OCR A 5.3.1 and 5.3.2 Transition Elements and Qualitative Analysis
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
d block elements
-some are transitional
transition elements
-can form at least 1 stable ion w/ partially filled d-subshell
-not Sc (only forms 1 stable ion w/ 3+ charge which has empty d-subshell) or Zn (only forms 1 stable ion w/ 2+ charge which has full d-subshell)
-Cr & Cu; e from 4s orbital move to 3d orbital to create more stable half full or full 3d subshell
-Cr: 3d54s1
transitional metals properties
-variable oxidation states; sit in 4s and 3d energy levels which are v close
-form coloured ions in sol
-good catalysts
-form coloured ion in sol
why transition metals ions form coloured compounds
-they have partially filled d subshell
Zn ion colour
Zn2+; no colour
Sc ion colour
Sc3+; no colour
Cu ion colour
Cu2+; blue
Cu+; no colour
Fe ion colour
Fe2+; green
Fe3+; brown
Mn ion colour
Mn2+: pink
MnO4-; purple
Vn transition metals colour
-V2+; violet
-V3+; green
-VO2+; blue
-VO+; yellow
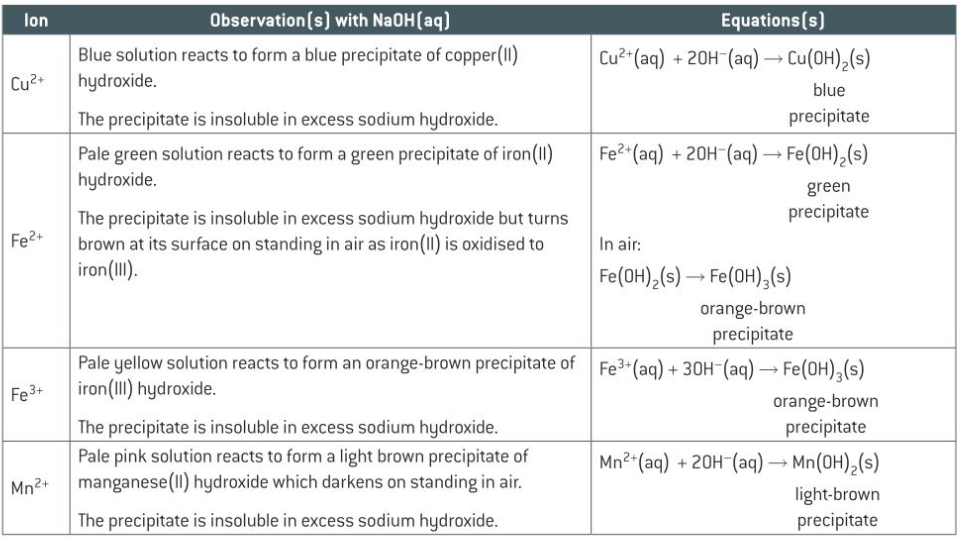
what happens when you add some OH- or NH3 to Cu2+

what happens when you add some OH- or NH3 to Fe2+

what happens when you add some OH- or NH3 to Fe3+

what happens when you add some OH- or NH3 to Mn2+

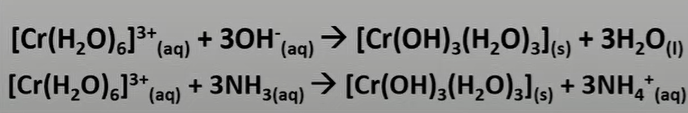
what happens when you add some OH- or NH3 to Cr3+

