Year 10 and Year 9 Physics Versiion For ABRITI
1/191
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
192 Terms
Refraction is
when light waves change direction when they pass from one medium to another
Waves travel
at different speeds through different densities
Higher density =
slower wave
Reflection- Angle of incidence=
angle of reflection
3 primary colours of light
red blue green
Red + Blue =
Magenta
Red + Green =
Yellow
Blue + Green =
Cyan
Blue + Green + Red =
White
why does a white shirt look white
because it reflects all colors of light
why does a red shirt look red
because it reflects the red light and absorbs the green and blue light
why does a green shirt look green
Because it absorbs red and blue light and reflects green light
why does a black blazer look black
because it absorbs all light
the 2 types of wave
Transverse, longitudinal
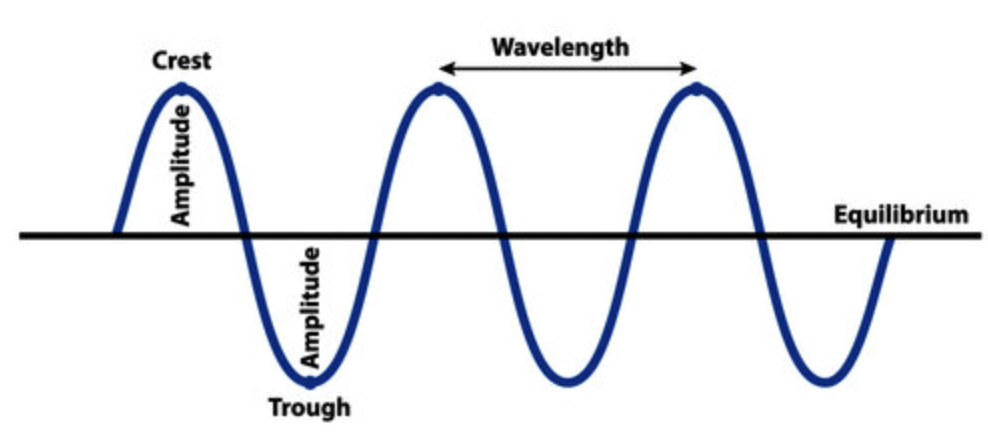
Examples of transverse waves include
Light waves, radio waves
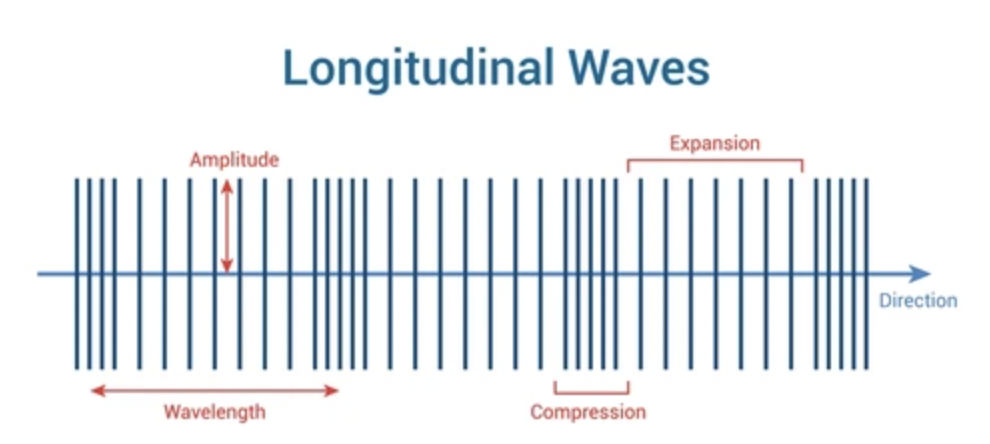
Examples of longitudinal waves include
Sound waves, seismic P waves
the wave equation
Wave speed = frequency X wavelength
Frequency
How many whole waves in a second
Amplitude
is the distance from the centre line (or the still position) to the top of a crest or to the bottom of a trough .
