Allergies and Immunological Diseases
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
What is another name for Recurrent Aphthous Ulcer?
Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis; Canker Sores
What is one of the most common oral mucosal apthoses?
Recurrent Aphthous Ulcer
In which demographic do you see Recurrent Aphthous Ulcer
Younger patients; 80% have their first ulceration before age 30
What is the cause of Recurrent Aphthous Ulcer?
No universal etiology but systemic disorders, stress, hormonal can be associated with aphthous ulcer. It is painful
Where would you find Recurrent Aphthous Ulcer?
Exclusively occur on movable mucosa (vs primary herpes)
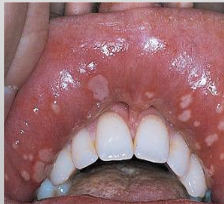
What are the 3 types of Recurrent Aphthous Ulcer?
Minor
Major
Herpetiform
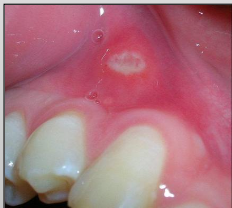
Minor Recurrent Aphthous Ulcer
Size: 3-10mm (small)
Healing time: 7-10 days
No scarring
1-5 lesions
Short duration
Few recurrences
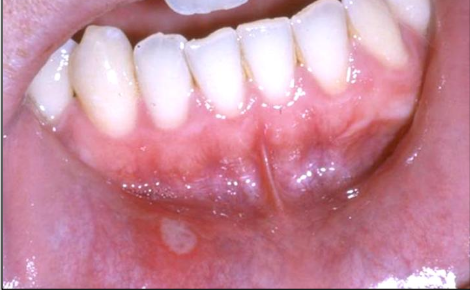
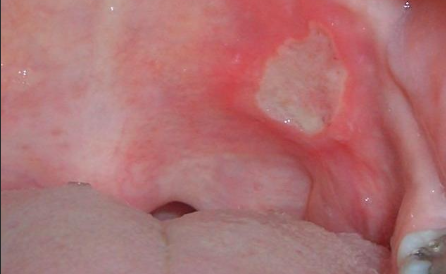
Major Recurrent Aphthous Ulcer
1-3 cm (large)
Healing time: 2-6 weeks
Biopsy to R/out cancer
Causes scarring sometimes
1-10 lesions
Longest duration
More than minor; less than herpetiform
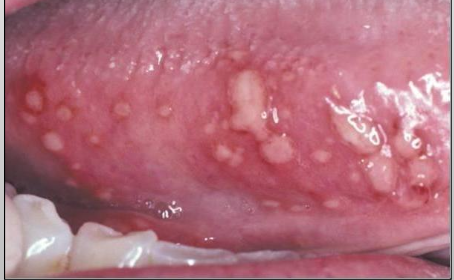
Herpetiform Recurrent Aphthous Ulcer
Size: 1-3mm (small)
7-10 days of healing time
No scarring
Up to 100 lesions
Most recurrences
Least common
What is another name for angioedema?
Quincke’s disease
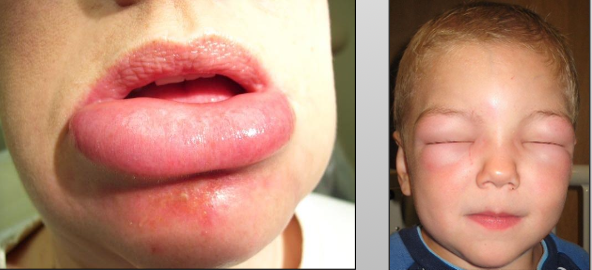
What is Angioedema?
A diffuse edema (swelling) of tissue caused by permeability of deeper blood vessels
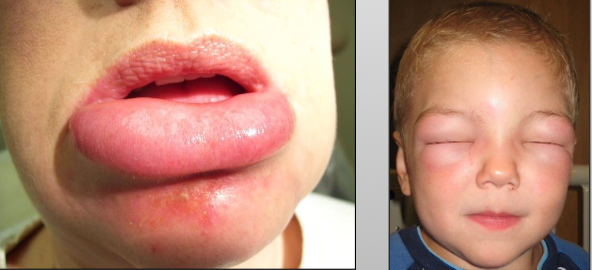
What are the two types of angioedema?
Hypersensitivity or medication (ACE inhibitors of things that end in -pril)
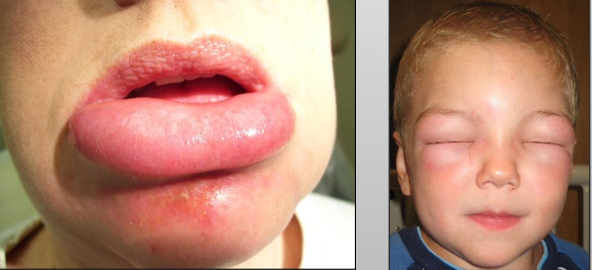
Where do you see angioedema?
Extremities (most common), face, trunk, neck
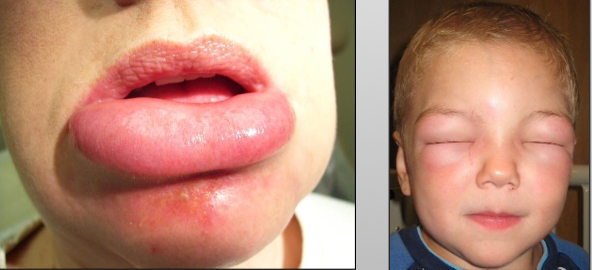
What are the clinical features of angioedema?
Rapid onset swelling, non-tender, single or multiple, resolves within 24-72 hours, itching, recurrent skin swelling, abdominal pain
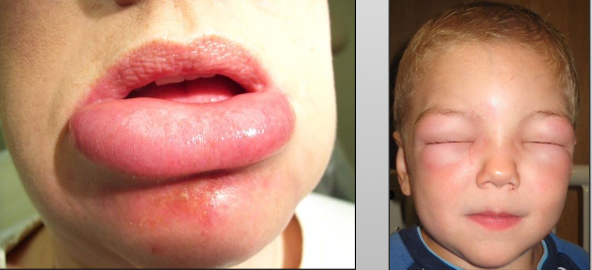
What can angioedema be confused with?
Cervicofacial emphysema due to air in tissue
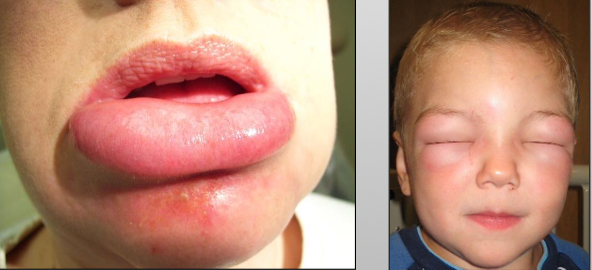
What is contact mucositis?
