3.3: AD-AS in Short- and Long-Run
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1JwEYM2CvMZVmS63Fy0r2LMlGUcLjQKGU/view
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
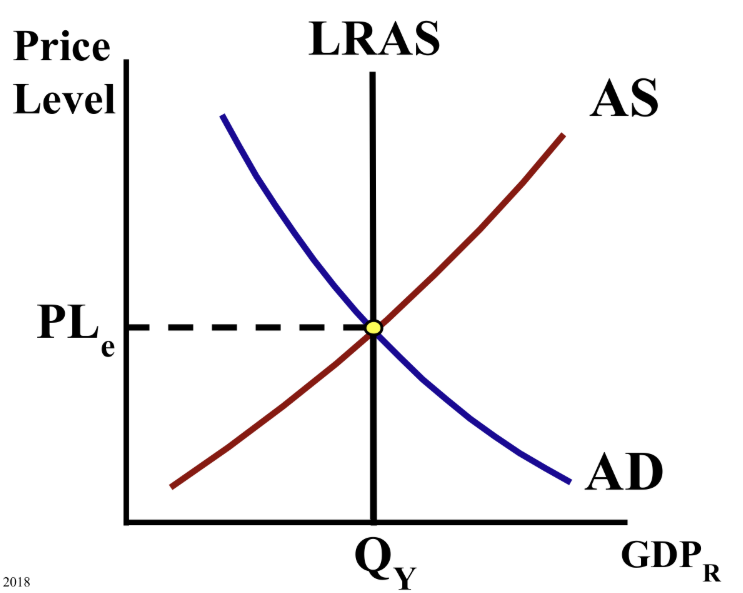
This is the economy at full employment output. Write out the full name of the terms LRAS, AS, and AD.
Long-term aggregate supply, aggregate supply, aggregate demand.
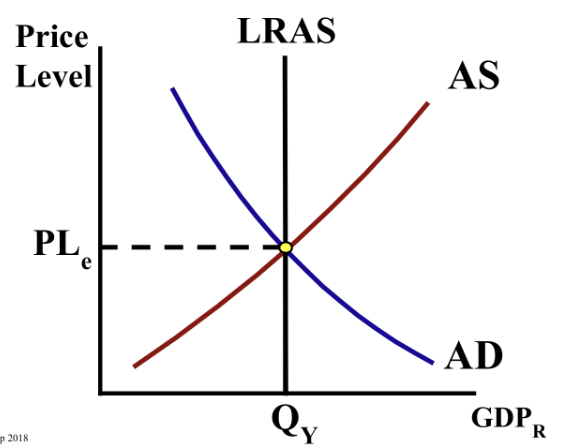
What is full employment also known as? The economy is (above/below/at) full employment (NRU), and there is a (positive/negative/no) output gap.
Actual GDP is (above/below/at) potential GDP.
at, no, at
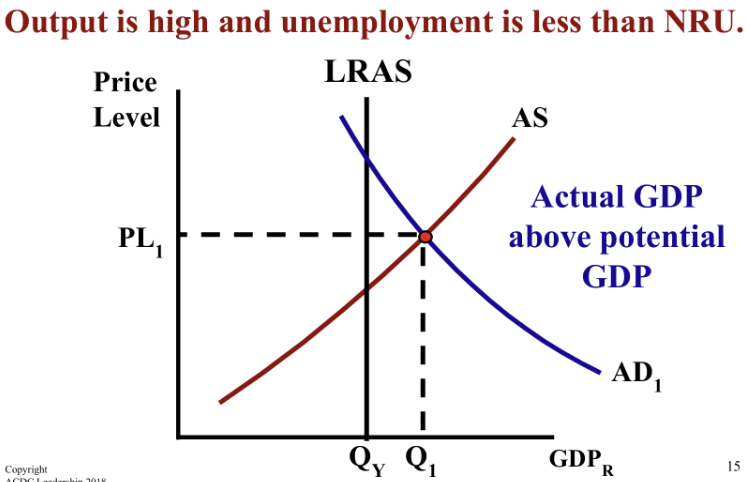
When the economy has an inflationary gap, the economy is (above/below/at) full employment (NRU), and there is a (positive/negative/no) output gap.