what happens when you add excess OH- or NH3 to Cu2+

what happens when you add excess OH- or NH3 to Fe2+

what happens when you add excess OH- or NH3 to Fe3+

what happens when you add excess OH- or NH3 to Mn2+

what happens when you add excess OH- or NH3 to Cr3+

why transition metals are good catalysts
-have variable ox states
-receive and lose e in d orbital to speed up reaction
-has surfaces that allow substances to absorb to surface which lower Ea of reaction
-makes product faster
-used at low temp
-save energy and money
risks of transition metal catalyst
-Cu; long term exposure causes damage to liver or cause copper poisoning
-Mn; long term exposure; cause psychiatric issues and physical tremors
how Cu copper acts as a catalyst for Zn + 2H+ → Zn2+ + H2
-Zn + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu (intermediate)
-Cu + 2H+ → H2 + Cu2+
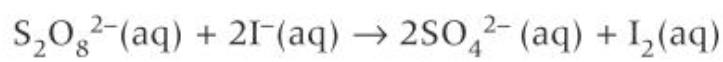
how Fe2+ catalyses
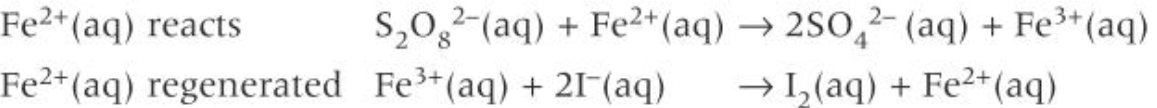
effect of ox state on transition metal
-in the lower ox state transition metal form monoatomic ions
-in higher ox state; they exist as poly atomic ions
-specie containing transition element in its highest ox state is often a strong oxidising agent
ligand
-donates a lone pair to metal ion
-forms dative covalent coordinate bond with metal ion
-can be mono/bi/polydentate
monodentate ligands
-have one pair of e
-H2O
-NH3
-Cl-
-CN-
-OH-
bidentate ligands
-have 2 lone pairs of e
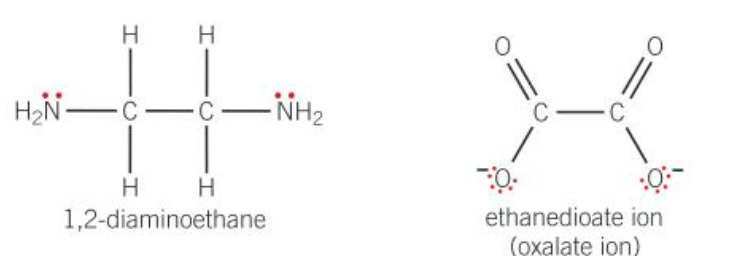
-1,2-diaminoethane(en)
-ethanedioate ion (oxalate)
coordinate number
equal to number of dative covalent bonds attached to central metal ion
complex ion
formed when ligands surround central metal ion with dative covalent bonds
shapes of complex ion
octahedral
tetrahedral
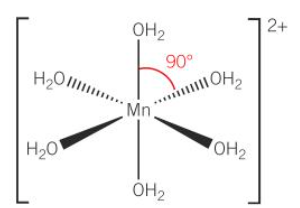
octahedral
-6 coordinate bonds
tetrahedral
-4 coordinate bonds
