Statistical Inference Definitions
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Sample space
All possible outcomes of an experiment
Events
Subsets of the sample space
Probability distribution (Pr)
Assigns numbers between 0 and 1 to events with pr(omega) = 1
Definition 1.1 (complement intersection and union)

Definition 1.2 (addition rule) (inclusion-exclusion)
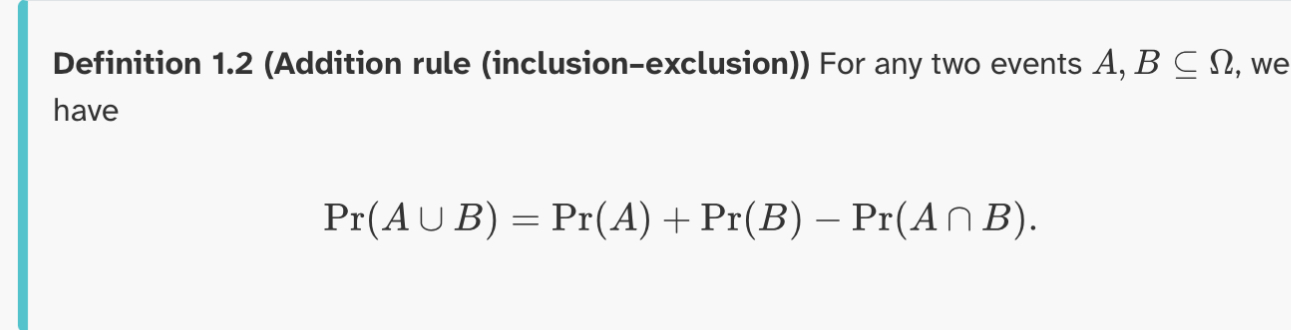
Definition 1.3 (mutually exclusive, exhaustive events, and partitions)

Definition 1.4 (conditional probability)

Definition 1.5 (independence)

Definition 1.6 (Marginal Distribution)

Definition 1.7 (Conditional Densities)

Definition 1.8 (Independence)

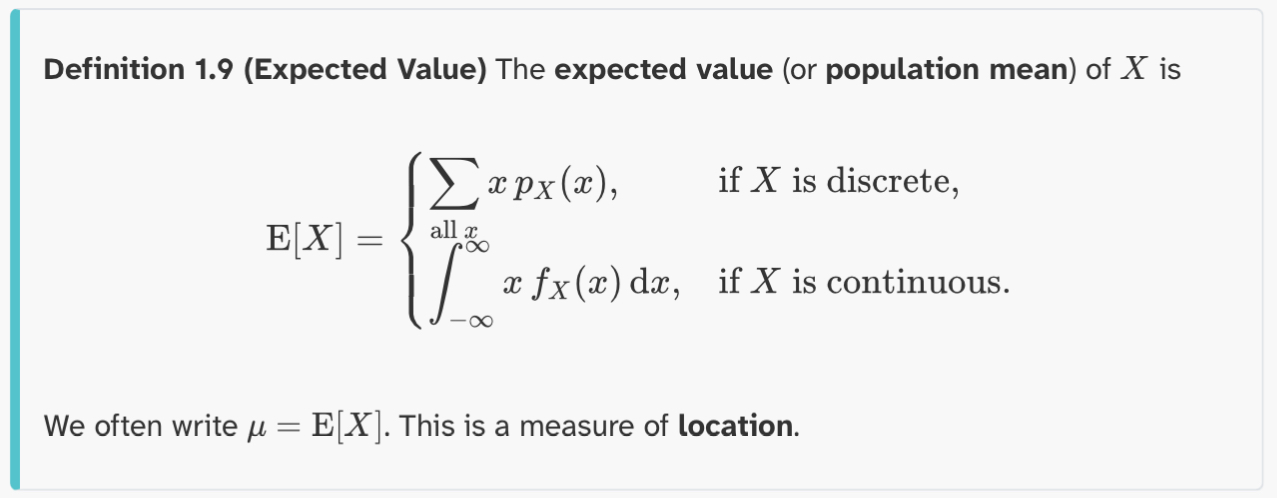
Definition 1.9 (Expected Value)
Definition 1.10 (expectation of g(X))

