Biology chapter 15 homeostasis and excretion
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
the body maintains a dynamic equilibrium with small fluctuations over a narrow range of conditions
Definition of homeostasis?
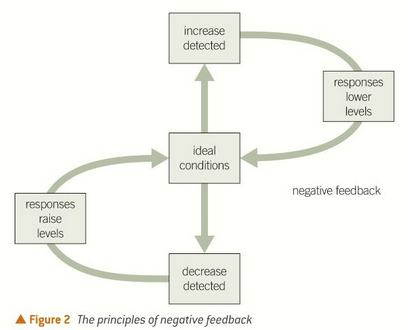
negative feedback systems work to reverse the initial stimulus
example: control of blood sugar with insulin and glucagon
what is negative feedback?
one example of a system in the body?
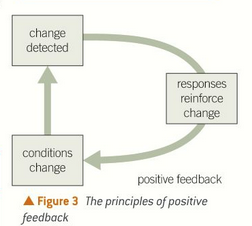
when a change is detected in the body, the effectors work to reinforce the change and increase the response
example: during childbirth, head presses against cervix which stimulates oxytocin and causes contractions which further pushes baby against cervix
what is positive feedback
one example
use surroundings to warm their bodies. core body temp is reliant on environment
fish, amphibians and reptiles
those living water don’t have problems as water has a high heat capacity and temp remains constantw
what is an ectotherm?
mammals and birds
rely on metabolic processes to warm up and maintain a stable core temp
What is an endotherm?
behavioural responses like going in the sun or shade, press body on warm ground through conduction.
some physiological responses such as being dark to absorb more heat
need less food and can survive in harsher habitats
how do ectotherms regulate temperatures?
receptors in the skin
receptors in hypothalamus
how do ectotherms detect temp changes?
vasodilation of blood vessels to force blood closer to the skin so heat can escape
increased sweating, when sweat evaporates from the skin, heat is taken with it and cools the blood
hairs lie flat on the skin to stop insulating
high SA:V ratio to maximise cooling
cooling mechanisms of endotherms?
shivering - the metabolic heat from contracting muscles heats up the body
some animals have small SA:V ratio or fat stores
vasoconstriction
hairs rise up to insulate
decreased sweating
warming mechanisms of endotherms?
the removal of waste products of the metabolism found in the body
CO2, bile bigments (billirubin) and urea from breakdonw of amino acids
excretion defintion
what do mammals excrete?
brings oxygenated blood to drive the metabolic reactions in liver
what does the hepatic artery bring to the liver?
brings blood straight from gut and is rich in glucose, amino acids
what does the hepatic portal vein bring?
called hepatocytes
large nuclei
prominent Golgi apparatus
Lots of mitochondria as they are metabolically active
features of the liver cells and what are they called?
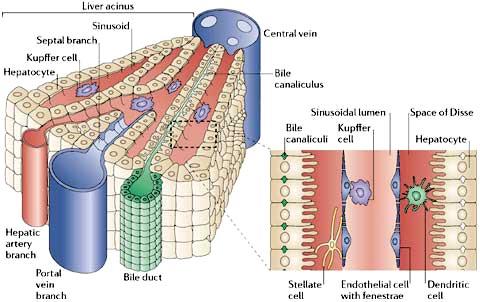
blood from hepatic artery and portal vein is mixed in sinusoids surrounded by hepatocytes
mixing increases oxygen content of the blood from the hepatic portal vein
sinusoids have Kupffer cells which are like macrophages and ingest foreign particles
hepatocytes secrete bile into the bile canaliculi which drains into bile ductules
label parts of the liver lobule
control blood glucose, amino acid and lipid levels
glycogen is stored in the hepatocytes
Synthesis of plasma proteins, cholesterol, RBC in foetus
detoxification of alcohol
Breakdown of hormones
Synthesis of urea from amino acids (deamination)
Convert one maino acid into one that is neccessary
functions of liver and hepatocytes
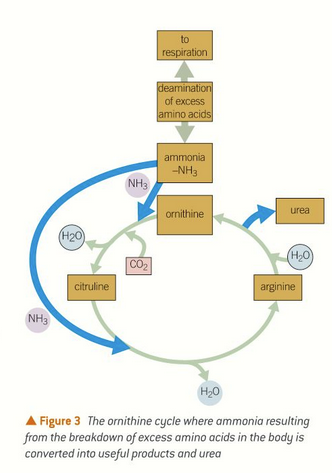
ornithine cycle
ammonia is produced from deamination of amino acids
in the ornithine cycle ammonia converted to urea and useful products
water, urea and CO2 made
what is the cycle that creates urea?
breakdown of hydrogen peroxide
hepatocytes have catalse, splits hydrogen peroxide into oxygen and water
alcohol dehydrogenase which breaks ethanol to ethanal
detoxification
cortex - dark outer layer where filtering of blood happens
medulla - lighter inner section which has tubules of the nephorns
the pelvis - central chamber where urine collects
kidney structure?
