Endocrine 2 - Posterior Pituitary
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
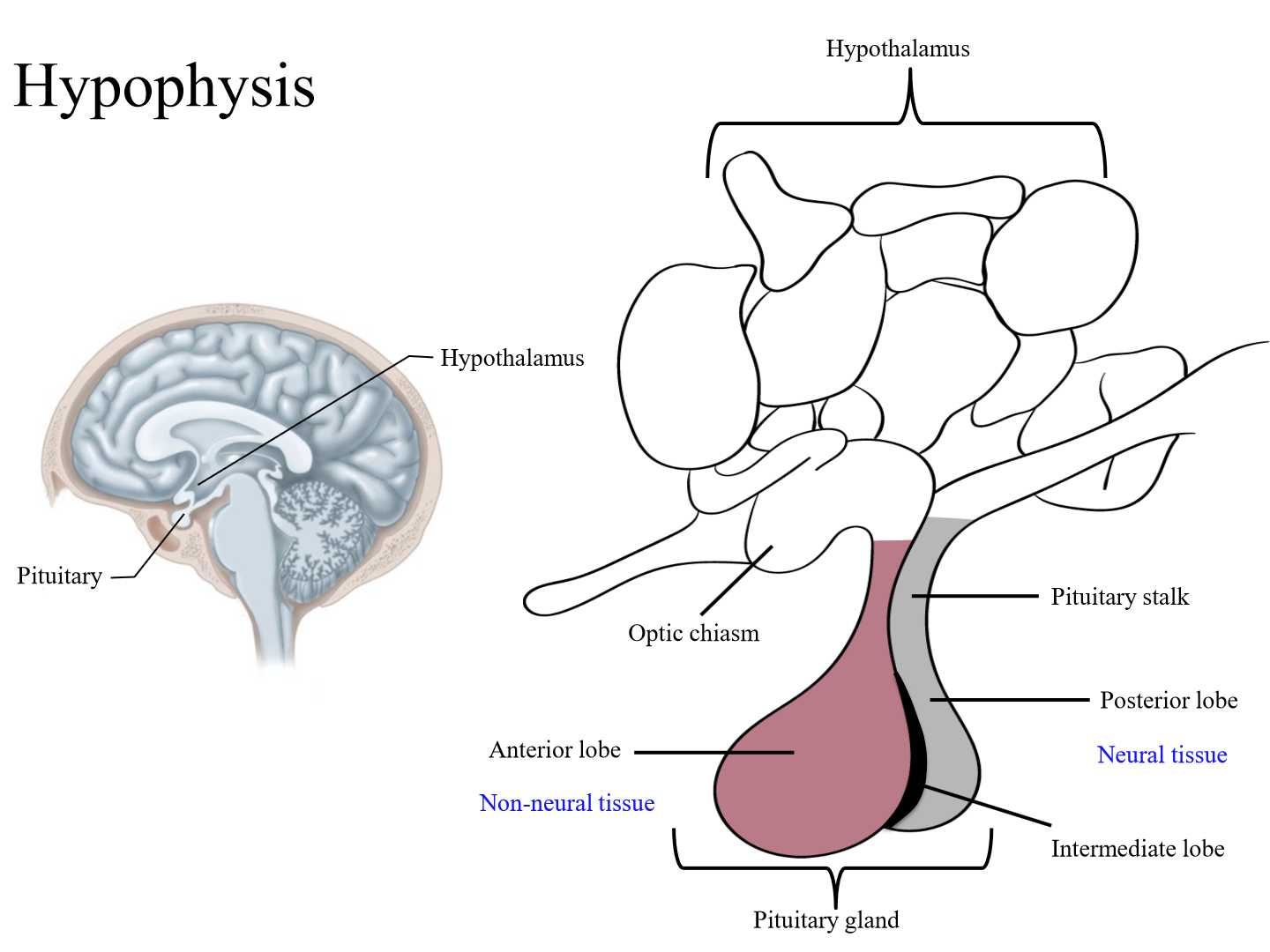
Location of pituitary gland
Ventral part of brain (base), nearby the hypothalamus
What is the hypothalamus made of
Cluster of neurons - distinct nuclei
2 components of the pituitary gland
Adenohypophysis (anterior) - non neural tissue
Neurohypophysis (posterior) - neural tissue
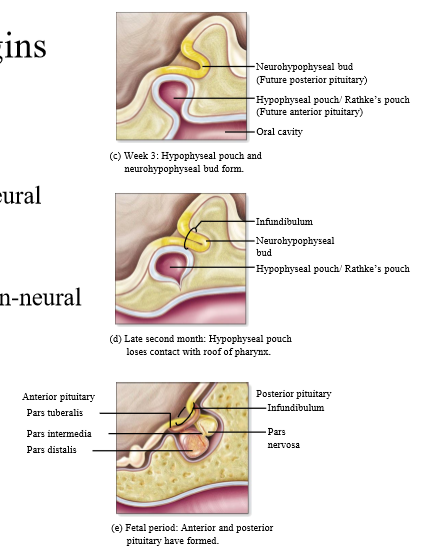
What does the posterior pituitary develop from
Downgrowth of tissue from brain (neural extension)
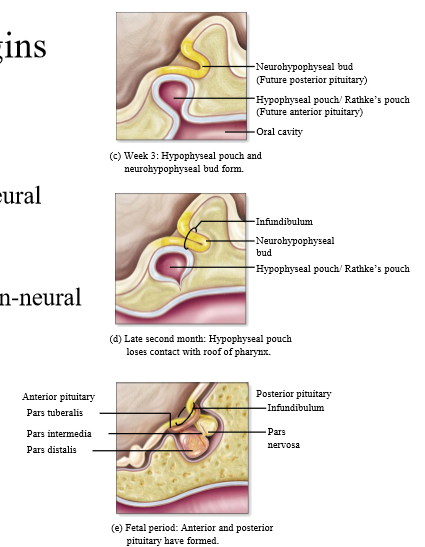
What does the anterior pituitary develop from
Rathke's pouch
Are hormones produced in the posterior pituitary?
