Lecture 3: Attitudes and Behaviour
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Allport - attitude
-a mental and neural state of readiness, organised through experience, exerting a directive or dynamic influence upon the individual’s response to all objects and situations with which it is related
Eagly & Chaiken - attitude
-a psychological tendency that is expressed by evaluating a particular entity with some degree of favour or disfavour
features of attitudes
affective → feelings/emotions
cognitive → beliefs/thoughts
behavioural → actions/intentions
LaPiere - method (attitudes predicting behaviours)
-in 1930s America was cultural segregation and negative attitudes towards Chinese people
-travelled around America with a Chinese couple
-visited 184 restaurants
LaPiere - results (attitudes predicting behaviours)
-only 1 restaurant refused to serve them
-when asked via letter if they would serve Chinese people → 92% of restaurants said they would not
-clear discrepancy between attitudes and behaviour
Wicker (attitudes predicting behaviours)
-reviewed studies on relationship between attitudes and behaviour
-relationship between the two is not very strong
-rarely above 0.3
principle of compatibility
-each attitude and behaviour has five elements:
action
actor
context
target
time
-correspondence between attitudes and behaviour will be greatest when both are measured at the same degree of specificity
Davidson & Jaccard (correlation between attitude and behaviour)
-measured people’s:
attitude towards birth control → 0.8
attitudes towards birth control pills → 0.32
attitude towards using birth control → 0.53
Shiloh (correlation between attitude and behaviour)
-attitude measure:
general attitudes towards vaccinations → 0.31
specific attitudes towards getting the COVID-19 vaccination → 0.50
-measuring general attitudes is not as effective for predicting behaviour
accessibility
-accessible attitudes can be recalled from memory more easily
temporal stability
-strong attitudes are resistant to change and stable over time
basis of attitudes
-attitudes based on feelings are less likely to change over time