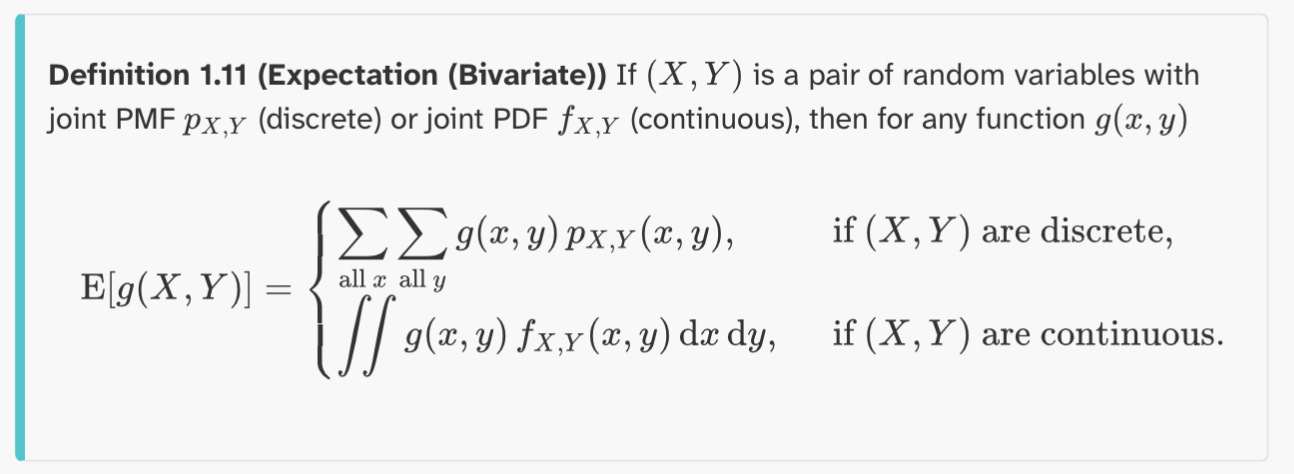
Definition 1.11 (Expectation (Bivariate))
Definition 1.12 (Moments)
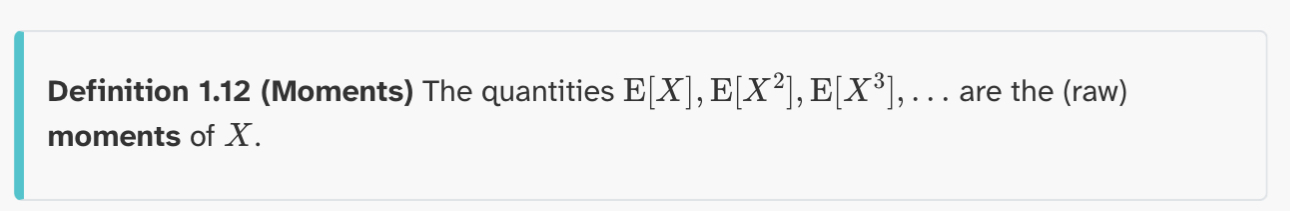
Definition 1.13 (Variance)