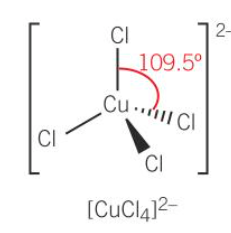
why 4 Cl surround Cu but 6 H2O surround Cu
-Cl- is bigger ligand than water ligand
-therefor less Cl ligand can surround Cu2+ ion
sqr planar
-coordination number; 4
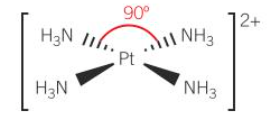
cis platin
-anti cancer drug
-sqr planar; 90
-Cl ions easy to displace; detach from complex
-complex can bond to N atoms on DNA in cancer cell
-stops cell from reproducing from cell division
-cell dies as it is unable to repair itself
-also prevents healthy cells from prod
-effects cells in blood which can supress immune system
-inc risk of infection
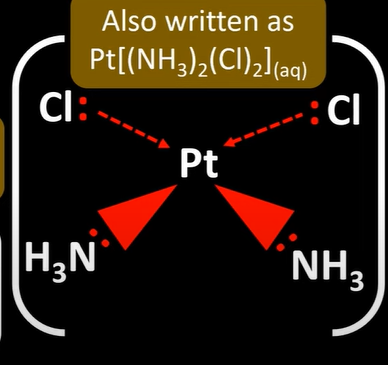
optical isomerism
-non superimposable mirror images
-octahedral complex w/ 2 or more bidentate ligands show optical isomers
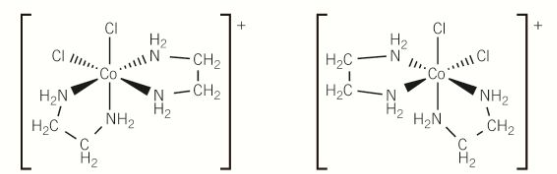
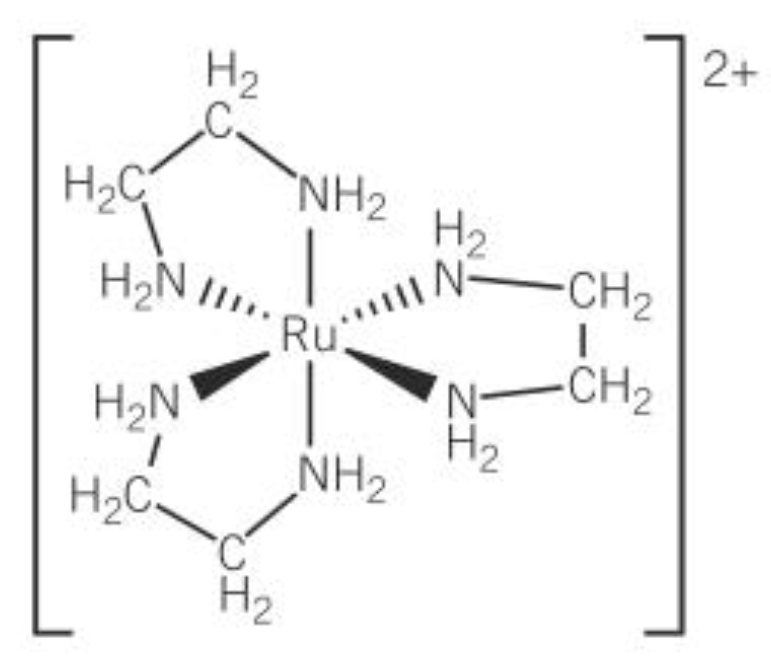
optical isomer of this
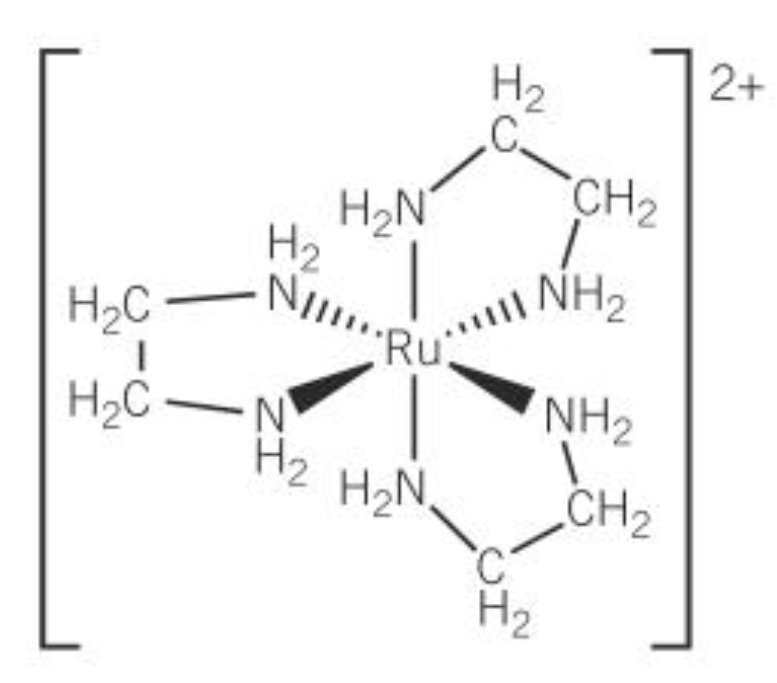
stereoisomer
same structural formula but a different arrangement of atoms in space
cis trans isomerism in sqr planar complex
-have 2 identical ligands attached to central metal ion
-cis; 2 identical groups are next to each other
-trans; 2 identical groups are oppo each other
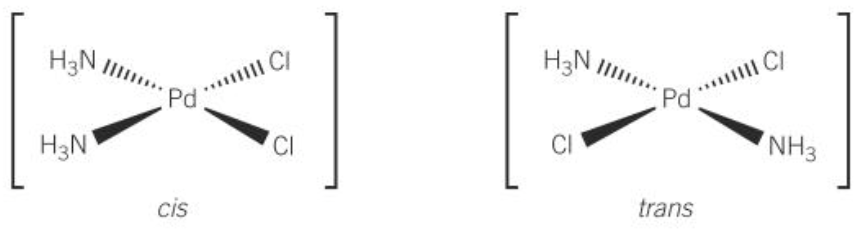
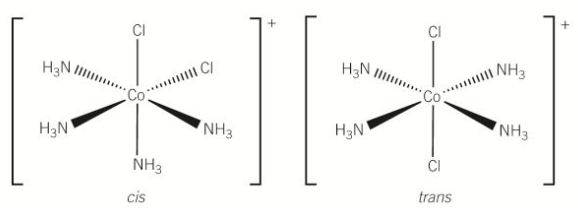
cis trans isomerism in octahedral complex; monodentate ligand
-contain 4 of 1 type of ligand and 2 of another type of ligand
-cis; the 2 ligands are next to each other
-trans; the 2 ligands are oppo to each other
cis trans isomerism in octahedral complex; bidentate ligand
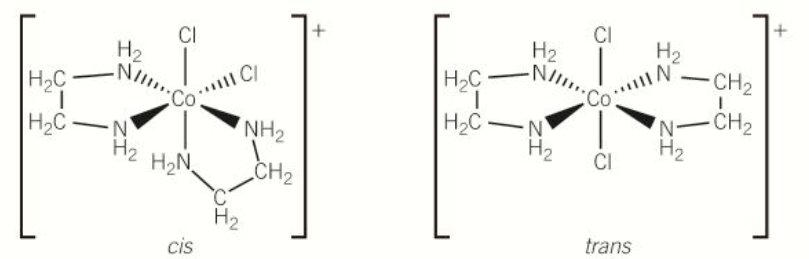
ligand substitution
-reaction where 1 ligand in a complex is replaced by another ligand
-occurs if second ligand will form a more stable complex (delta G is more -ive)
transition metal substitution reaction
-colour change can exist when ligands in a complex exchange

