Biology Unit 3 Humans and Global Change IHS Skavaril
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What is the sex ratio of males to females
50:50
What does the sex ratio show
Shows the # of babies that will be produced next generation
What does age structure graphs show
Whether or not populations are increasing, decreasing, or stable over time. They illustrate the distribution of various age groups within a population
What is population growth rate affected by
Birth
Death
Immigration
Emigration
Including the basic 4 factors, HUMAN population growth rate affected by
Culture
Conflict
Economy
Politics
Resources
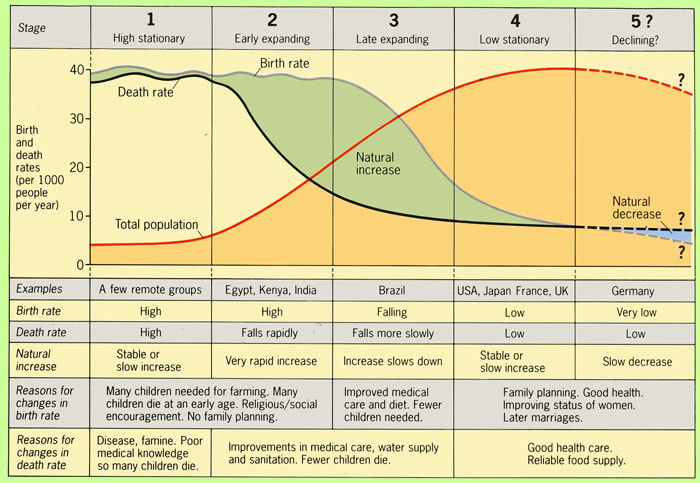
What does a demographic transition model show
Change in population from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates
What is stage 1 in an age structure diagram
High fluctuating; majority of population is young
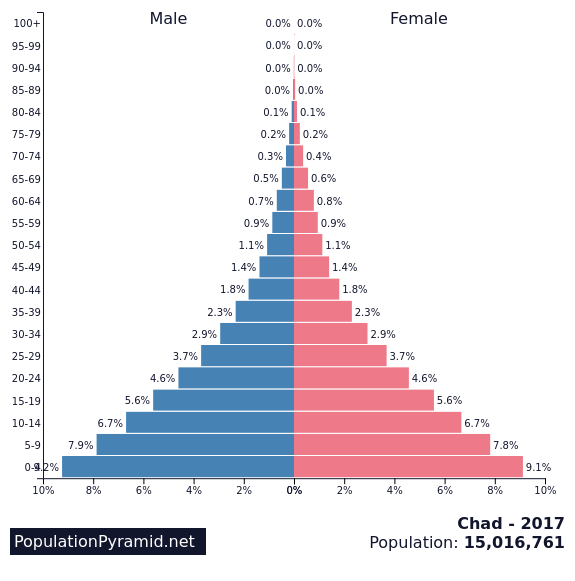
What is stage 2 in an age structure diagram
Early expanding; steady decrease from young to old
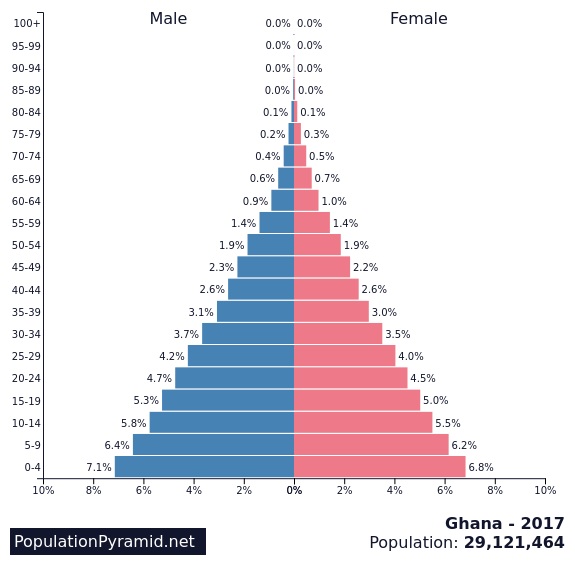
What is stage 3 in an age structure diagram
Late expanding; majority of the population is young adults/teens
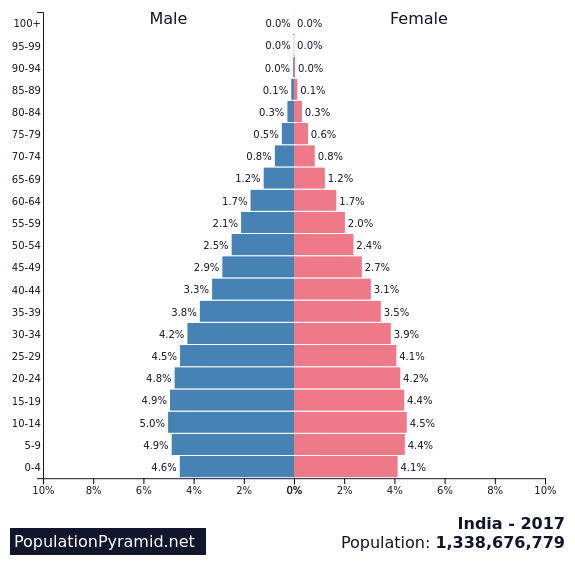
What is stage 4 in an age structure diagram
Low fluctuating; adults make up more of the population—still a “healthy” amount of younger children
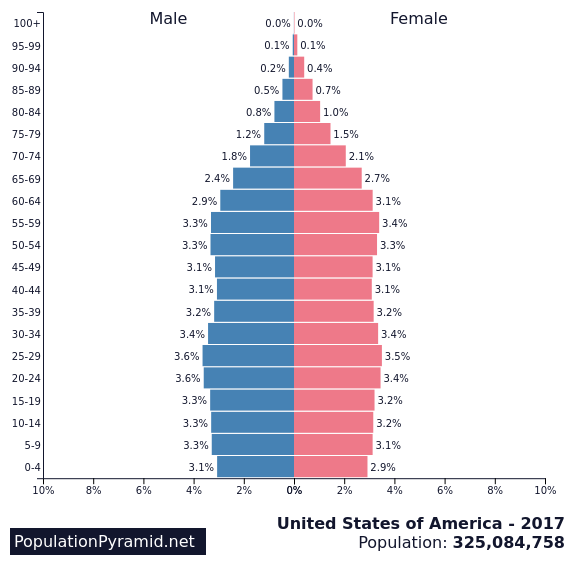
What is stage 5 in an age structure diagram
Decline; majority of the population are older adults—population of young children are decreasing
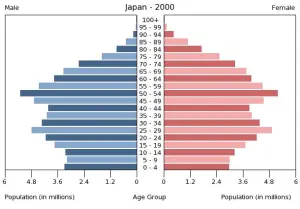
How has human population change over time
It increased/grew
How has human activities change the atmosphere and climate
