Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, and Oxidative Phosphorylation: Key Steps and Enzymes
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
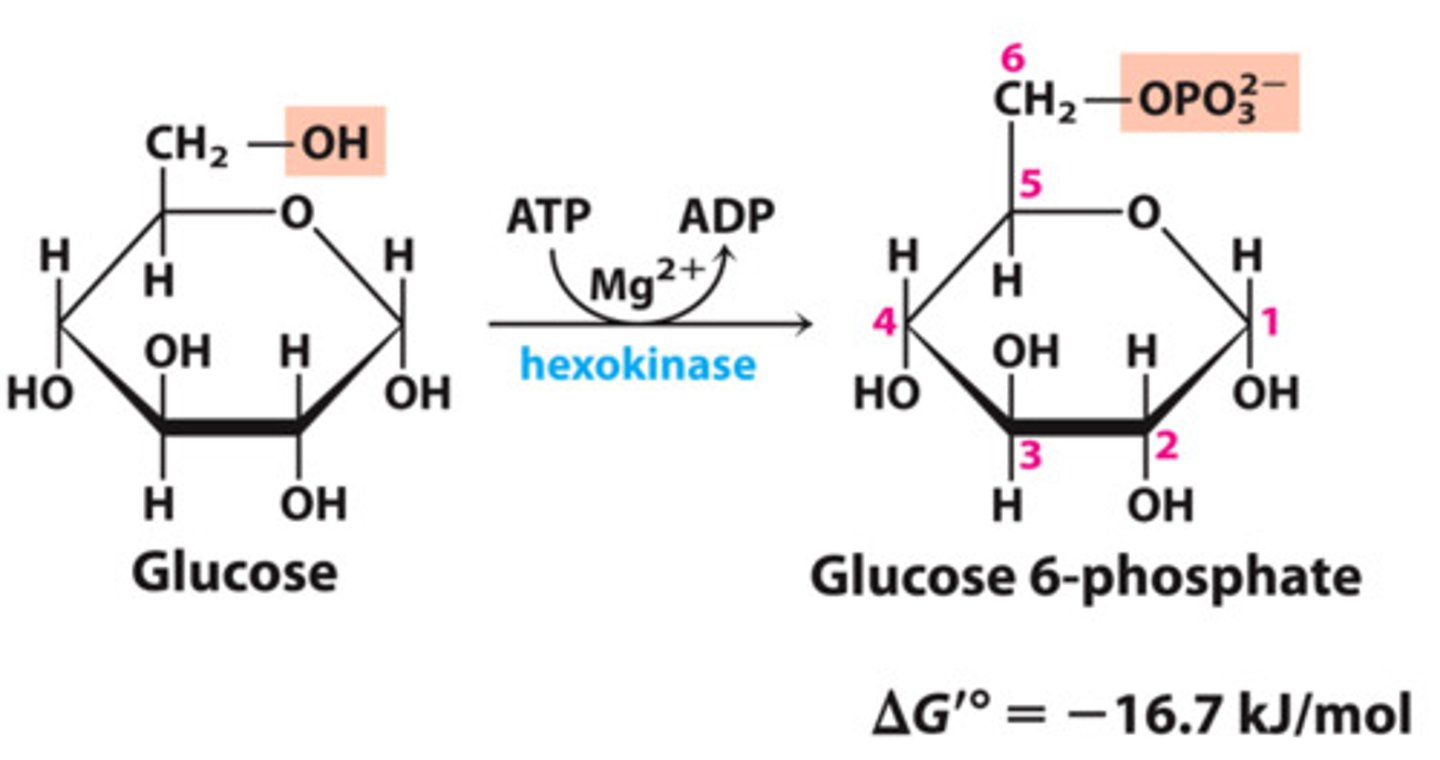
Step 1 of Glycolysis
Substrate → Product: Glucose → Glucose-6-phosphate
Enzyme: Hexokinase
Energy intermediates: ATP → ADP +iP (ATP consumed)
Other molecules: none
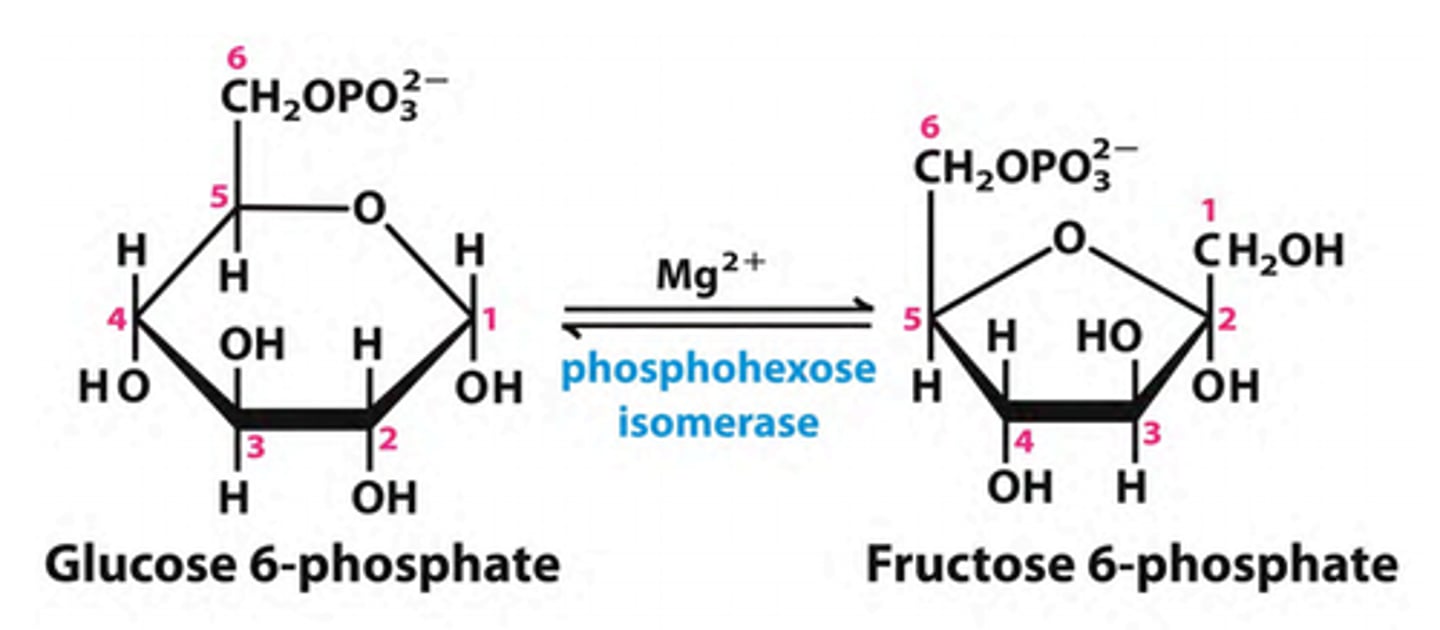
Step 2 of Glycolysis
Substrate → Product: Glucose-6-phosphate → Fructose-6-phosphate
Enzyme: Phosphoglucoisomerase
Energy intermediates: none
Other molecules: none
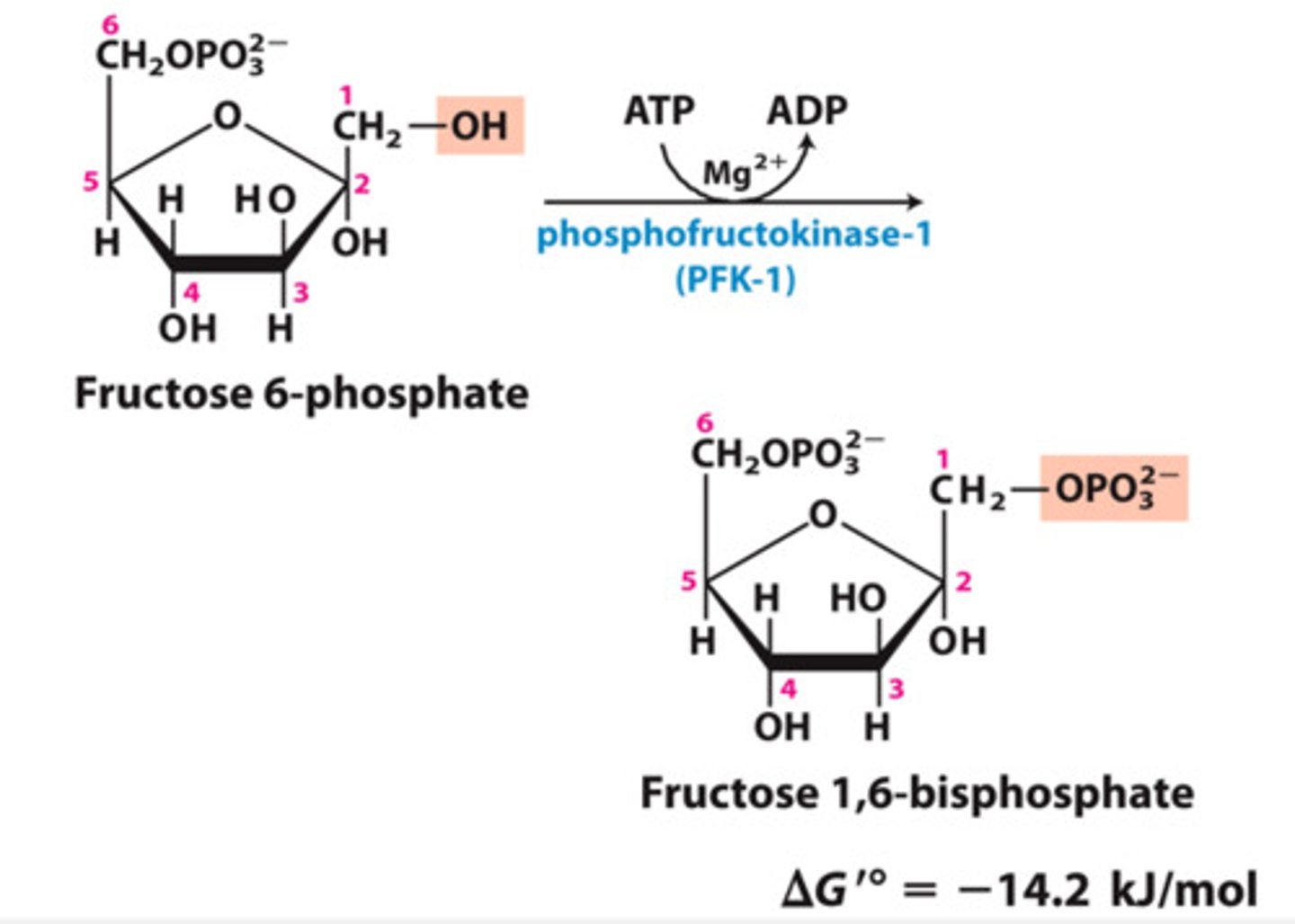
Step 3 of Glycolysis
Substrate → Product: Fructose-6-phosphate → Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
Enzyme: Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)
Energy intermediates: ATP → ADP + iP (ATP consumed)
Other molecules: none
Step 4 of Glycolysis
Substrate → Product: Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate → Glyceraldehyde 3 Phosphate (G3P) + Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
Enzyme: Aldolase
Energy intermediates: none
Other molecules none
Notes: Cleavage into two 3-carbon sugars.
