BIO 269 Exam 2 -Casotti WCU
Pulmonary Circuit
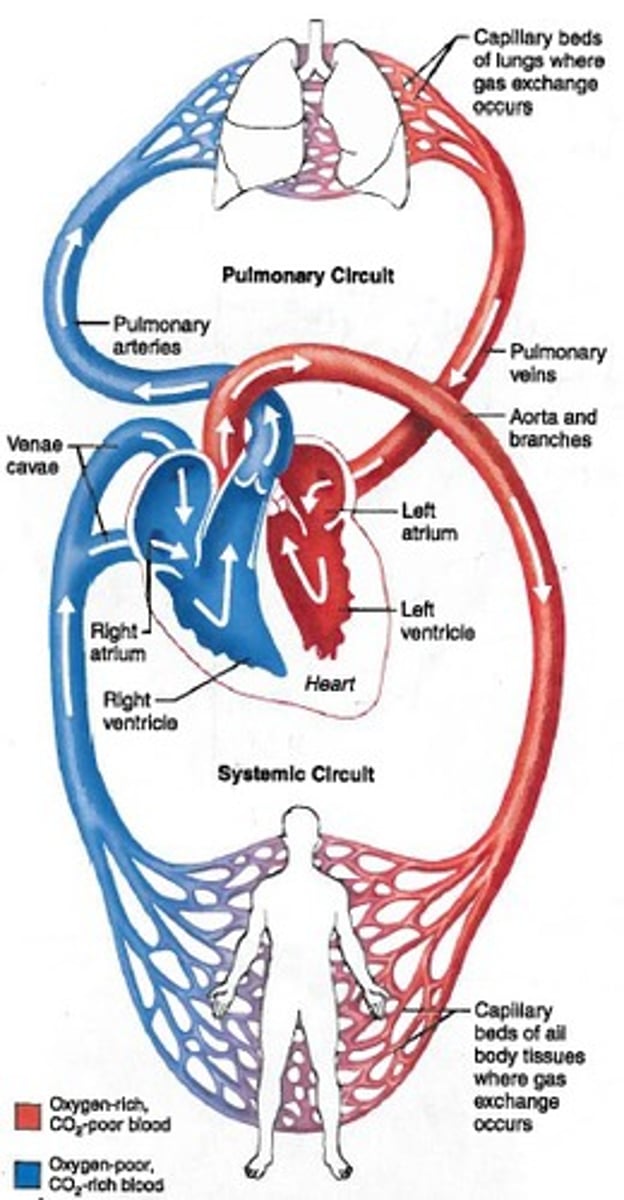
Carries blood from heart to the lungs for gas exchange and returns oxygenated blood to the heart
Systemic Circuit
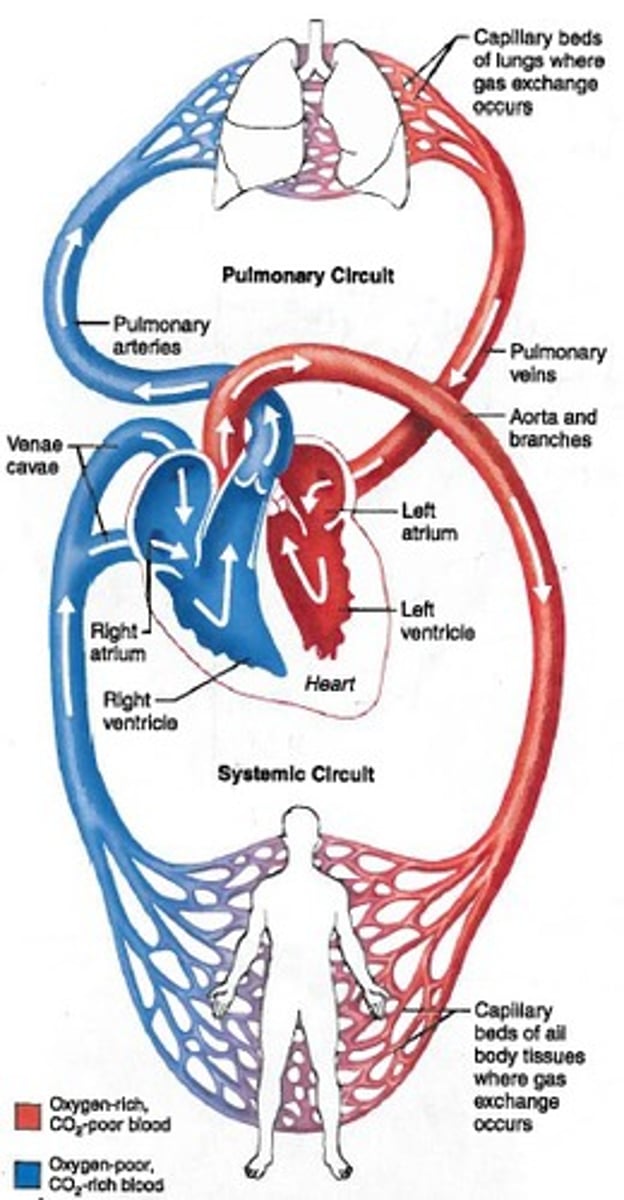
Carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body and returns deoxygenated blood to heart
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
147 Terms
Pulmonary Circuit
Carries blood from heart to the lungs for gas exchange and returns oxygenated blood to the heart

Systemic Circuit
Carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body and returns deoxygenated blood to heart

Artery
Carries oxygenated blood away from the heart
*Exception* Pulmonary Artery (carries deoxygenated blood to lungs)
Vein
Carries deoxygenated blood towards the heart
*Exception* Pulmonary Vein (carries oxygenated blood to the heart)
Overall path of blood flow
left ventricle → aortic arch → smaller arteries → arterioles → capillaries → venioles → veins → vena cavae → right atrium → right ventricle → pulmonary arteries → lungs → pulmonary veins → left atrium
Tissue that makes up the heart
Muscle tissue (cardiac muscle)
Why is the heart called a double pump?
contracts right and left atria/ventricles simultaneously to deliver blood to both the pulmonary and systemic circuits
What is the "fibrous skeleton" of the heart?
Cardiac muscle bundles
What is the function of the fibrous skeleton?
-wrap around atrium and ventricles
-when contract they squeeze the chambers
-stronger than skeletal muscle
Function of the pericardial sac and fluid?
