ch9 - electrochemistry
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
galvanic cells
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Explain electrochemistry
Since REDOX reactions involve transfer of electrons, its possible to physically separate the oxidant (oxidising agent) and reductant (reducing agent) into different locations
The process of electrons moving from reductant to oxidant is called ELECTRICITY
Redox reactions can be used to generate electricity if the two-half reactions are PHYSICALLY SEPARATED
define electrochemical cell
a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy (galvanic cells), or vice versa (electrolysis cells)
define a galvanic/voltaic cell
a type of electrochemical cell; a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy
define battery
a combination of cells connected in series
identify all the parts in creating a battery / Daniell cell
light globe or galvanometer (an instrument for detecting electric current)
salt bridge
2 electrodes (usually solid & are labeled as cathode or anode) with corresponding (electrolyte) solutions
2 beakers
wires to connect the electrodes to the light globe or galvanometer
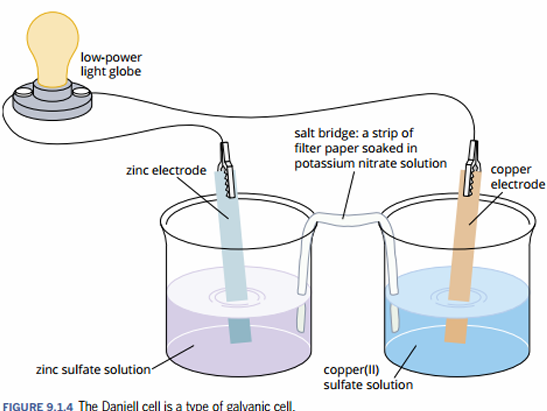
define cathode & anode
cathode: an electrode at which a reduction reaction occurs - has a + charge
anode: an electrode at which an oxdiation reaction occurs - has a - charge
define salt bridge
an electrical connection between the 2 half cells in a galvanic cell; usually made from a material saturated in (relatively unreactive) electrolyte soln
define electrode
a solid conductor in a half cell at which oxidation or reduction reaction occur
define electrolyte
a chemical substance that conducts an electric current as a result of dissociation into positively & negatively charged ions
in electrochemical cells, these ions migrate towards the negative & positive electrodes
ANY electrochemical cell consists of TWO half cells:
explain the setup of these half cells
state where oxidation occurs & why
state where reduction occurs & why
Each half cell consists of an electrode (metal or graphite) in contact with an electrolyte solution (sol. containing ions).
OXIDATION takes place at the ANODE (-ve electrode) as it generates electrons
(An Ox)Oxidation = loss of electron
REDUCTION takes place at the CATHODE (+ve electrode)
(Red Cat)Reduction = gain of electrons
Electrons flow from the ANODE to CATHODE (-ve to +ve)
define external circuit
identify what part/s of an electrochemical cell is an external circuit
the section of an electrochemical cell in which electrons move
this section of the circuit will include wires attached to the electrodes
define internal circuit
identify what part/s of an electrochemical cell is an internal circuit
the part of an electrochemical cell in which ions move
solutions & salt bridge
how is the reaction of chemical energy transforming into electrical energy found?
by adding the 2 related half equations together
in a half cell there is a conjugate redox pair - explain what this is
an oxidising agent & the product that’s formed when the oxidising agent gains electrons
or
a reducing agent & the product that’s formed when the reducing agent loses electrons
define inert
a substance that is unreactive
when labeling a diagram of a galvanic cell - what do you need to include?
anode
cathode
electrode polarity
direction of electron flow in external circuit
direction of flow of ions in the solns & the salt bridge
explain/draw the setup of a galvanic cell that uses gas & a metal anode
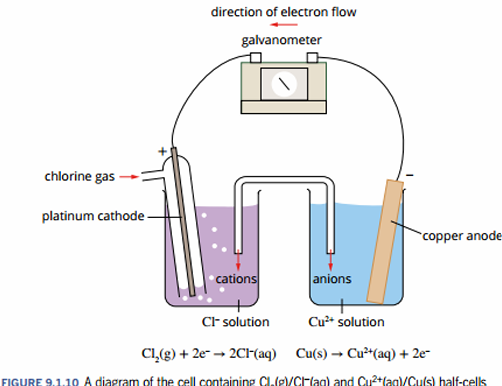
how does a salt bridge allow a cell to produce electricity?
it prevents the accumulation of charge
cations in the salt bridge move towards the cathode
anions move to the anode
how can a galvanic cell reaction produce heat energy instead of electrical energy?
if the reactants are allowed to come into direct contacts, the chemical energy is converted into heat energy instead of electricity
How do you get the Eoox from reading the data sheet?