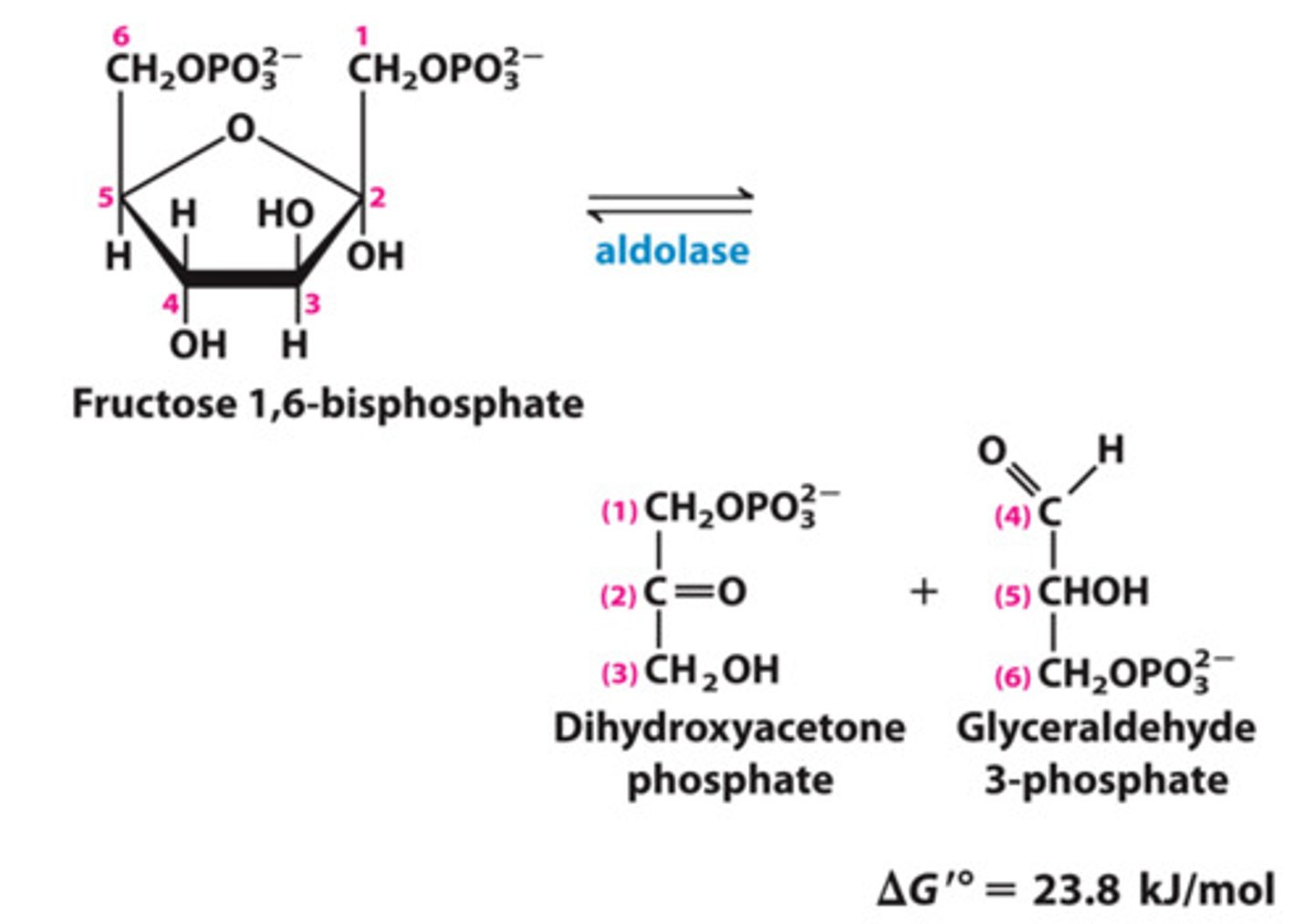
Step 5 of Glycolysis
Substrate → Product: Dihydroxyacetone phosphate ↔ Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate (G3P)
Enzyme: Triose phosphate isomerase
Energy intermediates: none
Notes: Interconversion maintains equilibrium between two triose phosphates.
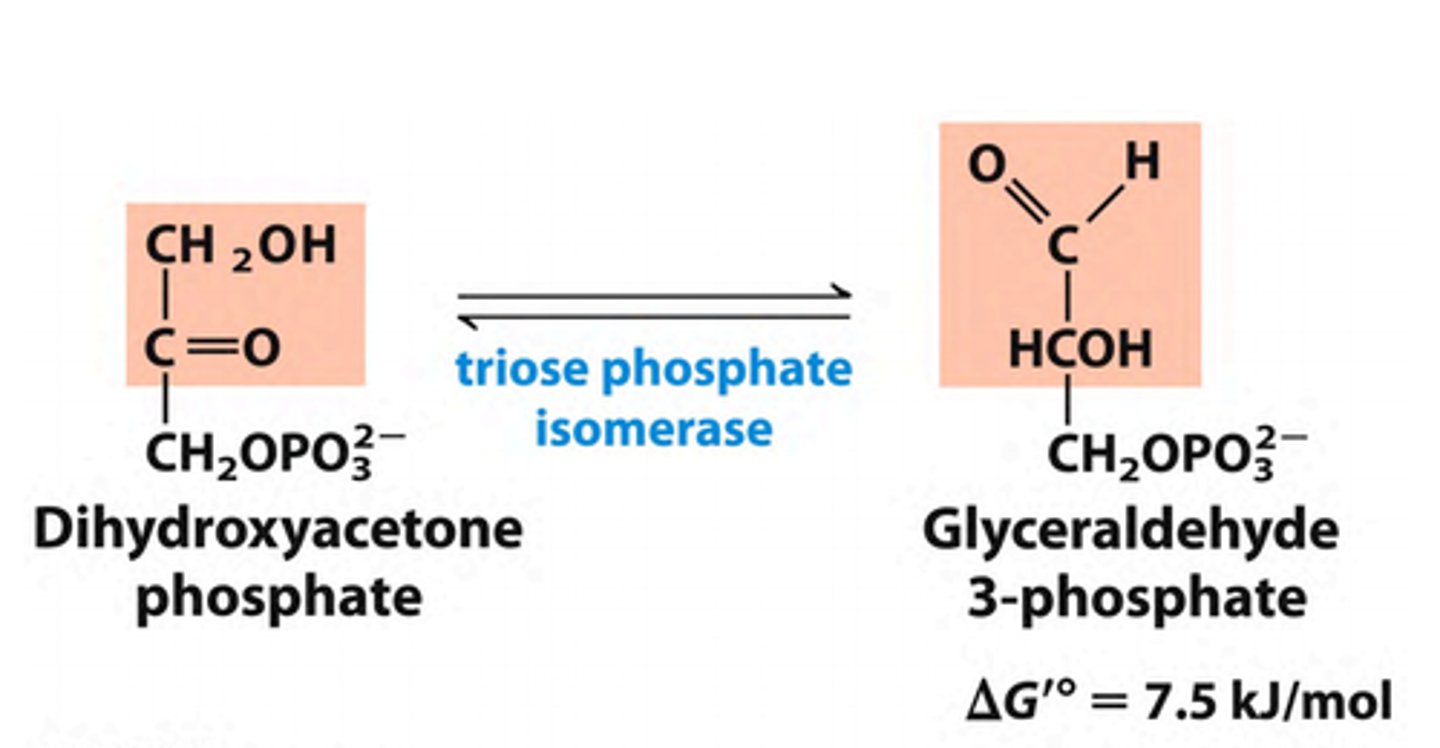
Step 6 of Glycolysis
Substrate → Product: Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate (G3P) → 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
Enzyme: G3P dehydrogenase
Energy intermediates: NAD⁺ + 2H⁺ +2e⁻ → NADH + H⁺
Notes: Oxidation and phosphorylation; first energy-yielding step.
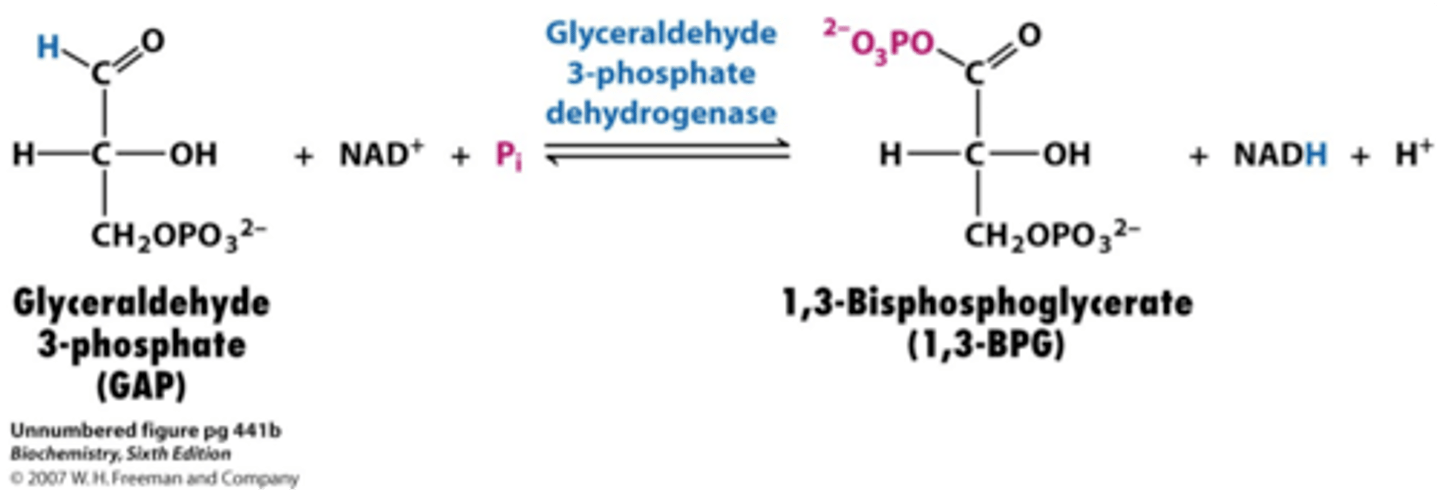
Step 7 of Glycolysis
Substrate → Product: 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate → 3-phosphoglycerate
Enzyme: Phosphoglycerate kinase
Energy intermediates: ADP +iP (cytosolic) → ATP
Notes: First substrate-level phosphorylation.