NO! they are secreted here but produced in the hypothalamus
Where in the hypothalamus are hormones produced
Supraoptic + Paraventricular nuclei
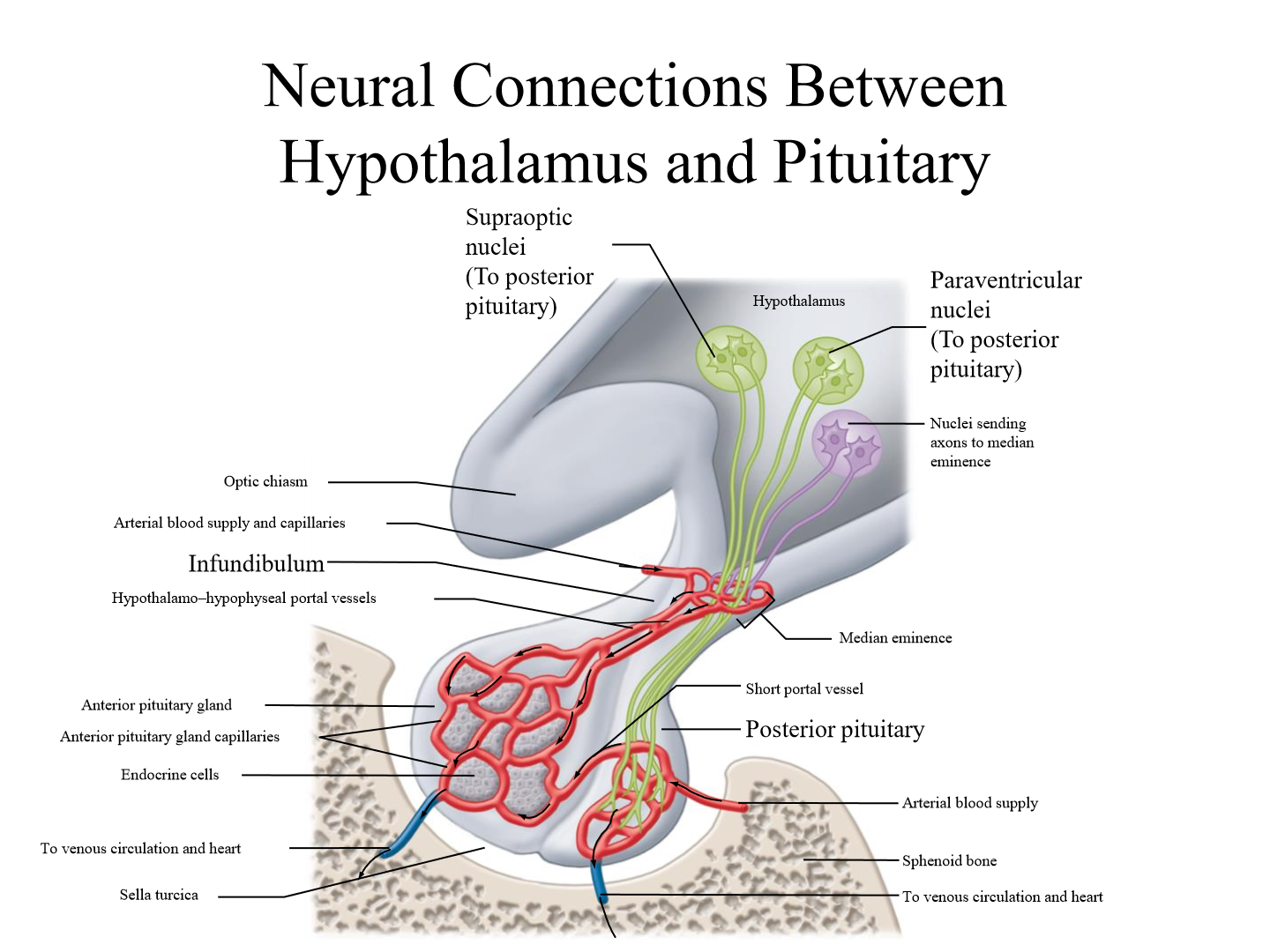
Infundibulum
A stalk that attaches the pituitary gland to the hypothalamus.
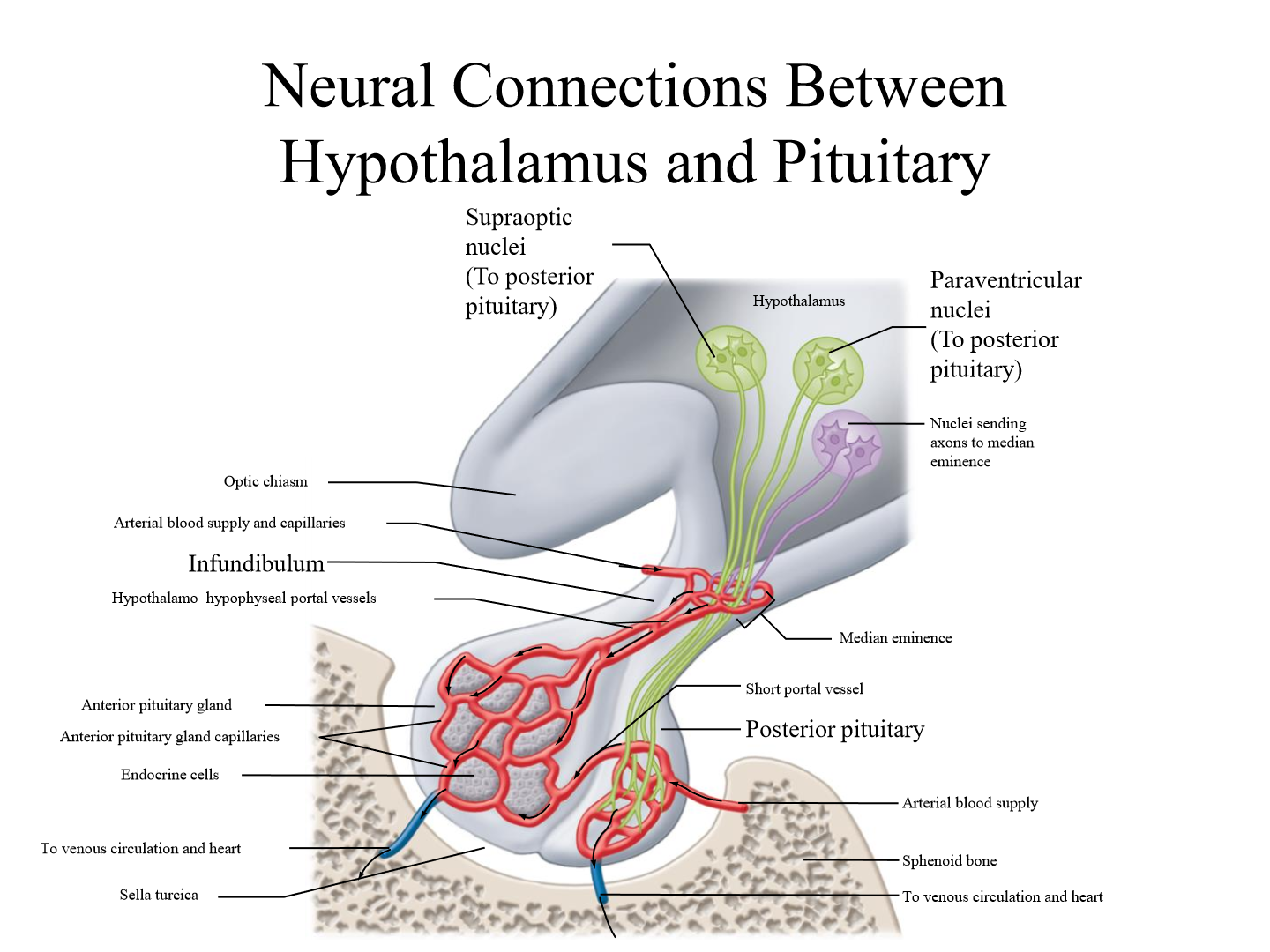
What hormones are secreted by the posterior pituitary?
ADH/Vasopressin and Oxytocin
Where is ADH produced
Supraoptic nuclei (SON) in hypothalamus
Where is Oxytocin produced
Paraventricular nuclei (PVN) of hypothalamus
What type of hormones are the hypothalamus hormones
Protein hormones
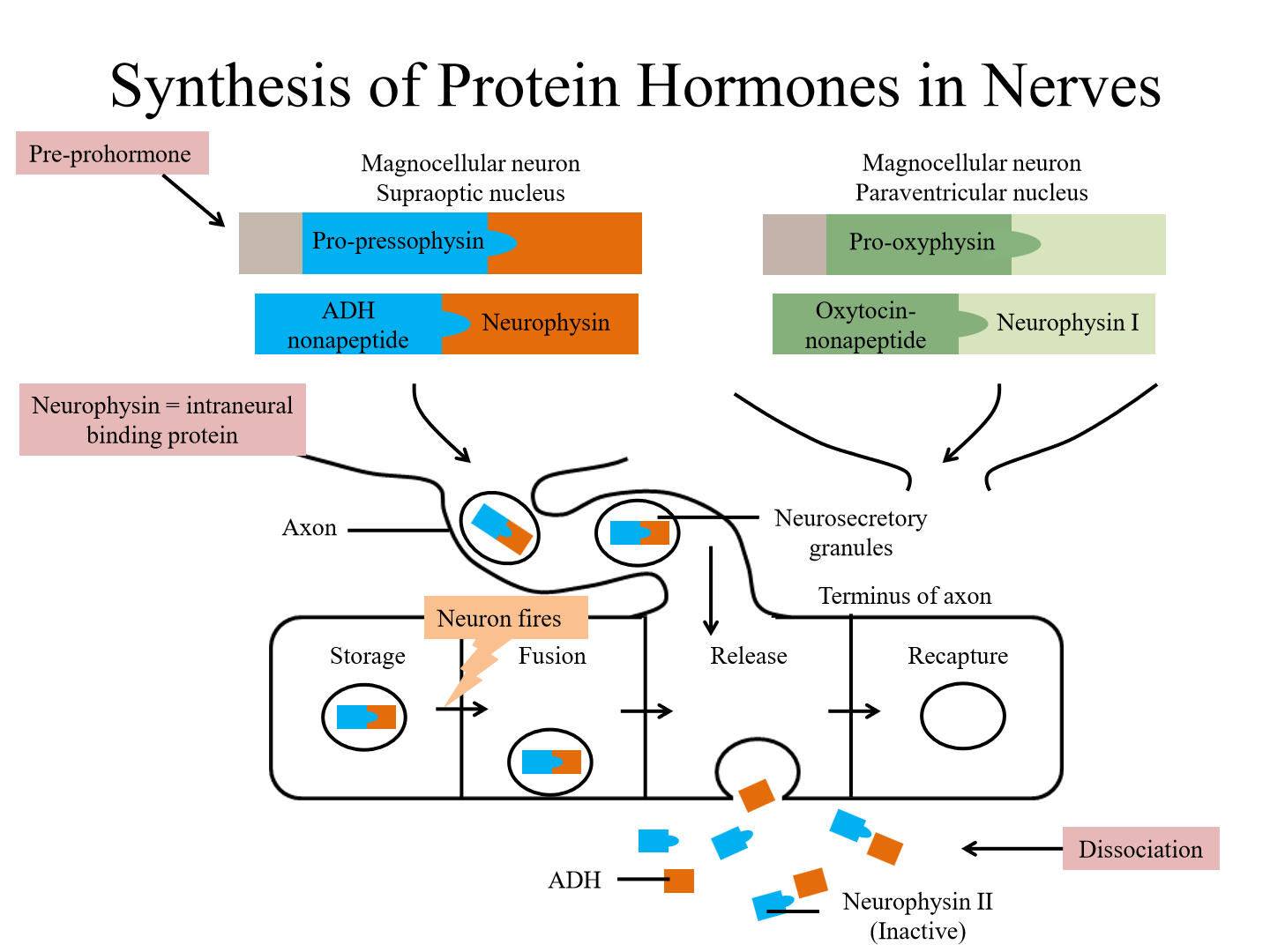
How are protein hormones synthesized
by translation on membrane bound ribosomes - synthesizes the pre-pro-hormones
