Bio quiz 1 SBI3U
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
kms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
what are all plants evolved from? (common ancestor)
Green Algae
order of phylogenetic tree of plants
green aglae → first land plants → first vascular plants → first seed plants
first land plants (name & examples)
Bryophytes
liverworts, mosses, hornworts
first vascular plants (name & example)
Pteridophytes
ferns, clubmosses
horsetails
first seed plants (names & examples)
Gymnosperm & Angiosperms
gymnosperm examples: spines, spruce cedars
angiosperm examples: flowering plants
traits of bryophytes
no vascular tissues, small, lives in moist environments, needs water to be reproduced by spores
traits of pteridophytes
first with vascular tissue, true roots, stems and leaves, reproduced with spores
traits of gymnosperms
has seeds, pollen = sperm transport, adapted to dry/cold climates
traits of angiosperms
seeds enclosed in fruit, double fertilization, flower → attract pollinators
photosynthesis equation

photosynthesis reactants
carbon dioxide, water, light energy
photosynthesis products
glucose, oxygen
what are plant needs?
energy, nutrients, water, gas exchange, habitat, production, reproduction
how do plants get energy?
they create their own glucose from the sun (photosynthesis)
how do plants get nutrients?
from water, they use the roots to absorb water from soil. they need nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium to make lipids and proteins.
how to plants get water?
absorbs from roots
how to plants do gas exchange?
carbon dioxide enters from stomata (in leaves) and is used for photosynthesis
oxygen exits from stomata & transpiration
how to plants protect themselves?
from adaptation and chemical secretions
what do plants need to reproduce? (sexual & asexual)
sexual needs gametes, asexual does not
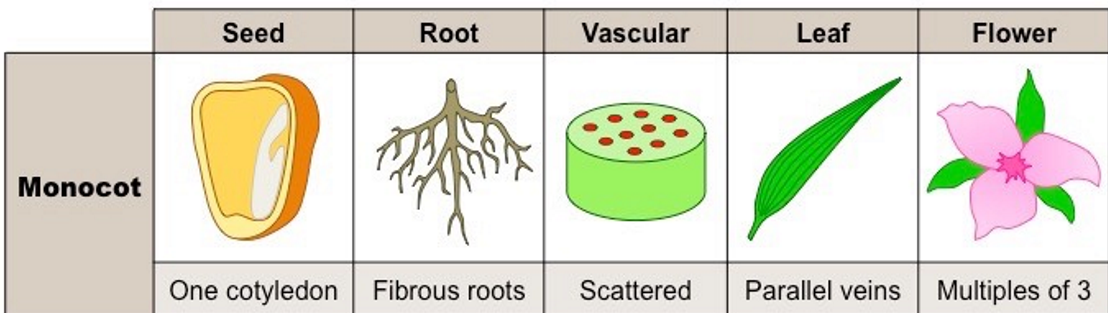
monocot
one cotyledon (in the seed of a plant), fibrous roots, scattered vascular, parallel veins, multiples of three. (lilies)
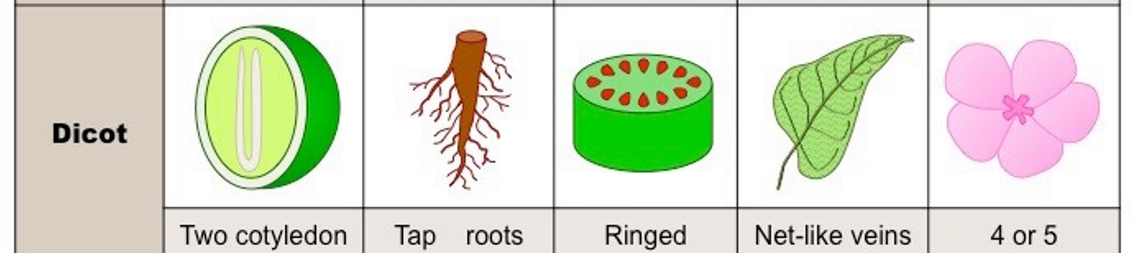
dicot
two cotyledons (in the seed of a plant), branched veins, taproot, ringed vascular, multiples of 4 or 5. (roses)
what are all the types of vascular tissues? (7)
epidermis (dermal), periderm (dermal), xylem (vascular), phloem (vascular), parenchyma (ground), collenchyma (ground), sclerenchyma (ground)
what does dermal mean?