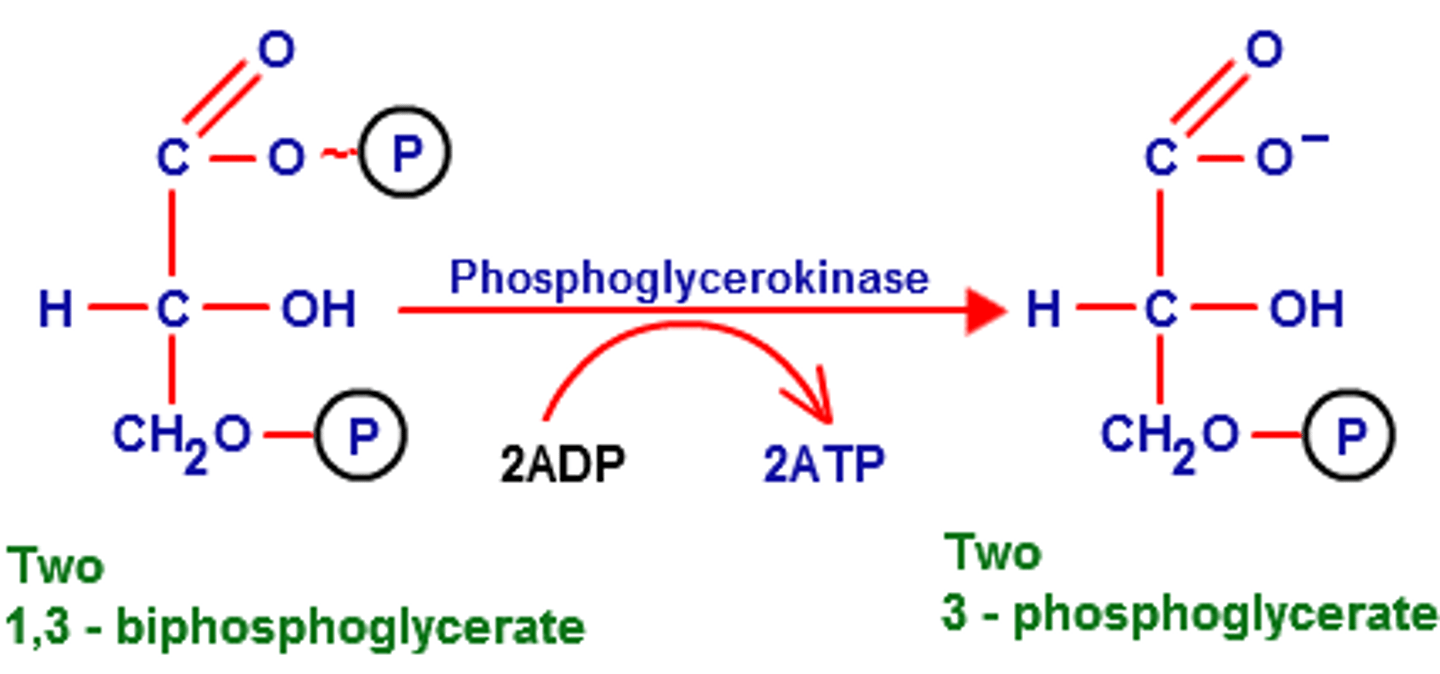
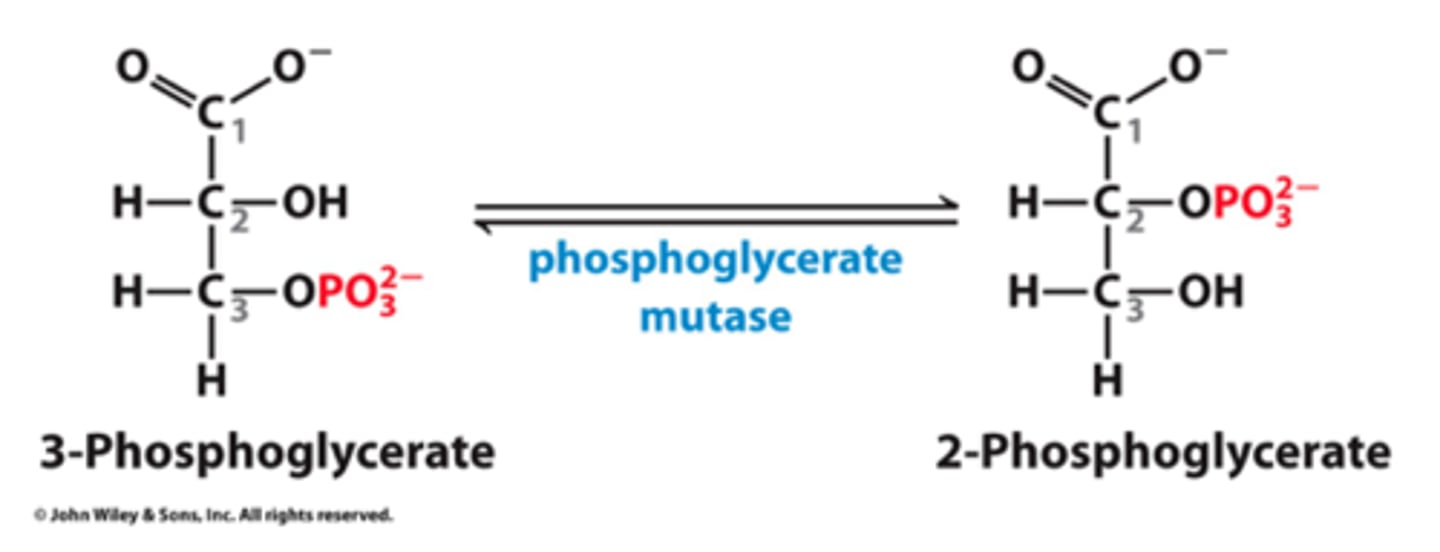
Step 8 of Glycolysis
Substrate → Product: 3-phosphoglycerate → 2-phosphoglycerate
Enzyme: Phosphoglycerate mutase
Energy intermediates: none
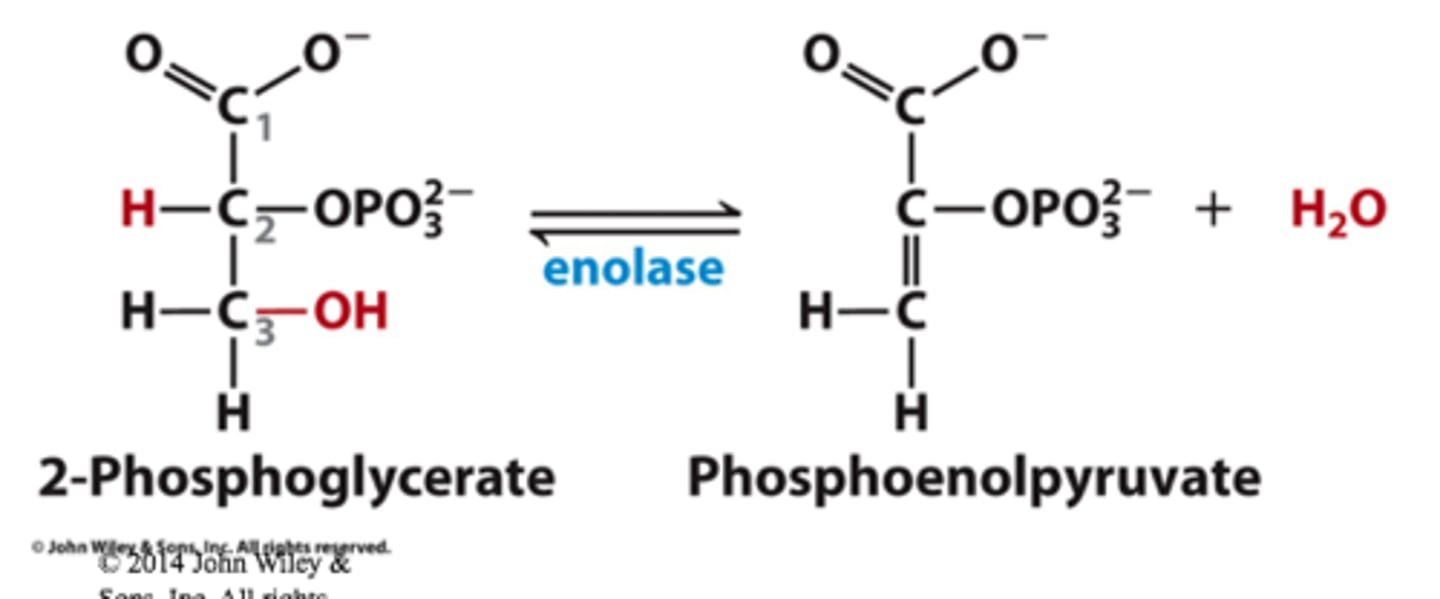
Step 9 of Glycolysis
Substrate → Product: 2-phosphoglycerate → Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)
Enzyme: Enolase
Energy intermediates: none
Other molecules: H₂O released
Notes: Dehydration reaction producing a high-energy phosphate compound.