Actual GDP is (above/below/at) potential GDP.
above, positive, above
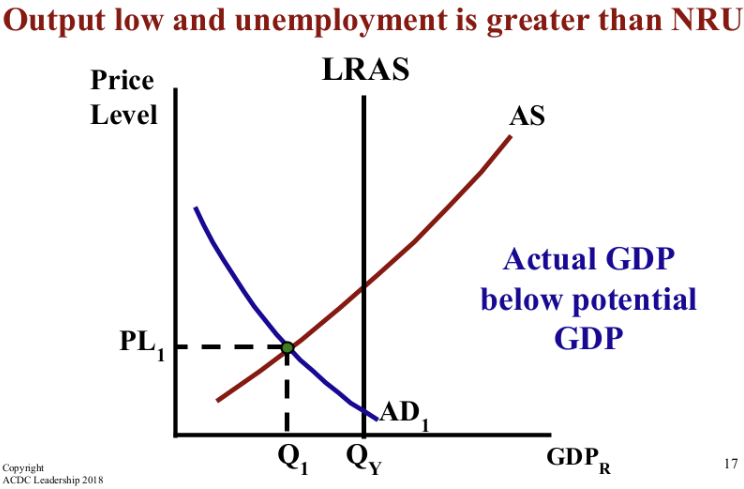
When the economy has a recessionary gap, the economy is (above/below/at) full employment (NRU), and there is a (positive/negative/no) output gap.
Actual GDP is (above/below/at) potential GDP.
below, negative, below
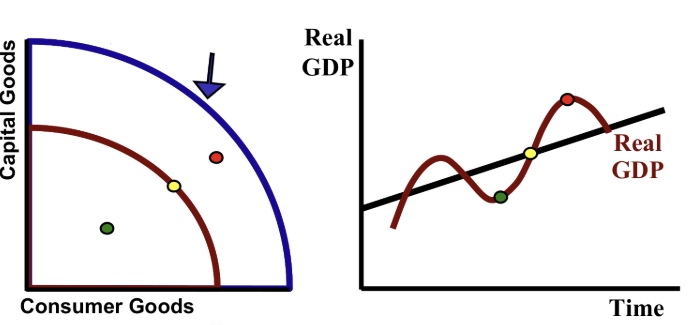
The economy can only be in one of three places at any time.
Explain:
What state is the economy at in the red dot?
What state is the economy at in the yellow dot?
What state is the economy at in the green dot?
What state is the economy at in the blue line (of the PPC)?
What state is the economy at in the red line (of the PPC)?
Inflationary gap
Full employment
Recessionary gap
Max capacity (0% unemployment)
Full employment
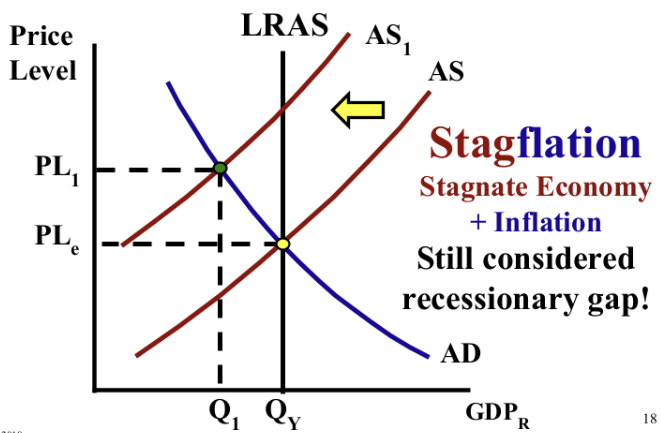
What is stagflation? Is it an inflationary or recessionary gap?
High inflation, slow/no economic growth, and high unemployment all at once. Recessionary gap.
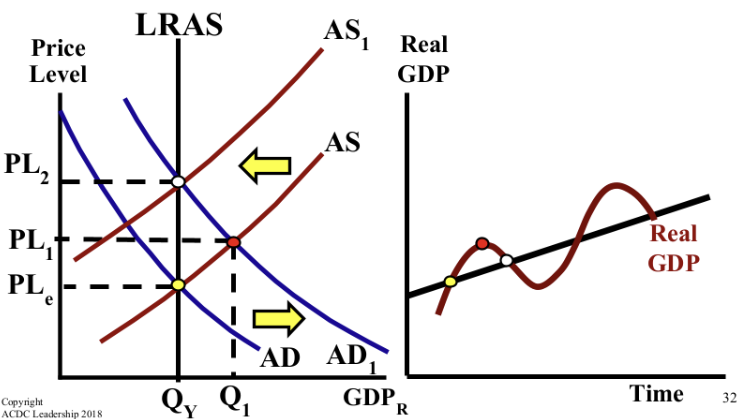
If consumer spending increases, what happens in the short-run and long-run? How does AS, AD, and the LRAS shift?
AD shifts right, AS shifts left. In the long-run, wages and costs increase.