Lesions that result from the direct contact of an allergen with the oral mucosa and skin
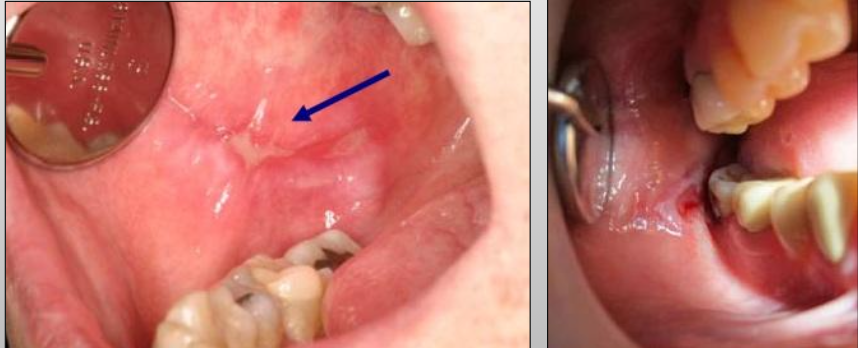
What is another name for contact mucositis?
Lichenoid mucositis
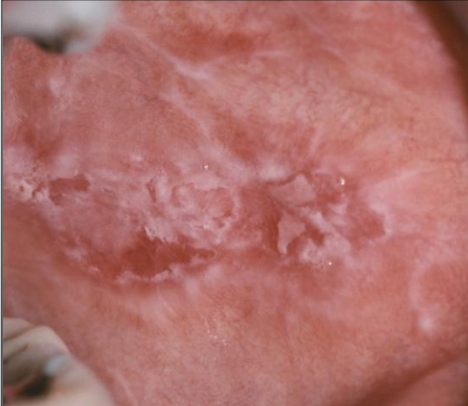
What are some products that can cause reactions in contact mucositis
Candy
Chewing gum
Toothpaste
Medication
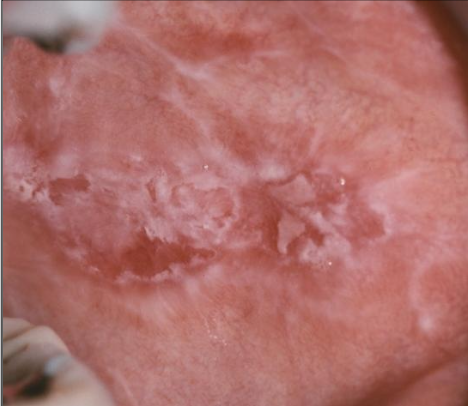
What are the clinical presentations of contact mucositis?
The presentations vary according to the delivery medium
Toothpaste causes a diffused appearance
Gum/candy cause a localized appearance
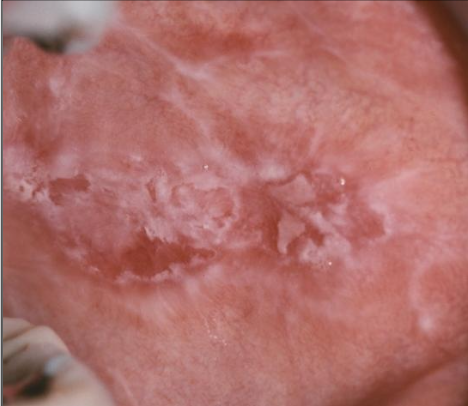
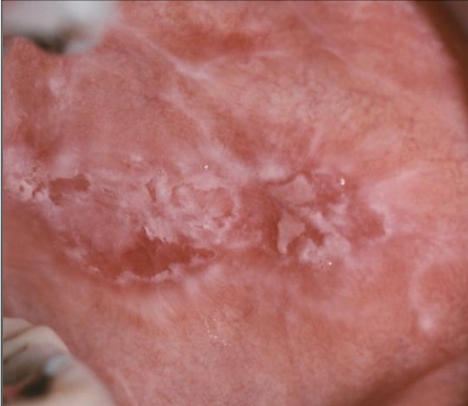
What does contact mucositis clinically look similar to
Lichen planus
What is the treatment for contact/lichenoid mucositis?
It will disappear within 1 week of discontinuation of product
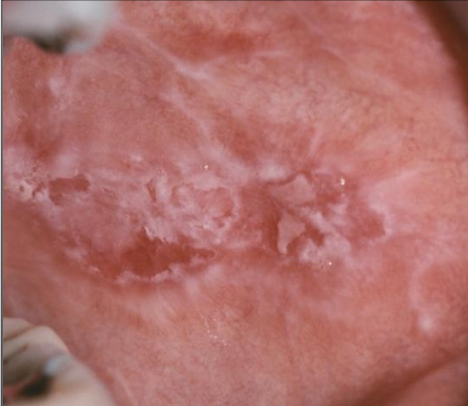
What is lichen planus?
An immune mediated, benign, chronic dermatologic disease that often affects oral mucosa
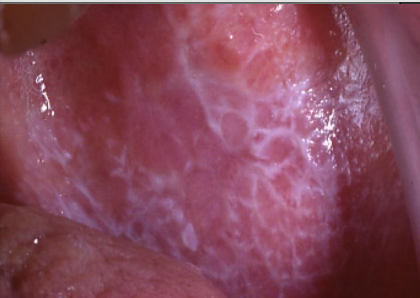
What demographic do you mostly see lichen planus in?
F > M (3:2), and middle aged people
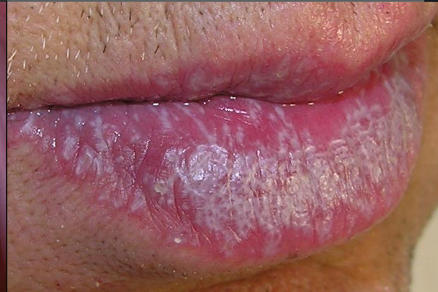
Where does lichen planus show up?
Buccal mucosa, gingiva, tongue, lip
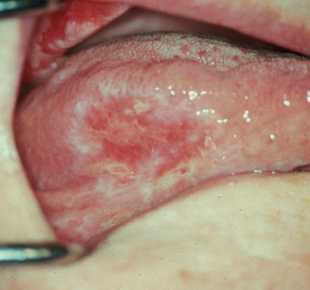
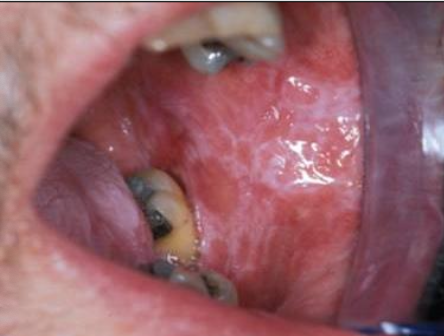
What is the clinical presentation of lichen planus intraorally?
White lace-like striations (Wickham striae), maybe erythematous, bleeding
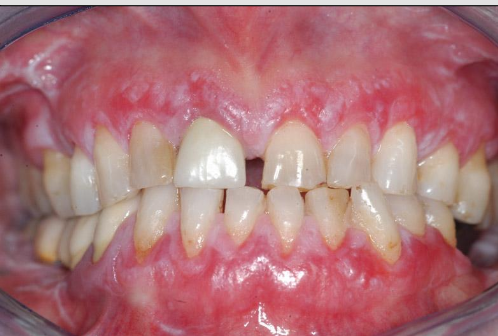
What is the clinical presentation of lichen planus on the skin?