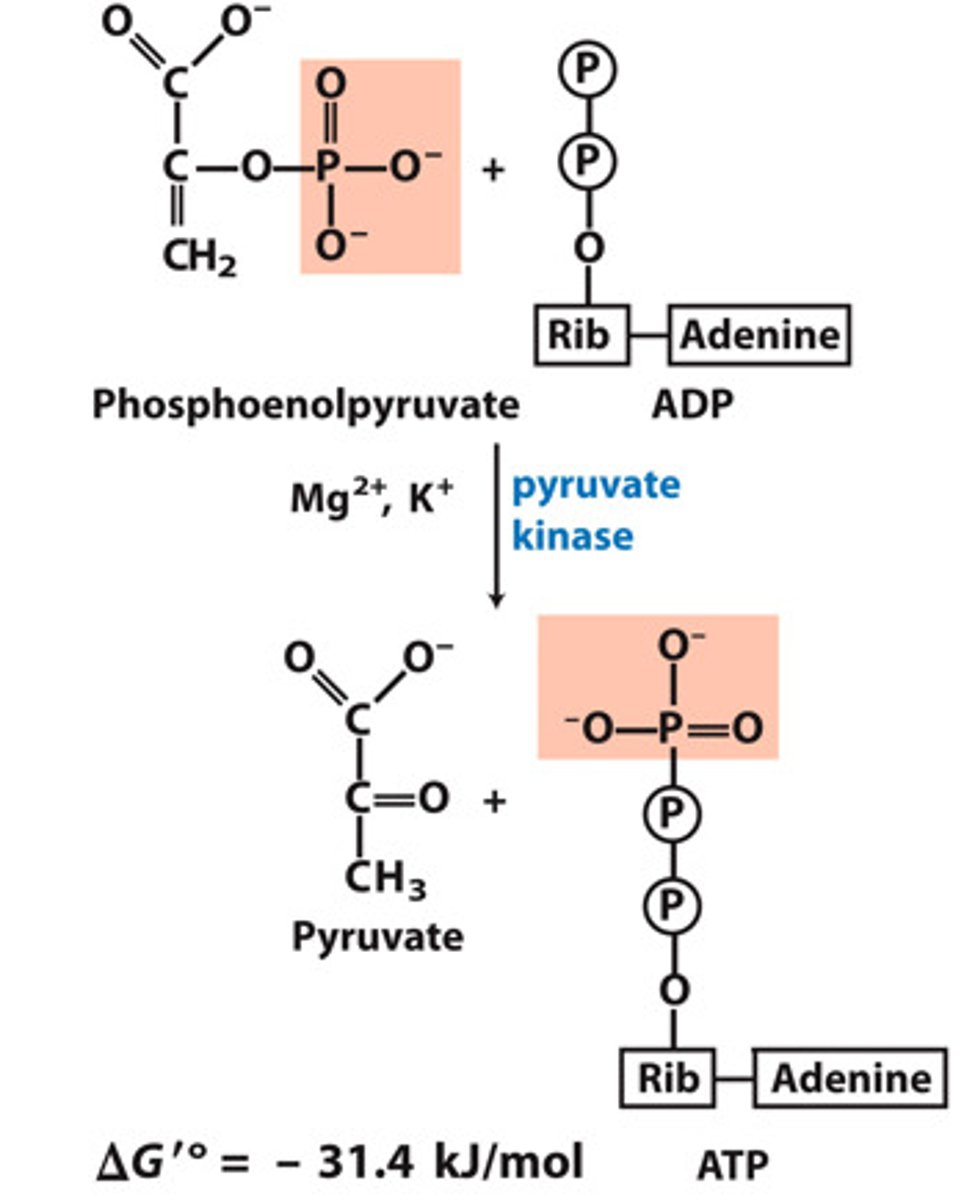
Step 10 of Glycolysis
Substrate → Product: Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) → Pyruvate
Enzyme: Pyruvate kinase
Energy intermediates: ADP+ iP → ATP
Notes: Second substrate-level phosphorylation; irreversible step.
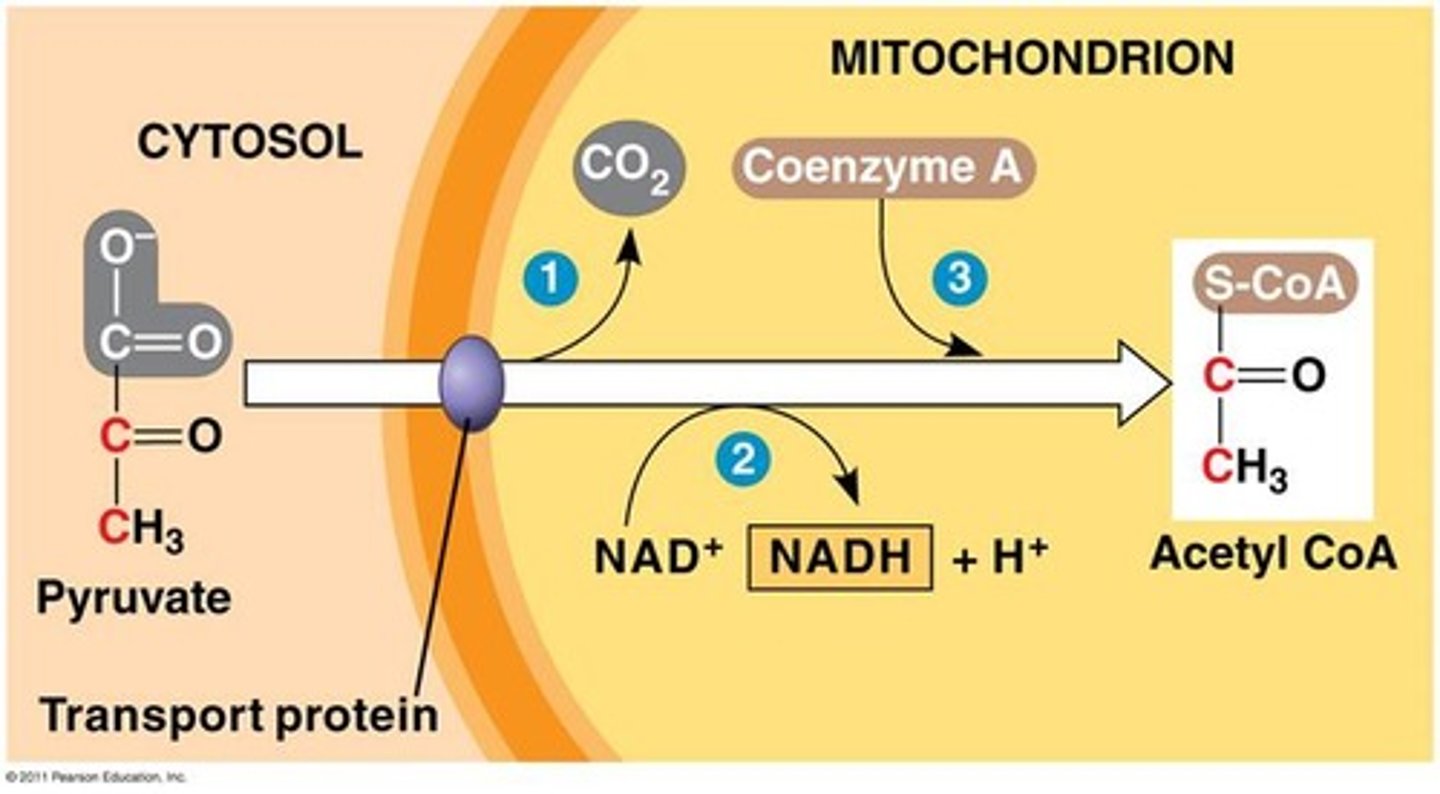
Pyruvate Oxidation step
Substrate → Product: Pyruvate → Acetyl-CoA + CO₂
Enzyme:
1) Pyruvate dehydrogenase (CO₂ removal)
2) Dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase/ Dihydrolipoyl transacetylase (adds CoASH)
3) Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase/ Dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (NADH + H⁺
Energy intermediates: NAD⁺ +2H⁺ + 2e⁻ → NADH + H
Other molecules: CO₂ released
Notes: Link between glycolysis and Krebs cycle; irreversible oxidative decarboxylation.
What is step 1 of the Krebs Cycle?
Substrate → Product: Acetyl-CoA + Oxaloacetate → Citrate
Enzyme: Citrate synthase
Energy intermediates
Other molecules: CoA-SH released
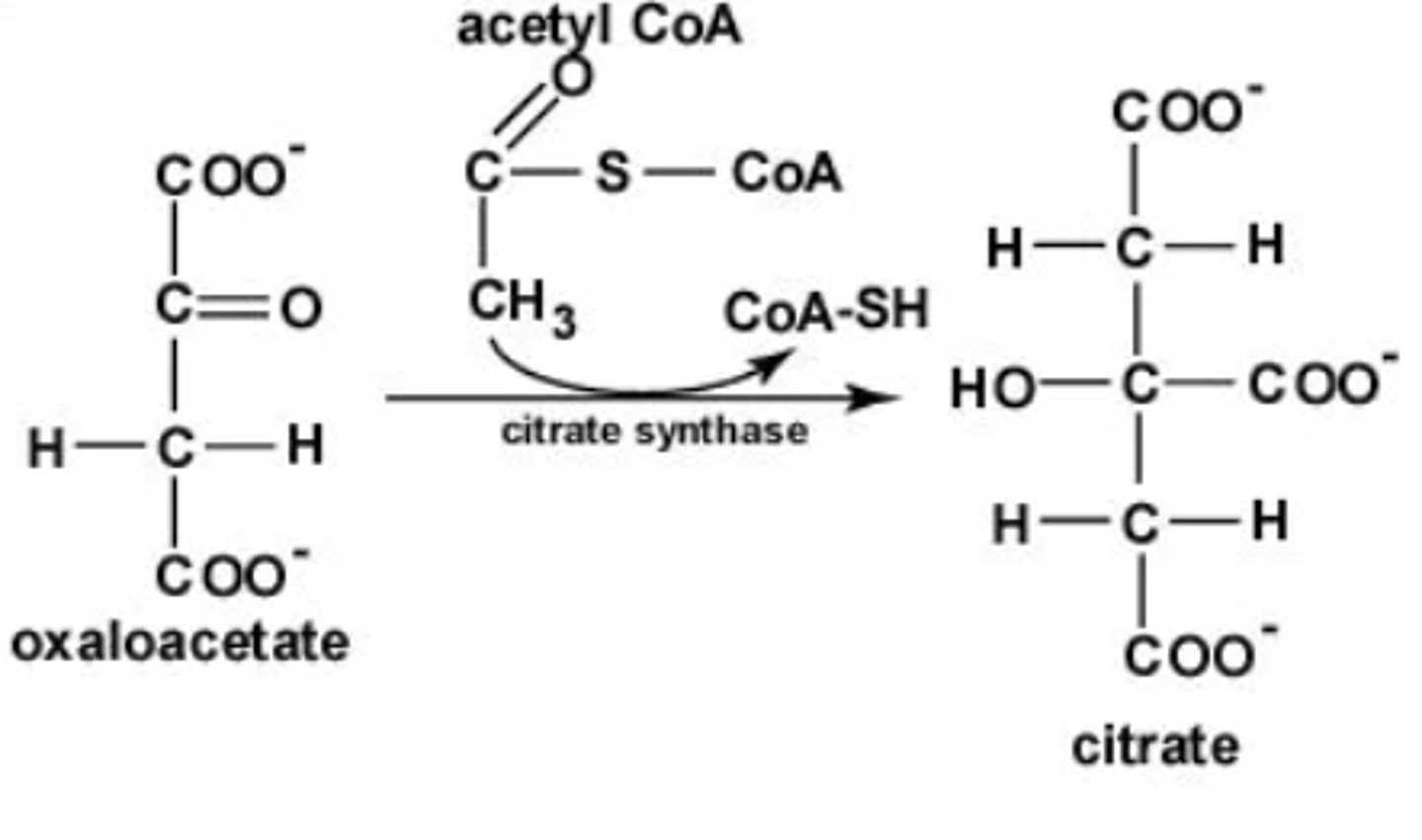
What is step 2 of the Krebs Cycle?