-sac: to hold the fluid directly surrounding the heart
-fluid: to reduce friction between the heart and the lungs
2 Atrioventricular Valves
tricuspid (right) and bicuspid or mitral (left)
2 Semilunar valves
pulmonary (right) and aortic (left)
Three layers of the heart wall (outer to inner)
-epicardium
-myocardium
-endocardium
What layer of the heart wall directly surrounds the atria?
Endocardium
Coronary Circuit
-the circulation of blood and nutrients directly to the heart muscle (attached to the heart)
-vessels go into myocardium
What circuit is the shortest?
Coronary
What circuit is the longest?
Systemic
Flow of blood in the coronary circuit
base of aorta → surround heart → deoxygenated blood empty to right atria
2 Types of Coronary Disease
-Angina pectoralis -temporary halt of blood flow, plague build up, painful
-Myocardial Infarction (heart attack) -severe blockage, heart cells die, non-contractile scar tissue is formed
Conduction Pathway
SA node→ interatrial pathway + internodal pathway →AV node→ bundle of His → bundle branches → purkinje fibers
Myogenic pacemaker
muscle cells modified to conduct electrical information
Excitation Sequence Steps
1. SA node spreads depolarization along interatrial and internodal pathway
2. Atria Contract
3. Delpolarization along bundle of His then bundle branches, then purkinje fibers
4. Ventricles contract
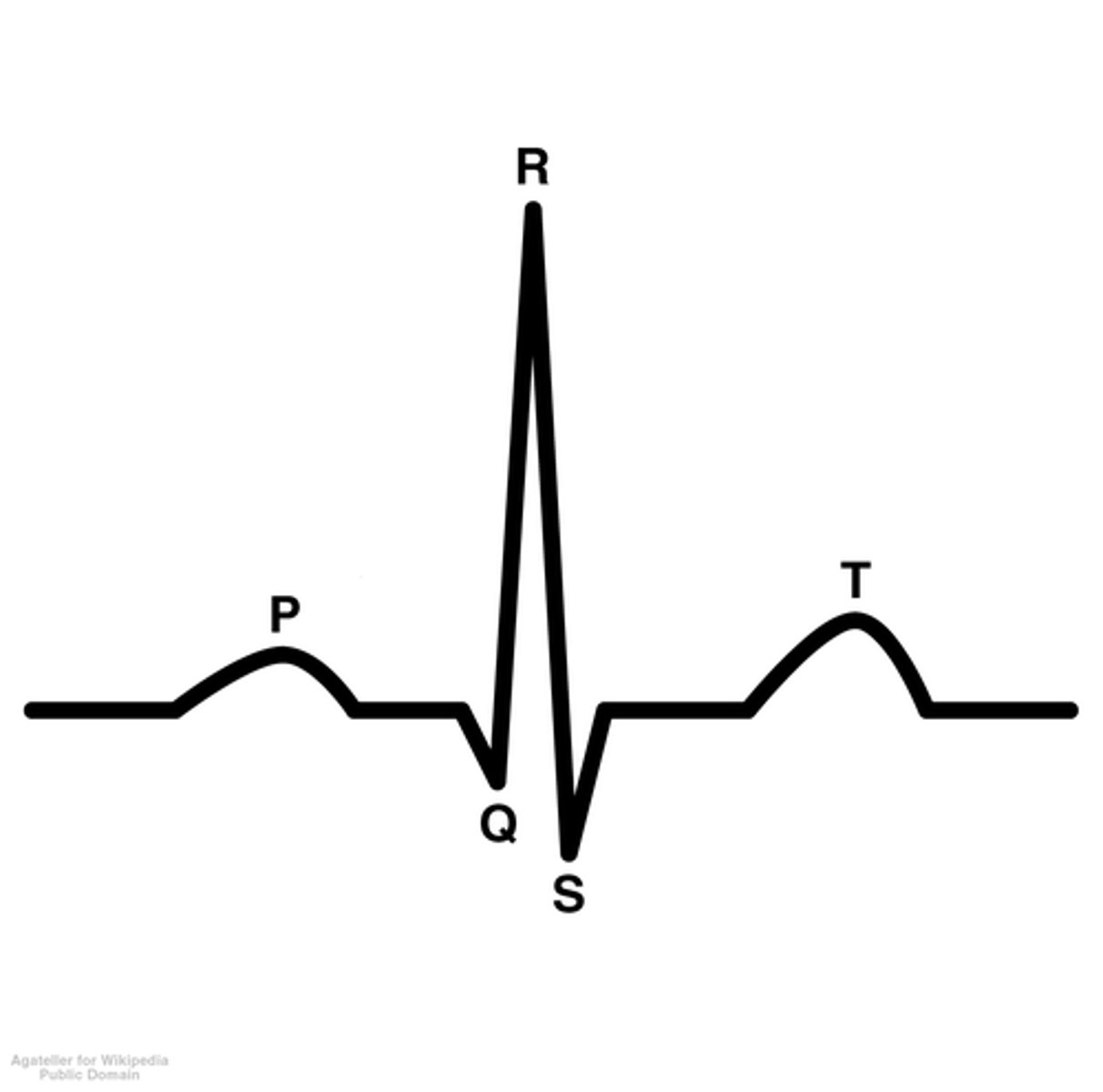
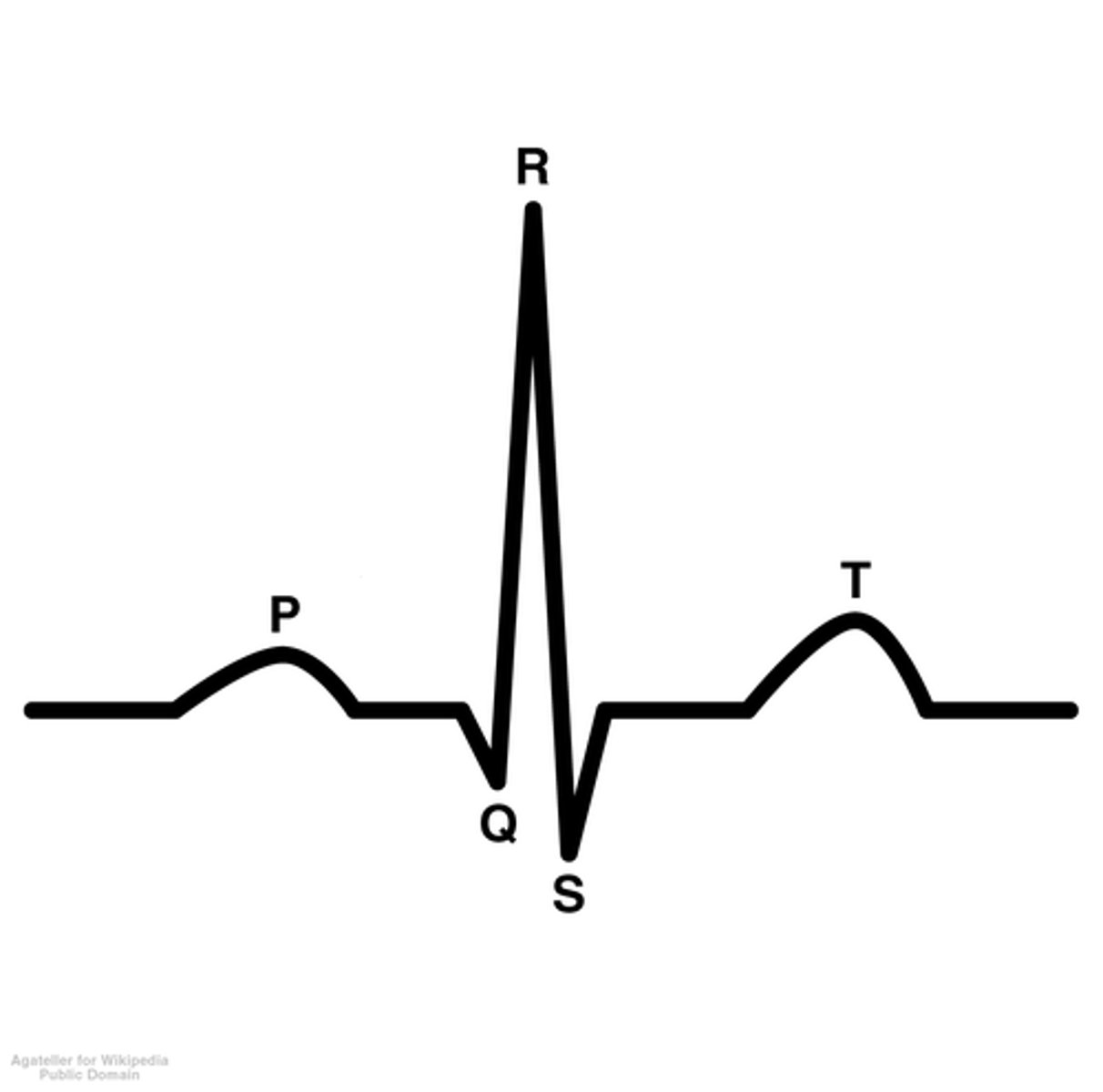
ECG Graph Point P
atria contracts
ECG Graph Point R
ventricle contraction
Gap junctions
-spaces that provide channels from one cell to another