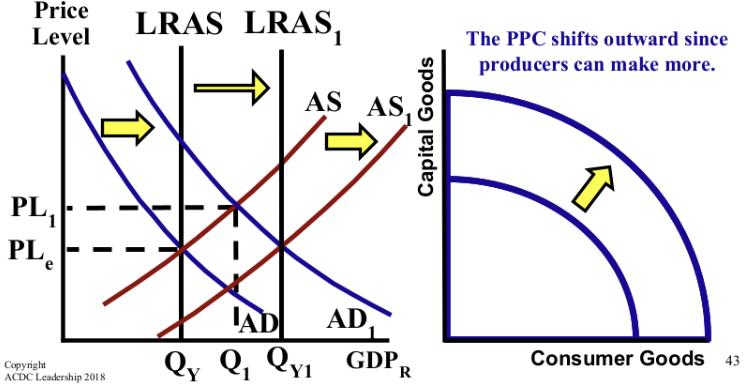
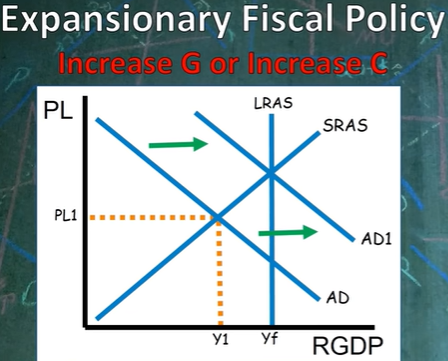
T/F: Increases in consumption or government spending causes economic growth.
If false, correct this statement.
False. Only investment causes growth because firms increase their capital stock.
(The image shows economic growth that results as firms increase their capital stock.)
What is capital stock?
Machinery and tools purchased by businesses that increase their output.
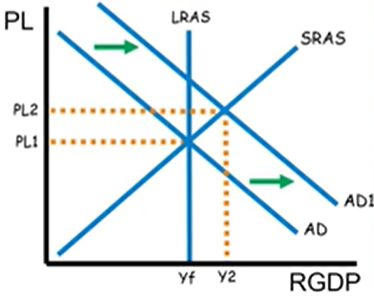
What type of shock is this—specifically, what is it called? If we wanted to create this shock with an adjustment to exports, what should happen to exports?
Demand-pull inflation is when AD shifts to the right. Exports would increase to cause this.
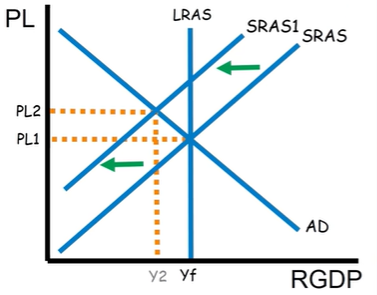
This is a negative SRAS shock. What are two other names for it?
Cost-push inflation and stagflation.
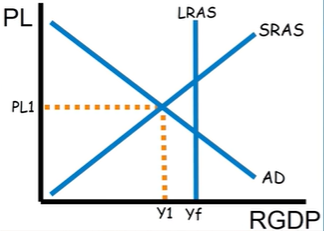
Is this a recessionary or inflationary gap?
Recessionary gap
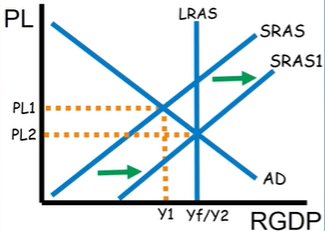
When an economy does its automatic long-run adjustment to a recessionary or inflationary gap, does the AD or SRAS curve move?
SRAS
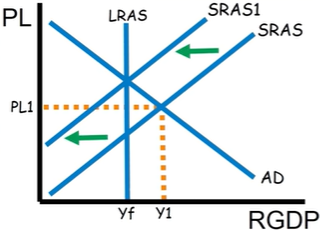
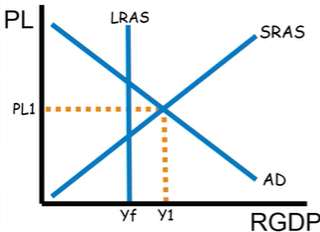
Is this a recessionary or inflationary gap?
Inflationary gap
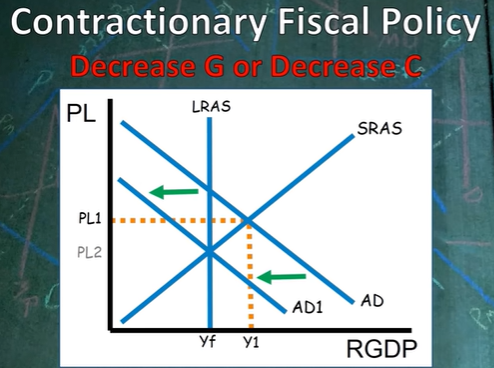
When fiscal policy is implemented (e.g. contractionary or expansionary fiscal policy), what moves? SRAS or AD?
AD