Wavelength
The wavelength of a wave is the distance between two waves
A light wave bend towards the normal when
When light passes from a less dense to a more dense substance, (for example passing from air into water)
a light wave bends away from the normal when
When light passes from a more dense to a less dense substance,
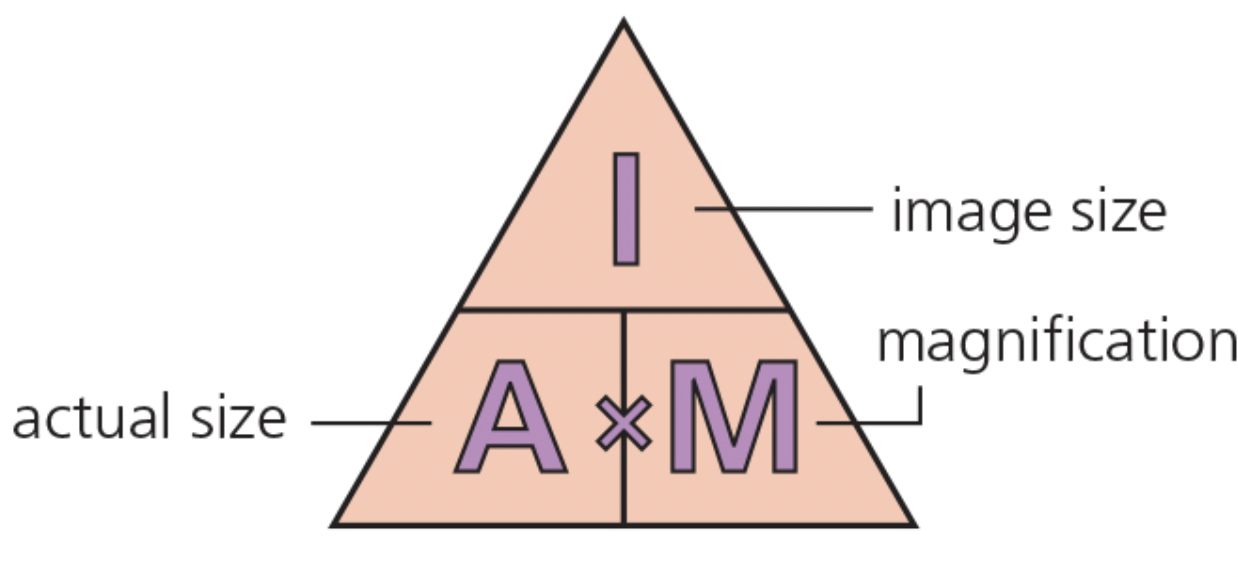
magnification =
image height
object height
Types of energy stores
thermal kinetic nuclear chemical gravitational elastic electrostatic magnetic
energy transferes are
mechanisms which allow energy to be moved from one location to another
Weight =
mass X gravity
Mass
is a measure of how much of an object there is and how mard is it to accelerate
Force
mg
GPE
mgh
work =
force X distance
Kinetic energy
½ mv²
Hookes law
The extension of a spring is directly proportional through the origin to the force applied, provided irs limit of proportionality is not exceeded
Hookes law equation
F = K X e
K=spring constant in N/m
Power =