-allow for spread of depolarization among the cells
What causes heart fluctuations?
Autonomic nervous system
What nerve increases heart rate?
What hormone? What ions?
-Sympathetic Cardiac Nerve
-Norepinephrine
-Na+ and Ca2+ influx
What nerve decreases heart rate?
What hormone? What ions?
-Vagus Nerve (innervates SA + AV node)
-ACh
-K + efflux
Steps of Electric Potentials in the Conduction Pathway
1. Pacemaker potential: slow depolarization bc open Na+ and closed K+
2. Action potential begins when threshold reached due to Ca2+ influx
3. Repolarization due to Ca2+ channels closed, K + channels open, brings membrane potential back to most negative
Restablish gradient of Na+, K+, and Ca2+ in Conduction pathway
-Na+/K+ pump
-Ca2+ pumped against gradient
Timing of Conduction
-interatrial pathway to atrial contraction: about 20-30 milliseconds
-AV node fires at about 110 milliseconds
-atrioventricular node fires to ventricle contraction: 150 milliseconds
Is depolarization longer in the atria or purkinje fibers?
Purkinje fibers
Depolarization of Purkinje fibers steps
1. Fast Na+ influx causes depolarization
2. Plateau (maintained depolarization) bc Ca2+ inflow while only some K+ channels open (majority closed)
3. Repolarization due Ca2+ channels close and K+ outflow, back to normal charge
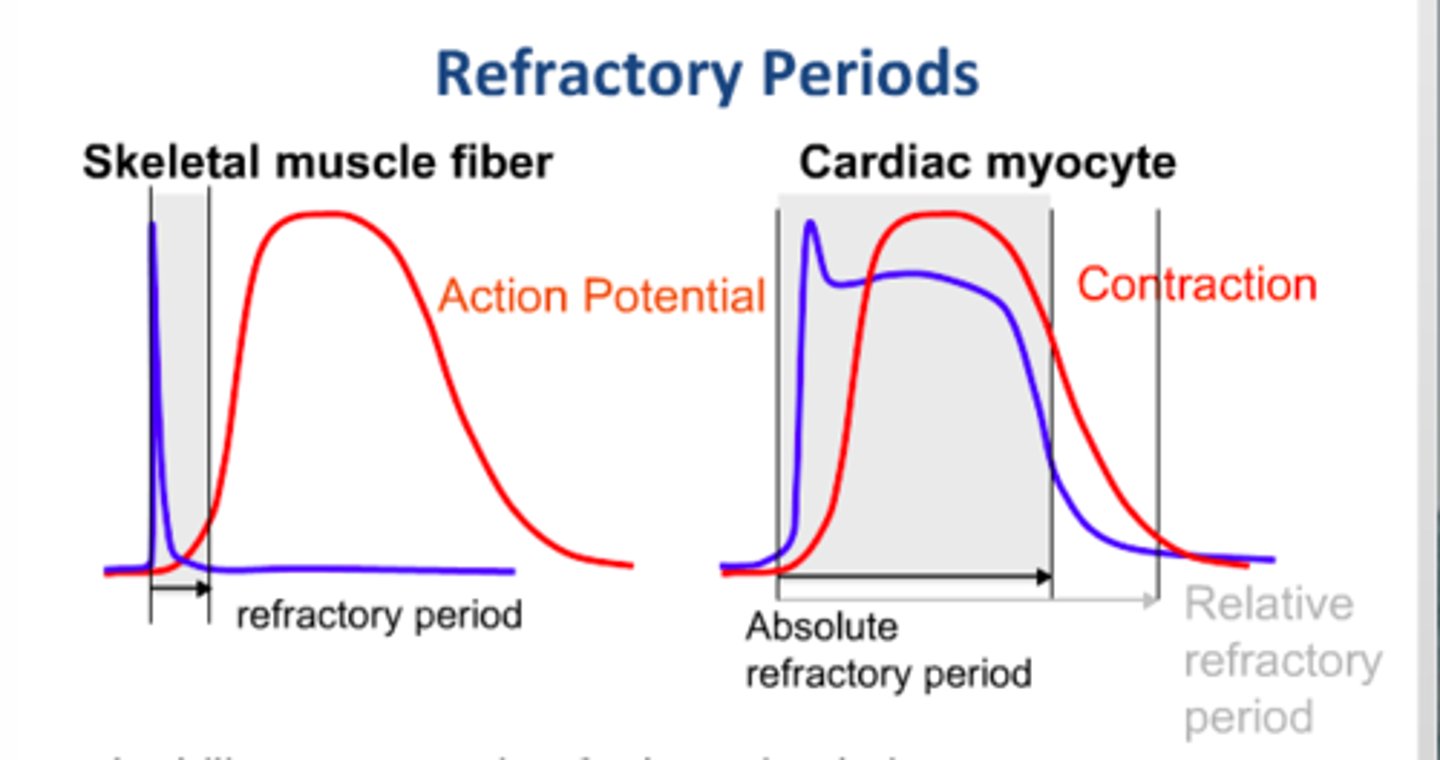
Refractory period
the time following an action potential during which a new action potential cannot be initiated
*measure of time*
Skeletal muscle refractory
-short refractory period
-can have tetanus (many action potentials causing prolonged muscle contraction)