skin
what does vascular mean?
transporting fluids
traits of epidermis tissue
young stems, leaves roots
primary protective covering
single layer of tightly packed living cells
provides protection
cover by cuticles to reduce water loss
controls exchange between plant and environment
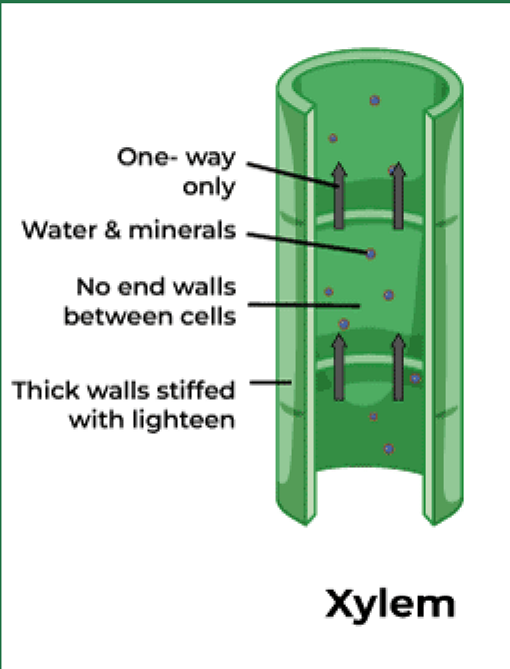
traits of xylem tissue
thin walled, dead at maturity
moves water and dissolved minerals upward from roots to leaves
dead, hollow cells form tubes
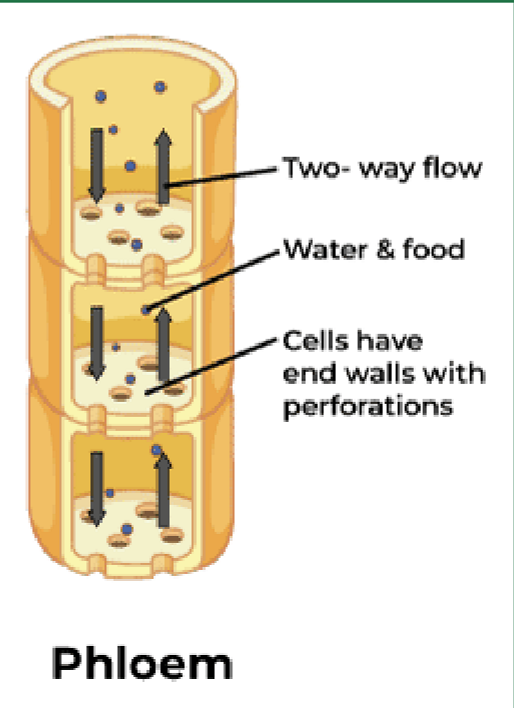
traits of phloem tisse
thin walled and alive
water and nutrient transport