work/time
Power also equals
Energy transfered/time
efficency =
useful power/total power input
When a current floes through a wire
a magnetic field is created around it
aNticlockwise
North
clockwise
south
LEFT hand grip rule
Thumb-Force , second-field, third-current
The motor effect
when a current flows through a magnetic field it will experience a force and it will move
Why do we get movement WITH THE MOTOR EFFECT
A CURRENT CARRYING WIRE WILL HAVE A MAGNETIC FEILD AROUD IT. THIS FEILD WILL INTERACT WITH THE MAGNETS AND BE PUSHED OUT OF THE FEILLD
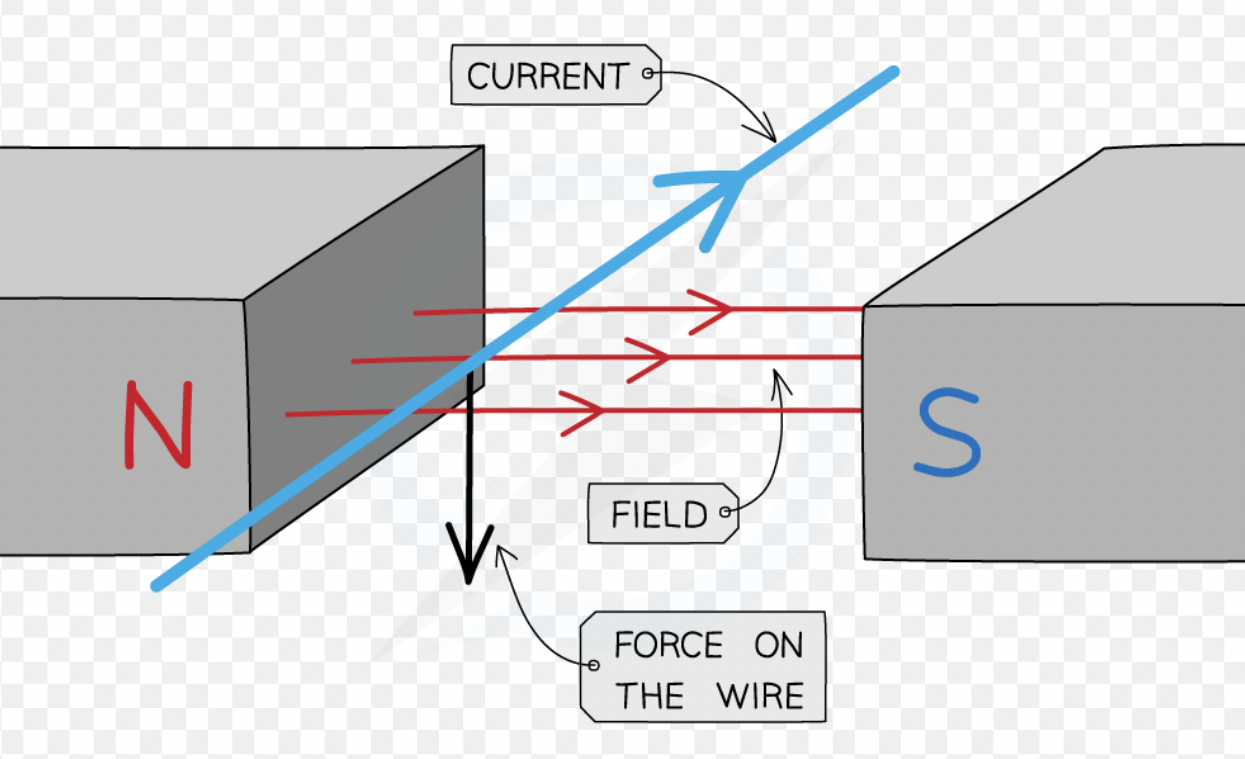
The biggest effect will be when
the current and field are at right angled to each other
If the current and field are parallel there will be
no force
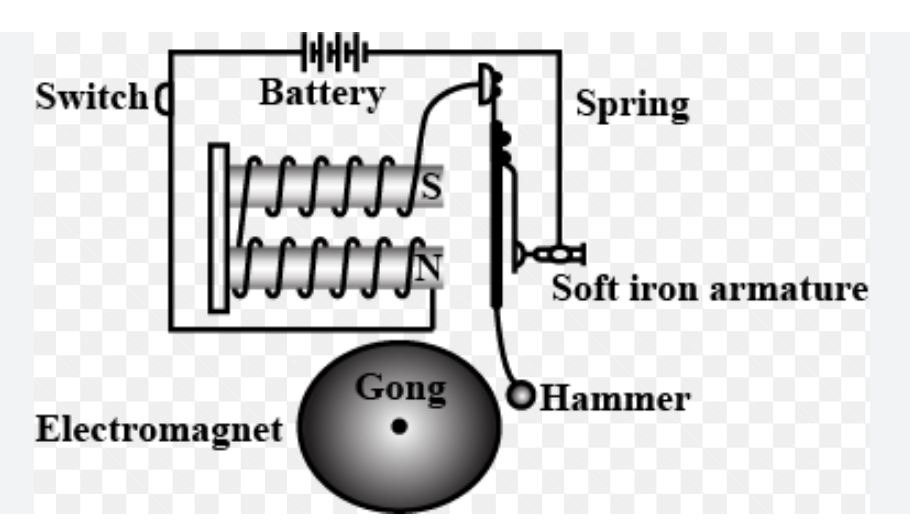
The electric bell
the current flows from the electromagnet because there is a complete circuit. This causes the iron core to become magnet and it attracts the soft iron armature this makes the hammer hit the gong.