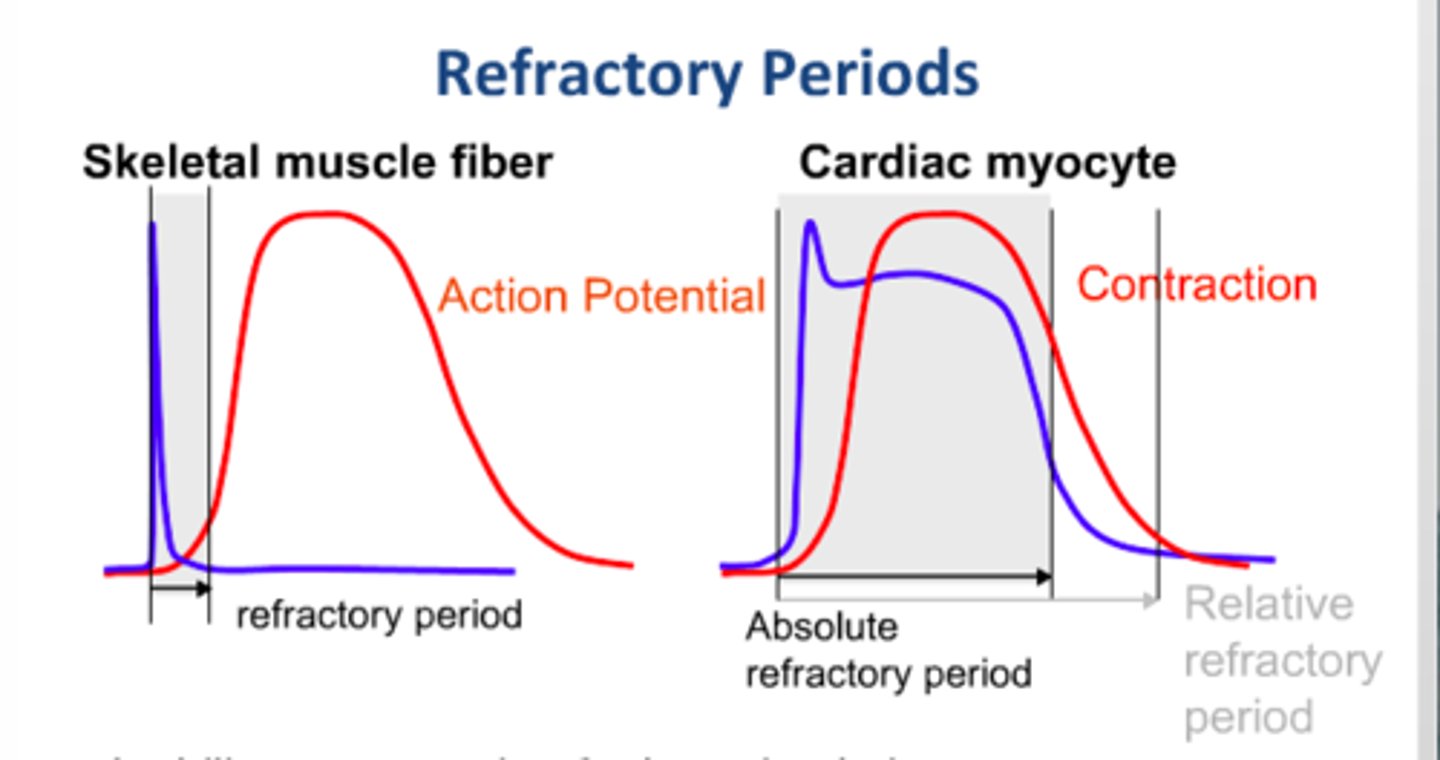
Cardiac muscle refractory
-long refractory period
-this allows ventricles to have time to contract before atria need to contract
-allows for regular heartbeat
-about 150 milliseconds (10x longer than skeletal muscle)
ECG
-electrocardiogram
-shows the atria depolarization and ventricular de/re-polarization
P-wave of ECG
-atrial depolarization
-both the UP AND DOWN represent depolarization
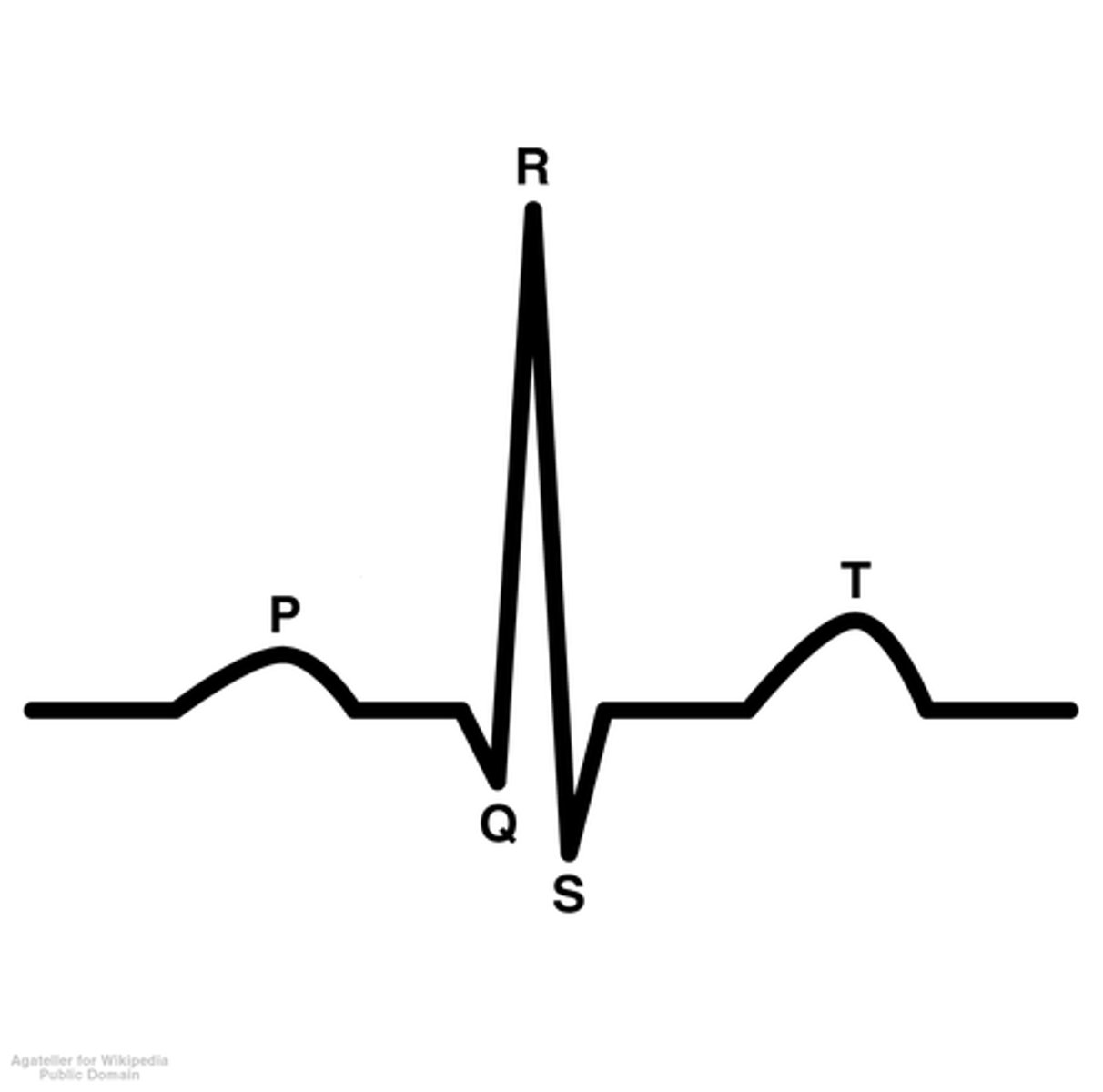
QRS Complex
-big spike
-represents depolarization of ventricles
-also where the atria repolarization would occur if shown
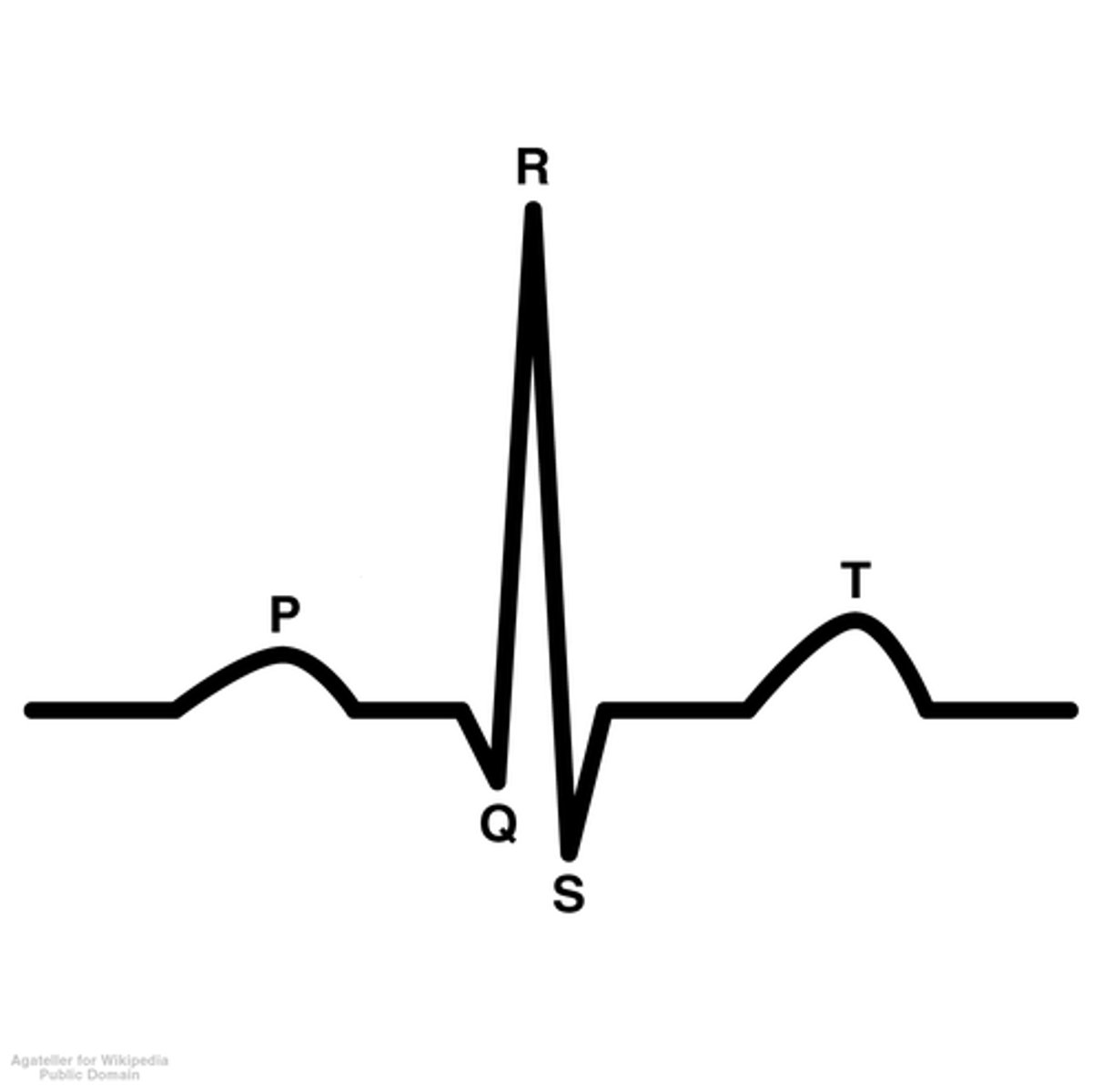
T-Wave of ECG
-repolarization of ventricles
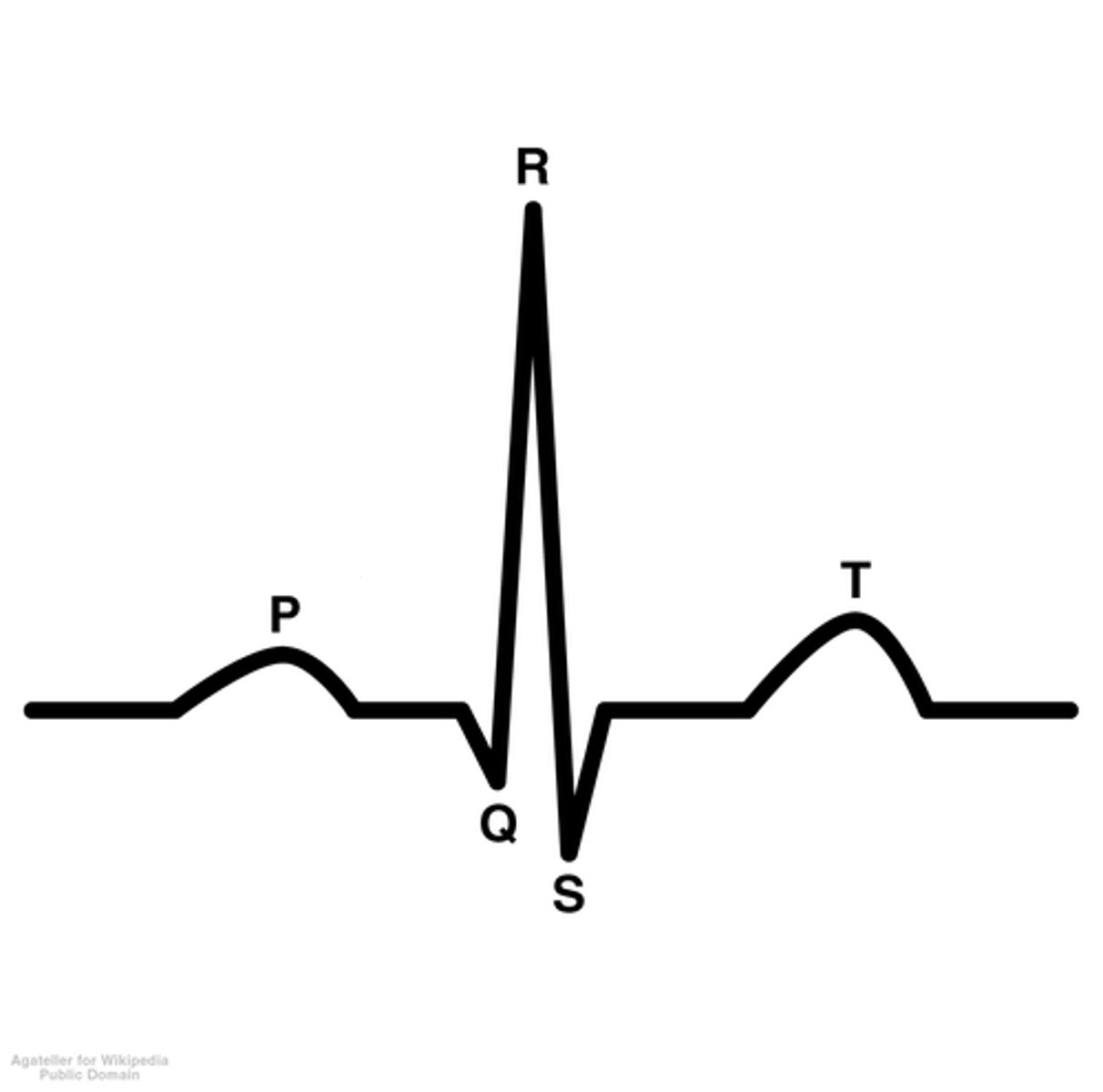
Overview of ECG Diagram
SA node fires → atria depolarizes → atria contracts → AV node fires → atria repolarizes WHILE ventricles depolarize → ventricles contract
What does de/re polarization mean in terms of muscles
-depolarization means muscle contraction
-repolarization means muscle relaxation
What happens during atrial systole
Atria Contraction
What happens during ventricular systole
Ventricles Contract
What happens during ventricular distole
Ventricle walls recover
What happens when SA node fires early
-not enough time to fill enough blood so less blood therefore less contractile force
-wants to get back on track so waits longer and more blood fills therefore greater contractile force
Ectopic Pacemaker
-AV node takes over role of SA node
-atria do not contract (no P-Wave)
-ventricles work harder
-slower heart rate
-use of pacemaker fixes this issue