Purple, pruritic, polygonal papules (4Ps)
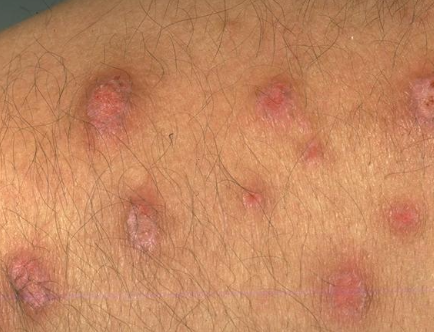
What is reticular lichen planus?
More common, asymptomatic, lace-like (Wickham striae)
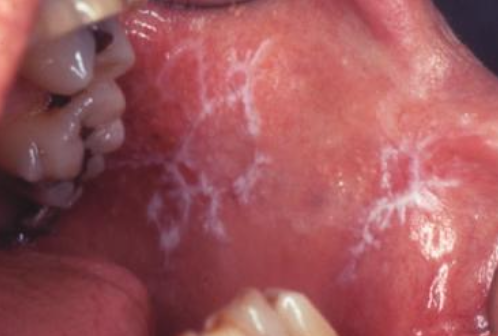
What is erosive lichen planus?
Not as common, painful, erythematous, bleeding
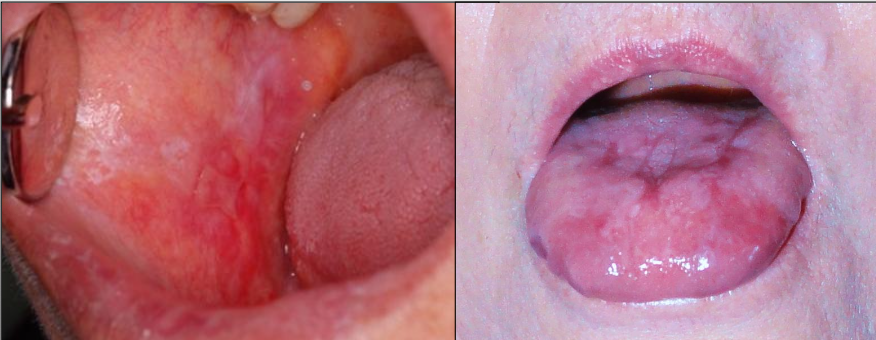
What is the treatment for lichen planus?
There is no treatment, only palliative. If patients are asymptomatic, do a follow up. If patients are symptomatic, use topical steroids. If a chronic condition, waxes and wanes. <1% may develop cancer

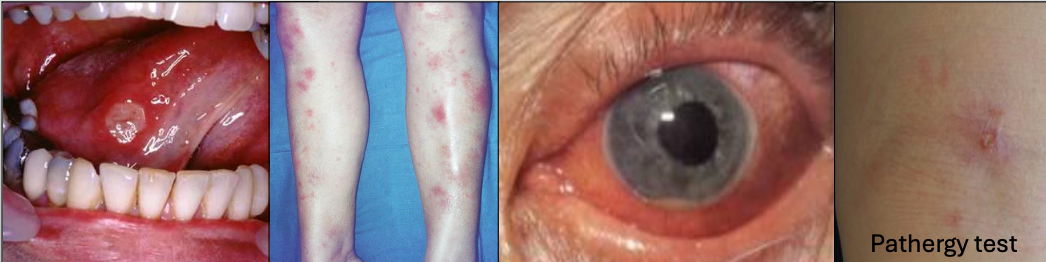
What is Behçet Syndrome?
A chronic recurrent autoimmune disease,20’s and 30’s, Mediterranean or Asian descent (Silk road)
What is the criteria for diagnosis of Behçet Syndrome?
Recurrent oral ulcers 3x/yr + 2 of
Recurrent genital ulcerations (75%)
Eye lesions (70%)
Skin lesions
+ pathergy test (results are variable)
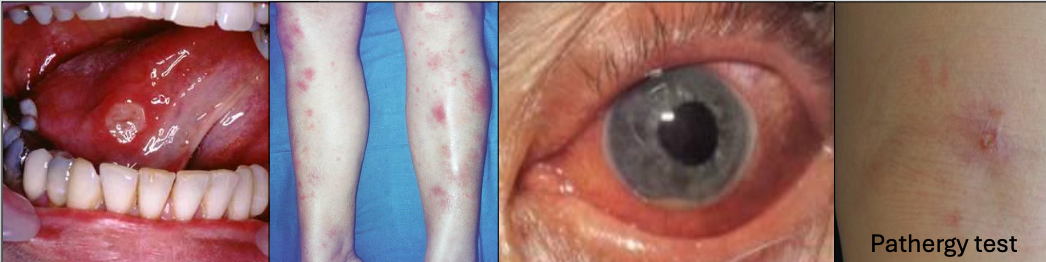
In which condition do you see arthritis
Behçet Syndrome
If a patient has an autoimmune condition, they are
More prone to having another autoimmune disease
What is sarcoidosis?
Multisystem granulomatous disorder of unknown cause
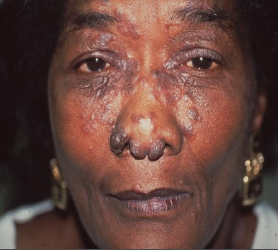
Which demographic does scarcoidosis affect?
F > M
African Americans >>> Caucasians
Prior to 50 yrs
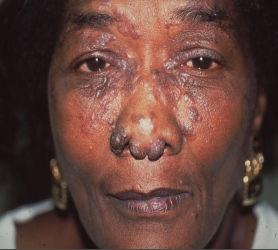
At the start of sarcoidosis, what are you expected to see?
Variable symptoms
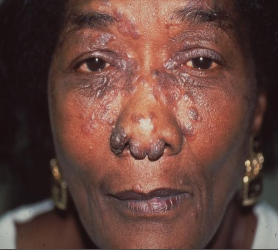
Where would sarcoidosis be located?
Organ involvement most common
Lungs
Lymph nodes
Skin
Eyes
Salivary glands
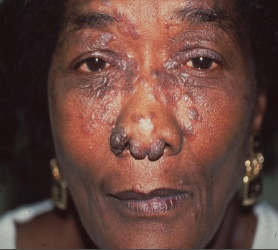
What would a chest x-ray look like in sarcoidosis?
90% will show abnormal chest x-ray
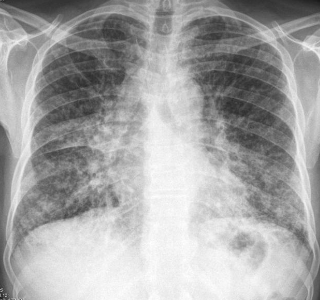
In almost all cases of sarcoidosis, what kind of tissue is involved?