The motor effect 3
A wire carrying a current creates a magnetic field . This can interact with another magnetic field, causing a force that pushes the wire at right angles.
An electro magnet
An electro magnet is a temporary magnet made by winding wire around an iron core.
Charge=
current x time
like charges
Different charges
REPEL
ATTRACT
Radial field
As you move away from the sphere the feild gets weaker
negitive sphere, - out + in
plus sphere, -in +out
Charge is measured in
Coulombs
Current is the
measure of the movement of charge and is measured in amps (coulombs per second)
Ametre
measures how much charge is moving around a current
Voltmetre
measure of p.d this is the measure of energy a cells gives to the charge§
Resistor
Resistance is a measure of hoe hard it is for current to flow through a component , measured in ohms.
V=
IR
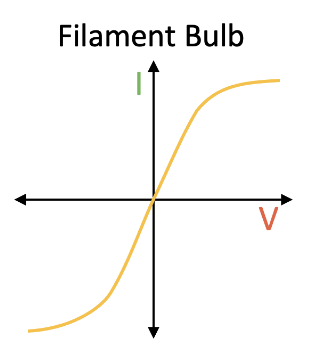
IV Graph filament bulb

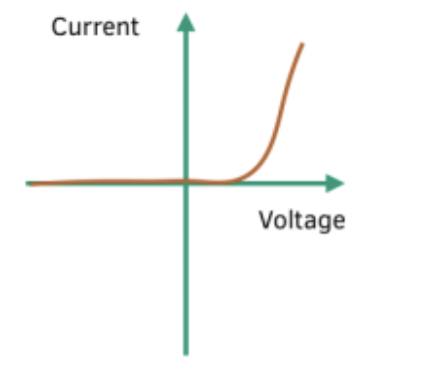
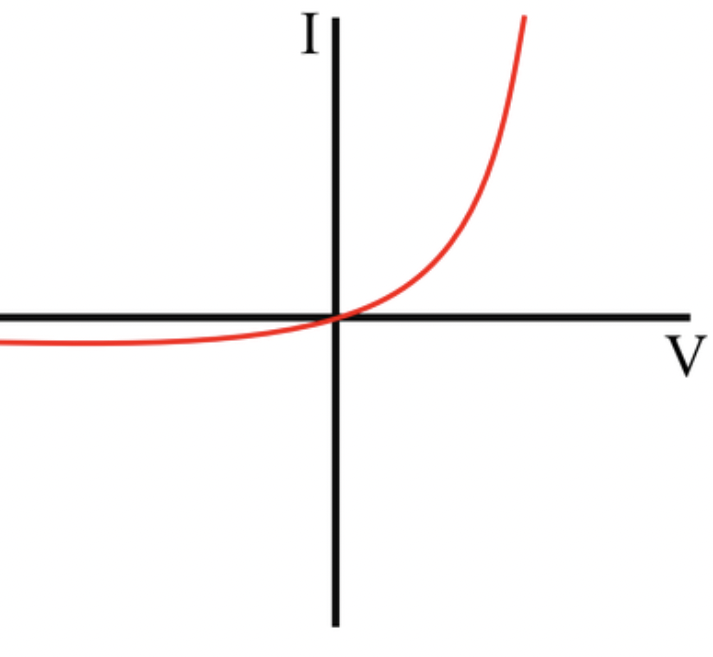
Diode

Light dependant resistor
As the light intensity increases the resistance falls
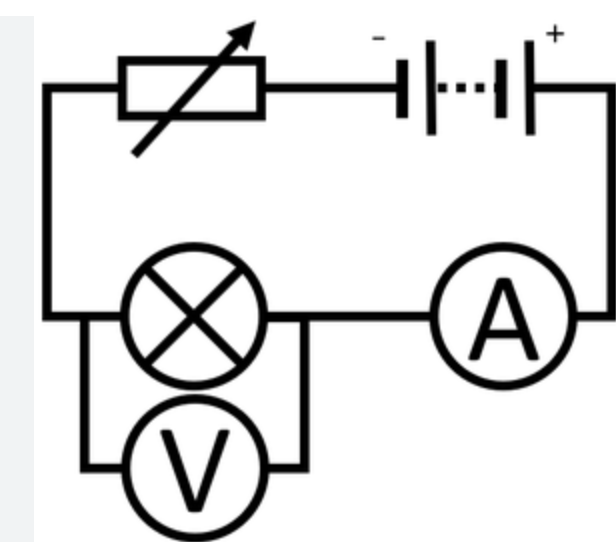
IV experiment
Variable resistor, bulb, ammeter in series, voltmeter in parallel
Change current and measure the P.d

Thermosistors
As temprature increases resistance falls
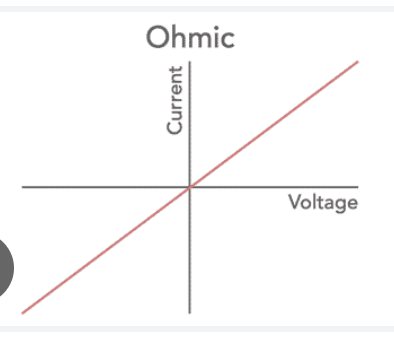
Ohmic resistor

LED graph

Series more bulbs=
more resistance
Parallel more bulbs =
more current and less resistance
Resistance in series and NO. of bulbs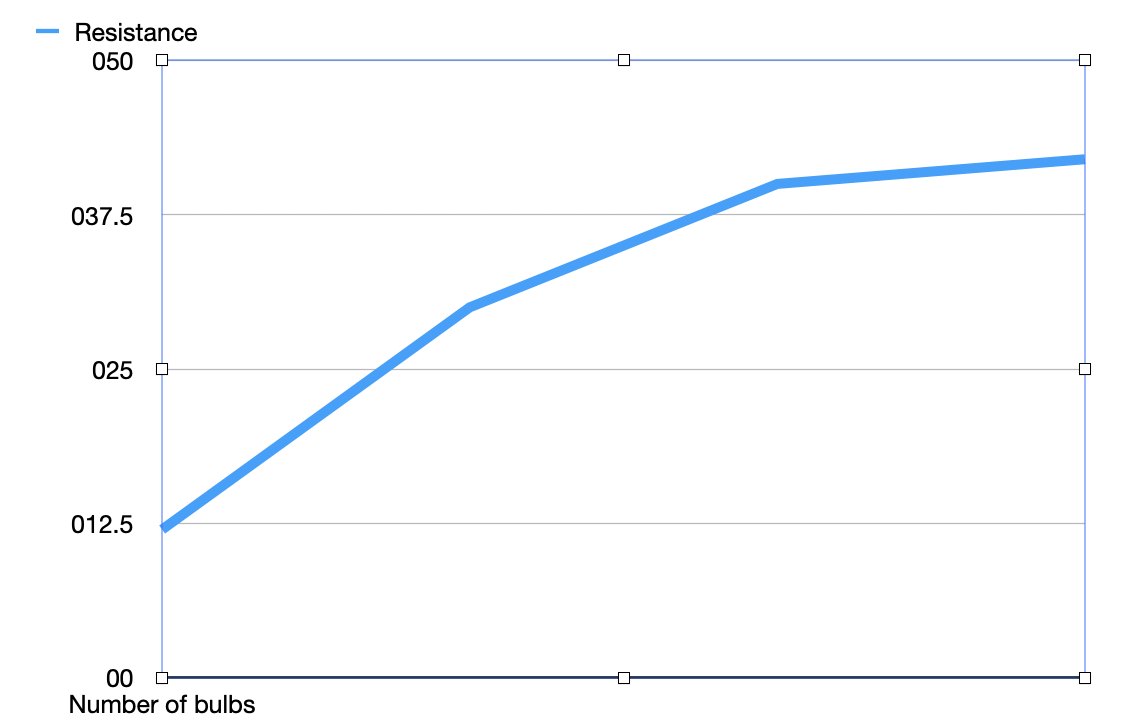
Graph goes up
Not straight because bulbs are less bright and cold.
