Exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 5:18 PM on 10/13/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
1
New cards
what does biology study
how the principles of chemistry and physics apply to living organisms
2
New cards
most common elements of living organisms
* oxygen
* carbon
* hydrogen
* nitrogen
* carbon
* hydrogen
* nitrogen
3
New cards
elements occuring as ions
* calcium
* phosphorus
* potassium
* sodium
* chlorine
* magnesium
* phosphorus
* potassium
* sodium
* chlorine
* magnesium
4
New cards
what is a cation and give examples
a positively charged ion
* sodium
* potassium
* calcium
* magnesium
* sodium
* potassium
* calcium
* magnesium
5
New cards
what is an anion and give an example
a negatively charged ion
* chloride
* chloride
6
New cards
mass of an electron
0
7
New cards
how to calculate number of neutrons
atomic mass - atomic number
8
New cards
valence electrons
an opportunity to form a chemical bond
9
New cards
covalent bond
bond created by the sharing of electrons
10
New cards
nonpolar covalent bond
electrons are shared equally between atoms forming the bond
* no charge separations
* no charge separations
11
New cards
polar covalent bond
electrons are shared unequally between the atoms forming the bond
* have slight charge separation
* have slight charge separation
12
New cards
ionic bond
a bond formed by the giving and taking of an electron
13
New cards
hydrogen bond
bonds that result from polar covalent bonds in between two molecules
14
New cards
water molecule drawing
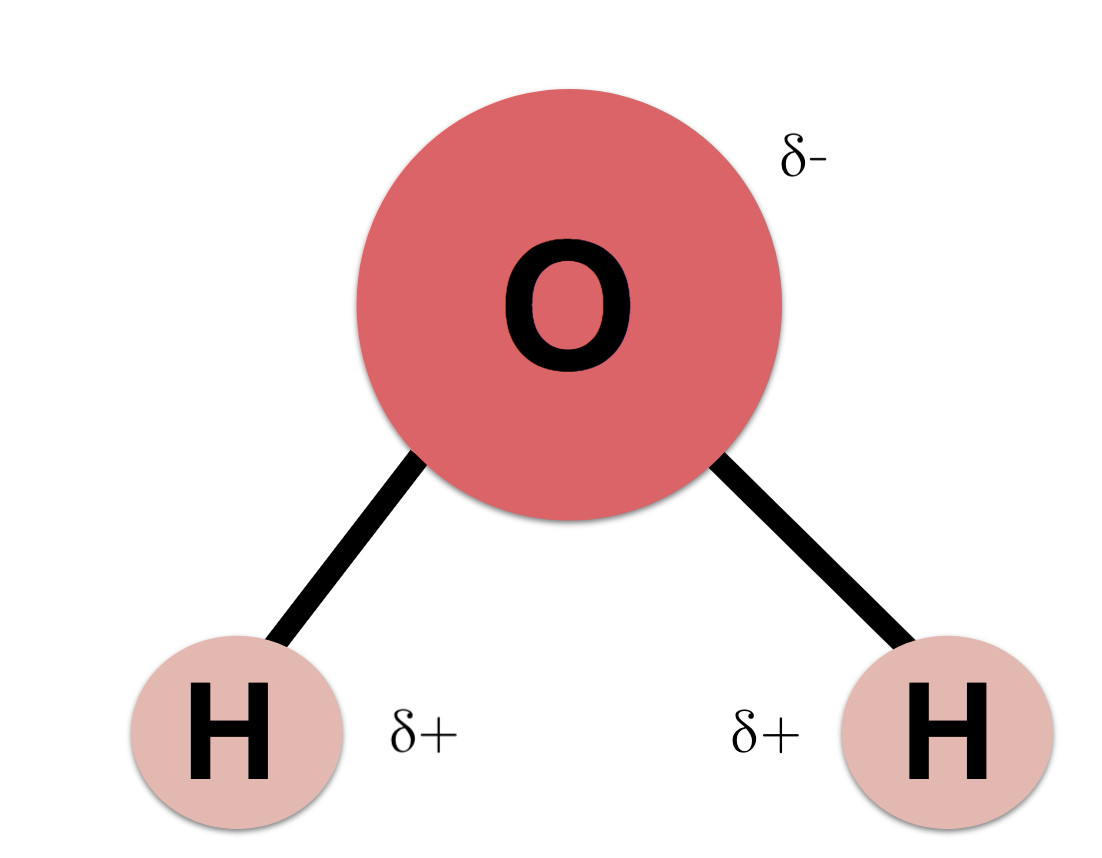
15
New cards
molecular oxygen drawing
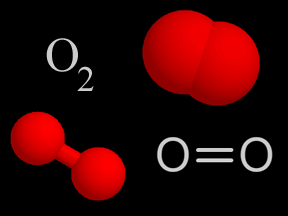
16
New cards
hydrogen bonds between water molecules
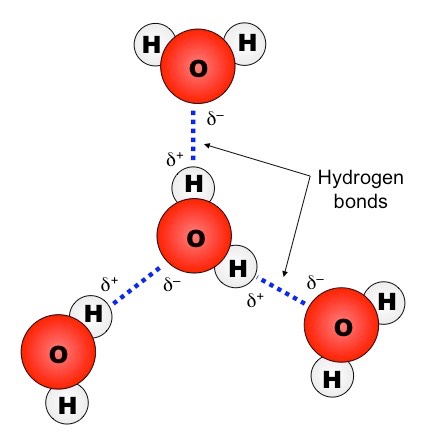
17
New cards
emergent properties of water
* cohesion behavior
* ability to moderate temperature
* expansion upon freezing
* versatility as a solvent
* ability to moderate temperature
* expansion upon freezing
* versatility as a solvent
18
New cards
cohesion
results from water molecules being attracted to each other
19
New cards
adhesion
attraction of a molecule to other polar or charged molecules
20
New cards
surface tension
ability of a liquid to resist forces pulling on the liquids surface due to cohesion
21
New cards
ionic solutes
the surrounding of a solute ion with water molecules all facing the opposite charge
22
New cards
hydophilic
* substances that have an affinity for water
* water soluble
* need to be charged or have polarity
* water soluble
* need to be charged or have polarity
23
New cards
hydronium ion
H3O+
24
New cards
hydroxide ion
OH-
25
New cards
