Lecture 37 - Pyretrhins, Pyrethroids, Chlorinated Hydrocarbons, & Cyanobacteria
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What are pyrethrins-pyrethrum and pyrethroids?
Natural (pyrethrins-pyretrhum) or synthetic (pyrethroids) insecticides or flea-tick repellants

Where are pyrethrins-pyrethrum and pyrethroids found?
agriculture, house-home, flea + tick products (93% dogs and cats)
Newer flea+tick products can have __% or greater pyrethrins-pyrethrum and pyrethroids for DOGS only
65
For cats >__% not recommended particularly with the pyrethroid ___ and ___ (but can tolerate others like ___)
1-5%,
permethrin, pyrethrin,
etofenprox
Dogs are very sensitive to ___.
bifenthrin
___ means crop, flowers or product extracted the flowers chrysanthemum.
___are active ingredients in pyrethrum
Six active ingredients in ___: pyrethrin I and II, cinerin I and II, jasmolin I and II
More than a dozen ___ (synthetic products)
pyrethrum,
pyrethrin,
pyrethrum,
pyrethroids
True or False? The toxicity of pyrethrins-pyrethrum and pyrethroids varies via compound, species and route, but in general they are highly toxic to mammals.
False. The toxicity of pyrethrins-pyrethrum and pyrethroids varies via compound, species and route, but in general they have LOW mammalian toxicity.
Cats very sensitive to high concentration products, particularly ___.
Dogs very sensitive to ___.
Reptiles very sensitive to ___.
cats: permethrin, pyrethrin
dogs: bifenthrin
reptiles: permethrin
What is important to know about permethrin or high concentration topical products?
dont use on dogs with cats in house → cats can groom off dog or lay on dog bed where dog has been treated/groomed themselves
some cats respond adversely to normal exposures
True or False? Residues are a problem with pyrethrins-pyrethrum and pyrethroids due to long half lives in the environment and body
False. Residues are NOT a problem with pyrethrins-pyrethrum and pyrethroids due to short half lives in the environment and body
Spot-on pyrethrins-pyrethrum and most commonly __, causes ___ leading to ___.
pyrethroids,
epidermal paresthesia,
inflammatory contact dermatitis
What is the MoA of pyrethrins-pyrethrum and pyrethroids?
CNS excitation
What clinical signs can be seen with pyrethrins-pyrethrum and pyrethroids toxicity?
salivation (irritant, products are bitter)
muscle tremors, twitching (paresthesia)
local effects to the paresthesia: agitated to subdued
temporary blindness (30% of dogs,cats)
convulsions (high doses in cats)
weakness, dyspnea
vomiting, diarrhea, depression
What clin path and lesions do you see with pyrethrins-pyrethrum and pyrethroids?
None, r/o other specific ddx
How do you diagnose pyrethrins-pyrethrum and pyrethroids?
history of use (often have this)
clinical signs: mimics OPs, carbamates, metaldehyde, tremorgenic mycotoxins
no clin path or lesions
chemical residue analysis not commonly run
What is the treatment for pyrethrins-pyrethrum and pyrethroids?
decontamination - clinical presentation, routes, after P is sedated bathe with mild dish soap, apply vitamin E to help with epidural paresthesia
AC-cathartic-gastric lavage w/ stomach tube
control tremors or seizures via methocarbamol or diazepam
wash mouth
maintain hydration, electrolyte statue, body temperature
IV lipid rescue therapy for permethrin considered
therapeutic plasma exchange with bifenthrin
Make sure staff and you wear ___ with pyrethrins-pyrethrum and pyrethroids!
PPE
Why must you be careful with controlling body temperature with pyrethrins-pyrethrum and pyrethroids (and other similar compounds)?
stop cooling at 103.5F to avoid rebound hypothermia
What is the prognosis for pyrethrins-pyrethrum and pyrethroids?
good with treatment over 24-72 hours,
poor in cats with high dose exposures and seizures
What are chlorinated hydrocarbons aka organochlorides?
popular pesticides of old, a group of structurally similar insecticides
True or False? Chlorinated hydrocarbons aka organochlorines are highly restricted in agriculture and veterinary medicine due to environmental contamination.
True.
How do chlorinated hydrocarbons poisonings occur?
products still around, improperly used, improperly stored, malicious
What is the toxicity of organochlorines?
varies, toxic to most mammalian systems
Describe the MoA of organochlorines
lipid soluble, stable → persists in environment and animals → biologic magnification and acts as diffuse nervous stimulant
Describe the onset of organochlorine toxicity
variable, 30-60 minutes
What clinical signs of organochlorine toxicity do you see?
early premonition period (restless, salivation) → muscle tremors of head, neck, entire body → tonic/clonic seizures (intermittent to continuous), excessive response to external stimuli
How do you diagnose organochlorine or chlorinated hydrocarbon toxicity?
history of exposure
tremors and/or seizures; excessive response to external stimuli
chemical residue testing - body fat, serum, milk, liver, brain, GI contents, etc
Describe the treatment of organochlorine or chlorinated hydrocarbon toxicity?
pateitn based
control tremors and treatment
decontaminate
maintain hydration, acid-base status, temperature, etc
What is the prognosis of organochlorine or chlorinated hydrocarbon toxicity?
variable, depends on exposure dose, time to treatment, decontamination
True or False? Organochlorine or chlorinated hydrocarbon toxicity is concerning in production animals and is a regulatory issue due to residues left in body fat.
