Dental Trauma
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
what is luxation injury
displacement of a tooth due to traumatic forces (sports injury)
most common injury in primary teeth
why does trauma to permanent teeth matter
commonly causes pulpal necrosis resulting in long term restorative problems
when are the peak times for dental trauma to occur
2-4 - learning to walk and are small, height of a table
8-10 - riding bikes skateboards etc
14-16 - contact sports like hockey etc
how do we prevent dental trauma
difficult
incidence increases with increased overjet so have ortho tx
can make or advise to buy mouthguards
how do we manage dental
trauma
proper diagnosis tx planning and follow ups
quicker the tx the more likely to aid pulpal recovery
what do we do first
check for head injury - also dizzyness nauseousness etc
assess facial/dental injury
where does
story fit/where are the bits
do emergency tx first to stabilise injuries
clean up pt
review and treat or refer to specialist
document everything
what does distal bleeding of the eye corner mean
potential cheeckbone fracture
what do we tell pts not to do and why when potential facial fractures
blow their nose to stop infection / swelling in and around the eye
what types of injuries occur from a blow to the teeth
crown/root fracture =
due to the impact of something hard ie road a golfclub etc
injuries to the socket =
tooth is intact but displaced within the socket
due to impact of something soft ie elbow or fist
what do we do immediatley with dental injuries
bacteria can invade pulp quickly so we cover asap
aids revascularity but vitality of tooth needs monitored
cover exposed dentine with calcium hydroxide
why are dento-alveolar (socket) injuries bad
cos movement of the tooth with likely sever all blood vessels into the pulp via apical foramen so pulp becomes necrotic
what are the types of dental trauma
luxation
avulsion
crown fracture
root fracture
what is luxation
Displacement of the tooth in the alveolar bone
subdivuded into;
concussion
sublaxation
intrusive luxation
extrusive and lateral luxation
this happens because alveolar bone is less calcified and has decresed elasticity so tjat trauma to primary is lilely to cause displacemnt or evulsion
what is concussion
is an injury to the tooth without displacement or mobility of the tooth
occurs when minor damage to pdl so increase of bacterual injury - OH needs to be stressed
what is subluxation
tooth is mobile but not displaced
occurs when minor damage to pdl so increase of bacterual injury - OH needs to be stressed
what are the clinical signs of concussion/sublaxation and why
TTP
haemorrhage and oedema in PDL but gingival bleeding only happerns if sublaxated
what do we do if there is mobility
if there is mobility dont check TTP and vitality check the teeth 1 week