hydrogen ion
H+ (proton)
26
New cards
acid vs base
* acid adds H+ to a solution
* base removes H+ from a solution
* base removes H+ from a solution
27
New cards
equation for pH
pH = -log\[H+\]
28
New cards
buffer
substances that minimize changes in pH by accepting or donating H+ ions
29
New cards
what does organic chemistry study
carbon-based compounds
30
New cards
isomers
have the same chemical formula but different chemical structures
31
New cards
7 functional groups
hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, sulfhydryl, phosphate, methyl
32
New cards
hydroxyl
\
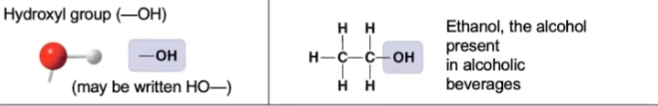
33
New cards
carbonyl
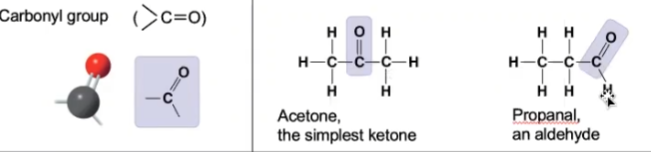
34
New cards
carboxyl
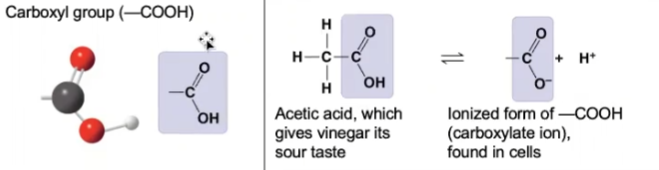
35
New cards
amino
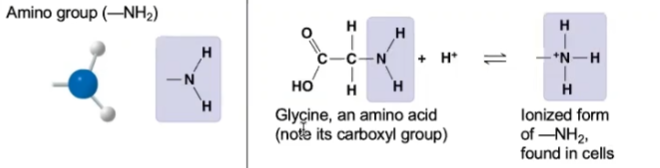
36
New cards
sulfhydryl
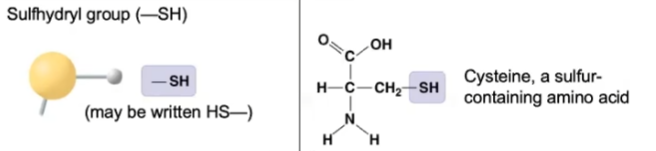
37
New cards
phosphate
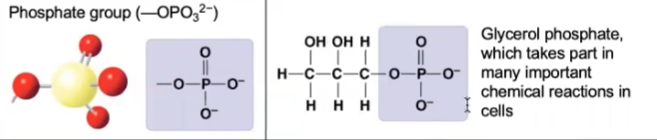
38
New cards
methyl
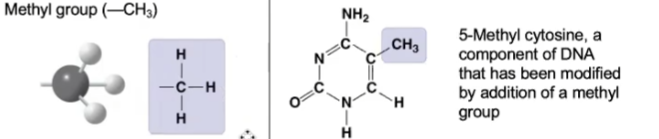
39
New cards
four types of large biological molecules
* carbohydrates
* lipids
* proteins
* nucleic acids
* lipids
* proteins
* nucleic acids
40
New cards
what large molecule is not a polymer (macromolecule)
lipids
41
New cards
polymer
molecule made by joining together multiple monomers
42
New cards
polymerization
process of making a polymer from monomers
* occurs via dehydration reaction (removing water)
* occurs via dehydration reaction (removing water)
43
New cards
depolymerization
action of breaking down a polymer into monomers
* occurs via hydrolysis (adding water)
* occurs via hydrolysis (adding water)
44
New cards
function of carbohydrates
* energy storage
* structural support
* structural support
45
New cards
monomer of carbohydrates
monosaccharide or simple sugar
* glucose, fructose
* glucose, fructose
46
New cards
how many carbons do pentose and hexose have
* pentose = 5
* hexose = 6
* hexose = 6
47
New cards
monosaccharide
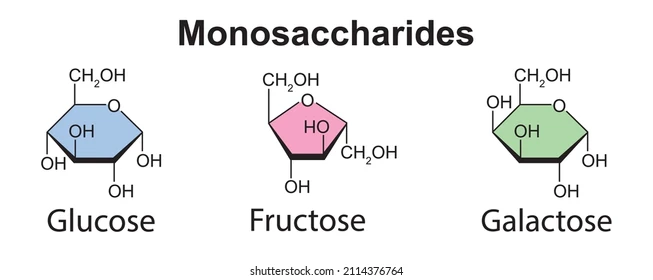
48
New cards
disaccharide
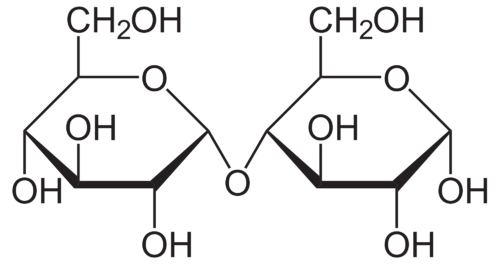
49
New cards
examples of disaccharides
* maltose
* sucrose
* lactose
* sucrose
* lactose
50
New cards
parts of polsaccharides
* energy storage
* starch (plants)
* glycogen (animals)
* structure
* cellulose (plants)
* chitin (fungi)
* starch (plants)
* glycogen (animals)
* structure
* cellulose (plants)
* chitin (fungi)
51
New cards
types of carbohydrates
* monosaccharides
* disaccharides
* polysaccharides
* disaccharides
* polysaccharides
52
New cards
3 groups of lipids
* fats (triglycerides)
* phospholipids
* steroids
* phospholipids
* steroids
53
New cards