Lymphoid
Name the most common types of sarcoidosis
Lymphoid
Pulmonary
Cutaneous
Ocular
What other things can show up in sarcoidosis?
25% of people have ocular involvement
25% of people have skin lesions
What are the intraoral manifestations of sarcoidosis?
Enlarged salivary gland, xerostomia
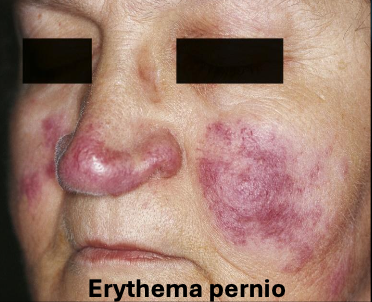
What is lupus pernio?
A type of sarcoidosis that is chronic, purple and has indurated lesions on head and neck
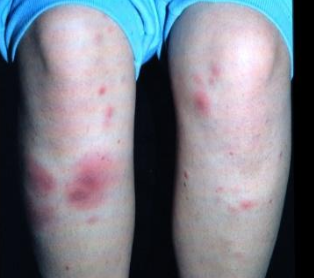
What is erythema nodosum?
A type of sarcoidosis that is scattered, nonspecific, tender, red nodules on lower legs
What is the diagnosis of sarcoidosis?
Increased serum angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) levels which is mainly located in the capillaries of the lung but also in the kidney
Use a chest x-ray!
What is no longer used for the diagnosis of sarcoidosis?
Kveim test
What is the treatment and prognosis of sarcoidosis?
60% of symptoms resolve spontaneously in 2 years
Corticosteroids if patients have progressive disease
5-10% succumb to disease and have further complications
What is another name for granulomatosis with polyangiitis?
Wegener Granulomatosis
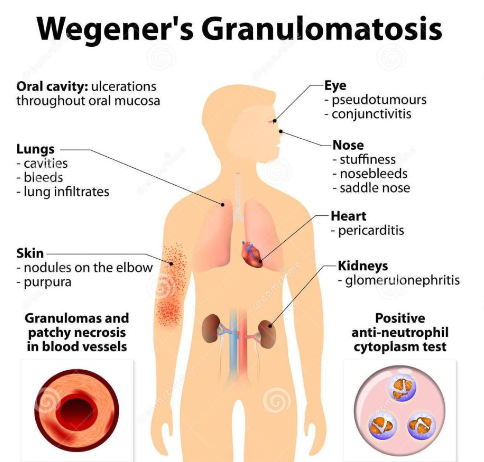
What is the cause of granulomatosis with polyangiitis?
Abnormal immune reaction, it causes vasculitis in small and medium blood vessels
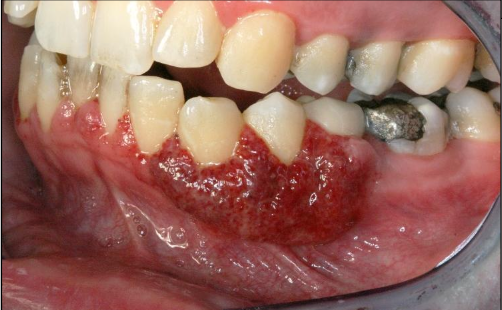
What demographic does granulomatosis with polyangiitis show up in?
M = F, average age is 40
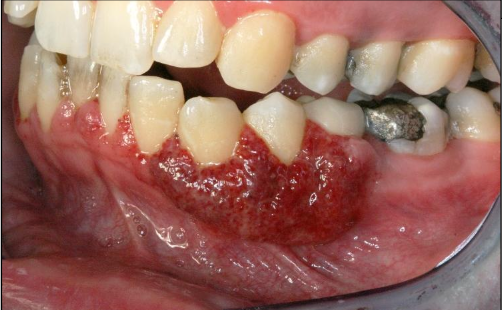
What are the clinical features of granulomatosis with polyangiitis?
Commonly affects the respiratory system (nose, sinuses, throat, lungs)
Nose bleeds, saddle nose deformity
Kidney (most common cause of death)
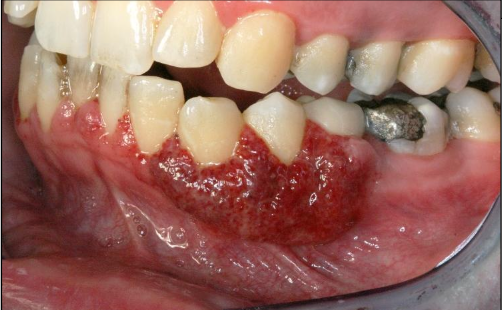
What are general signs and symptoms of granulomatosis with polyangiitis?
Fever, night sweats
Fatigue, lethargy
Loss of appetite
Weight loss
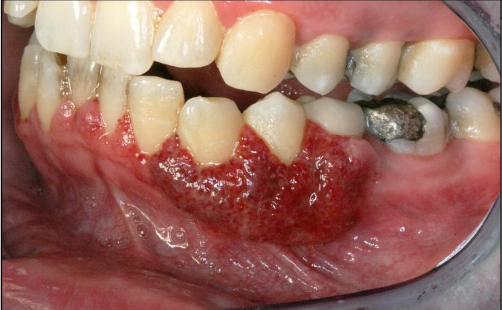
What are the intraoral manifestations of granulomatosis with polyangiitis?
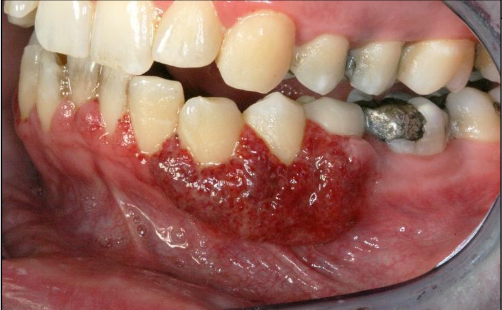
(2%) Strawberry gingiva is red, friable, granular gingiva, non-
specific ulcer
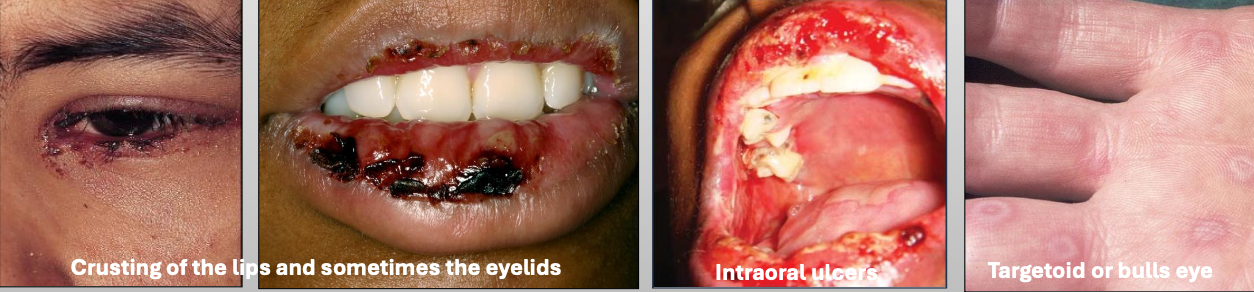
What is Erythema Multiforme (EM)
A blistering ulcerative mucocutaneous condition of uncertain pathogenesis. You see a spectrum of hypersensitivity reaction. The sisease lasts 2-6 weeks (self limiting); 20% have recurrent episodes
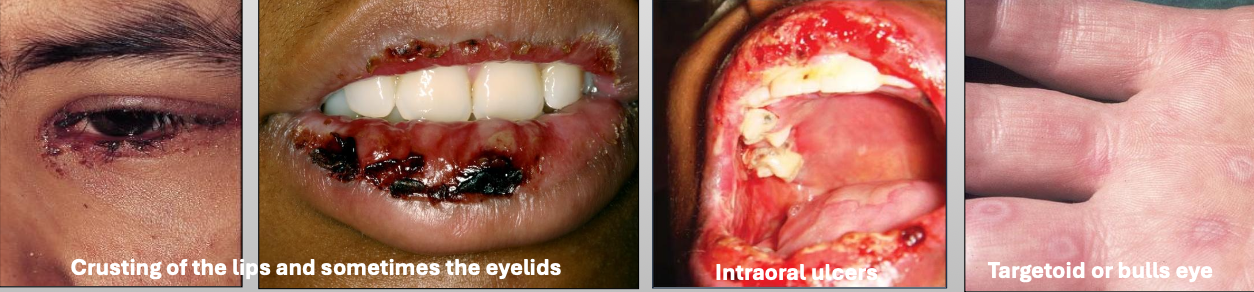
What is the cause of Erythema Multiforme (EM)?