how do we manage concussion/sublaxation
PA
soft diet for a week
advice to parents possible sequelae
follow up
check imms status ie tetanus
what is intrusive luxation
most common upper primary incisors
usually palatal and superior displacement of the crown
is usually not issue to permanent tooth
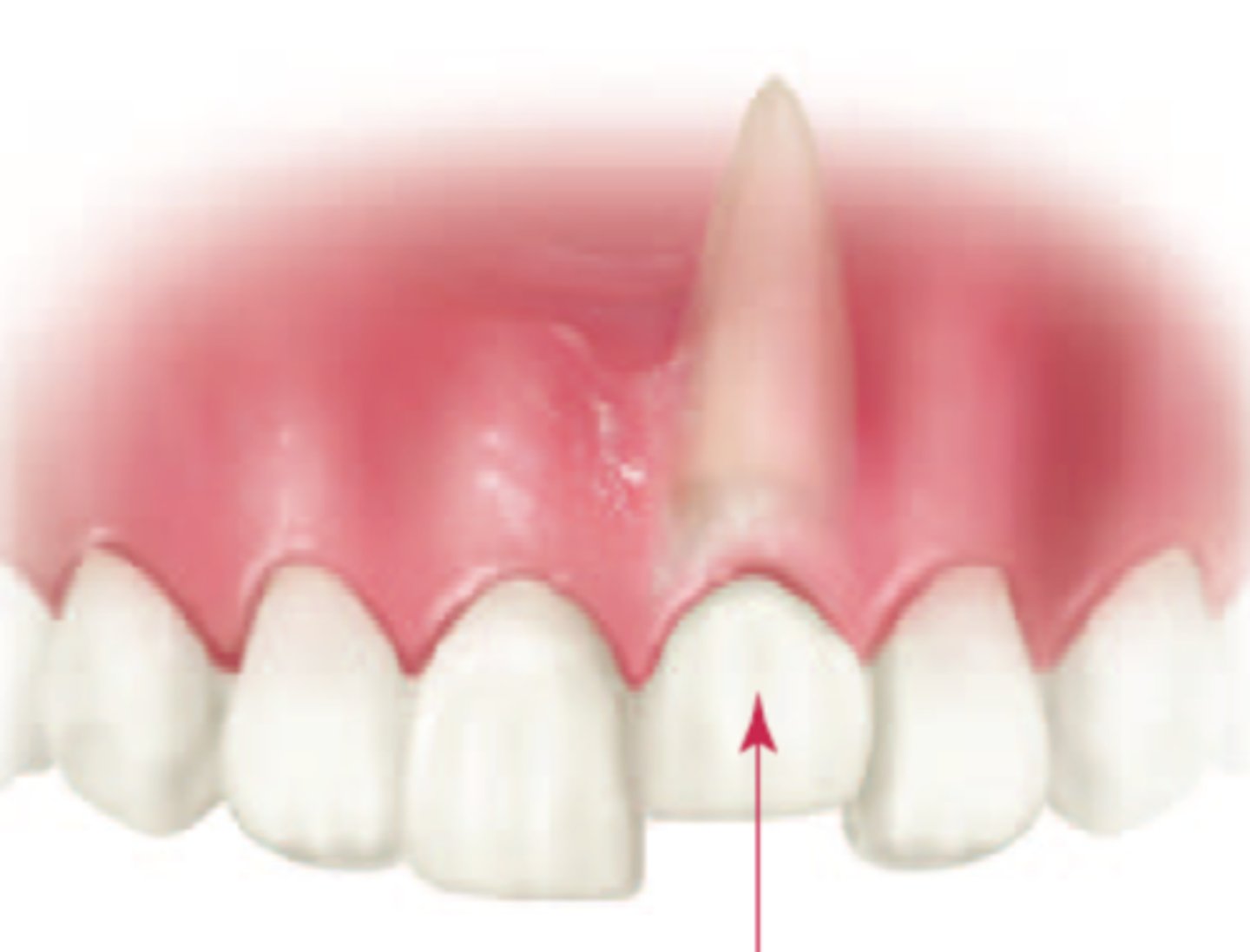
how do we manage intrusive luxation
crown visible with minor alveolar damage - usually just leave it as it will probs re erupt
whole tooth intruded - needs extracted as its likely of damaging perm follicle
if alveolar bone and ginviae inboled probs extraction but is pt dependant
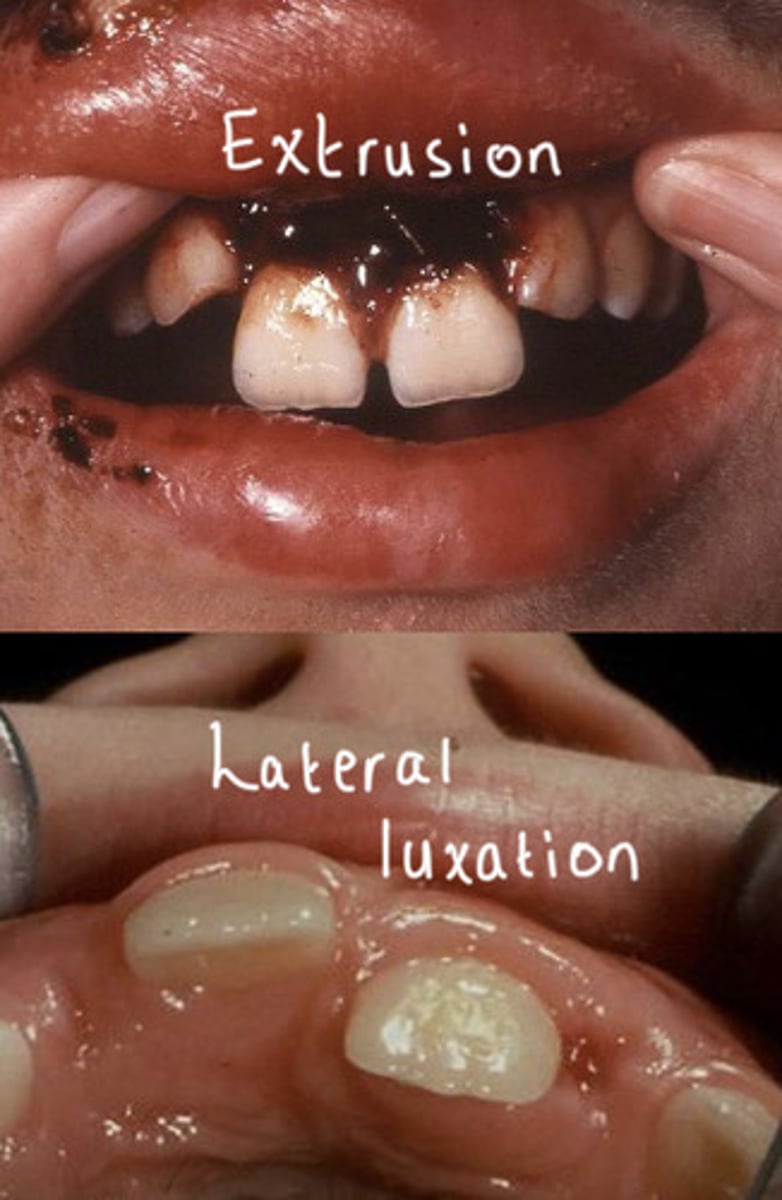
what is extrusive and lateral luxation
extrusive - tooth moved out the socket due to pdl
lateral - direction thats not straight up or down
tx dependant on mobility and extent of displacement
if excessive mobility then extract
what is avulsion
tooth completelt knocked out the socket
primary avulsion shouldnt be replanted cos of lack of pt cooperation and damage to perm follicle with blood clot
if it already is replanted by parent and is viable then leave it
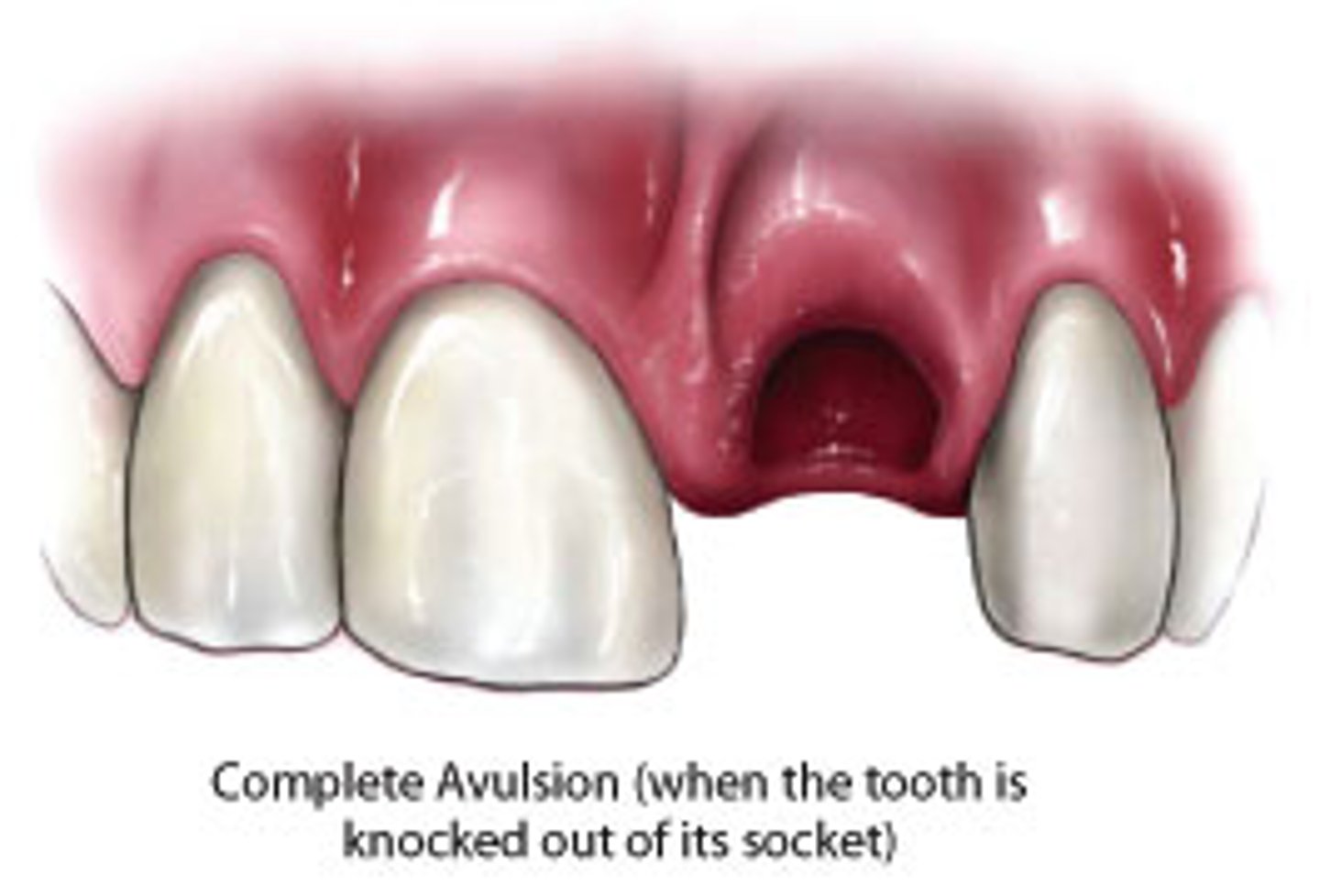
how do we manage avulsion of permanent tooth
replant immeditatly
pdl is viable only 30 mins
store in milk or isotonic saline or saliva
dont rinse or scrub it
wrap in clingilm to not dry out pdl
90mins and its only 10% chnace
ask child to bite in clean cloth until tx
how do we fix primary incisors
not pulp - smooth with disc and restore with GI or comp
complicated crown/root - more likely pulp and below gingival margin
can get pulpal plyp after injuty
how do we manage fractures of primary incisors
frgaments should be removed
remaining tooth can be extracted at a later date
small pieces of root remaining in socket after a fracture cn be left
root fracture - if signs of pulpal necrosis, excessive mobility sinus etc remove coronal portion and the root will resorb
minimal fracture just smooth it and no tx needed
what is sequalae after trauma to primary teeth
all traumatised teeth rewuire follow up
difficult to predict prognosis esp w perm teeth so guarded prognosis
reassure pt and parents
discuss w pts possible options
how do we initially manage permanent fractures
initial manegment matters
time is of essence
ensure injury is stable and reduce infecton risk
how do we treat permanent fractures
uncomplicated - treat crown fracture close to pulp, if no ine available treat with comp bandage
if pulp is involved, refer to be seen same day
what possible damage can occur to primary and perm teeth after trauma
necrosis of the pulp and grey discolouration and abcess formation like me
internal resorption of the primary tooth
ankylosis of the primary tooth
MIH of successor teeth
dilaceration of perm tooth germ