If you read the table backwards (right to left), the electrons are now gained and the Eo sign is flipped; Eoox
The numerical value of - Eored = Eoox
How do you know if a reaction is spontaneous or non-spontaneous?
The Eo cell determines whether a reaction will be spontaneous or not (i.e. whether electricity will be produced). When adding two half cell e naughts together;
a positive Eo = spontaneous
a negative Eo = nonspontaneous
Explain what it means when the Eored is positive or negative on the data sheet
The more positive the value of Eored the stronger the oxidising agent (reduction).
The more negative the value of Eored the stronger the reducing agent (oxidation).
what does Eo stand for & how are these values found?
standard electrode/reduction potential
found by connecting the half-cell to a standard hydrogen half-cell and measuring the volage produced
what is Eo a numerical measure of? & what is the table showing these values called?
a measure of tendency of a half-cell reaction to occur as a reduction reaction
in other words: The voltage produced is a measure of the driving force for a redox reaction to occur.
electrochemical series
what can comparing Eo values determine & what is the purpose of determining this?
we can determine relative strengths of oxidising & reducing agents which can be used to predict half-cell & overall cell reactions
Explain ‘E naught’ values in redox reactions
This property is used to rank the strength of different oxidising agents.
The table of standard reduction potentials is such a ranking.
(These are found on your Data Sheet and are called ‘E naught’ values.)
for a spontaneous reaction to occur, can you use 2 oxidising agents or 2 reducing agents?
no - has to be 1 oxidising agent & a reducing agent
How do you find (cell) potential difference & what is this used for
difference = higher half-cell Eo - lower half-cell Eo
higher = oxidising agent
lower = reducing agent
difference is used to see whether a reaction is spontaneous or not
the standard half-cell potentials in the electrochemical series are measured under standard conditions - why?
other conditions, the order of half-reactions may be different, therefore predictions based on the electrochemical series may not be reliable
what are the type of galvanic cells that convert chemical energy directly into electrical energy
primary, secondary & fuel cells
how can a cell be rechargeable?
the products of the discharge reaction have to remain in contact with electrodes
define primary cell
a galvanic cell that is non-rechargeable because the products of the reaction migrate away from the electrodes
define secondary cell
a rechargeable cell
how can a secondary cell be rechargeable?
by connecting them to an external source of electricity
during the recharging of a secondary cell, the equation for the reaction that occurs during recharging is the ___ of the equation for the cell discharging
during the recharging of a secondary cell, the equation for the reaction that occurs during recharging is the reverse of the equation for the cell discharging
A secondary cell can act as a galvanic cell & a electrolytic cell - explain how
acts galvanic when it discharges = releasing electrical energy
acts electrolytic when recharged = converting electrical energy into chemical energy
define fuel cell
a type of electrochemical cell in which the reactants are supplied continuously, allowing continuous production of electrical energy
explain 2 pros of using fuel cells than combusting fuel
electricity generation using fuel cells is more efficient than if the electricity were generated by the combustion of the same fuel
less emissions of greenhouse gases from using fuels cells than if the fuel were burnt in a power station or vehicle
some scientists predict that fuel cells will play a key role in the transition from a dependence on ___ ___ for energy to a ____ economy
some scientists predict that fuel cells will play a key role in the transition from a dependence on fossil fuels for energy to a hydrogen economy
define dry corrosion
the oxidation of a metal by oxygen gas
define wet corrosion
involves oxygen gas & water
can be considered as an electrochemical process
explain wet corrosion relating to iron
during wet corrosion, the iron is oxidised to Fe2+ (aq) & oxygen gas is reduced to OH- (aq)
these form a precipitate of Fe(OH)2 (s), which is converted to rust → Fe2O3·xH2O
what are the protection measures against corrosion?
surface coating, alloying, cathodic protection & the use of a more reactive metal as a sacrificial anode
are galvanic cells spontaneous or non-spontaneous?
spontaneous