Herpes virus (HSV)
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Medications
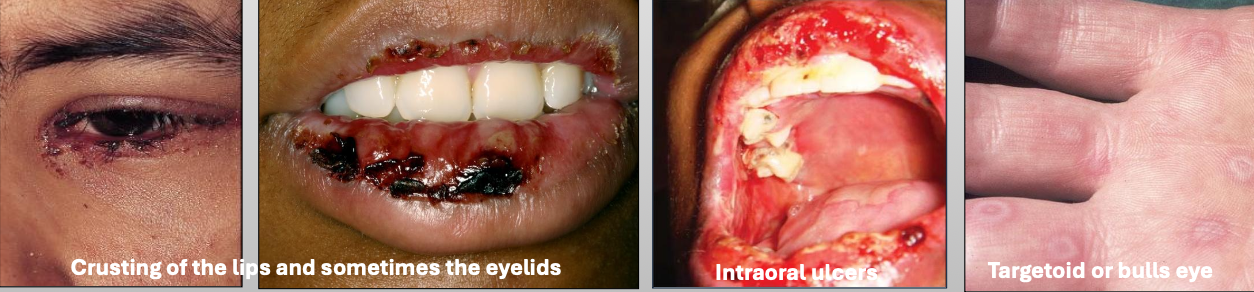
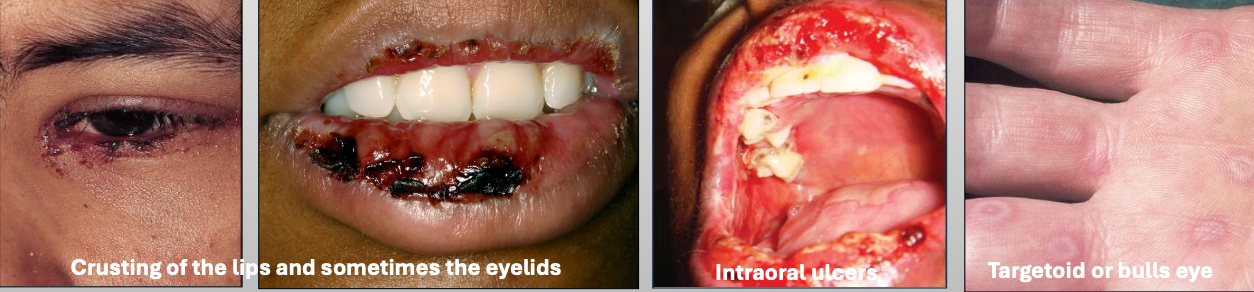
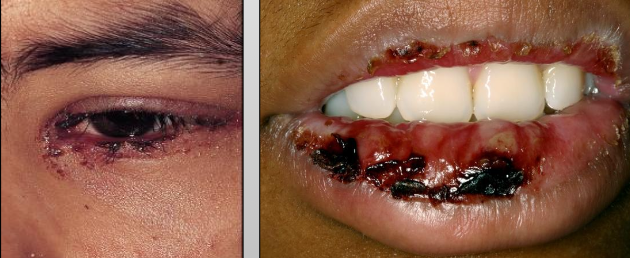
What are the clinical features of Erythema Multiforme (EM)
You get prodromal signs a week before
Crusting of the lips and sometimes the eyelids
Intraoral ulcers
Targetoid or bulls eye
What demographic does Erythema Multiforme (EM) affect?
Young M>F
What is the treatment for Erythema Multiforme (EM)?
Steroids
IV rehydration
Topical anesthetic
Discontinue drug
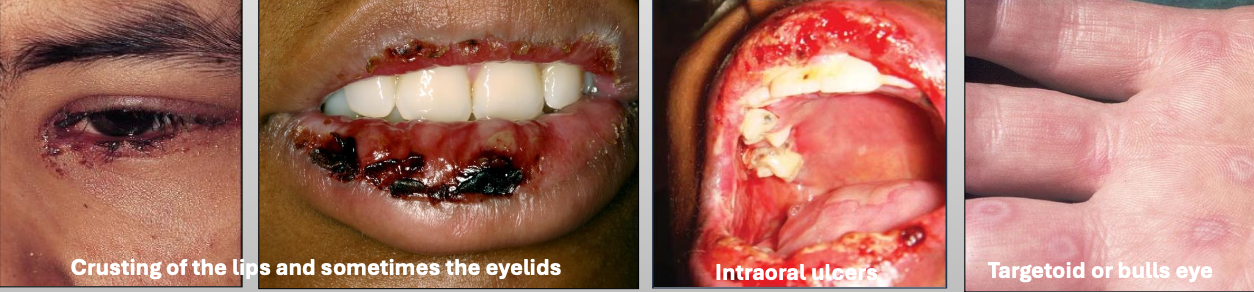
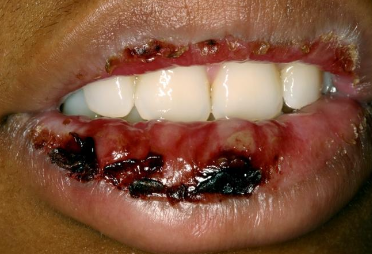
What are characteristics of minor Erythema Multiforme (EM)?
Mild
Young, Male > female
Starts on skin of extremities, oral lesions appear
Crusting on lips
Usually due to herpes (HSV)
What are characteristics of major Erythema Multiforme (EM)?