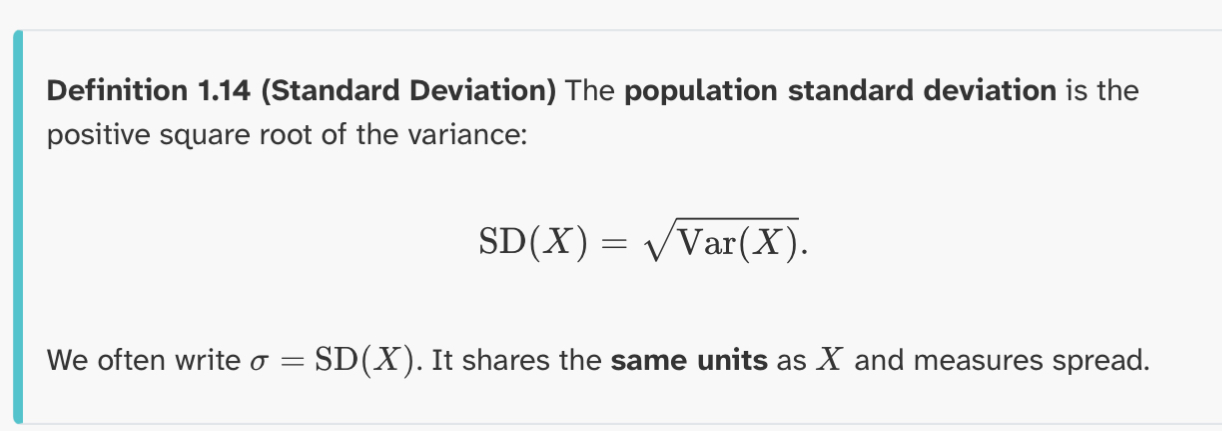
Definition 1.14 (Standard Deviation)
Definition 1.15 (Covariance)

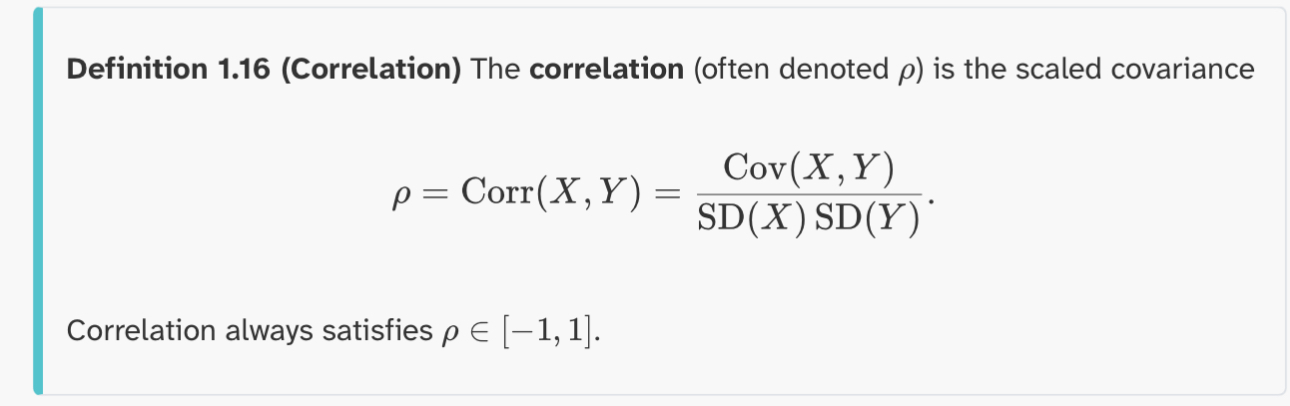
Definition 1.16 (correlation)
What is univariate data and give an example
univariate data: is a single measurement per observational unit. Eg the height of each student in a class.
Continuous data:
Can take any real value in an interval.
e.g. height, weight , reaction times .
Models: Normal, Exponential, Uniform.
Discrete numeric:
Counts, usually non negative integers.
E.g. number of accidents in a week, number of goals in a football match.
Models: Binomial, Poisson, Geometric.
Nominal data:
Category’s with no natural order.
E.g hair colour, brand of cereal, country of birth.
Ordinal data
Categories with a natural order, but not numerical spacing.
E.g. customer service satisfaction rating. (“Poor”, “fair”, “good”, “excellent”)