Created the Anthropocene
Human emission of greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, methane) drive climate change
Describe how atmospheric changes drive climate change
Greenhouse gases (CO2 and methane) in the atmosphere act as an insulator (keep heat in). This heat is changing the global temperature and driving climate change
What greenhouse gas does cows release
Methane
What are three major greenhouse gases
Carbon dioxide (CO2), methane, nitrous oxide
What are the effects of CO2 emission
Increase in temperature
Increase in sea levels
Decrease in ice caps
What are 4 countries in stage 5 of the demographic transition model
Italy, Russia, Germany, Japan
What are the characteristics of a stage 1 demographic transition model
Stable population
High birth and death rate
Birth and death rate are about the same
Pre-industrial society
Population essentially determined by the food supply
Family planning and contraception are virtually nonexistent
Population fluctuates rapidly due to natural events
Examples: Angola, Amazon basin tribes
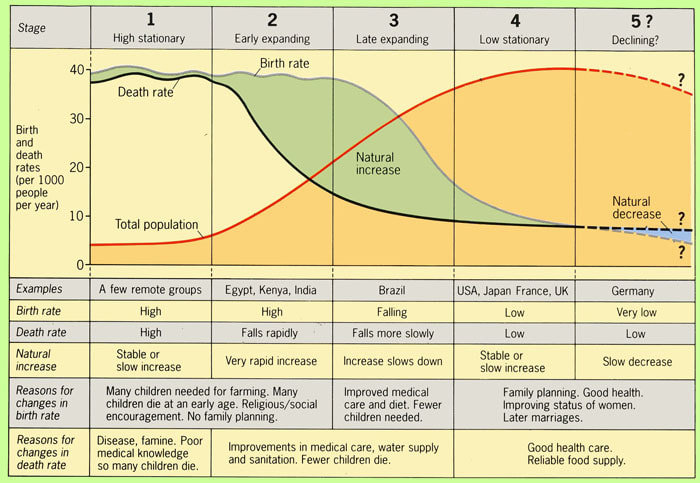
What are the characteristics of a stage 2 demographic transition model
Increasing population
High birth rates and decreasing death rates
Developing countries
Improvements in food and water systems
Improvements in medicine/public health
Examples: Kenya, Ethiopia, Yemen, Afghanistan
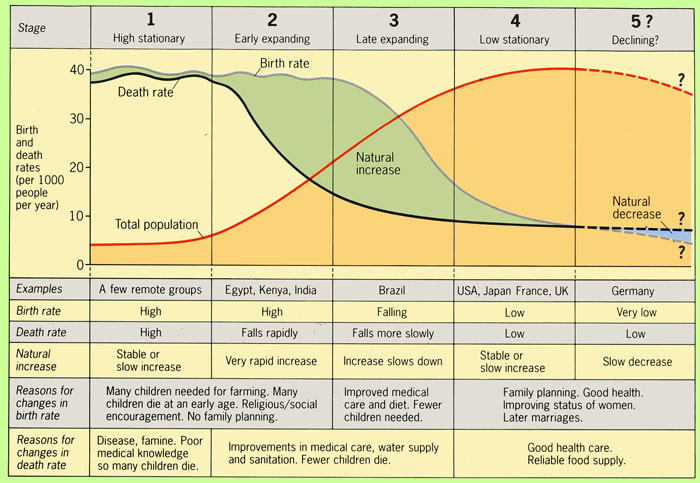
What are the characteristics of a stage 3 demographic transition model
Increasing population
Birth rate begins to decrease and low death rate
The value of women increases
Increased access to contraceptives (condoms, birth control, etc.)