support
moves sugars and hormones from leaves to the rest of plant
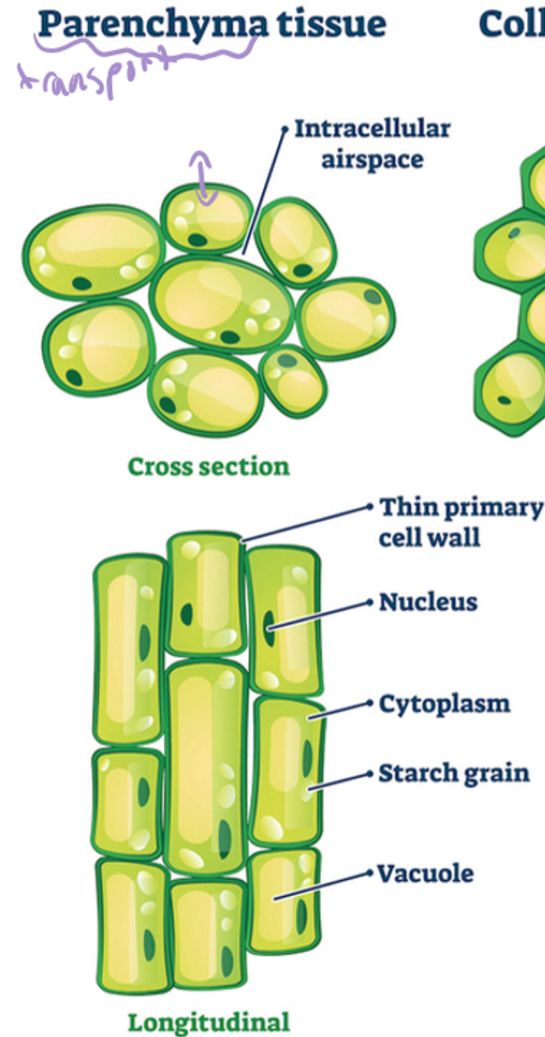
traits of parenchyma tisse
thin walled
living
storage of food, carbs (starch)
cell process for growth and development
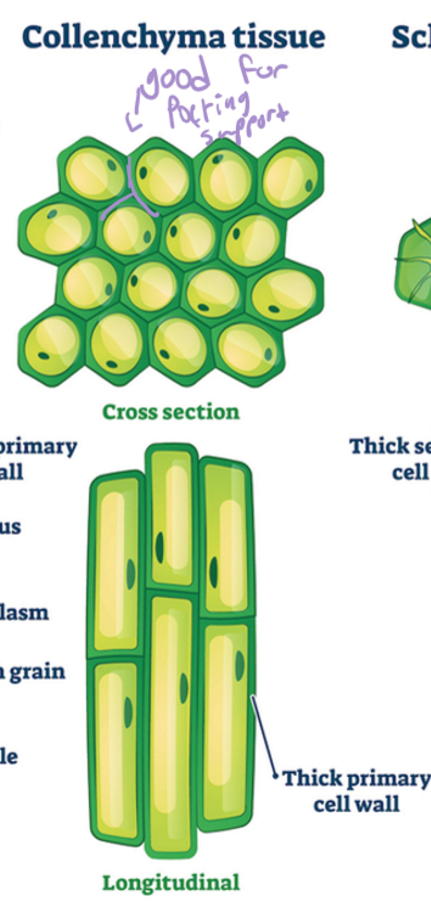
traits of collenchyma tissue
thick(er) walled
living
support
protection
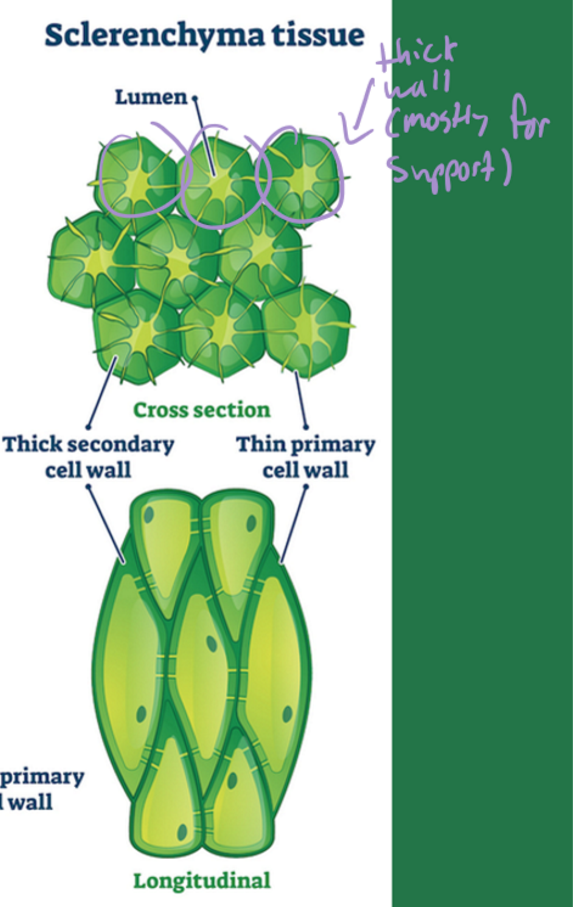
traits of sclerenchyma tissue
thick(est) walls
rigid structural support
lignin in cell walls (which makes it rigid)
dead at maturity
support and protection
two types of leaves?
simple and compound !