functions of fats (triglycerides)
* energy storage
* cushion organs
* insulation
* cushion organs
* insulation
54
New cards
what makes up triglycerides
* glycerol
* 3 fatty acids
* 3 fatty acids
55
New cards
what makes up phospholipids
* two fatty acids (2 hydrophobic tails)
* phosphate - R group (hydrophilic head)
* phosphate - R group (hydrophilic head)
56
New cards
amphipathic molecules
any molecule that has a hydrophilic part and a hydrophobic part
57
New cards
function of phospholipids
* formation of plasma membrane
* formation of intracellular membrane
* formation of intracellular membrane
58
New cards
functions of steroids
* stabilize plasma membrane
* steroid hormones
* steroid hormones
59
New cards
example of a steroid
cholesterol
60
New cards
globular vs fibrous protein
* globular
* spherical
* soluble
* fibrous
* long and thin
* less soluble
* spherical
* soluble
* fibrous
* long and thin
* less soluble
61
New cards
what is the monomer of protein
amino acid
62
New cards
amino acid structure
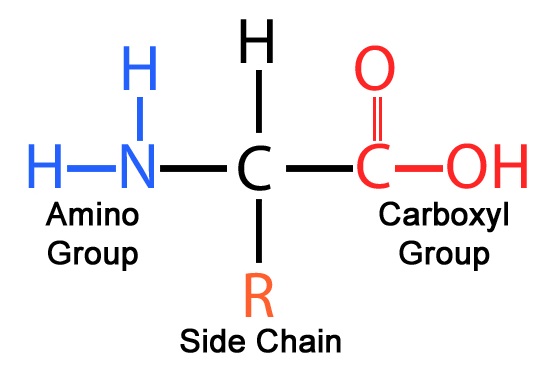
63
New cards
polypeptide
long string of amino acids that are linked by peptide bonds
64
New cards
c-terminus
the end of protein that has a free carbon group
65
New cards
n-terminus
the start of protein that has a free amino group
66
New cards
four levels of protein structure
* primary
* secondary
* tertiary
* quaternary
* secondary
* tertiary
* quaternary
67
New cards
primary structure of protein
linear chain of amino aicds
68
New cards
secondary structure of protein
regions stabilized by hydrogen bonds between atoms of the polypeptide backbone
* alpha helix
* beta pleated sheet
* alpha helix
* beta pleated sheet
69
New cards
tertiary structure of proteins
3-dimensional shape stabilized by interactions between side chains
70
New cards
quaternary structure of protein
association of two or more polypeptides
71
New cards
denaturation
when a protein loses its shape (unfolding)
72
New cards
denaturing agents
pH, heat, agitation, etc. things that cause denaturation
73
New cards
renaturation
returning a protein to its original shape/form
74
New cards
function of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA)
information storage and use of the information
75
New cards
what is the monomer of nucleic acids
nucleotides
76
New cards
parts of a nucleotide
* sugar
* 5 carbon sugar
* phosphate
* nitrogen containing base (nitrogenous)
* 5 carbon sugar
* phosphate
* nitrogen containing base (nitrogenous)
77
New cards
polynucleotide parts
* sugar backbone
* nitrogenous base
* 5’ end (phosphate end)
* 3’ end (hydroxyl end)
* nitrogenous base
* 5’ end (phosphate end)
