basis of the Iberian influence in Latin America
Treaty of Tordesillas divided South America between Spain and Portugal in 1494
Describe the economic and social development of Latin America
Development broadly refers to the wealth and well-being of individuals, regions, and states
GNI Per capita: Value of total produced both internal and external to state, per person
GDP: value of total production inside the state
What are the four sectors of the economy
Primary: Raw materials
Secondary; Manufactured items from the primary sector
Tertiary: Services
Quaternary: Knowledge production, research and development
What is primary export dependency
Dependency on the export of raw materials, usually economically specializing in one or two major commodities
What was the economic model of Latin America in the 1930s-1960s
Import Substitution: manufacturing intended for consumption inside the state for consumption by citizens
this attempts to avoid imports
What is neoliberalism and its relation to Latin America
If the state stays out of the regulation of trade and corporations, markets will grow and the growth will trickle down
Maquiladoras
Remittances
Ecotourism and foreign direct spending
What is the informal sector and its importance in Latin America
Economic activities of the urban periphery
Widespread informal sector employment signals the poverty of a region, not the wealth
What are the stages of Rostow stages of economic growth
Stages of economic development that follows the British historical example, from traditional to modern society in a stepwise. Every step up in the ladder is a step in economic and social development
What does Taylor state in 1992?
State are in a relationship
What is world economic system
There is one system, one world economy, and different states experience different processes in that system
Incorporating the periphery
Periphery is not a location, it is a space where peripheral processes dominate
What are common traits of the core
High Wages
Advanced technology
Diversified production mix
Globalized labor force
What are common traits of the periphery
Low wages
Rudimentary technology
Simple production mix
Localized labor force
What is the basis of “space is not a container”
Core and periphery processes structure space (make space)
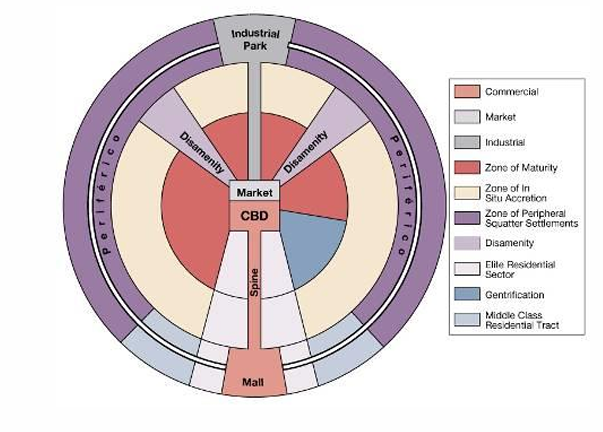
Describe the Latin American city
No country is less than 50% urban
Rural-to-urban migration
Historical patterns
Contemporary alterations
Describe Urban vocabulary
Urban primacy: the condition of state having a city 3-4 times larger than any other city in the state
Primate City: the city that is the largest in the state
Megacities: Cities that have a population of 10 million or more
Megalopolis: a continuous belt of urban development
Discuss squatter settlements
Makeshift housing on land legally owned or rented by urban migrants, usually in unoccupied spaces in or near a rapidly growing city
Describe the urban morphology in Latin America
Based on European cities