True.
Cyanobacteria can produce toxins that are separated into two major categories:
hepatotoxic, neurotoxic
True or False? Cyanobacteria blooms is mostly in saltwater and can be seen ALL YEAR ROUND!
False. Cyanobacteria blooms is mostly in FRESHWATER and can be seen ALL YEAR ROUND!
What factors are required for cyanobacteria blooms?
stagnant, eutrophic (low O2, high nutrients), warmish water T, calm weather for 3-5 days, light intensity, pH

What neurotoxins are produced from cyanobacteria?
anatoxin-a: mimics Ach, nicotonic receptor agonist
anatoxin-a(s): now known as guanitoxin, inhibhits AChE, nictonic and muscarinic, more potent than anatoxin-a
What is anatoxin-a?
anatoxin-a: mimics Ach, nicotonic receptor agonist
What is anatoxin-a(s)?
anatoxin-a(s): now known as guanitoxin, inhibits AChE, nicotinic and muscarinic, more potent than anatoxin-a
What are other toxins in cyanobacteria?
sodium channel blockers: saxitoxin, neosaxitoxin
hepatotoxin: microcystin
dermatotoxin: aplysiatoxin, lyngbyatoxin-a
Describe the onset of neurotoxins from cyanobacteria
acute, starts with initial stimulation, and as progresses, paralysis due to continuous depolarization and fatigue
What clinical signs do you see with neurotoxins from cyanobacteria?
premonition
muscle tremors, DUMBSLED, seizures // paralysis
death due to respiratory paralysis
rapid progression
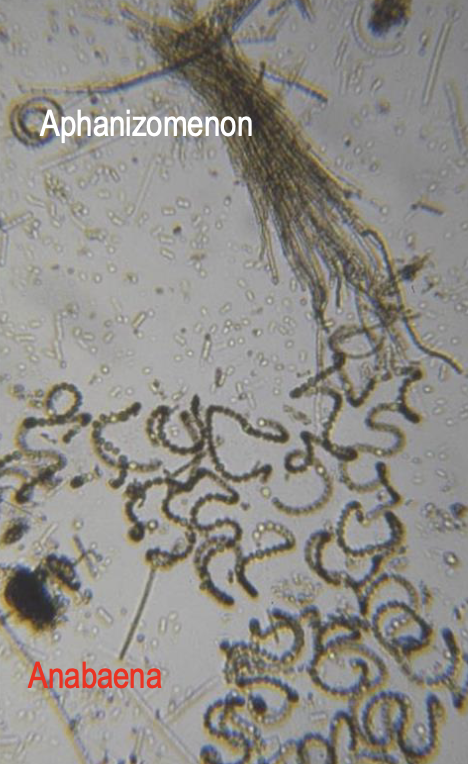
What clinical pathology or lesions do you see with neurtoxins from cyanobacteria?
None
How do you diagnose cyanobacteria neurotoxicosis?
history of exposure
clinical signs similar to OP and carbamates
No clinpath or lesions,
cholinesterase inhibition (blood,brain) as screening
stick test
Algae ID via light microscopy from water, GIT
Test for toxins in water, GIT,
contact Dept of Health
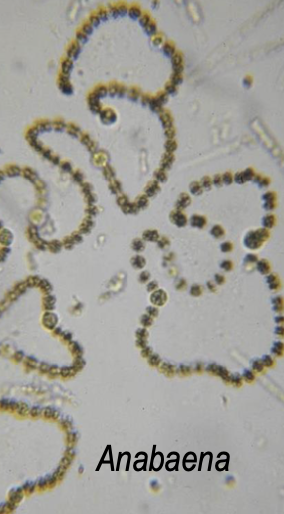
What is the treatment of neurotoxicity from cyanobacteria?
symptomatic and supportive
control tremors and seizures with methocarbamol, support ABCs, temperature
maintain adequate respiration (mechanical, physical)
decontaminate?? atropine for muscarinic signs
cholestyramine — likely excreted via bile, stop hepatic recirculation
What should you do with regards to outside your patient with cyanobacteria toxicity?
Cu sulfate, improve water quality, alert health department as public health concern
What toxins can cause a temporary blindness?
pyrethrins-pyrethrum, synthetic pyrethroids, ivermectin, metaldehyde
lead blindness in cattle tend to be permanent ☹