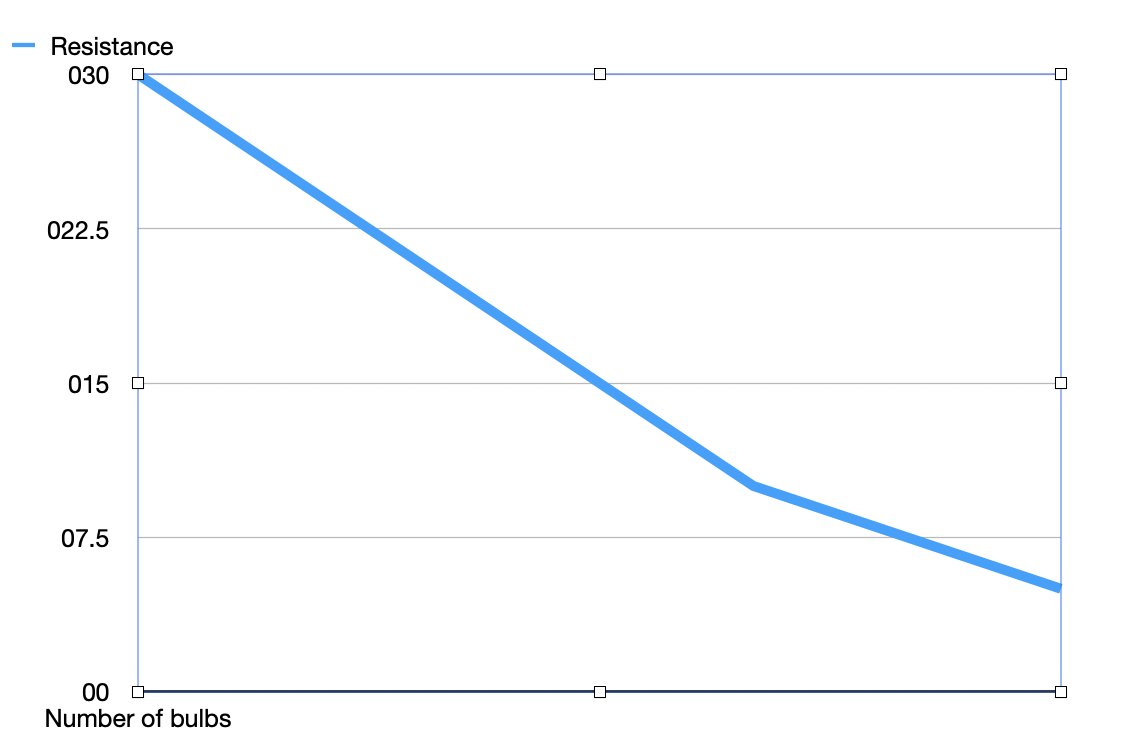
Resistance in parallel and NO. of bulbs

Series
resisatance can be added, current same everywhere, potential differences add to supply.
Parallel
Potential difference = same for all resistors, total current = all current added together.
Parallel Rtotal =
V/I total.
Using a LDR to measure light intensity
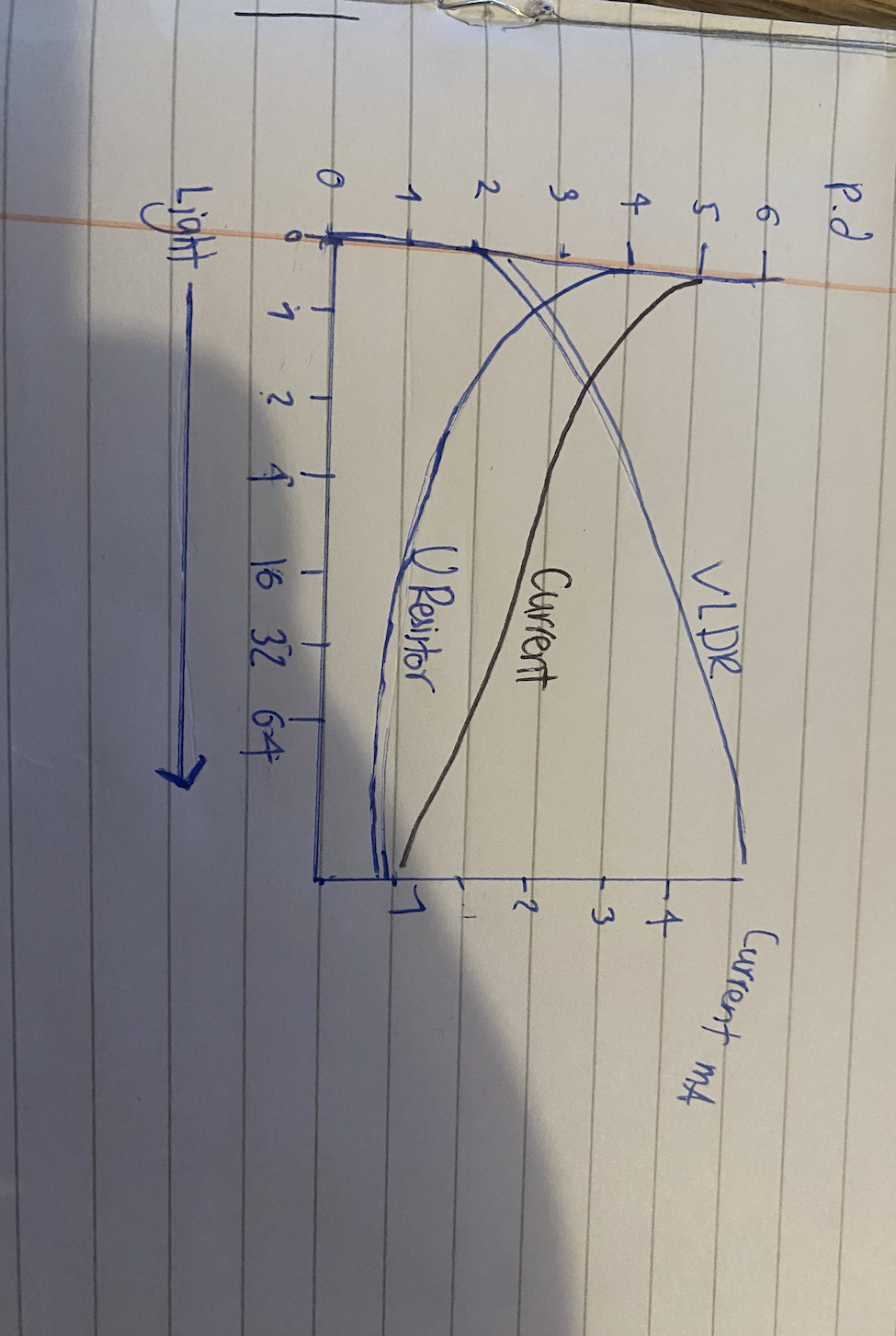
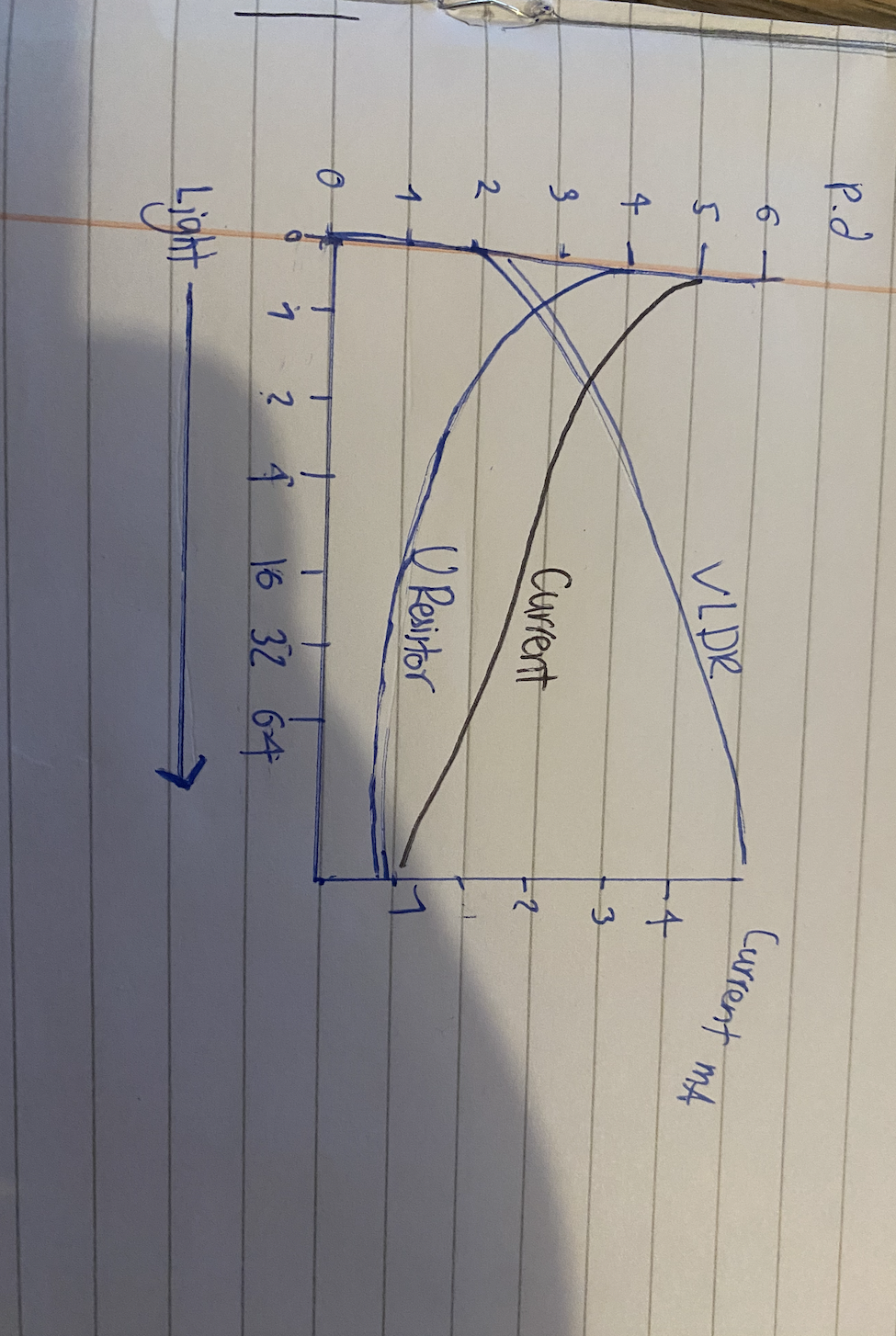
V =
E/Q
Energy transfered =
Charge x P.D
P=
E/T
I=
Q/T
Power =
I² x R
density =
mass/ volume
Density Eureka Can experiment
use balace to measure mass, submerge object into eureka can with water in it with a measuring cylinder underneath the spout, record the volume of water in the cylinder, work out density with d=m/v formula
Density of a liqiud
place measuring cylinder on balance and zero it. pour 10ml of liquid into cylinder and measure the mass, pour another 10ml and record total volume and mass, repeat process until measuring glass full, for each measurement find density, take an average, to get an accurate density.