Wide spread skin lesions + 2 or more mucosal sites
(Oral + ocular or genital)
Ocular scarring may occur in severe cases (Symblepharon)
Usually due to herpes (HSV)
What are characteristics of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome?
Almost Always triggered by drugs (medication)
<10% of body surface is affected
Younger
Initially on trunk
Sever sloughing of skin
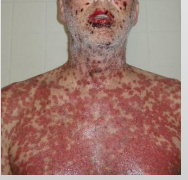
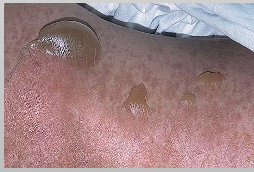
What are characteristics of Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (Lyell disease)?
Almost Always triggered by drugs (medication)
≥30% body surface is affected
Older females
Initially on trunk
Sever sloughing of skin
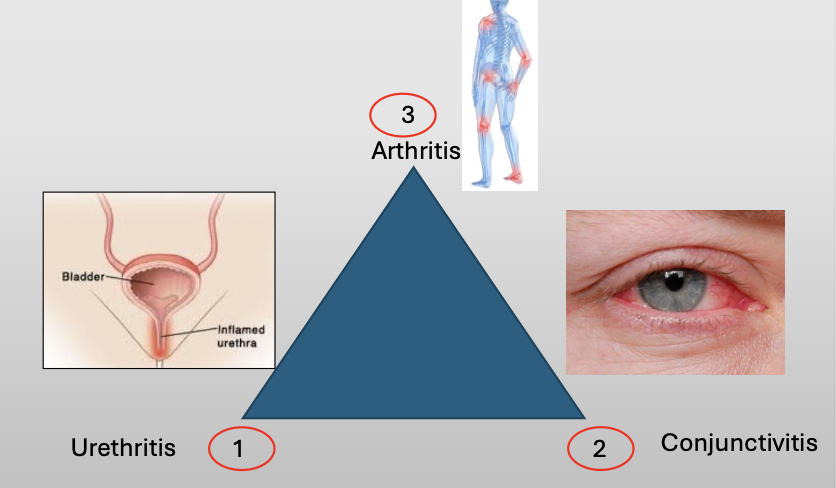
What is another name for reactive arthritis
Reiter Syndrome
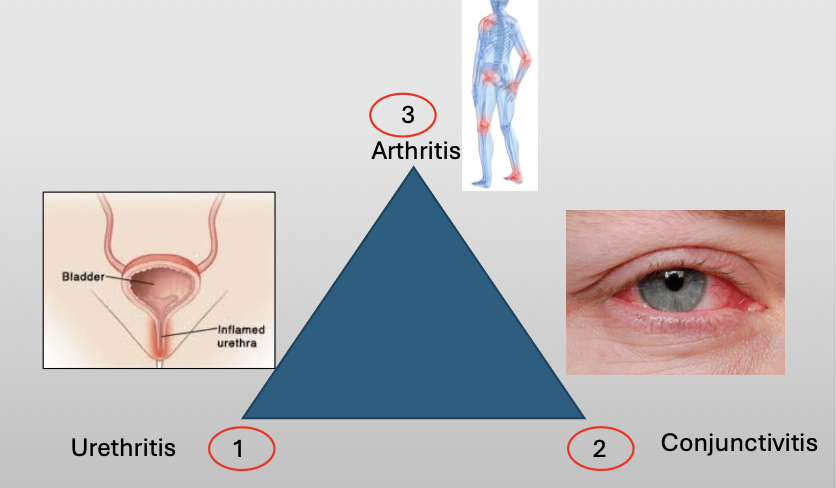
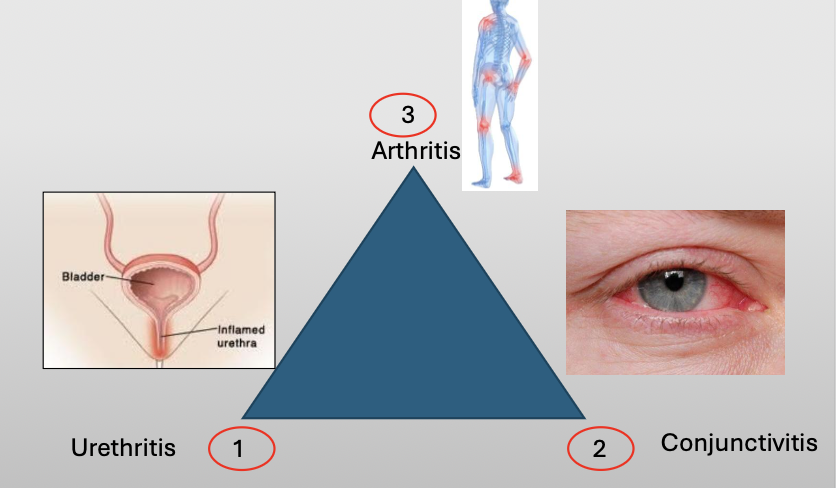
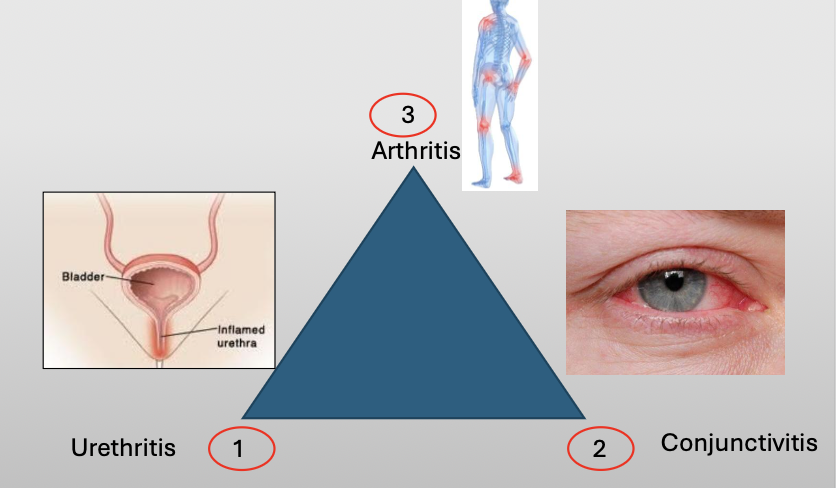
What is Reiter Syndrome?
A chronic disease that classically compromises a triad of three featuers:
Urethritis
Conjunctivitis
Arthritis
What is the cause of Reiter Syndrome?
Unknown, 10% have HLA-B27
Oral lesions are 20% (nonspecific)
NSAID/AB if infection/steroids
What demographic does Reiter Syndrome show up in?
M:F (9:1)
What is Lupus Erythematosus?
An acute and chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease of unknown cause
What is the most common collagen-vascular disease?
Lupus Erythematosus
What demographic does Lupus Erythematosus show up in?
Gender: F >>>M (8:1)
Age: child bearing age (average age 31 yrs)
What are the 3 categories of Lupus Erythematosus?