Synthesis of ADH (steps)
1. RNA translation produced the pre-prohormone, consisting of pro-pressophyrin
2. ADH is bound to neurophysin (intraneural binding protein). This is transported down to neuron axons and vesicles
3. When released, ADH splits from neeurophysin and moves into blood
What two actions does ADH have
Vasoconstriction action and Anti-diuretic actions
Vasoconstrictive action of ADH
- Contracts blood vessel smooth muscle
- Increases blood pressire
- High levels of ADH prevent hemorrhage (constricts muscle)
Antidiuretic action of ADH
- Increases permeability of renal collecting duct by increasing number of water channels
- Vasoconstriction reduces GFR
- Contraction reduces the size of glomerulosa cells, reducing SA for filtration
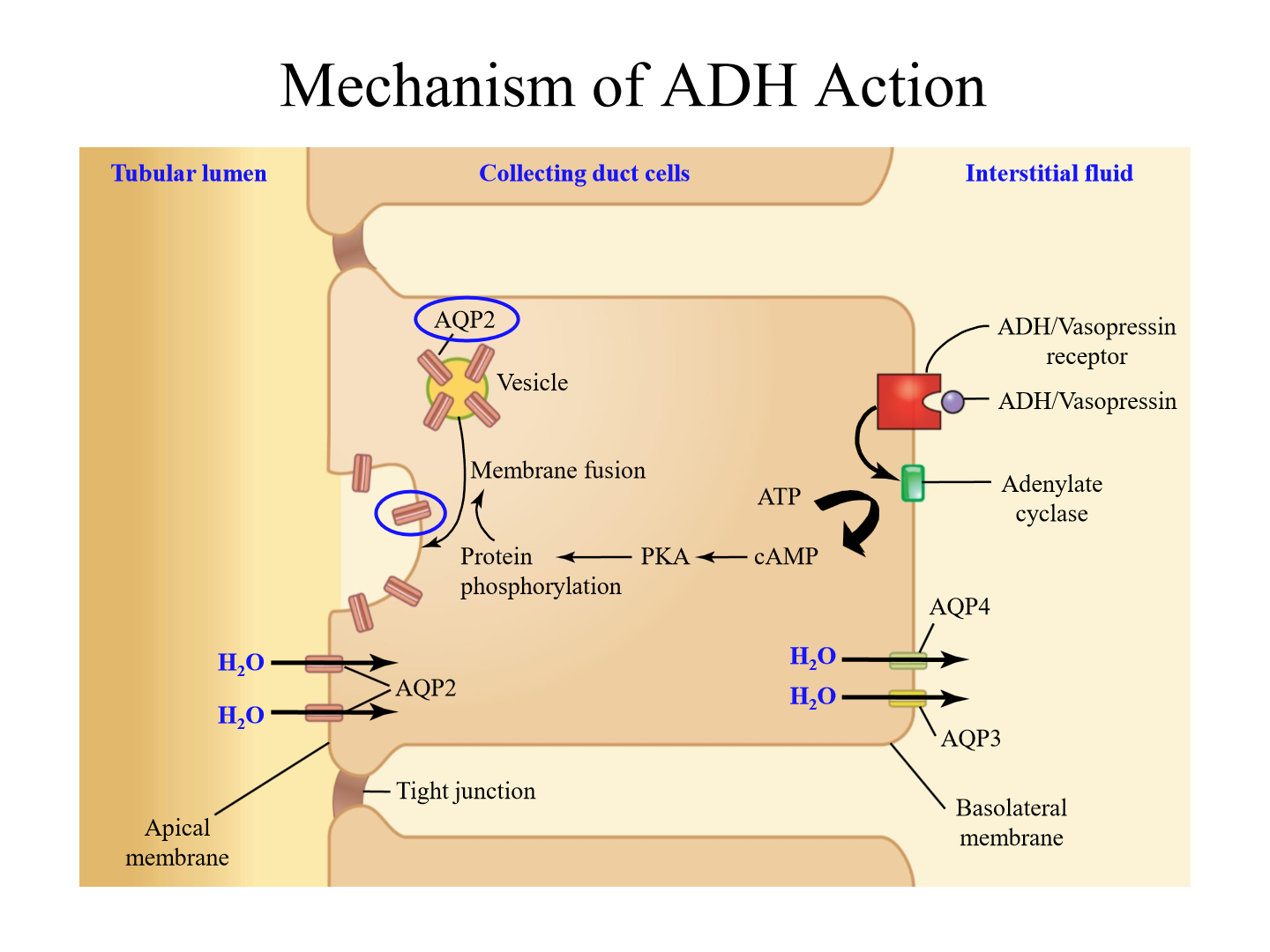
Mechanism of ADH action
1. ADH travels from posterior pituitary to kidneys and binds to receptor
2. ADH binding induces cAMP production
3. cAMP activates PKA, which upregulates Aquaporin II duct in collecting tubule
4. More water is reabsorbed
What are the 2 main factors that affect secretion of ADH and Vasopressin
1. Plasma volume
2. Plasma osmolality
What osmoreceptors are used to regulated ADH secretion
Hypothalamus cells; supraoptic nucleus and paraventricular nucleus
How do baroreceptors impact ADH scretion
Baroreceptors sense changes in BP based on degree of wall stretching. BP is proportional to osmolality (blood volume)