Rocklage & Luttrell - method (basis of attitudes)
-asked to recall a recent gift received
-then asked to think about one adjective to describe the gift
-month later were then asked to think of one adjective to describe the gift
Rocklage & Luttrell - results (basis of attitudes)
-found description was less likely to change over time if the gift had emotional connection (affect)
-if the gift was functional, people were more likely to have a less stable opinion about it
Howe & Krosnick (personal importance)
-attaching personal importance to an attitude causes an enhanced resistance to change
-if something is important to us, our attitude towards it will be strong and more likely to drive our behaviour
Holland - method
-session 1: questionnaire
attitudes towards Greenpeace on an 11-point scale
attitude strength
-session 2: behaviour
opportunity to donate money toward Greenpeace
Holland -result
-significant link between attitudes and behaviour, but only for those with strong attitudes
relatively weak attitudes → -0.10 relationship to donations
relatively strong attitudes → 0.36 relationship to donations
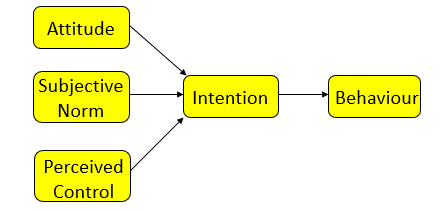
theory of reasoned action
-attitudes shape our intentions
-our intentions then cause/influence/drive behaviour
-indirect link between attitude and behaviour
behavioural intention
-assumed to capture the motivational factors that influence a behaviour
-indicate how hard people are willing to try, or how much effort they would exert to perform a behaviour
subjective norms (theory of reasoned actions)
-added to theory of reasoned action
-what other people think you should do
-personal attitudes and subjective normative beliefs combine to form our intentions which then influence and drive our behaviour
components of subjective norms
beliefs about whether important others approve or disapprove of you performing the behaviour
motivation to comply
Sheppard, Hartwick & Warshaw (support for the theory of reasoned action)
-meta-analysis of 87 studies
-correlations:
0.66 → attitudes/subjective norms and intentions
0.53 → intentions and behaviour
theory of planned behaviour
-adds construct of perceived control
