AP Human Geography Ch.1 Flashcards
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Absolute location
the precise spot where something is located on earth, determined by latitude and longitude
Acculturation
the process of cultural change and adaptation that occurs when one culture becomes influenced by another culture
Assimilation
the process by which a group’s cultural features are altered to resemble those of another group
Cartogram
a map in which the size of an area is proportional to the value of a variable
Cartography
the science of making maps
Choropleth map
a map in which areas are shaded or patterned in proportion to the measurement of the variable

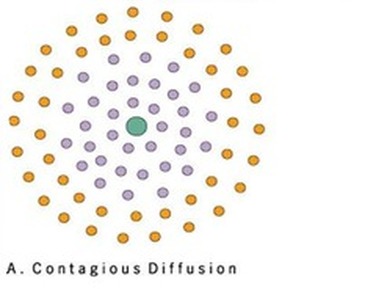
Contagious diffusion
the rapid widespread diffusion of a feature or trend throughout a population
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC)
the time in the zone encompassing the prime meridian or 0∘ longitude
Cultural Landscape
an approach to geography that emphasizes the relationships among social and physical phenomena in a particular study area
Distance Decay
the further away people are from each other, they less they interact
Environmental Determinism
a nineteenth- and early twentieth-century approach to the study of geography that argued that the general laws sought by human geographers could be found in the physical sciences. Geography was therefore the study of how the physical environment caused human activities
Expansion Diffusion
the spread of a feature or trend among people from one area to another in an additive process
Formal(uniform) Region
an area in which everyone shares in at least one distinctive characteristic
Functional(nodal) Region
an area organized around a node or focal point
Geographic Information System(GIS)
a computer system that captures, stores, queries, and displays geographic data
Geotagging
identification and storage of a piece of information by its precise latitude and longitude coordinates
Global Positioning System(GPS)
a system that determines the precise position of something on Earth through a series of satellites, tracking stations, and receivers
Hearth
a place from which an innovation originates
Hierarchical Diffusion
the spread of a feature or trend from one key person or node of authority or power to other persons or places
Possibilism
the theory that the physical environment may set limits on human actions, but people have the ability to adjust to the physical environment and choose a course of action from many alternatives
Relocation Diffusion
the spread of a feature or trend through physical movement of people from one place to another
Remote Sensing
the acquisition of data about Earth’s surface from a satellite orbiting the planet or from other long-distance methods