Location of the baroreceptors and where they connect to
Aortic arch and carotid sinus - stimulus goes to hypothalamus
Regulation of ADH secretion via baroreceptors
1. Decreased blood volume is sensed by baroreceptors
2. Baroreceptors decrease activity in inhibitory afferents to hypothalamus
3. Increased hypothalamus release and PP release of ADH.
4. ADH acts on collecting duct to reabsorb more water to increase BP
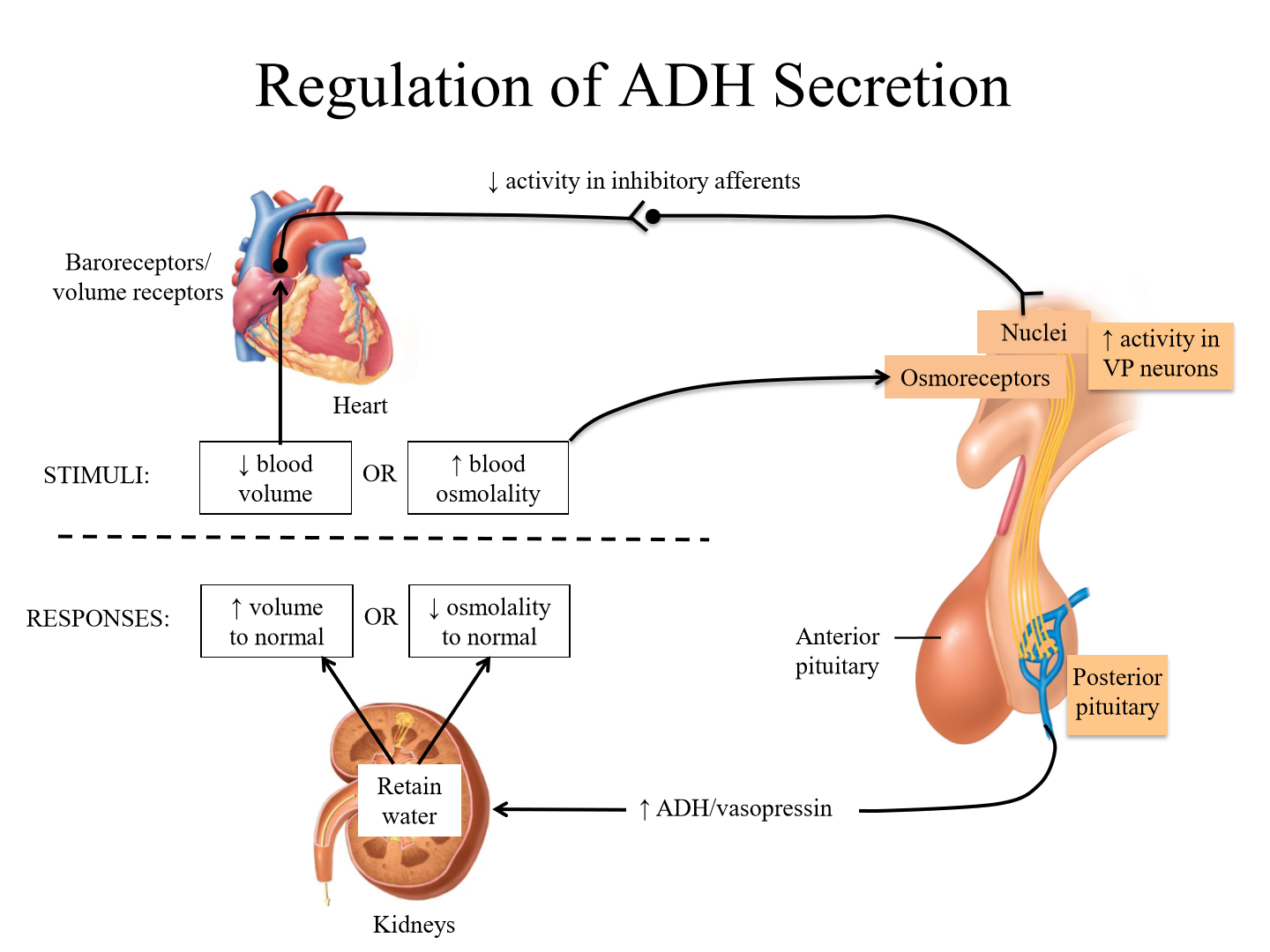
Regulation of ADH secretion due to increased blood osmolality
1. Osmoreceptors of hypothalamus (SON, PVN) sense increased blood osmolality
2. Posterior pituitary releases more ADH
3. Kidneys retain more water, returning osmolality to normal
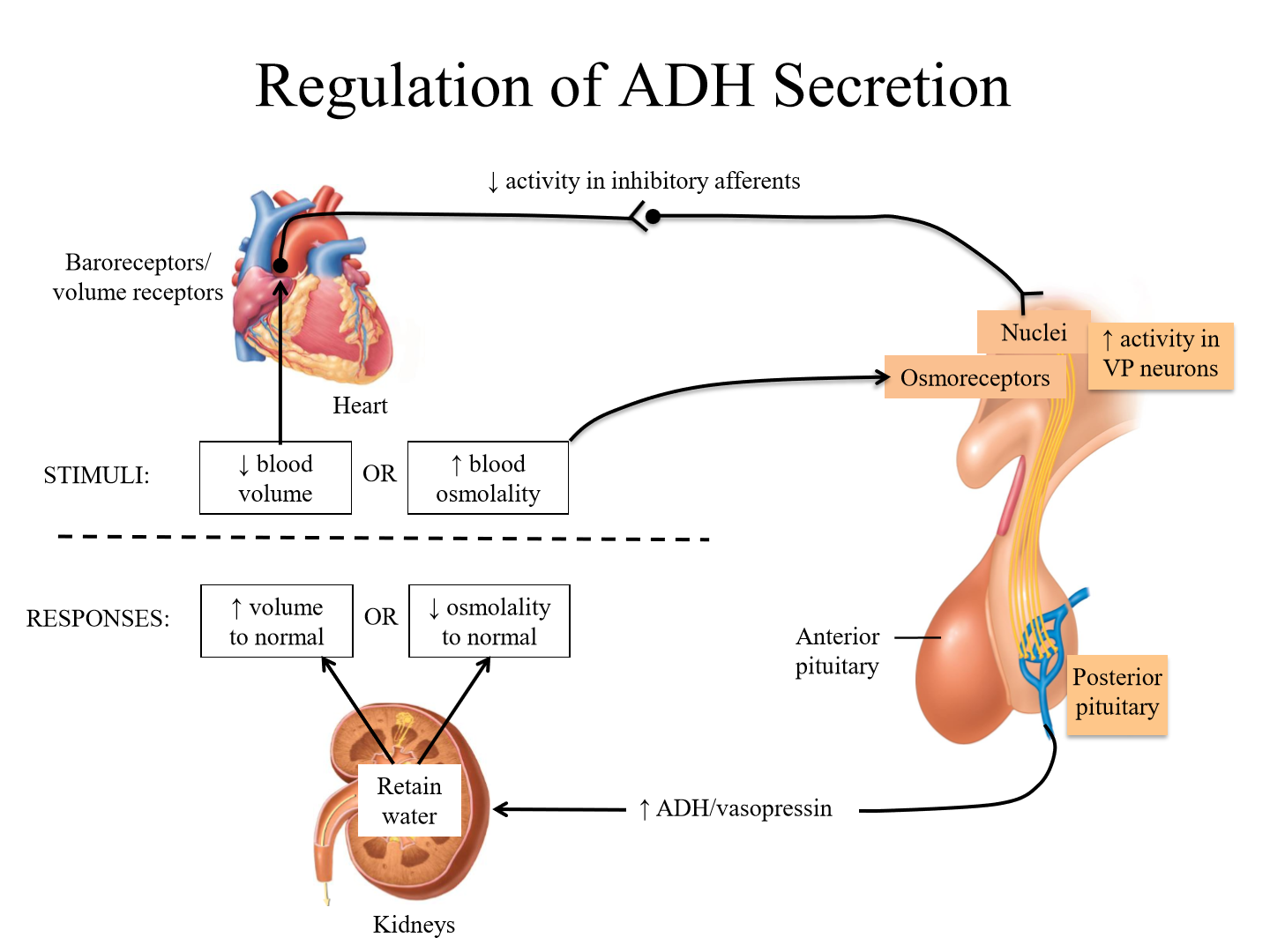
Effect of dehydration on ADH secretion
1. Dehydration cause decreased extracellular fluid volume and increased osmolality
2. Baroreceptors sense decreased blood volume, osmoreceptors sense increased osmolality
3. ADH released from posterior pituitary
4. Plasma ADH increases to increase collecting duct water permeability, more water is reabsorbed and less secreted
5. Osmoreceptors also signal thirst, causing increased water intake
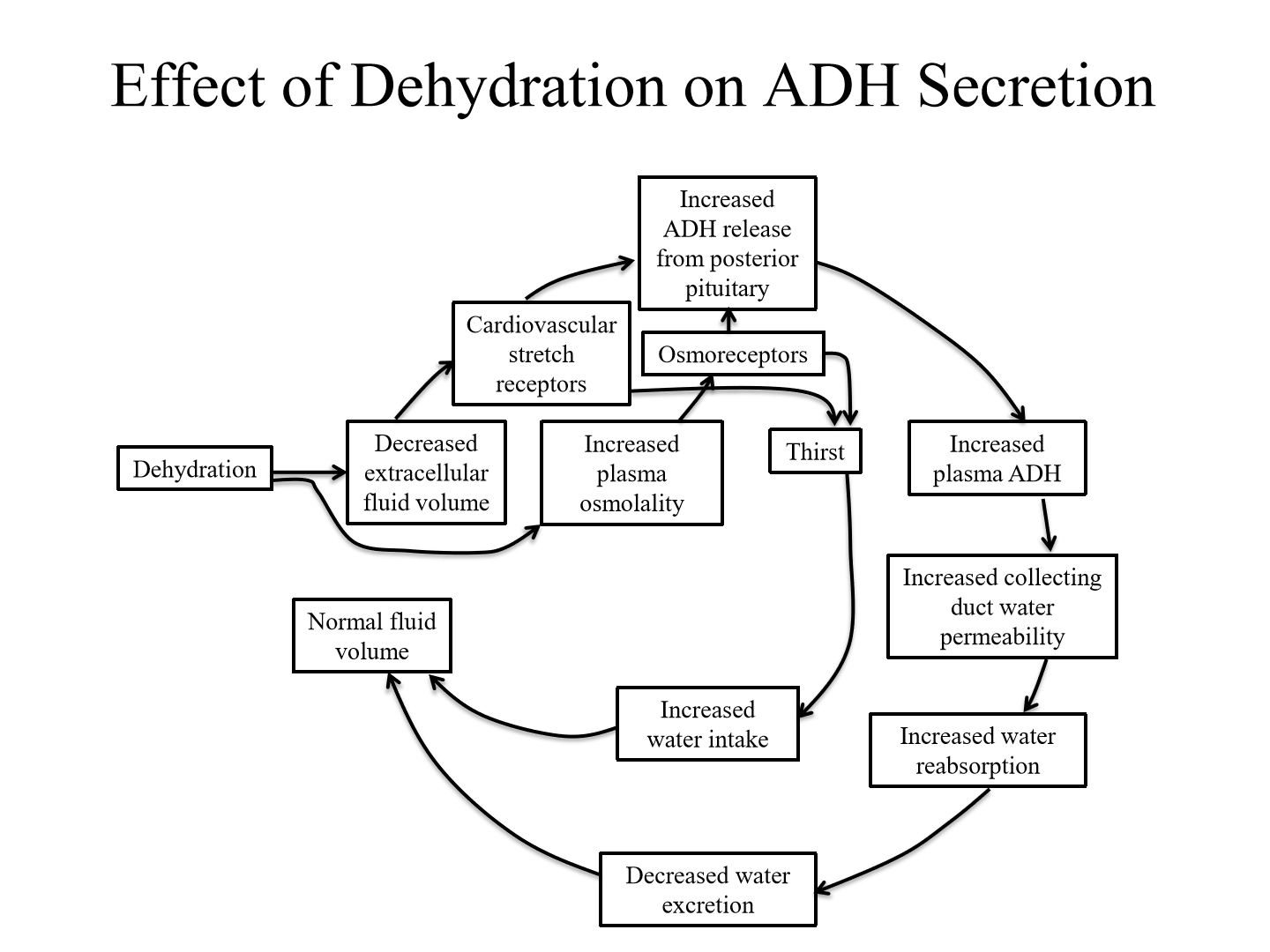
Effect of high amount of ingested water on ADH secretion