Ray Box Experiment
Place transparent block on paper, trace around it, Use ray box to shine laser through it, trace incident ray band mark where it emerges, remove block and join up lines, measure anglw of incidence and refraction, repeat with other materials,
Types of lenses
Concave/ diverging and Convex/ converging
Uses for concave lenses
telescopes, binoculars,
Uses for convex lenses
microscopes, camera
2 types of magnet
permanant and induced,
field line arrows go
north to south
induced magnets are only magnetised
when in another magnetic field
what is an electromagnet
a metal core with a coil of wire around it and current flowing through it
Solenoid
coil of wire
How to increase power of elecromagnet
increase coils and increase current flowing through it
Uses of electromagnets
scrap yards, in circuits,
How loudspeakers work
ac current sent through coil of wire attached to base of a paper cone, coil surrounds one pole of magnet, and is surrounded by the other pole, so current causes force on wire, causes cone to move, when current reverses force acts in opposite direction, variation and curent causes cone to vibrate and air which causes sound.
Order of EM waves
radio, micro, infrared, visible, ultra violet, x rays, gamma,
Ripple tank
set up ripple tank make sure rod touches the water, turn on increasing frequency until low frequency waves can be seen, distance between each wave = one wavelength, measure waves that are 10 wavelengths apart, divide distance by 10,
range of sound
20Hz- 20kHz
Sound is causes by
objects vibrating
ultrasound
UV waves can pass through the body but when it reaches 2 different medias some of the waves are reflected back.
Ultrasound uses
babies, finding cracks, unterwater exploration.
Ultrasound unterwater question
distance = speed x time, halve distance
radio waves made
by oscillating charges