* 3’ end (hydroxyl end)
78
New cards
resolution
measure of how close two objects can be together and still be seen as separate
79
New cards
light microscope features
* uses visible light
* uses glass lenses
* use dyes and stains for contrast
* uses glass lenses
* use dyes and stains for contrast
80
New cards
electron microscope features
* uses electrons as illumination
* uses magnets instead of glass lenses
* uses heavy metals for contrast
* uses magnets instead of glass lenses
* uses heavy metals for contrast
81
New cards
types of electron microscopes
* transmission electron microscope (TEM)
* scanning electron microscope (SEM)
* scanning electron microscope (SEM)
82
New cards
cell fractionation
breaking a cell apart and looking at the various parts
83
New cards
what is the basic unit of life
cell
84
New cards
minimal structure required by all cells
* plasma membrane
* ribosomes
* cytosol
* DNA
* ribosomes
* cytosol
* DNA
85
New cards
characteristics of prokaryotic cells
* nucleoid - region
* smaller
* found in bacteria or archaea
* DNA has single circular chromosome
* smaller
* found in bacteria or archaea
* DNA has single circular chromosome
86
New cards
characteristics of eukaryotic cells
* nucleus - membrane enclosed structure
* larger
* found in eukarya
* has multiple linear chromosomes
* larger
* found in eukarya
* has multiple linear chromosomes
87
New cards
main parts of a eukaryotic cell
* plasma membrane
* nucleus
* cytoplasm
* extracellular structures
* nucleus
* cytoplasm
* extracellular structures
88
New cards
organelle
complex internal structures that eukaryotic cells have in their cytosol
89
New cards
what organelles have 2 membranes
mitochondria and chloroplasts
90
New cards
nuclear envelope
2 membranes surrounding the nucleus
91
New cards
nuclear pores
channels that allow macromolecules to move in and out of the nucleus
92
New cards
nuclear lamina
network of proteins that support the inner nuclear membrane
93
New cards
nuclear matrix
help form attachment sites for DNA
94
New cards
chromatin
DNA wrapped up with protein
95
New cards
nucleolus
area where DNA is being transcribed to RNA
96
New cards
cytosol
thick liquid loaded with proteins
97
New cards
ribosomes
make proteins
98
New cards
endomembrane system
connects the nucleus to the plasma membrane
99
New cards
parts of endomembrane system
* nuclear envelope
* ER
* transport vesicle
* Golgi apparatus
* lysosomes
* plasma membrane
* secretory vesicles
* vacuoles
* ER
* transport vesicle
* Golgi apparatus
* lysosomes
* plasma membrane
* secretory vesicles
* vacuoles
100
New cards
rough ER function
involved in making proteins