transition metal substitution reaction
-partial sub
-reaction w/ excess ammonia
-pale blue → pale blue ppt(Cu(OH)2) → deep blue sol

[Cr(H2O)6]3+ colour
-pale purple colour
Cr2(SO4)3 dissolved in water
-from pale purple to green
-[Cr(H2O)5SO4]+
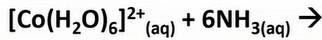
transition metal substitution reaction

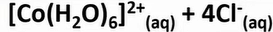
transition metal substitution reaction
-as Cl is a larger ligand than H2O
-only 4 Cl- ion ligands can fit round

-if u add conc HCl carefully
-green sol forms; mix of yellow and blue
-Cl ligand is large so coordination number decrease
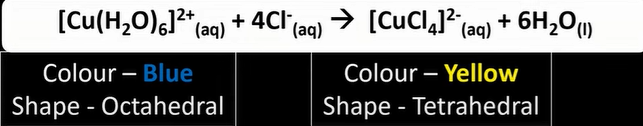


what does the colour of complex ion depend on
-size of ΔE
-which is affected by change of ox state
-coordinate number and change of ligand
haemoglobin
-protein used to transport O around blood in body
-present in all RBC
-contains 4 protein chains held tgthr by weak intermolecular molecules
-each protein contains haem molecule
haemoglobin structure
-haem is a multidentate ligand
-octahedral
-central atom has 6 coordinate bonds
-4 are N
-1 is a large protein called globin
-1 is an O or water molecule
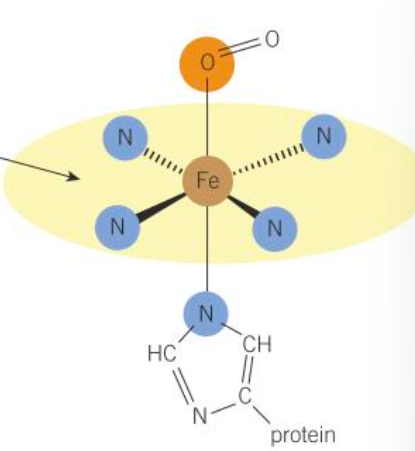
how haemoglobin transports O
-as blood passes thru lungs
-Fe2+ in haemoglobin bonds dative covalently to O due to inc O pressure in capillaries of lungs
-H2O is replaced by O2
-forms oxyhaemoglobin which releases this O to body cells when needed
-Fe2+ in haemoglobin in rbc can dative covalently bond to CO2
-which is carried back to lungs
-released from rbc and exhaled
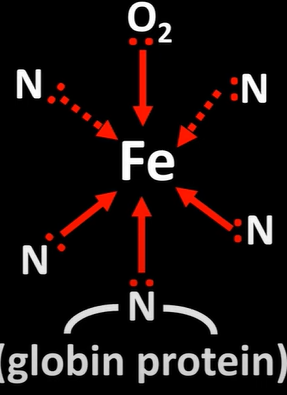
haemoglobin and carbon monoxide
-CO can also bind to Fe2+ ion haemoglobin
-when CO inhaled ligand substitution takes place
-O in haemoglobin is replaced by CO
-CO binds more strongly to O; small conc of CO prevent large proportion of haemoglobin from carrying O
-bond is so strong is irreversible as it is more stable strong as delta G is negative but to bond with O delta G in presence of CO is positive
-if CO conc gets too high, O cant be transported; death
Precipitation reaction
-occurs when 2 aq sol containing ions react together
-to form an insoluble ionic solid called precipitate
-transition metals react w/ NaOH and aq ammonia to form precipitates
-some will dissoleve in excess NaOH or ammonia to form complex ions