1. Increased water causes increased extracellular fluid volume and decreased osmolality
2. Baroreceptors sense increased BP, and inhibtory afferents act on the hypothalmus to release less ADH. Osmoreceptors also sense osmolality and lead to less ADH secretion
3. Less ADH = decreased collecting duct water permeability = increased water secretion
4. Fluid volume returned to normal
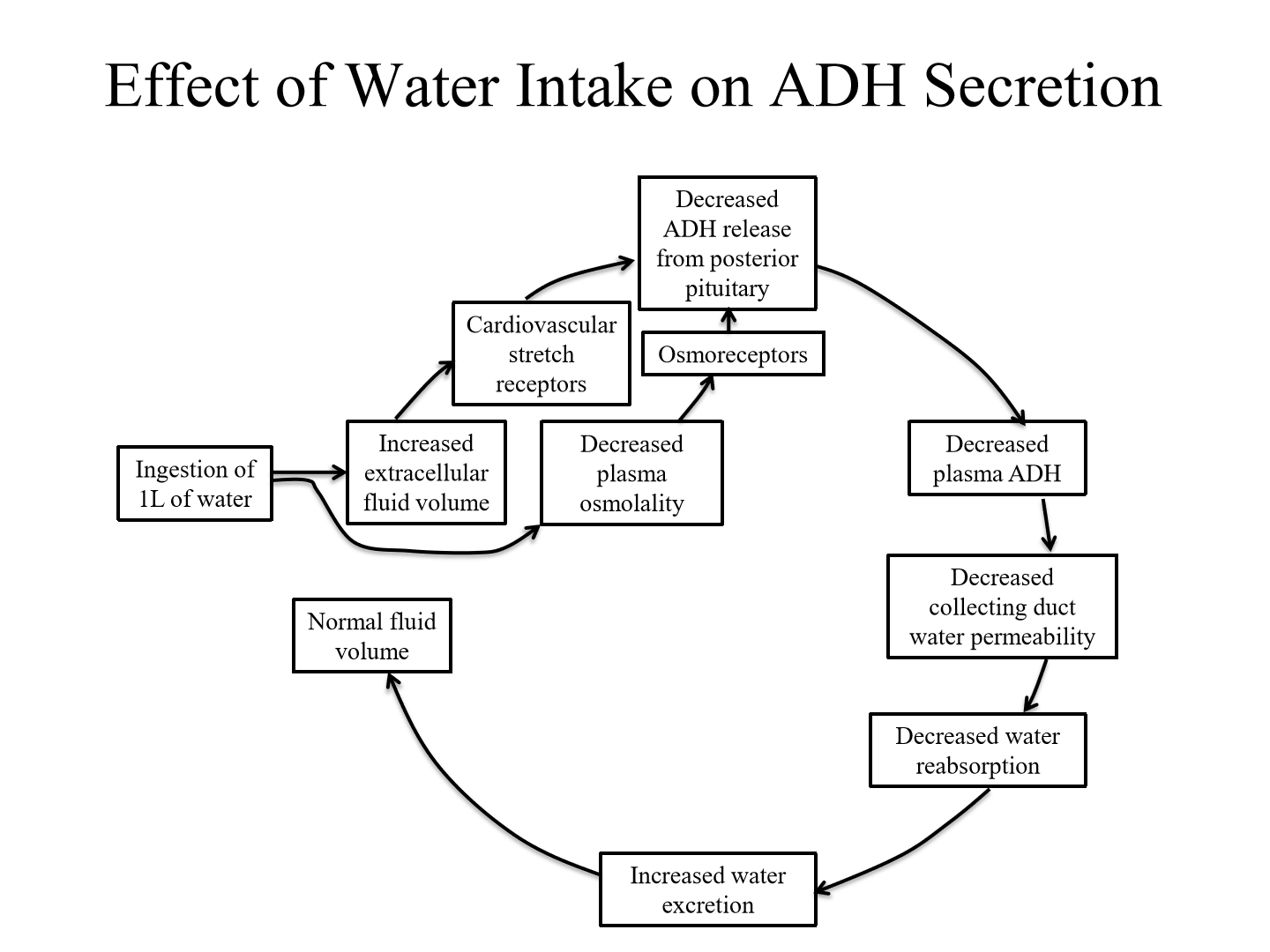
Relationship between plasma osmolality and plasma ADH
Linear releationship. As osmolality increases, ADH increases
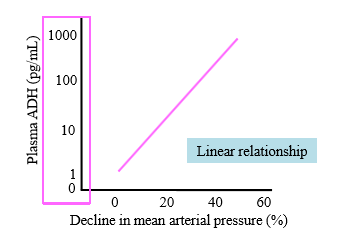
Relationship between decline in MAP and plasma ADH
Log scale, but linear relationship. When MAP declines, ADH is secreted. Causes vasoconstriction from ADH to increase BP
Non water factors of increased ADH secretion
- Stress/emotion
- Heat (save water as we lose it through sweat)
- Nicotine
- Caffeine (at kidney - blocks ADH action, but increases secretion at hypothalamus)
Non water factors of decreased ADH secretion
- Cold
- Alcohol
Main pathogenic issue of ADH deficienct
Diabetes insipidus
Hypothalamus/central diabetes insipidus
No ADH production/release
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
No ADH action (problem with receptors or intracellular signaling)