Heart Block
-thick atria wall (tumor) and blocks pathway between SA and AV node
-slower heartbeat
-multiple P waves (2-5) bc signals not getting to AV node
-atria contract more times than ventricles
Fibrillation
-having myocardial infarction (heart attack)
-continuous disorganization of AP pattern
-decreased refractory period
-"cure": defibrillator stops heart to reset AP pattern
Cardiac Cycle
All events in 1 heartbeat
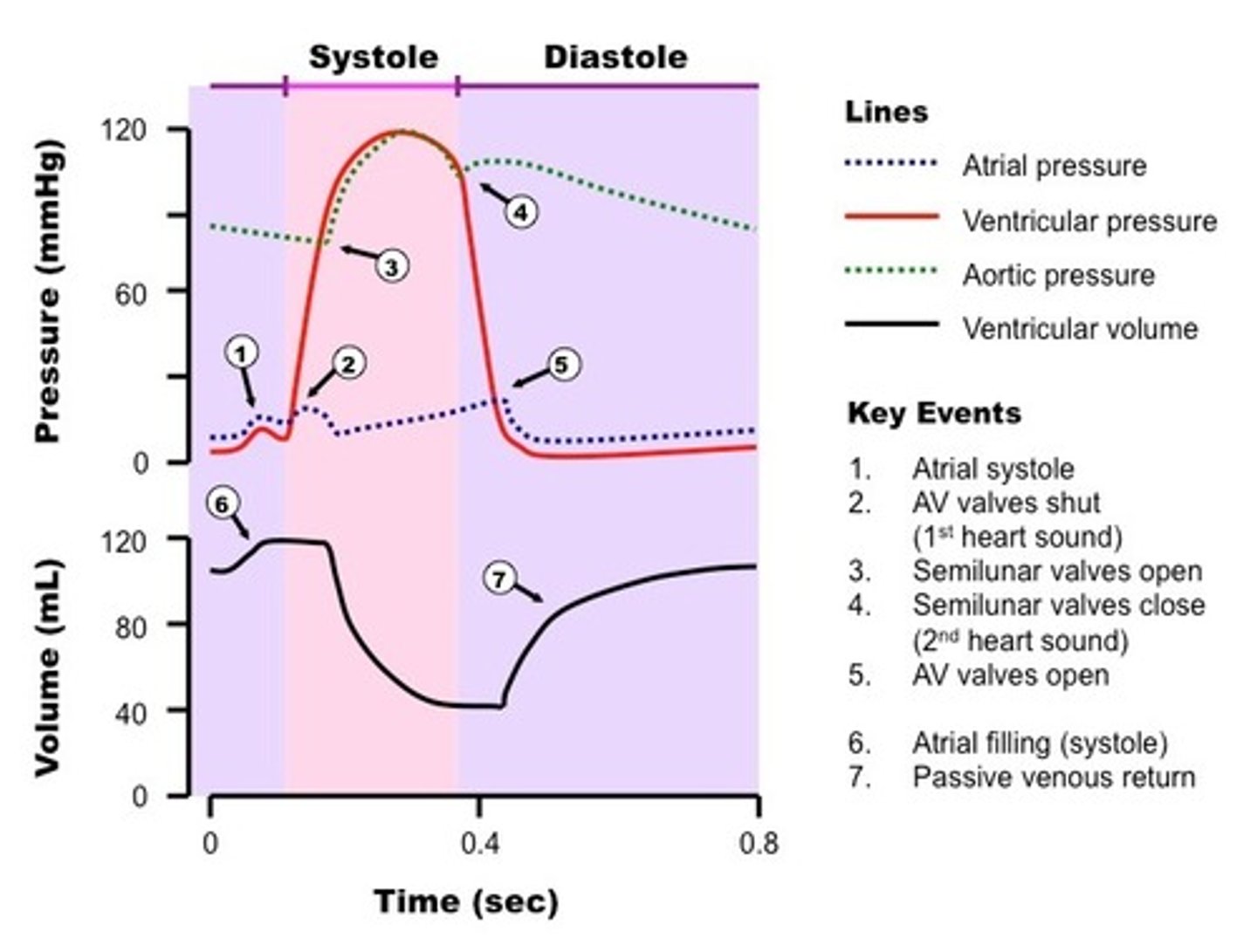
Stages of Diastole
-Early Diastole
-Mid-Late Diastole
-Late Diastole
Systole
high pressure in ventricles
Diastole
low pressure in ventricles
Mid-diastole Events
-atria and ventricles relaxed
-semilunar valves closed, AV open, allowing ventricles to fill up to 80% by gravity (passive filling)
Late-diastole Events
-SA fires and depolarizes atria (contract)
-other 20% fill ventricles (active filling)
-atria pressure increases bc contraction
-End Diastolic Volume
EDV
End Diastolic Volume- max amount fo blood in ventricles
Systole Events
-begins at R in QRS complex
-ventricle pressure increases
-atria reverberation @ end of QRS
-all valves close cause isometric pressure build up to open semilunar valves
-ventricles contract and blood volume decreases until reaches ESV
-atria pressure increases then relaxes, relieving pressure
-aorta pressure rises
-ends after t wave (ventricles repolarizing)
-AV valves open, semilunar valves close, 2nd heart sound
ESV
End Systolic Volume -minimum amount of blood in ventricles
Stroke Volume
= EDV - ESV
-amount of blood ejected from ventricles during one heart beat