Increasing urbanization
Examples: India, Mexico, South Africa
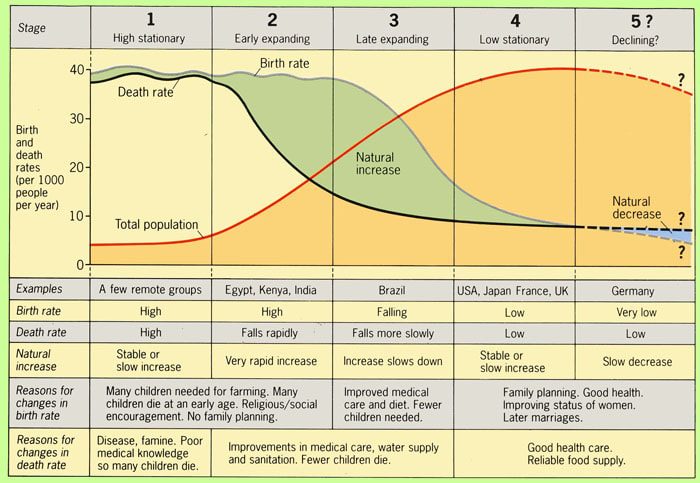
What are the characteristics of a stage 4 demographic transition model
Stable population
Low birth and death rates
Children are a choice
Increase access to family planning
Women are more independent and gain more work opportunities
Low rates of diseases and high production of food
Examples: Canada, United Kingdom, United States, Turkiye, Guam, Peru
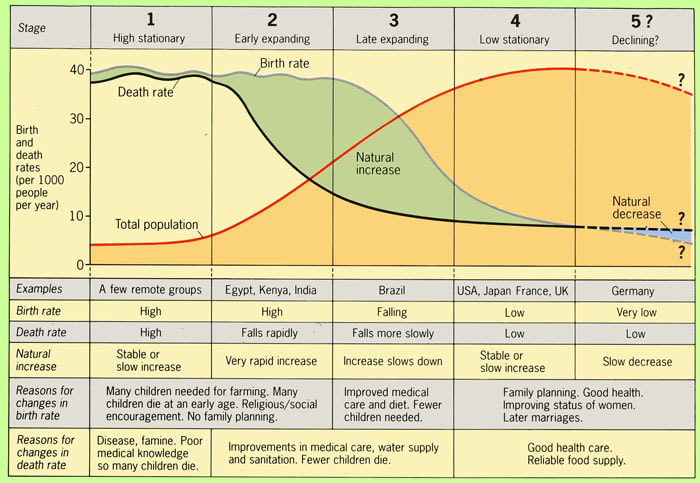
What are the characteristics of a stage 5 demographic transition model
Decreasing population
Decreasing birth rate and death rate is higher than birth rate
Children are an option and people are CHOOSING NOT TO HAVE CHILDREN
What are 8 human impacts to the Earth
Acid rain
Ocean acidification
Biological magnification
Deforestation
Monoculture
Habitat fragmentation
Overharvesting
Invasive species
What is acid rain
When air pollution combines with water and falls as rain that is acidic and especially damaging to forests and lakes
What is ocean acidification
When the water continues to decrease in pH due to carbon dioxide absorption from the atmosphere. More CO2 in atmosphere → more CO2 dissolves into water → water becomes more acidic → acidity dissolves shells
What is biomagnification
The increase concentration of a substance (usually pollutants) in organisms as the food chain level goes up
What is deforestation
The loss of forests, which has negative effects on soil, water, carbon storage, and animals
What is monoculture
When humans plant large areas with a single, high production crop every year (NO BIODIVERSITY)
What is habitat fragmentation
When parts of a habitat are destroyed, leaving behind smaller unconnected areas. This causes biodiversity loss and makes ecosystems more vulnerable to other disturbances
What is overharvesting
When humans use a natural resource in an unsustainable way
What are invasive species
They are species that can be introduced to new places by humans and disrupt the ecosystem