perceived control → will not do something that we have no control over
perceived behavioural control
-people’s perceptions of their ability to perform a given behaviour
-similar to self-efficacy
-typically measured in terms of confidence
Armitage & Conner (support for the theory of planned behaviour)
-meta-analysis of 185 studies
-correlations:
0.49 → attitude and intention
0.34 → subjective norm and intention
0.43 → intention
0.47 → intention and behaviour
0.37 → perceived control and behaviour
intention-behaviour gap
-intentions do not always translate into behaviour
moderator variable
-a variable that influences the strength of the relationship between two variables
moderator variable - theory of planned behaviour
-perceived control is a moderator variable between attitude and behaviour
Webb & Sheeran (evidence for perceived behavioural control)
-effect of a medium-to-large sized change in intentions on behaviour
criticisms of theory of planned behaviour
sufficiency assumption → the influence of other variables should be fully mediated by the specific social-cognitive variables
are there additional variables that predict intentions and behaviour
too rational and rigid → do people engage in such complex decision making processes
prediction is not the same as explanation
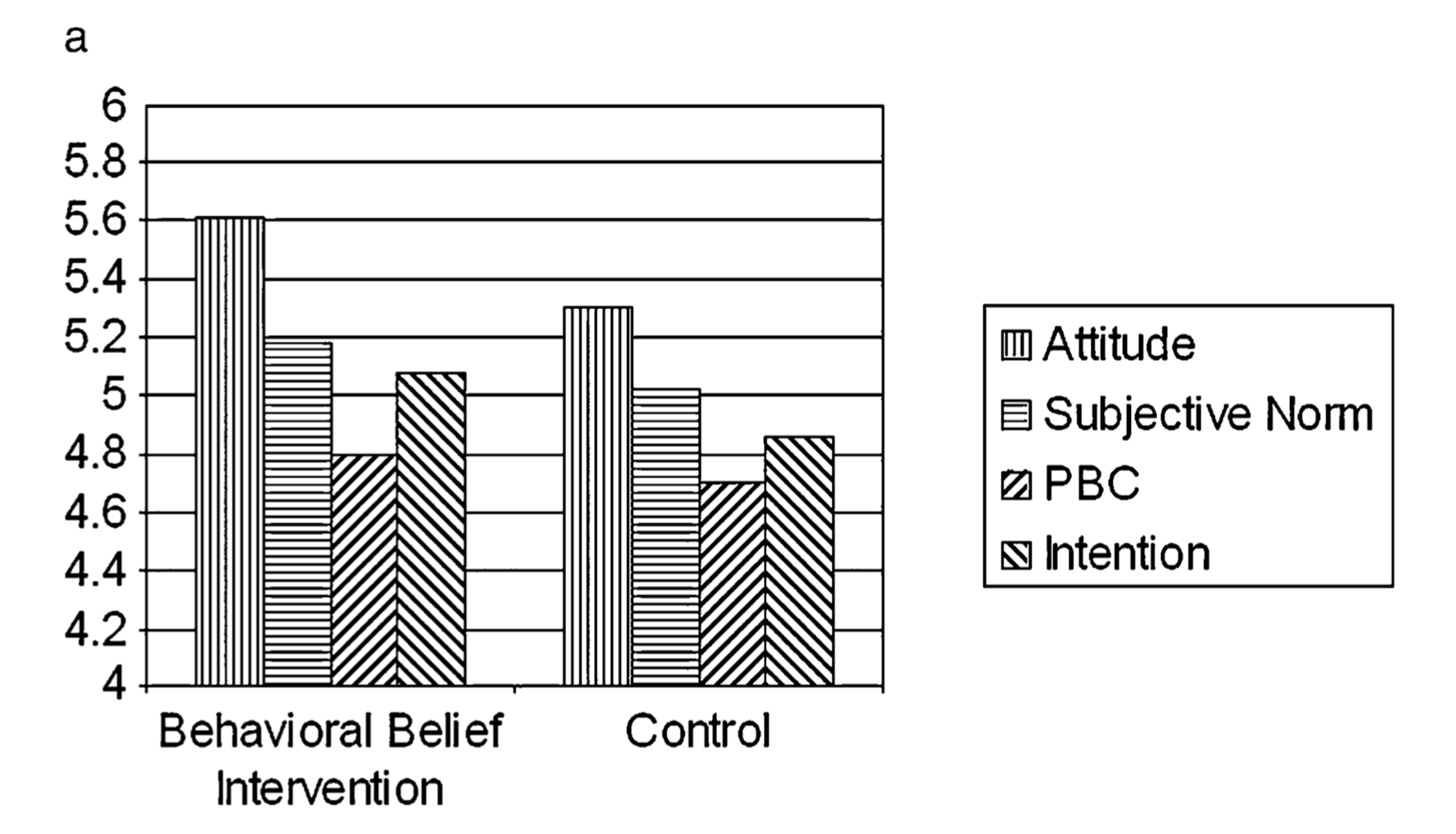
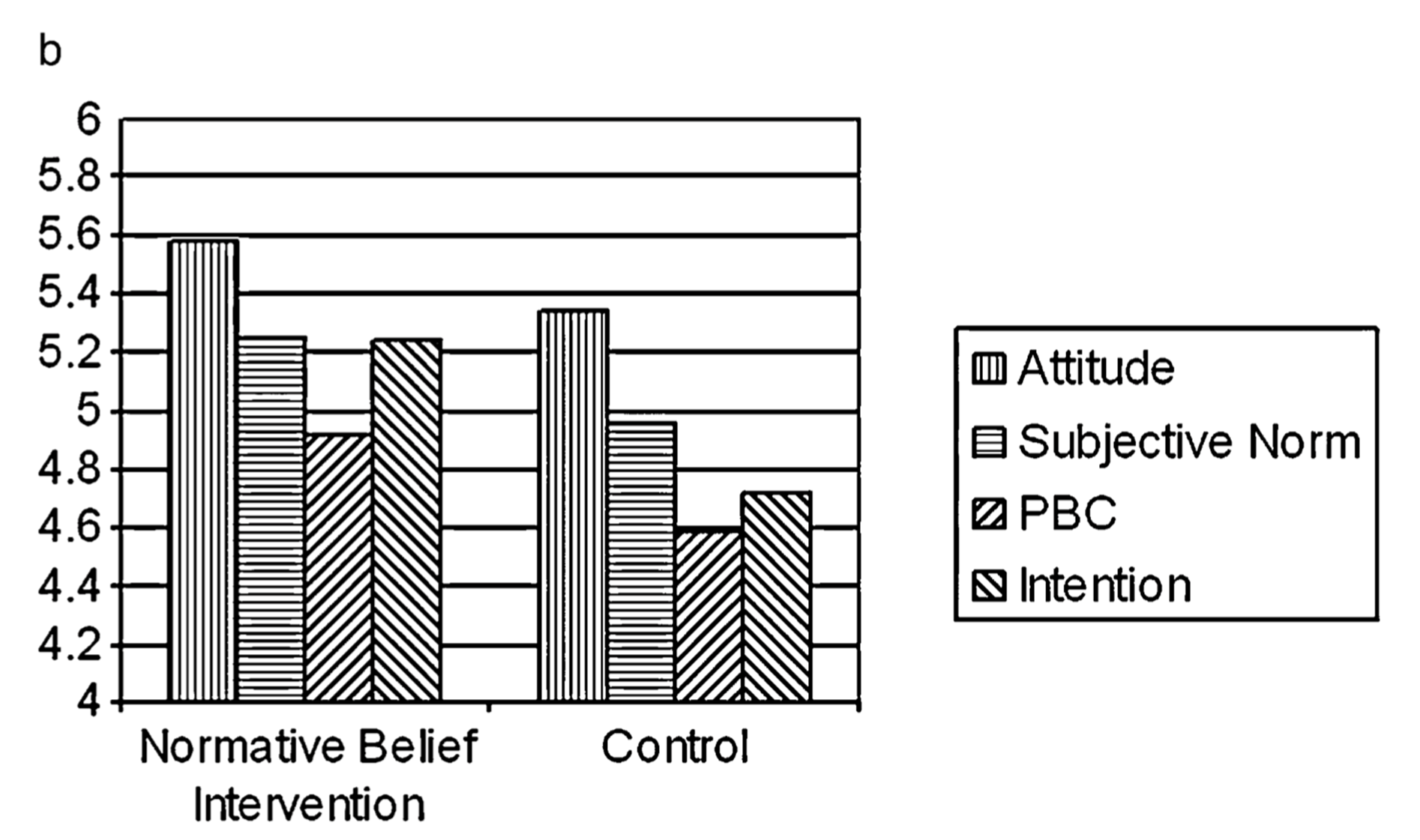
Sniehotta - method (experimental test of theory of planned behaviour)
-2 X 2 X 2 factorial design → 8 conditions
behavioural belief intervention
normative belief intervention
control belief intervention
-people either got these messages or did not get them
-DVs:
changes in beliefs
attendance at university sports facilities over 2 months
Sniehotta - behavioural beliefs results (experimental test of theory of planned behaviour)
Sniehotta - normative beliefs results (experimental test of theory of planned behaviour)
predictions based on the theory of planned behaviour
behavioural belief intervention leads to changed attitudes
normative belief intervention leads to changed subjective norms which leads to a changed intention
control belief intervention showed no change in perceived control