-decreases with exercise
-increases at rest
Dicrotic Notch
interuption of blood pressure in the aorta bc aortic valve shuts
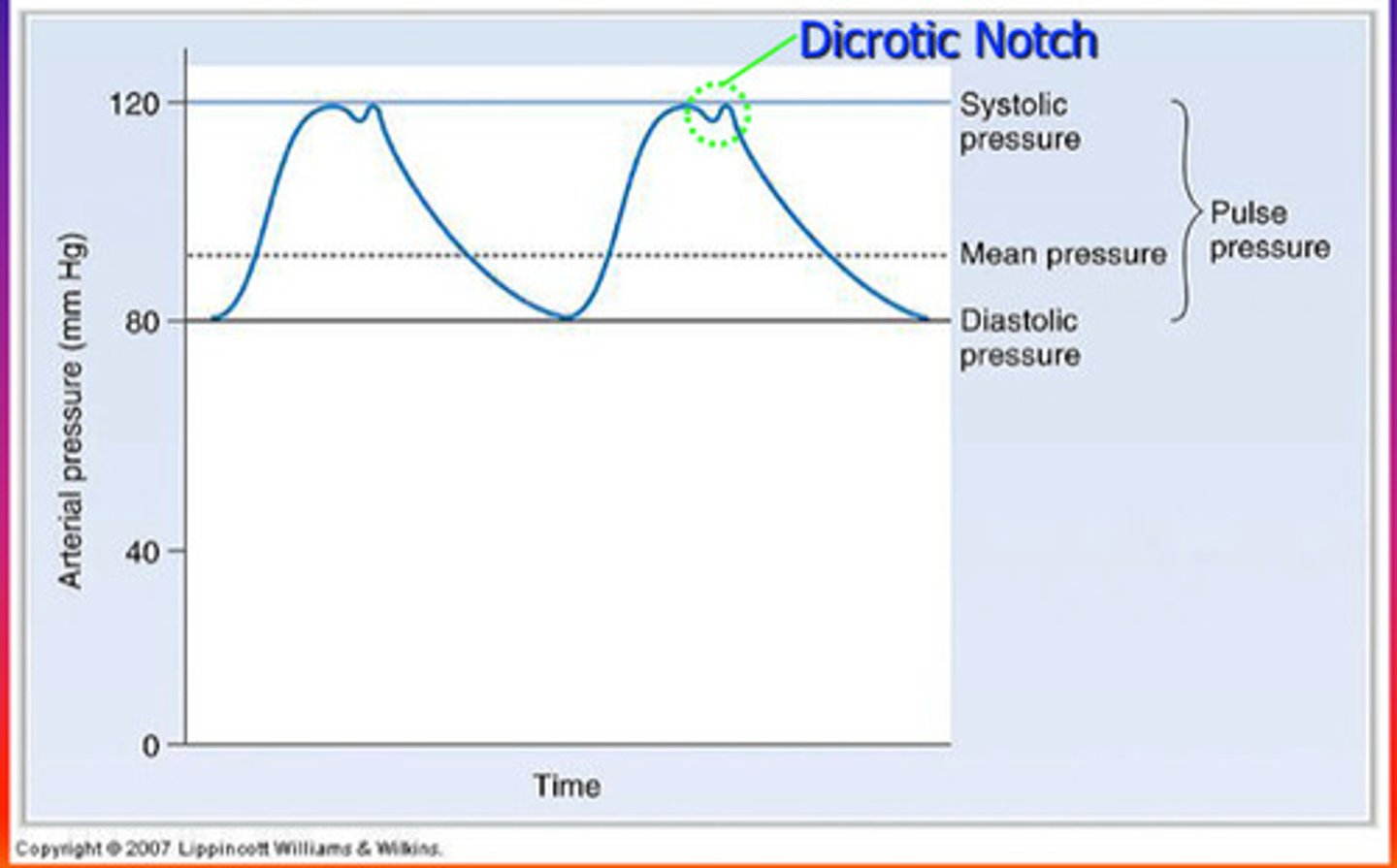
Early-diastole events
-atria fill with blood
-AV valves open while semilunar valves closed
-low atria and ventricle pressure
Heart Sounds -Lub
-turbulent flow as a result of AV valve closure
-in atria
-beginning of systole
Heart Sounds -Dub
-turbulent flow as a result of semilunar valve closure
-in ventricles
-start of diastole
Heart Murmurs
-common in children bc thin myocardium
-in adults: irregular flow through valves
-either: stenosis (narrow valve opening) or regurgitation (leakage of blood through valve)
-"cure": surgery
Blood Vessels
Arteries, Arterioles, Capillary Beds, Venules, Veins
What vessel has the biggest change in blood pressure?
-Arterioles
-about 50 mmHg change
-norepinephrine (controls vasoconstriction/dilation) targets here to control BP for capillaries
What vessel has the highest pressure?
Aorta
What vessel has the lowest pressure?
Vena Cava
Systemic BP
-average 120/80
-systolic/diastolic
Systolic BP
-Highest pressure in arteries
-ventricles contract
Diastolic BP
-Lowest pressure in arteries
-ventricles relax
Pulse Pressure
Systolic - Diastolic
-pulse pressure declines when nearing capillaries
Mean Arteriole Pressure (MAP)
-average blood pressure in arteriole system
-MAP = diastolic pressure + (pulse pressure/3)
-usually 85-90 mmHg
Cardiac Output
-amount of blood coming out of the heart EACH MINUTE
-increasing preload pressure increases heart rate and stroke volume (faster heart beat and increased force of contraction)