Substrate → Product: Citrate → Isocitrate
Enzyme: Aconitase
Other molecules: H₂O removed then added
Energy intermediates: None
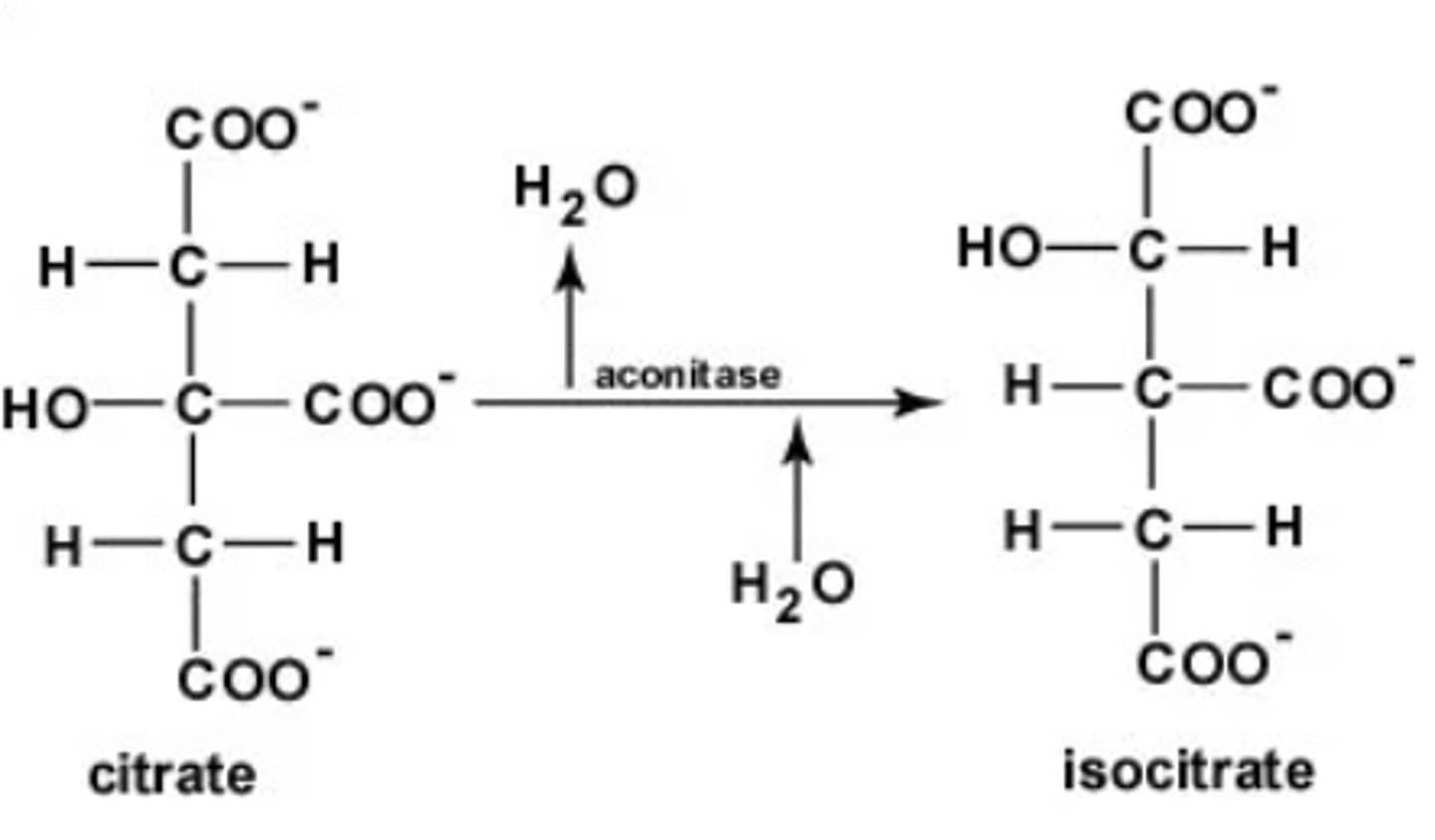
What is step 3 of the Krebs Cycle?
Substrate → Product: Isocitrate → α-Ketoglutarate + CO₂
Enzyme: Isocitrate dehydrogenase
Energy intermediates: NAD⁺ + 2H⁺ +2e⁻ → NADH + H⁺
Other Molecules: CO₂ removed
Notes: First oxidative decarboxylation
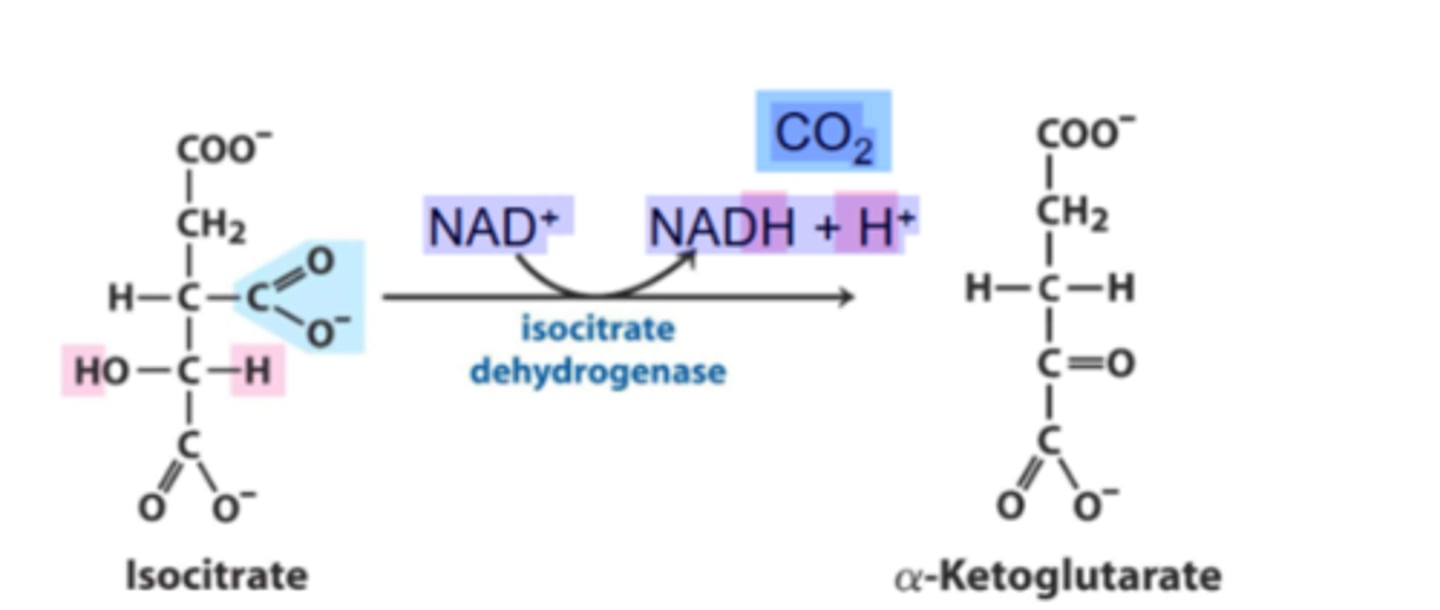
What is step 4 of the Krebs Cycle?
Substrate → Product: α-Ketoglutarate → Succinyl-CoA + CO₂
Enzyme: α-Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
Energy intermediates: NAD⁺ + 2H⁺ +2e⁻ → NADH + H⁺
Other Molecules: CO₂ removed, CoASH added
Notes: Second oxidative decarboxylation; similar to PDH complex.
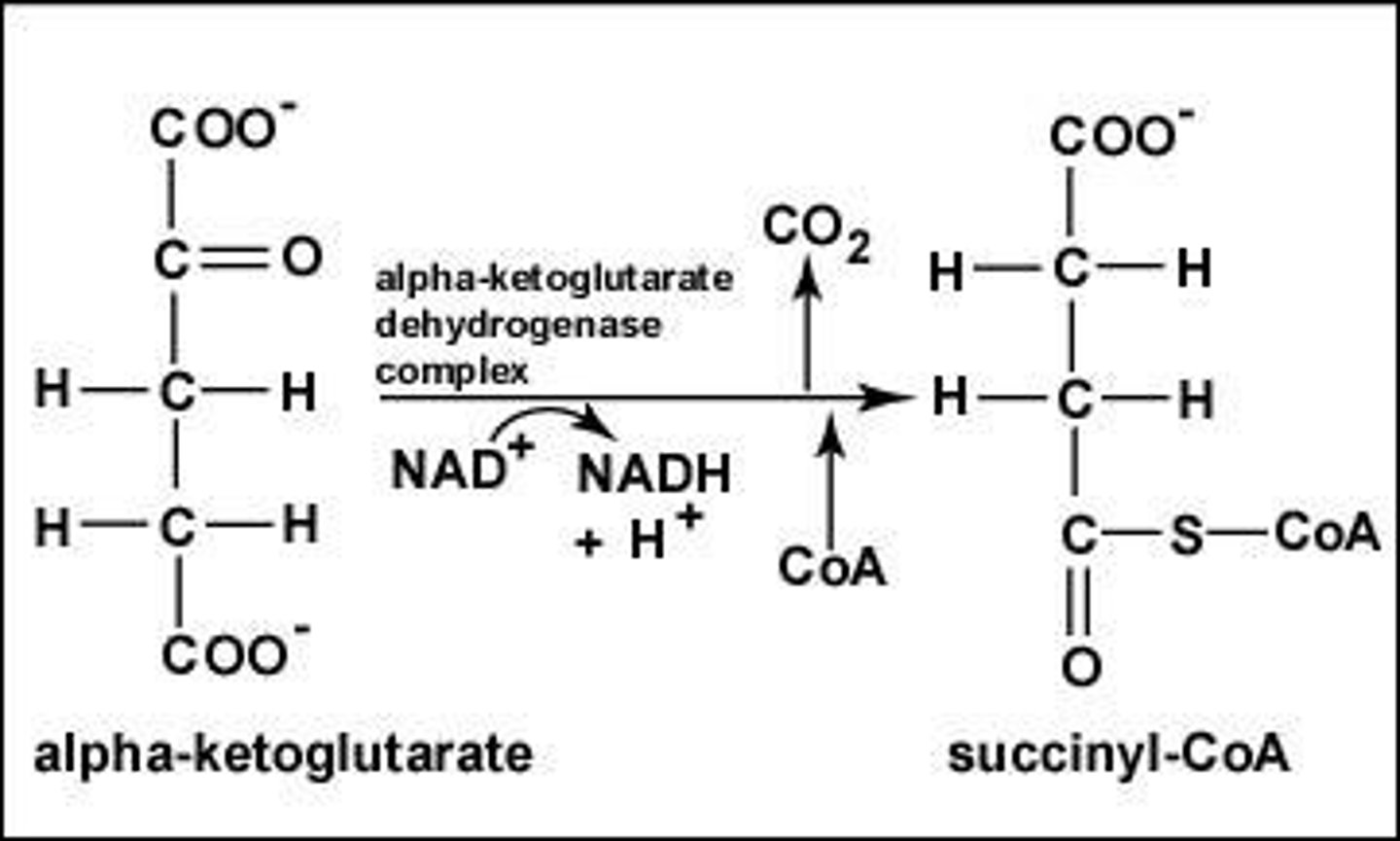
What is step 5 of the Krebs Cycle?