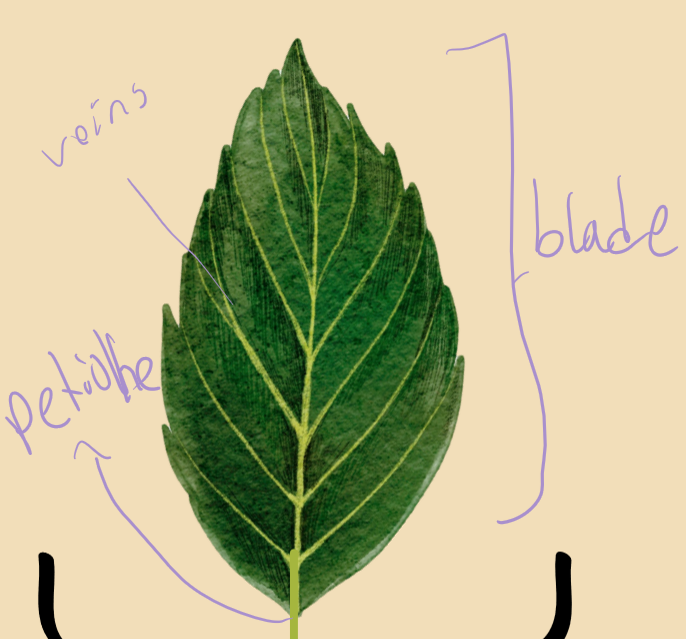
labeling of the simple leaf
veins - transports water, nutrients, sugars
blade - flat surface that maximizes light absorption
petiole - stalk that attaches blade to stem

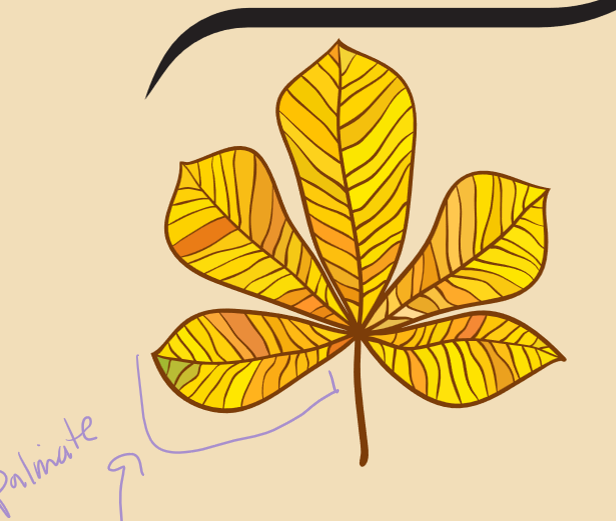
two different types of compound leaves?
palmate compound and pinnate compound
how are palmate compounds structured?
leaflets from a single point
how are pinnate compounds structured?