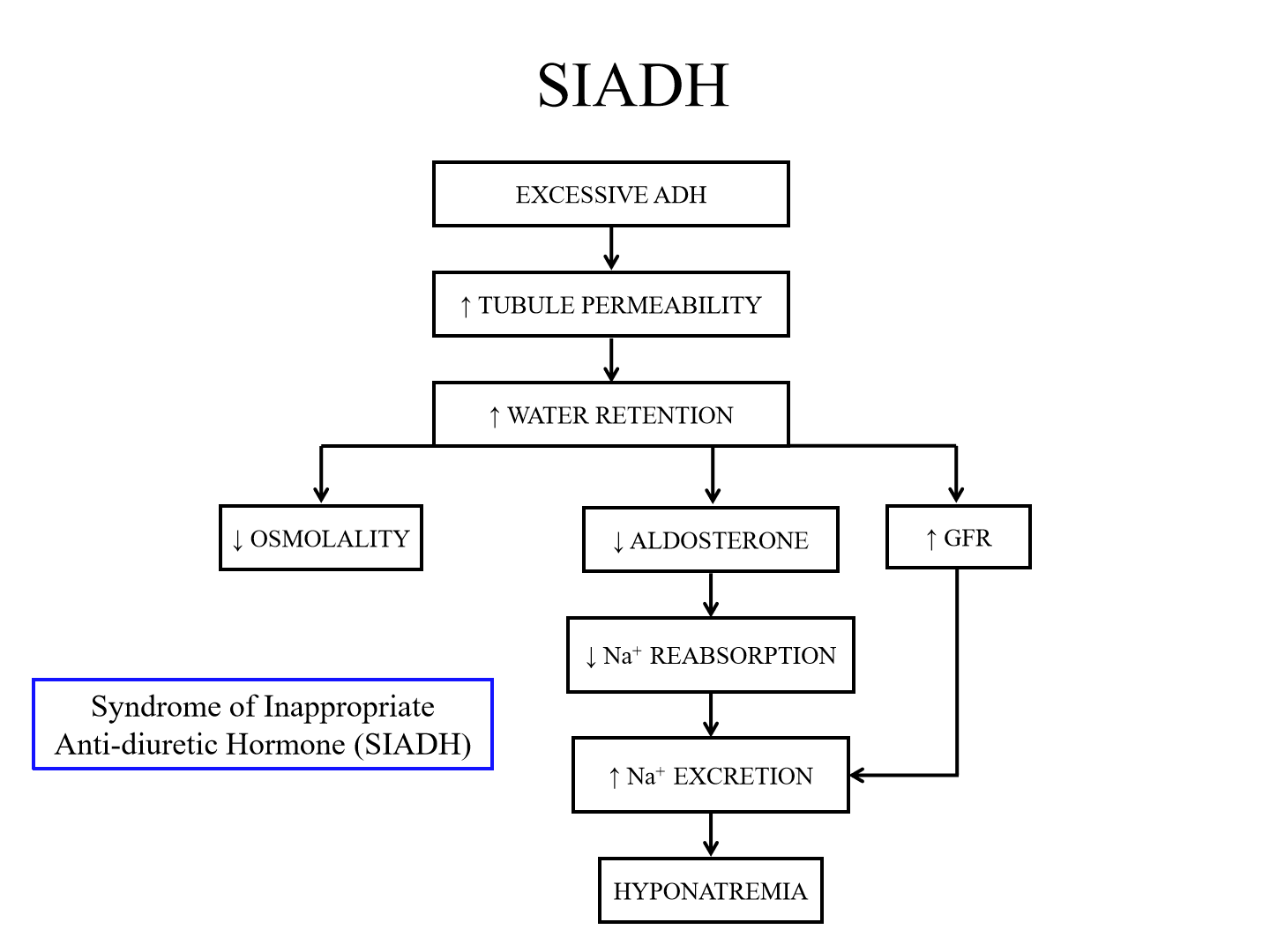
Main pathogenic issue of ADH excess
Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH (SIADH)
Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH (SIADH)
Problem of ADH production or feedback failure
Symptoms of diabetes insipidus
Polyuria - production of large amounts of dilute urine
Polydipsia - excessive thirst and fluid intake
Unable to decrease urine flow even when water deprived
How to treat Central diabetes insipidus
Desmopressin - synthetic ADH
How to treat nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
Other antidiuretics that aren't ADH
Mechanism of SIADH
Excessive ADH causes excessive water retention. This increases GFR and decreases aldosterone
- Decreased aldosterone prevents na+ reabsorption, causing hyponatremia
- Decreased osmolality as well
Oxytocin actions on the uterine myometrium
- Parturition (not a requrement but it helps)
- Clamps rupture blood vessels from hemorrhage
- Restores uterine size after child birth
- Stimulates sperm movement
- Stimulates cervix movement ("sucks up sperm")
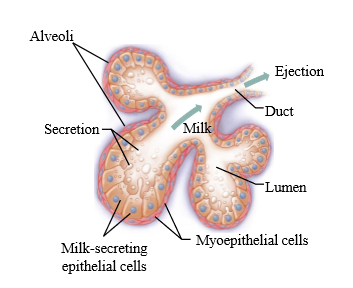
Oxytocin actions on mammary myometrium
Milk let down
What kind of feedback does oxytocin have
Positive