Substrate → Product: Succinyl-CoA → Succinate
Enzyme: Succinyl-CoA synthetase
Energy intermediates: GDP + Pi → GTP and ADP+ iP → ATP
Other Molecules: CoASH released
Other molecules: CoA-SH released.
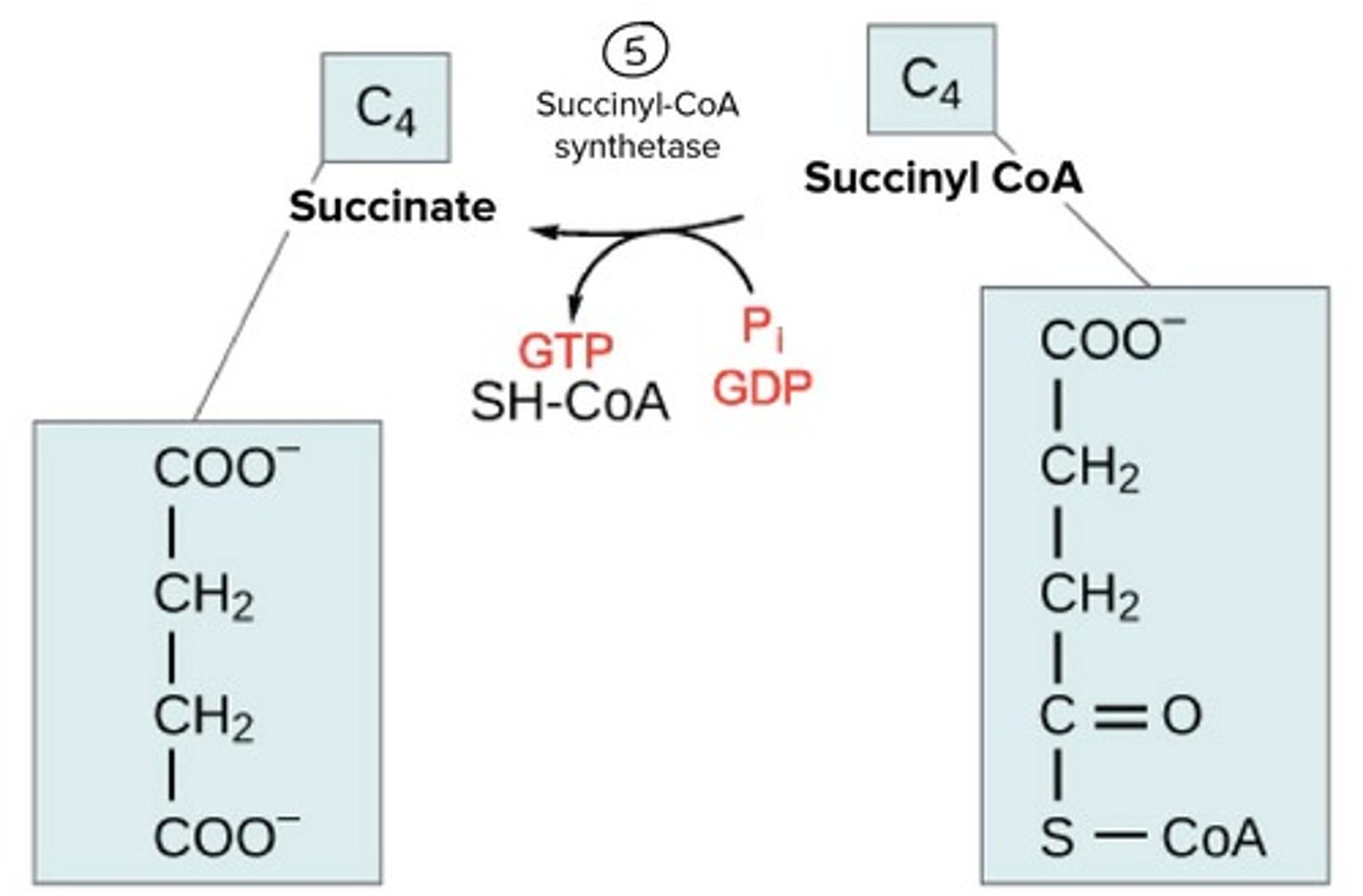
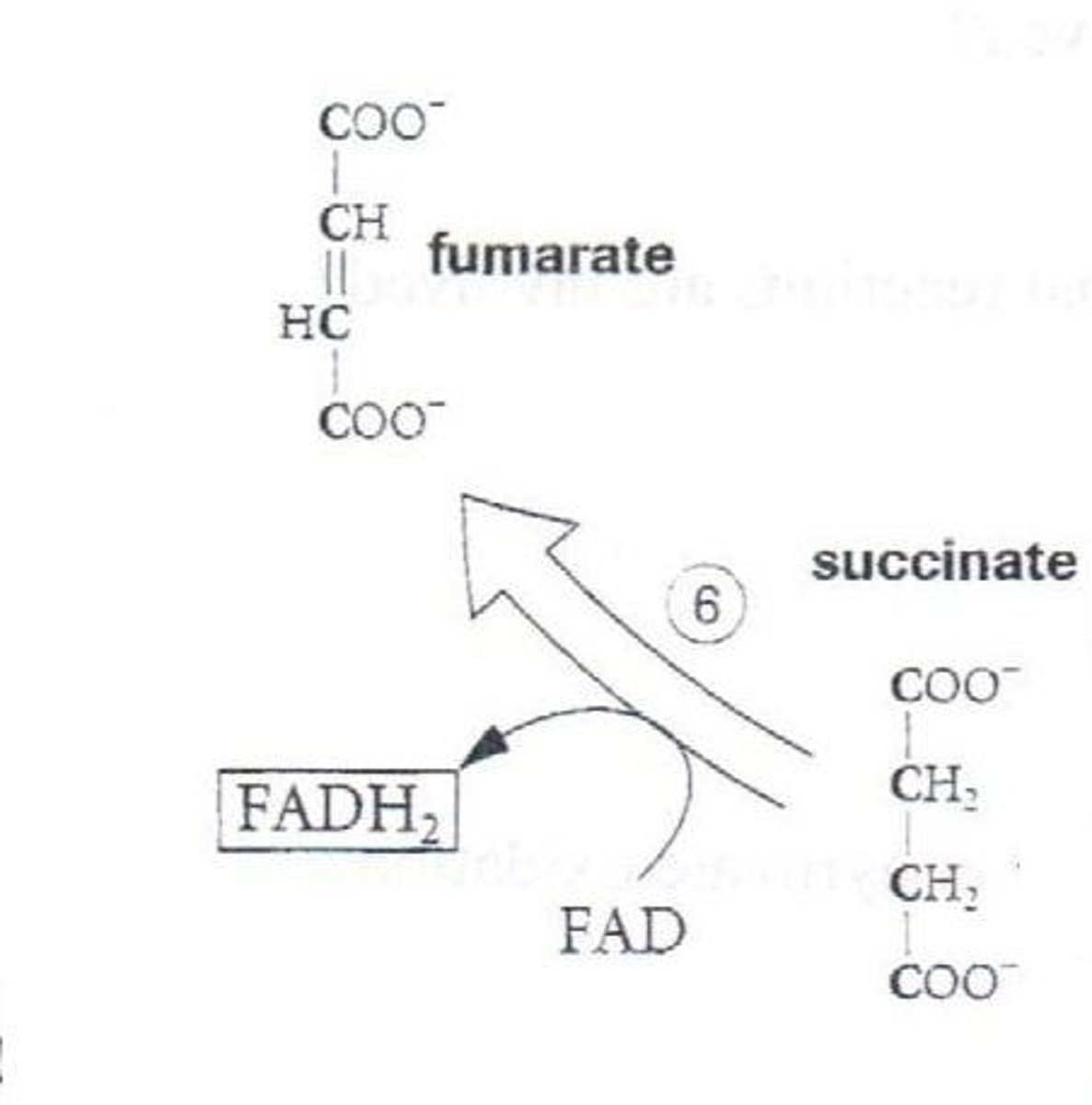
What is step 6 of the Krebs Cycle?
Substrate → Product: Succinate → Fumarate
Enzyme: Succinate dehydrogenase
Energy intermediates: FAD⁺ + 2H⁺ +2e⁻ → FADH₂
Notes: Only membrane-bound enzyme (Complex II of ETC).
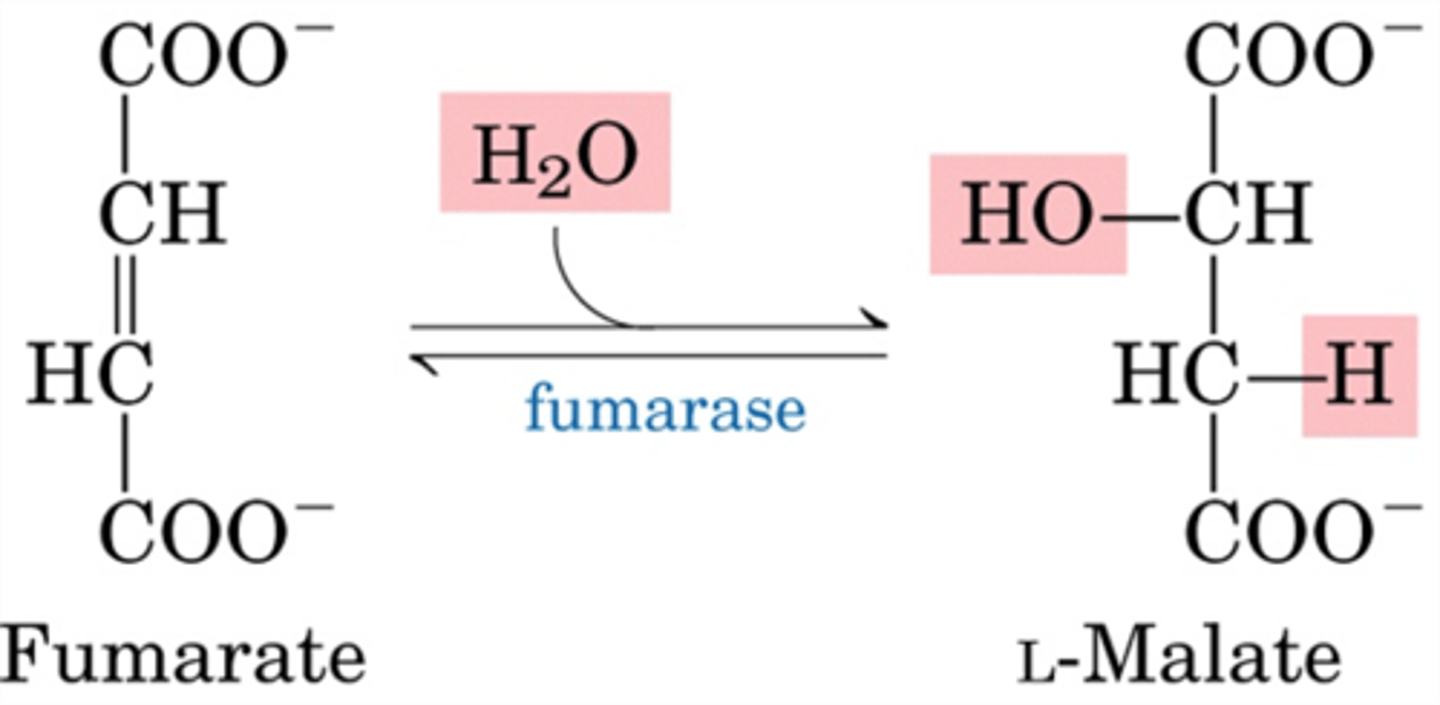
What is step 7 of the Krebs Cycle?