leaflets have feather-like arrangements around a midvein (RACHIS)
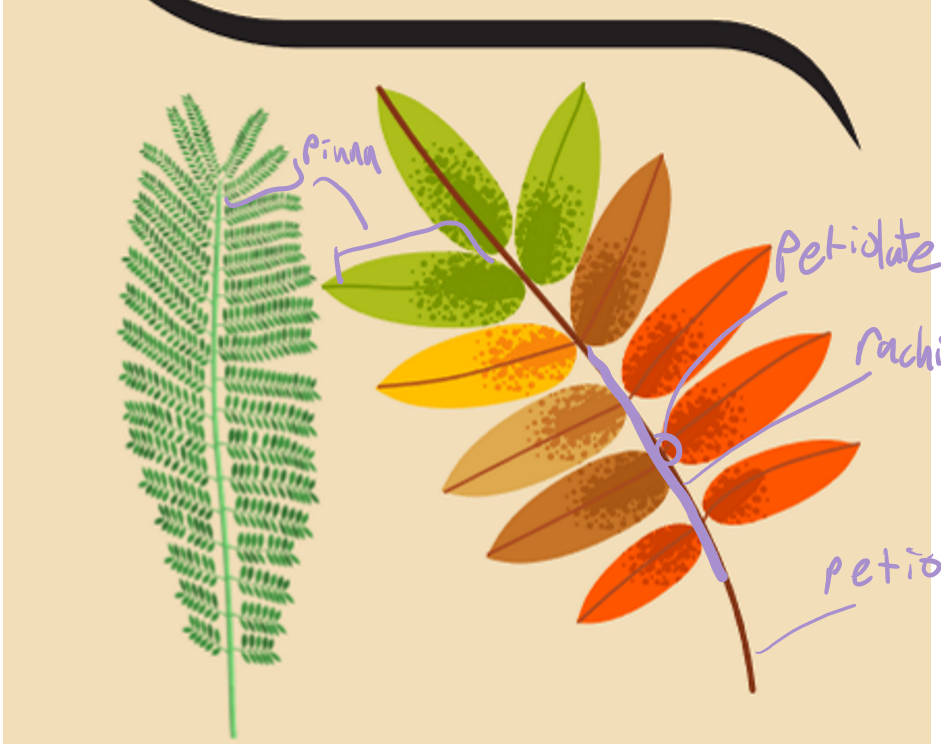
labelling the pinnate compound leaf
pinna - the leaf
petiolate - the little branch that connects the pinna and the rachis
rachis - the stem that holds all the leaves (pinna)
petio - the stem that connects the plant to the branch (no pinnas attached)
how are leaves adapted?
large surface to maximize light absorption
thin so there is a short distance for carbon dioxide to diffuse into leaf cells
cells in the plant leaves contain chloroplasts to facilitate photosynthesis
tiny pores (stomata) to help gas exchange
why are lichens not considered plants?
Lichens are not considered plants because they are composite organisms, formed by a partnership between a fungus and a photosynthetic partner, usually an alga or cyanobacterium, rather than a single, independent plant organism
turgid vs flaccid?
turgid = swollen and rigid, when the guard cells swell. full of water and firm
flaccid = when it has lost all the water and is soft, limp, and weakened
what does potassium do?
when potassium ions (K+) move into guard cells, water follows by osmosis. the guard cells then swell (turgid) and the pore (stomata) opens.
when potassium ions move out, water leaves too causing the guard cells to shrink (flaccid) then the pores (stomata) close.
where are guard cells located?
they surround the stomatal pore
what are 4 specialized plant structures
bulbous leaves, hairs & spines, fleshy leaves, needles & scales

what are bulbous leaves and how are they helpful?
stores carbs and water underground
protected from herbivores and weather
eg. onions

what are hairs & spines and how are they helpful
tiny hairs protect the leaves from sunburn and prevents drying out in wind
spines protect against herbivores
eg. kiwi, cacti, rose

what are fleshy leaves and how are they helpful?
stores water and food
has thick cuticle for protection against elements
eg. succulents

what are needles and scales and how are they helpful
small leaves with thick cuticle to prevent water loss
survives winter
eg. pine trees

what are 4 uses of leaves?
herbs, teas, leafy greens, polish and wax
how are herbs used
fragrant leaves used to add flavour to food
some have medicinal properties
other used in ceremonial traditions
eg. rosemary ( deftones reference ), basil
how are teas used
teas made of plant leaves
some for medicinal
eg. peppermint, pine
how are leafy greens used
big source of minerals such as iron and magnesium
provides vitamins B, C, E, K
eg. kale
how are polish and wax from plants used
waxy cuticle of some plants are used to make car and furniture polishes
also used to make some lipsticks and surfboard wax
types of asexual reproduction
vegetative propagation, bulbs, cutting, plantlets
traits of asexual reproduction
only one parent,
offsprings are genetically identical
fast reproduction