C24 - Gauss's Law
Card Sorting
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:43 PM on 7/31/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

Add studentsNo students in these sections. Invite them to track progress!
5 Terms
1
New cards
Electric flux
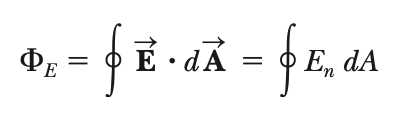
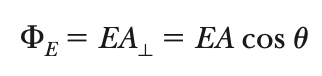
product of area ⊥ field lines and electric field
The “amount” of electric field passing through a given surface
2
New cards
Gauss’s Law
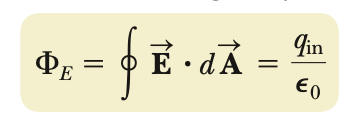
Net flux is dependent only on charge inside the gaussian surface
3
New cards
gaussian surface
a closed surface which, by definition, follows Gauss’s Law & whose e-flux can be found
4
New cards
electrostatic equilibrium
Net charge motion is zero
∑Fe = 0
5
New cards
conductor in ES equilibrium
E = 0 inside surface (including cavities)
Charge (if there is one) accumulates on the surface
E = σ/ε0 just outside surface
Smallest radius of curvature = greatest charge
for irregularly-shaped surfaces