Substrate → Product: Fumarate → Malate
Enzyme: Fumarase
Other molecules: H₂O added
Energy intermediates: None
Notes: Hydration across double bond.
What is step 8 of the Krebs Cycle?
Substrate → Product: Malate → Oxaloacetate
Enzyme: Malate dehydrogenase
Energy intermediates: NAD⁺ + 2H⁺ +2e⁻ → NADH + H⁺
Notes: Regenerates OAA to restart cycle.

What is Complex I of Oxidative Phosphorylation?
NADH dehydrogenase (Complex I)
Function: Transfers electrons from NADH to ubiquinone (CoQ)
Energy intermediates: NADH + H⁺ → NAD⁺ + 2H⁺ +2e⁻
Protons: 4 H⁺ pumped into intermembrane space.
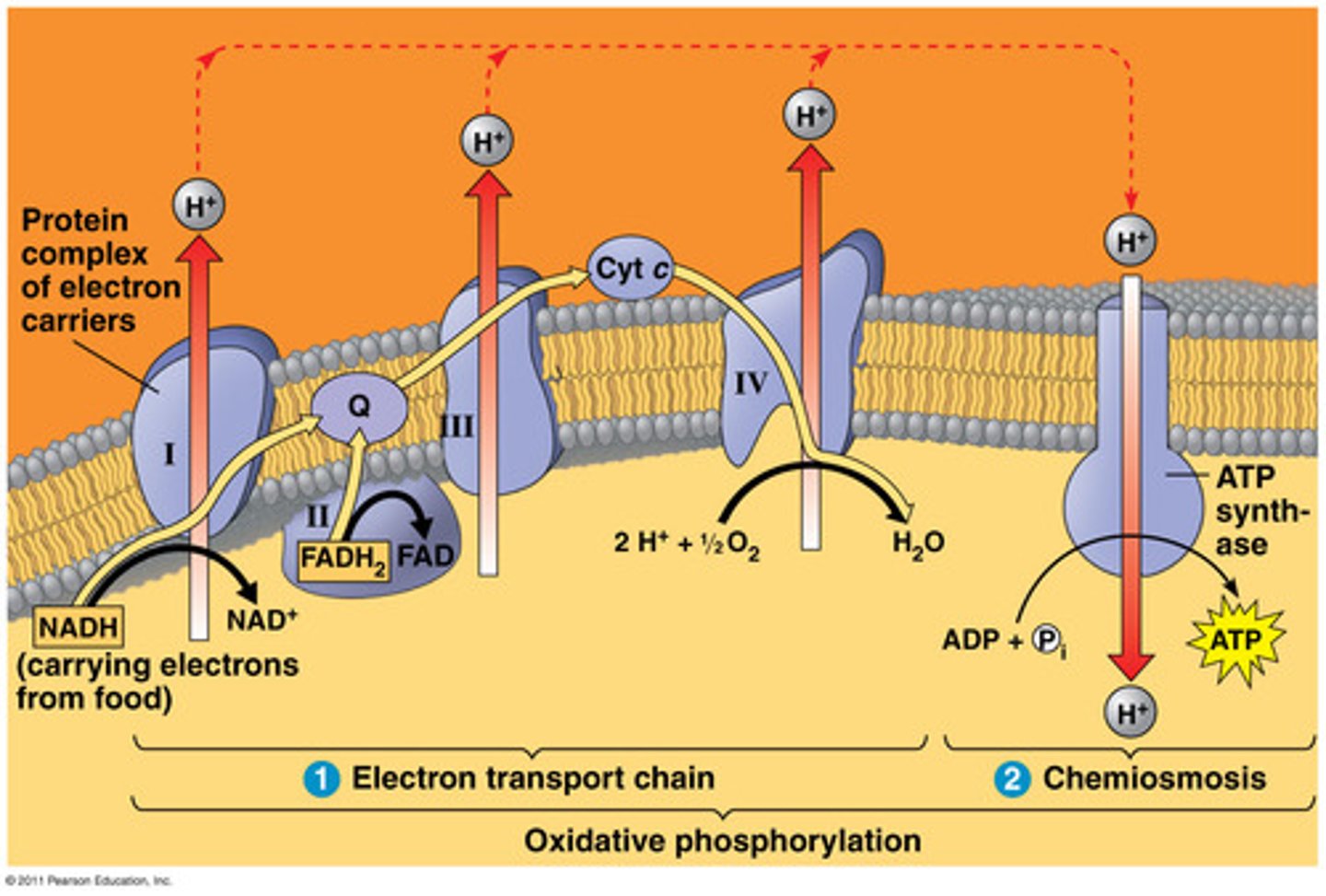
What is Complex II of Oxidative Phosphorylation?
Succinate dehydrogenase (Complex II)
Function: Transfers electrons from FADH₂ to CoQ
Energy intermediates: FADH₂ oxidized to FAD⁺ + 2H⁺ +2e⁻
Protons: none pumped.
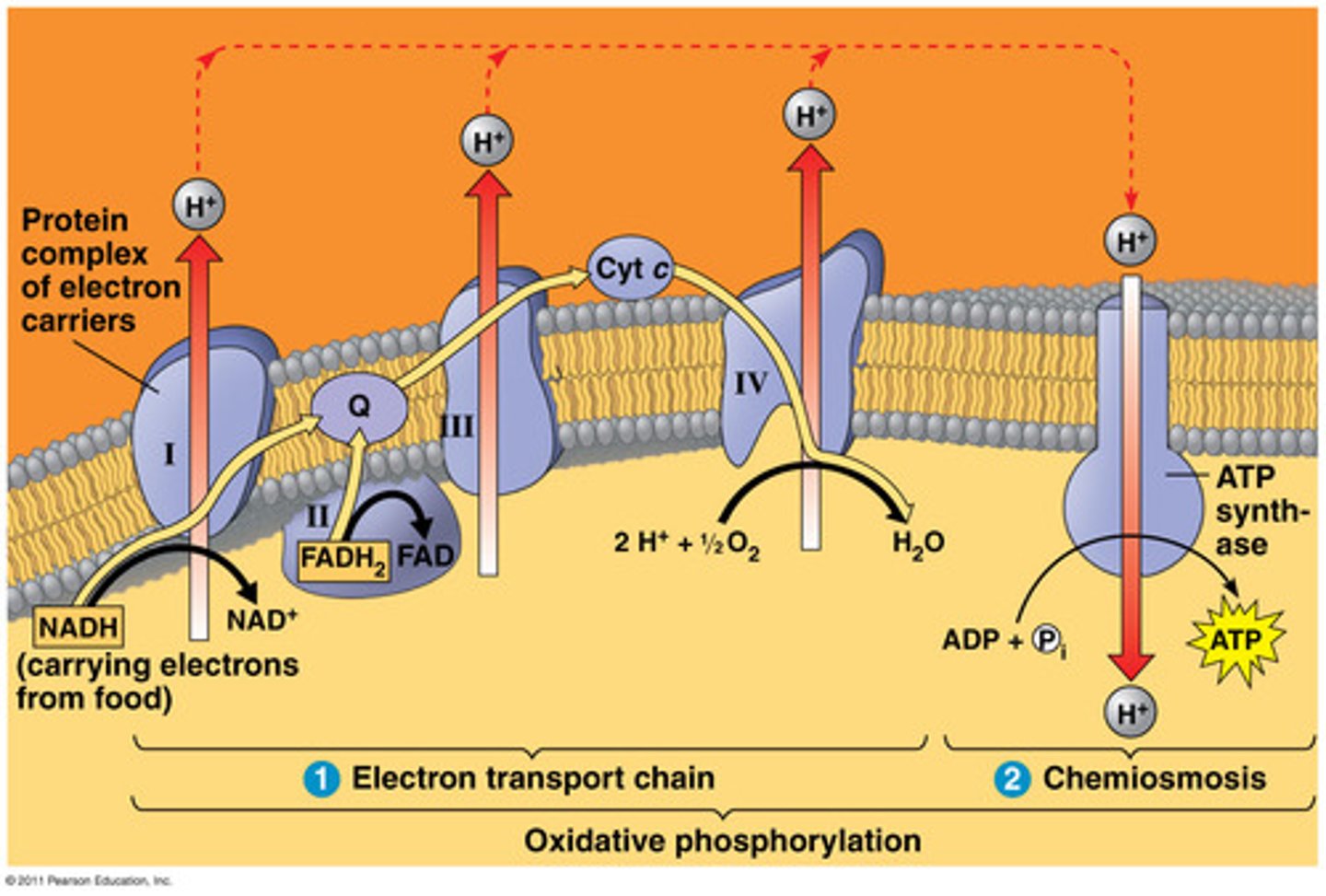
What is Complex III of Oxidative Phosphorylation
Cytochrome bc₁ complex
Function: Transfers electrons from CoQH₂ to cytochrome c
Protons: 4 H⁺ pumped.