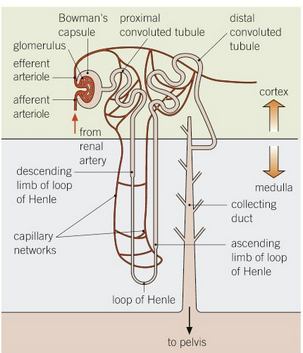
bowman’s capsule - has glomerulsu which is a tangle of capillaries
proximal convulated tubule - many substances are reabsorbed here
loop of henle - long loop that has high solute conc
distal convoluted tubule - fine tuning of water balance in blood, ions and pH
collecting duct - sensitive to ADH
structure of the nephron label
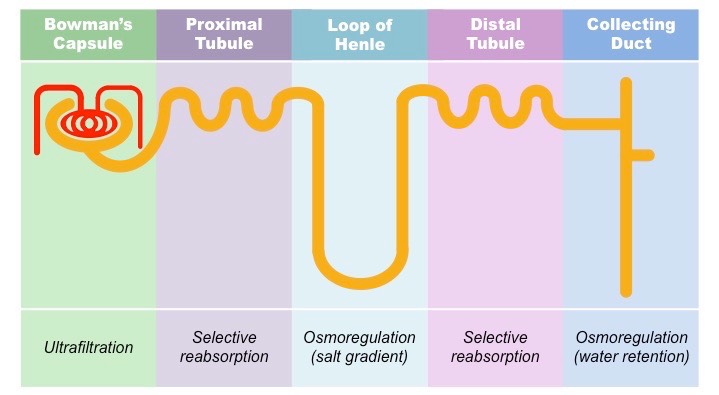
what happens in each part of nephron?
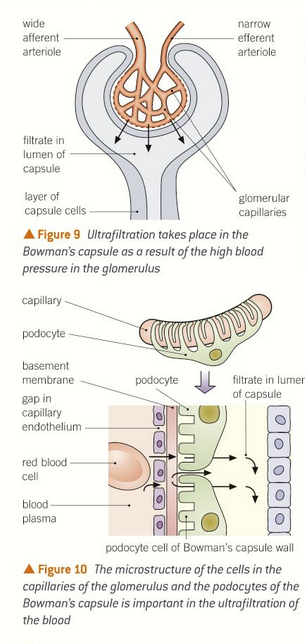
glomerulus and bowman’s capsule
the glomerulus is supplied with blood from the afferent arteriole and leaves through narrower efferent arteriole
high hydrostatic pressure forces blood through capillary wall, through basement membrane and pediciles of the podocytes
proteins and many blood cells are retained as they are too big
filtrate then eneters the capsule and has glucose, salt, urea.
ultrafiltration
where does it happen?
process?
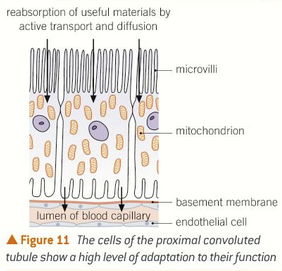
proximal convoluted tubule:
all of the glucose, amino acids, vitamins and hormones are reabsorbed back into the blood by active transport
the cells are adapted by:
covered with microvili which increases the surface area
many mitochondria to make ATP for active transport
once they are removed, they diffuse into capillary network
the filtrate reaching the loop of henle is isotonic with tissue fluid. 80% of filtrate has been reabsorbed
selective reabsorption
where does it happen and process?
Na+/K+ pump uses ATP and pumps Na+ ions into the blood from PCT cells
This means there is a low conc of Na+ in the PCT so by a cotransport protein, Na+ and glucose are reabsorbed into PCT cells
Glucose can then diffuse into the capillaries down their conc gradient
water follows by osmosis
how are glucose and amino acids actively reabsorbed in PCT?
called the countercurrent multiplier system
The ascending limb actively pumps out sodium and chloride ions into the medulla to reduce the water potential of the medulla
The ascending limb is impermeable to water
Water then leaves the descending limb by osmosis due to the low water potential in the medulla.
The fluid at the bottom of the loop of Henle is very concentrated, so when it starts moving up the ascending limb, ions can passively move down conc gradient into the medulla
Desert animals have longer loops of Henle to reabsorb more water
What happens in the loop of henle?
permeability varies with ADH
cells are adapted to carry out active transport
if body lacks salt, sodium ions will be pumped out and Cl- will follow due to gradient
water can also leave and make the urine more concentrated
what happens in the DCT?
water moves out by diffusion down a concentration gradient so urine is more concentrated
the level of sodium ions in the surrounding tissue fluid increases through medulla so more water can be reabsorbed
permeability is controlled by ADH
ADH made by the hypothalamus and secreted by the pituitary
ADH increases permeability
what happens in the collecting duct?
released from pituitary and doesn’t cross cell
binds to receptors and triggers formation of cAMP as a second messenger
vesicles in collecting duct cells fuse wth cell surface membrane
they have aquaporins which make CD permeable to water
mechanisms of ADH action
in hypothalamus
when too less water, water potential drops so nerve impulses are sent to posterior pituitary to release ADH
when too much water ADH release is inhibited
where are osmoreceptors located and how to they work?
mobile monoclonal antibodies made to be complementary to hCG are attached to a small coloured bead
hCG in urine binds to mobile antibodies and form hCG/antibody complex
immobilised monoclonal antibodies arranged in a line and only bind to hCG/antibody complex
another line of immobilised monoclonal antibodies bind to mobile antibodies whether hCG is present or not, to show if the mobile antibodies are moving up the stick
how do modern pregnancy tests work?
drugs that mimic the action of testosterone and stimulate muscle growth
can be detected by gas chromatography of the urine
what are anabolic steroids?
damage to basement membrane or podocytes
cysts
damage to structure of epithelial cells
causes of kidney failure?
protein in urine due to Bowman’s capsule damage
Blood in urine
high blooc pressure
build up of toxic urea in the blood
measured by measuring glomerular filtration rate (cm3/min)
effects of kidney failure?
Haemodialysis:
blood leaves body through artery into the machine
flows between partially permeable dialysis membranes
mimic the basement membrane
urea moves out down the concentration due to dialysis fluid which has no urea
but has same plasma and glucose levels as blood
Transplant:
risk of rejection
better for patient if it works, as dialysis takes too long
Immunosuppressant drugs can be harmful
treatments to kidney failure?
how does each of the methods work and pros and cons?