Preload Pressure
-pressure right before the entrance of the heart
-preload pressure increases with more blood input
Cardiac Output Calculation
Cardiac Output = Heart Rate x Stroke Volume
Starling's Law
The greater the filling of the heart (EDV), the greater the amount pumped by the heart (stroke volume)
Blood Pressure Factors
-cardiac output
-vascular resistance
-blood volume
Short term BP regulation -Neural
-stimulus: decrease in BP
-neural: ANS
-hormonal: epinephrine and norepinephrine
-study flow chart
venous return
The amount of blood returned to the heart by the veins
Pumps that increase venous return
-muscle pump
-respiration pump
How stroke volume increases
Increase EDV at the same time you decrease ESV
What happens when BP increases?
-Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP) released by right atrium targets kidney to allow more filtration of fluid out of blood
-lower blood volume lower BP
Vascular resistance
-altering blood flow by changing vessel diameter
-vasodilation (beta receptors) and vasoconstriction (adrenaline)
Long term BP regulation -Renal autoregulation
-stimulus: decreased aterial BP
-kidney detects this through baroreceptors and filters less fluid and reabsorb more fluid in blood
-higher blood volume higher BP
Long term BP regulation -Angiotension II
-kidney detects this through baroreceptors
-sympathetic NS activated
-renin released into blood stream from kidney to eventually make Angiotension II
-Angiotension II causes vasoconstriction, ADH release, and aldosterone release