Systemic lupus erythematous (SLE)
Chronic cutaneous lupus erythematous (CCLE)
Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematous (SCLE)
How does Lupus Erythematosus show up in the kidneys?
One of the main complications that may lead to HBP, kidney failure and death
What complications do you see in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus?
Weight loss
Fever
Arthritis
Fatigue/malaise
Where does Systemic Lupus Erythematosus show up?
Skin, kidney, heart, lungs
What are the intraoral manifestations of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus?
May appear lichenoid or non-specific
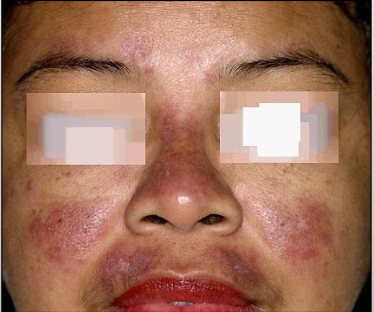
50% have butterfly rash over malar area of nose sparing the nasolabial fold
Lupus cheilitis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
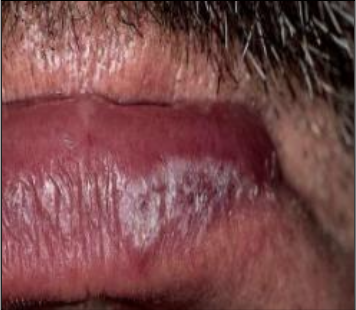
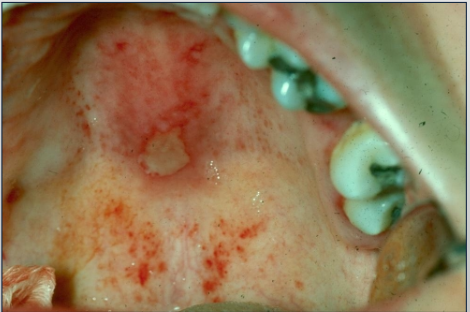
Non-specific ulcer in
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Butterfly rash in
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
What is Chronic Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (CCLE)?
Few or no systemic signs or symptoms, mild form
Skin and mucosal surfaces (25% of cases of oral lesions)
What are the clinical features of Chronic Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (CCLE)?
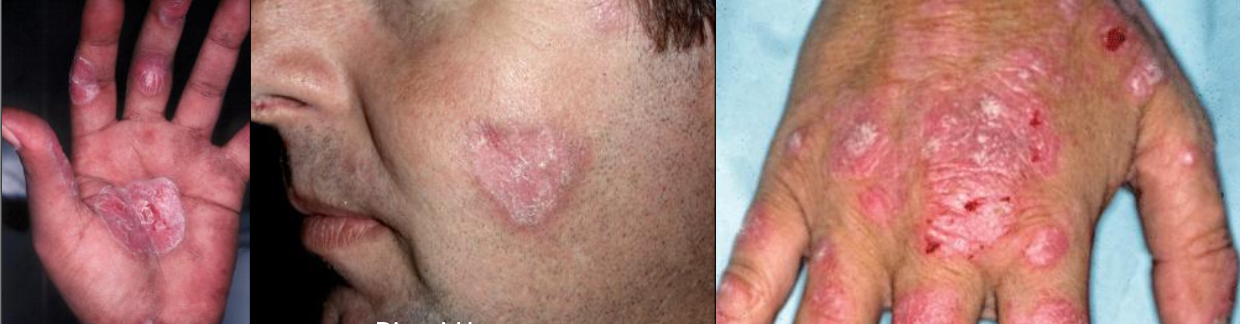
Discoid lupus erythematosus: Scaly, erythematous patches on sun exposed areas
Scar and hypopigmentation
What is another name for scleroderma?
Systemic sclerosis; Hide Bound Disease
What is scleroderma?
An immunologically mediated condition that is caused by an increase in collagen deposition
What are the types of scleroderma?
Systemic
Localized (Morphea-localized scar)
What demographic does scleroderma affect?
F > M (5:1)
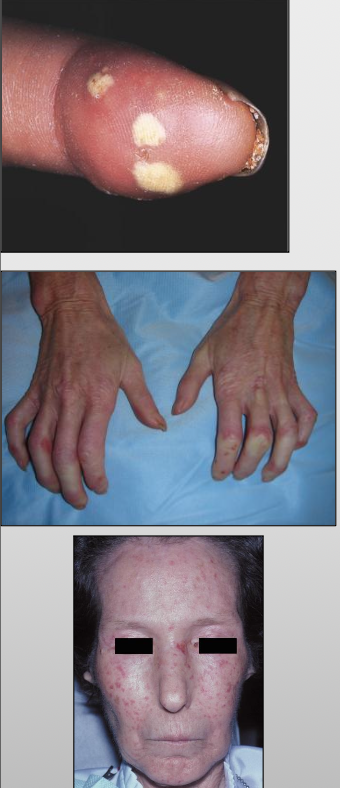
What are the clinical features of scleroderma?
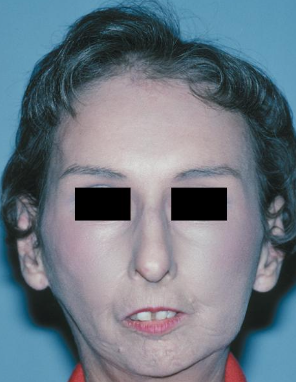
Raynaud phenomenon (not specific for scleroderma)
Mask-like face, loss of ala of nose
Resorption of the terminal phalanges and flexion contractures to produce shortened, claw-like fingers
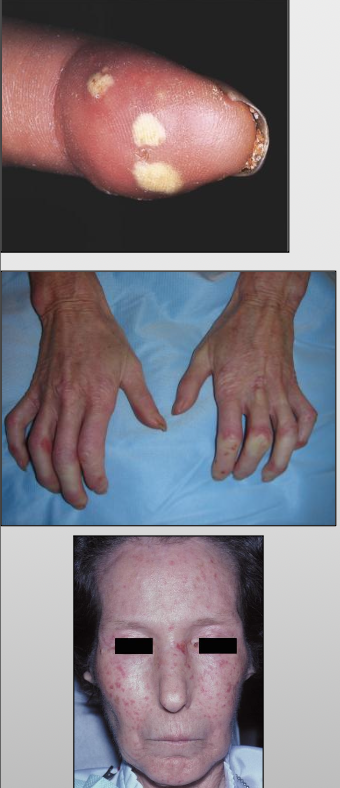
The limited symptoms of scleroderma are referred to as CREST
C-calcinosis- calcium deposits in the skin
R-Raynaud’s phenomenon-spasm of blood vessels in response to cold or stress
E-esophageal dysfunction, acid reflux and decrease in motility of esophagus
S-sclerodactyly-thickening and tightening of the skin on the fingers and hands
T-telangiectasis- dilation of capillaries causing red marks on surface of skin
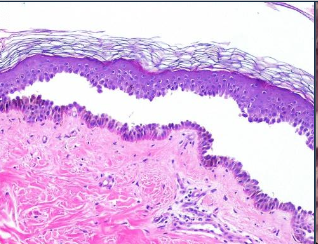
What is Vesiculo-bullous Disease look like histologically?