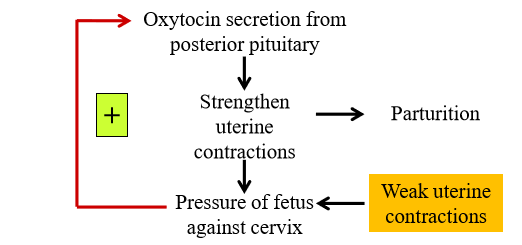
Oxytocin feedback loop of parturition
1. Uterine contractions push fetus toward cervix
2. Fetus on cervix sends message to release oxytocin
3. Acts on uterine myometrial layer to cause more contractions
4. Repeats until fetus comes out of cervix
Oxytocin positive feedback loop of milk-let down
1. Suckling of nipple increases oxytocin release
2. myoepithelial cells to contract on milk secreting epithelial cells
3. Milk released into lumen and can be ejected from nipple
Conditioned response of milk let down
Visual and auditory stimuli related to infant can stimulate milk let down
Non-maternal functions of oxytocin
1. Released during sexual intercourse and stimulates orgasm
2. Increased in social bonding
Oxytocin function on male reproductive function
Action unknown, possible aid in sperm release and erection
How is oxytocin secretion increased
Tactile stimulation of genital tract (parturition, orgasm), or nipples (milk let down)
How is oxytocin secretion decreased
Psychogenic/physical: Stress can cause difficulty with lactating
Impacts of oxytocin deficiency
- Impaired child delivery (but not required)
- Impaired lactation (not a problem if access to baby formula)
Impacts of oxytocin excess
No issues seen