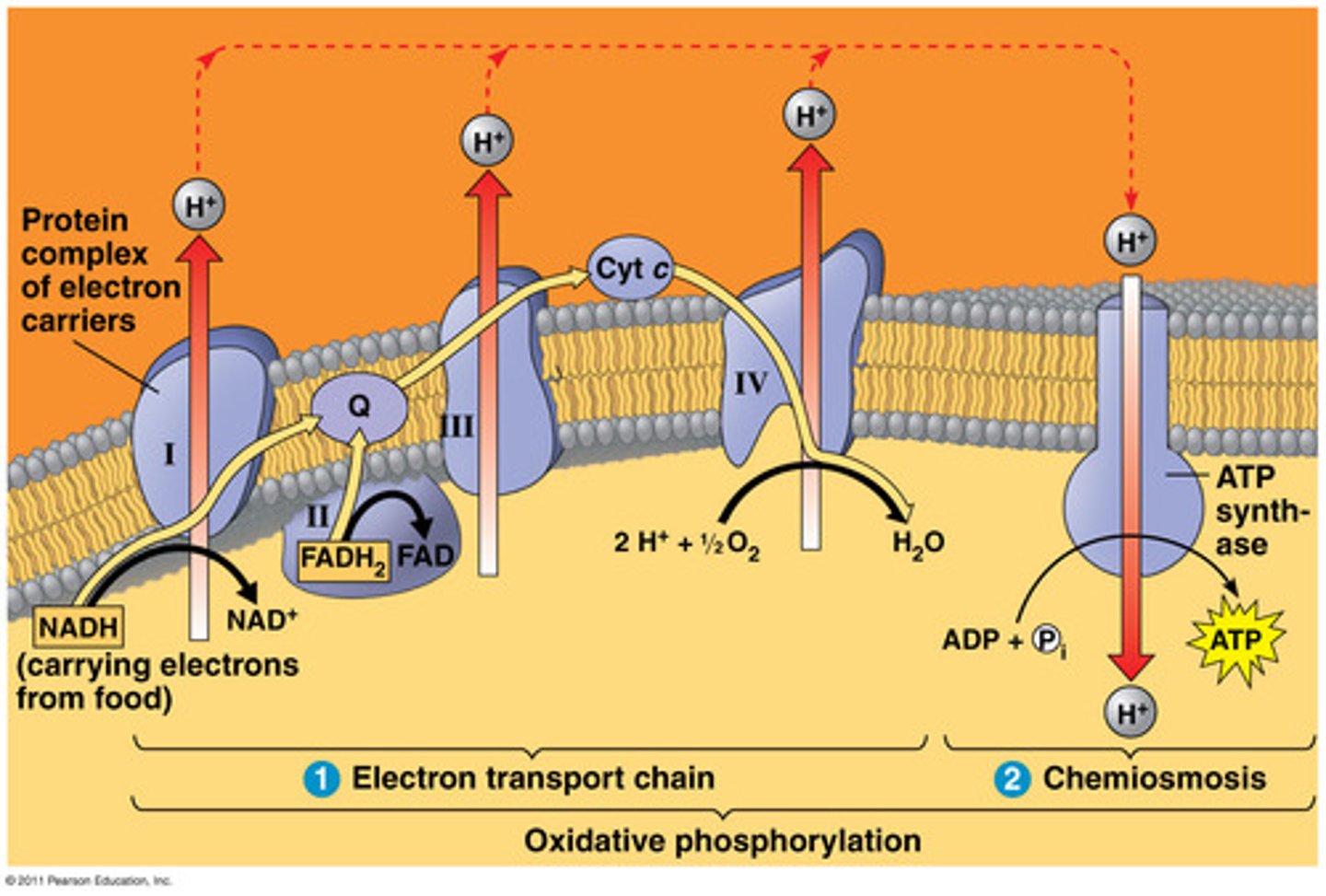
What is Complex IV of Oxidative Phosphorylation
Cytochrome c oxidase
Function: Transfers electrons from cytochrome c to O₂
Other molecules: O₂ reduced → H₂O
Protons: 2 H⁺ pumped.
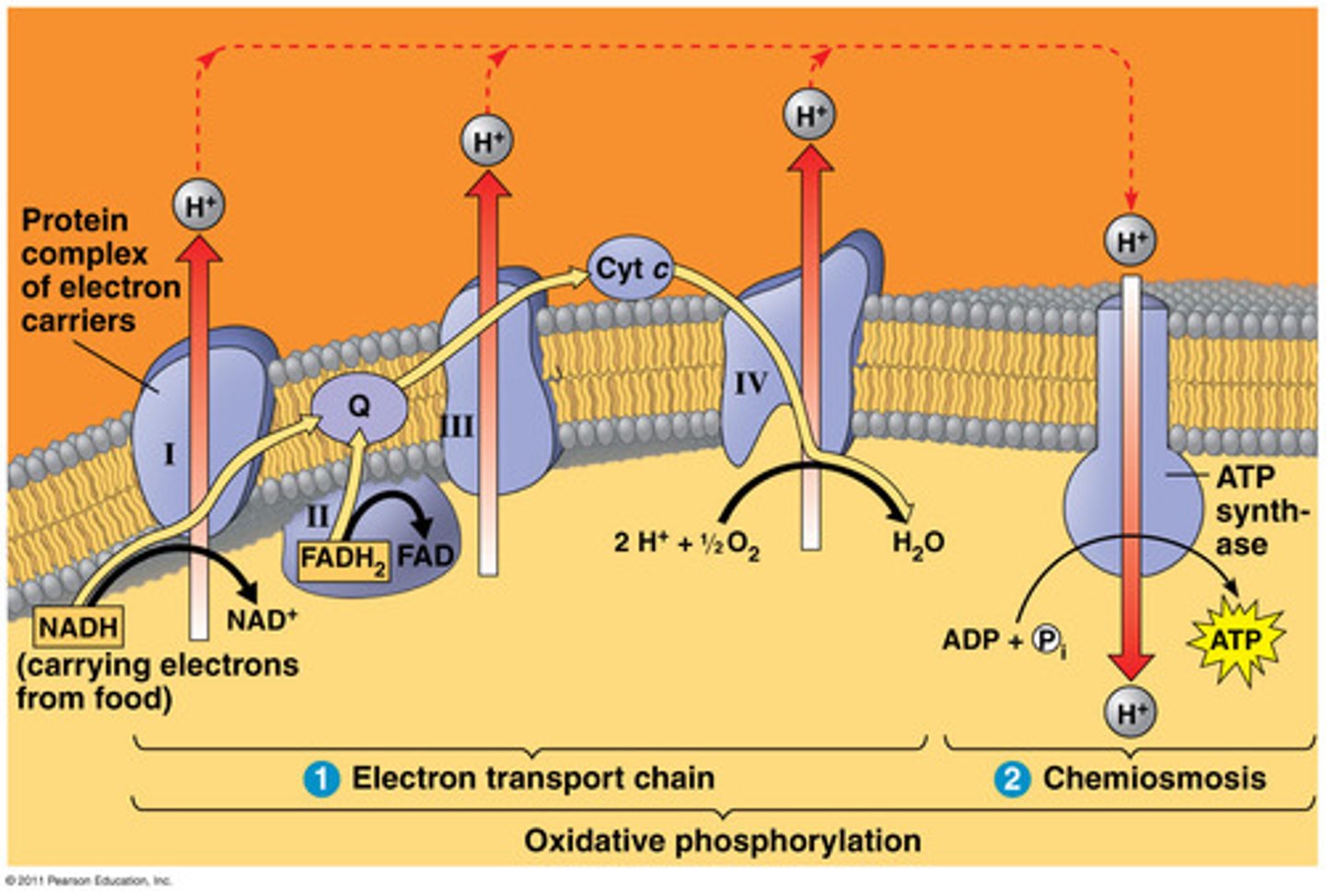
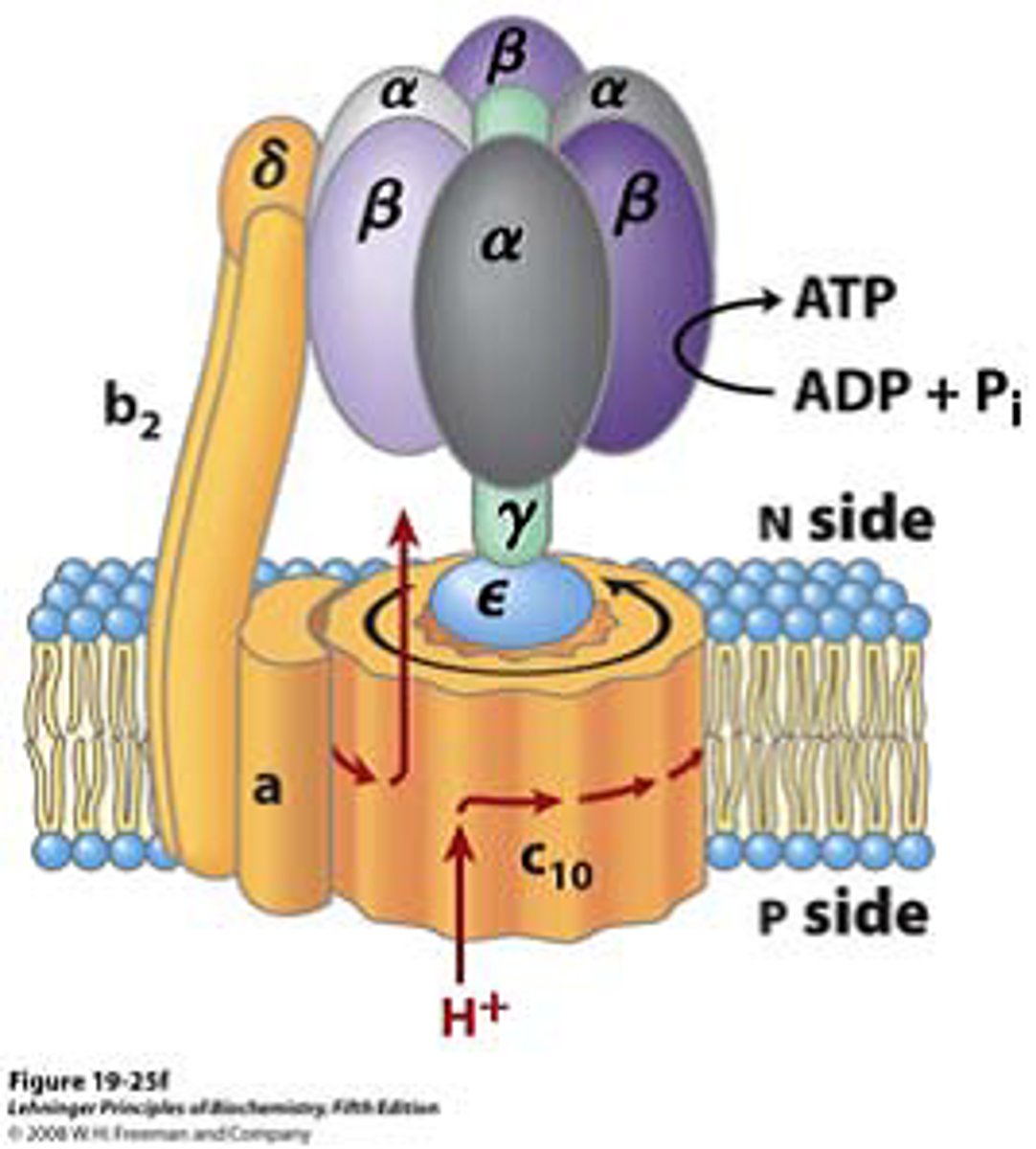
ATP Synthase
Complex V
Function: Uses proton gradient (chemiosmosis) to synthesize ATP from ADP + Pi
Notes: ~3 H⁺ per ATP generated.