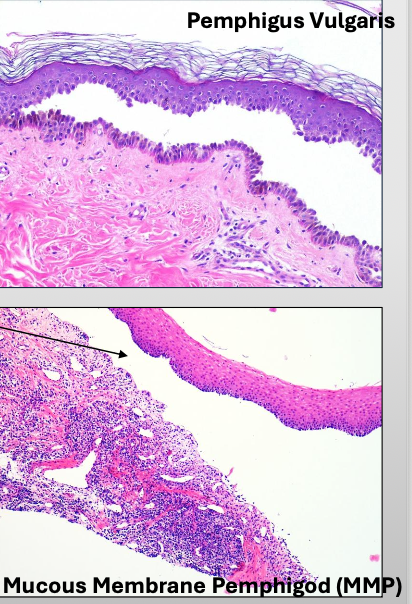
What is Pemphigus Vulgaris?
A severe, progressive autoimmune disease that affects both the skin and mucous membranes
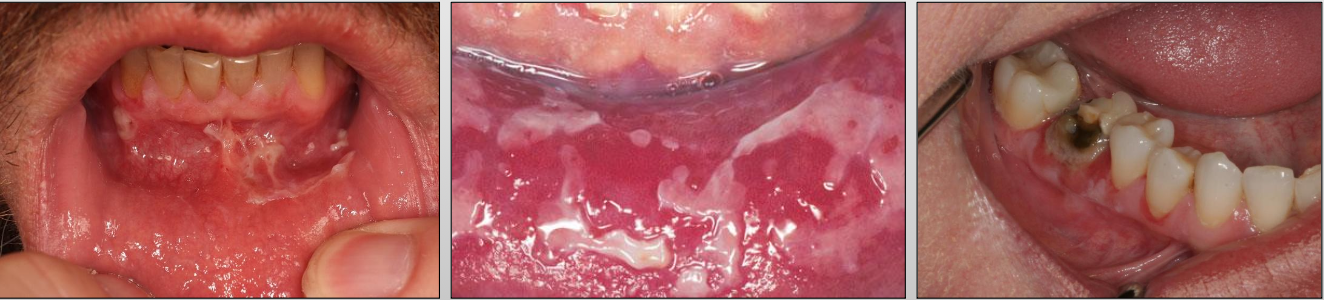
What is acantholysis in Pemphigus Vulgaris?
Epithelial cell separation “INTRA-EPITHELIAL”
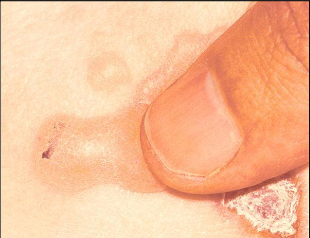
What is Nikolsky sign in Pemphigus Vulgaris?
Gentle finger pressure with movement on clinically normal mucosa can produce acleavage in the epithelium and result in the formation of a bulla
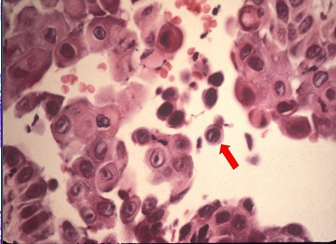
What are Tzank cells in Pemphigus Vulgaris?
Loss of attachment between the epithelial cells results in detached cells that appear rounded, present in the area of separation
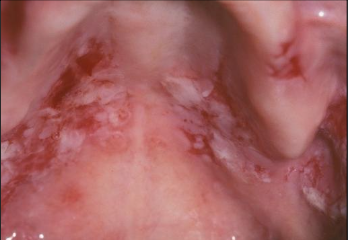
Sloughing of the epithelium Ulcers in Pemphigus Vulgaris
What is the diagnosis for Pemphigus Vulgaris?
Biopsy and Direct immunofluorescence (DIF)- INTRA-EPITHELIAL separation

What is the treatment for Pemphigus Vulgaris?
High does of steroids
What is another name for Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid?
Cicatricial pemphigoid and Benign mucous membrane pemphigoid
What is Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid?
A chronic autoimmune disease that affects the oral mucosa, conjunctiva, genital mucosa, and skin
Which is more severe, Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid or Pemphigus Vulgaris?
Pemphigus Vulgaris
How could Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid heal?
With scarring (cicatricial pemphigoid)
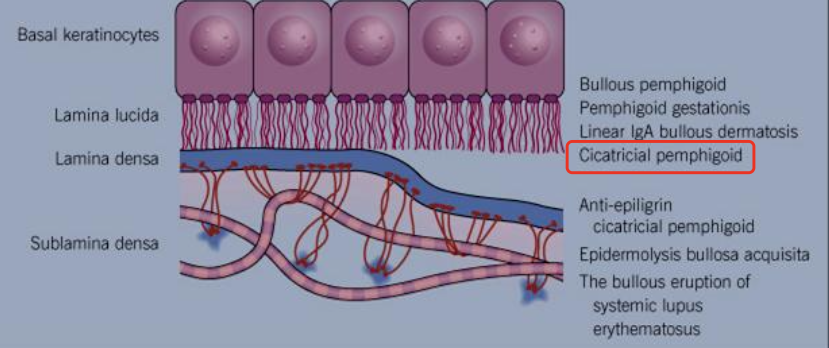
What demographic does Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid affect?
Gender: F > M (2:1)
Age: older adults (60’s) compared to PV
Where might you find Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid?
Skin and mucosa (mouth, genital, eye)
And intraorally: gingiva (most common)
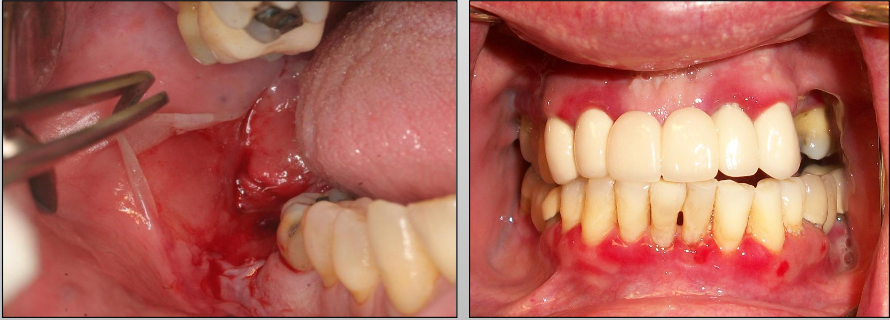
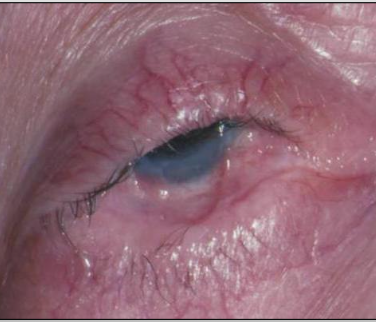
What is a unique clinical feature of Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid?
Symblepharons (fibrous scars) along the eye