-all of these pathways happen at the same time
-look at flow chart
Baroreceptors
-nerve endings in blood vessels that detect stretch
-most important in aortic arch and carotid arteries because early detection of BP
-this stretch info is sent to the brain
Components of Lymphatic System
-lymphatic vessels
-lymph cells and tissues (nodes)
-lymph organs
Lymphatic Vessels
-"mop up" fluid lost from capillaries and bring back to blood supply
-maintain blood volume and BP
-collect 10% of lost fluid and returns it to the blood vessels
-one-way system to the heart
Hydrostatic pressure
-the pressure within a blood vessel that tends to push water out of the vessel
-physical force of water
Osmotic pressure
-movement of a substance along its osmotic gradient
Filtration
direction of water
Net Filtration Pressure
= Net hydrostatic pressure -Net osmotic pressure
Arteriole end of capillary pressure
NHP > NOP
-positive NFP so means water leaves capillary
-more water leaving so decreases NHP
Venous end of capillary pressure
NHP > NOP
-negative NFP so water going into the capillaries
-more water coming in so increased NHP
Where are the only places that lymphatic vessels are NOT found?
-bone
-teeth
-CNS
Lymphatic Vessel Structure
-minivalves that open when interstial pressure rises
-collagen fibers that overlap the flaplike minivalve
-lacteals in villi
Name of any fluid that enters lymphatic vessels
lymph
Lacteals
-inside every villi between veins and arteries
-fat enters into here and enter blood stream
How is cancer spread?
-when cancer cells enter the interstitium then into minivalves
-travels as lymph