Anatomy Final (Part 1)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Ionic bonds vs. covalent bonds
give up electrons
share electrons
Hydrogen bonds are important for shaping which molecules?
Proteins and DNA
What is the only type of carbohydrate that can be used for energy?
monosaccharides
Polysaccharides
cellulose, starch, glycogen
saturated fatty acid structure
carboxyl group + fatty acid tail with no kinks
unsaturated fatty acid structure
carboxyl group + fatty acid tail WITH kinks
What is the polarity of a phosphate head versus the fatty acid tail in a phospholipid?
head - polar
tail - non polar
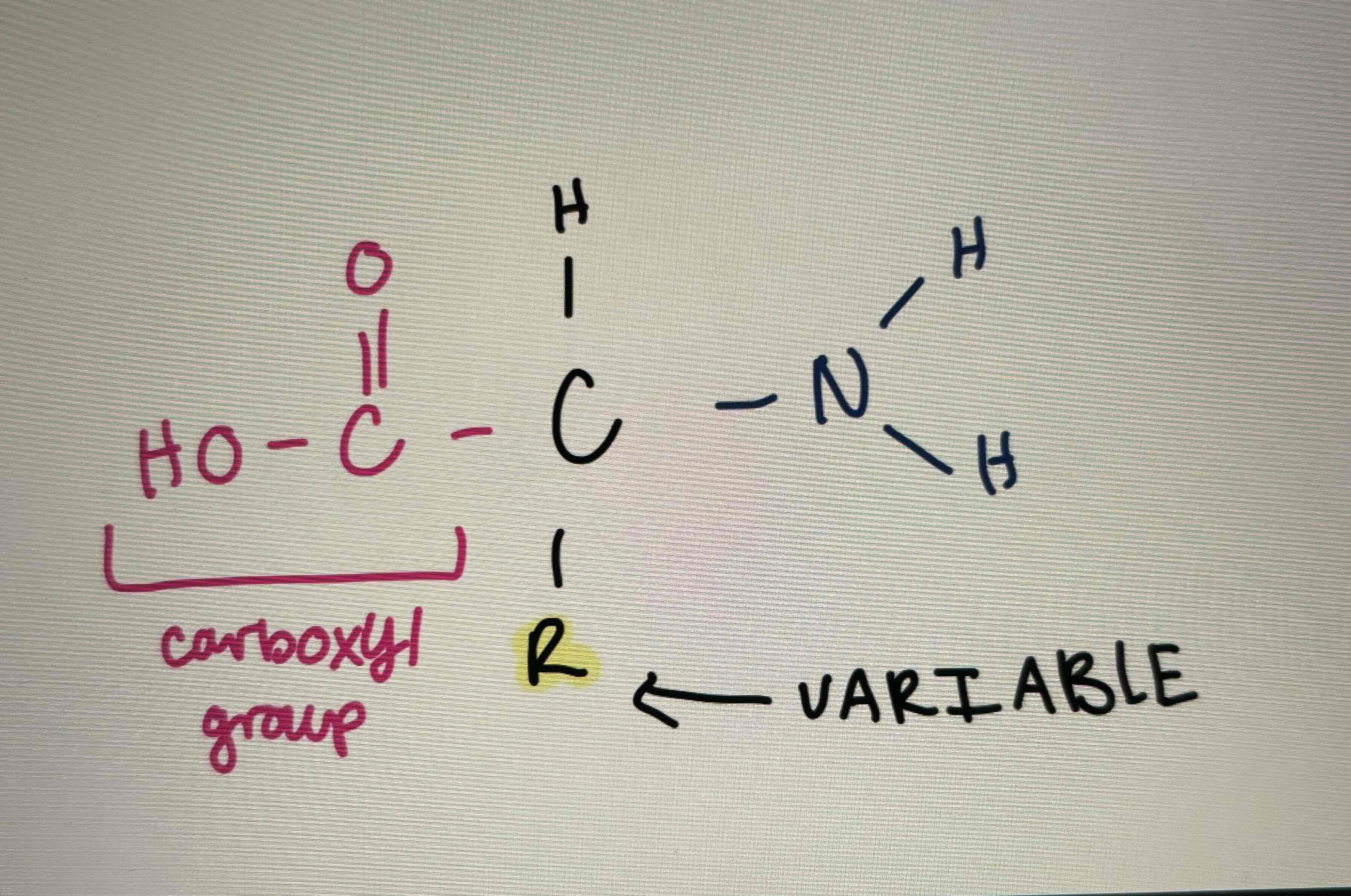
What is this?
Protein structure
What is secondary protein structure a result of?
H bonding
codon
sequence of 3 nucleotides
anticodon
binds with the matching codon - contained in tRNA
End product of glycolysis
2 pyruvic acid
4 ATP
2NADH
2H+
End product of glucose catabolism
about 36 ATP
Stratified squamous ET location
High stress areas - skin
Simple cuboidal ET location
Kidney tubules, pituitary, ovaries
Simple columnar ET (non-ciliated) location
Inner lining of the small intestine
Simple columnar ET (ciliated) location
respiratory tract, fallopian tubes
(T/F) cartilage is vascularized
false
Fibroblasts
Produce CT fibers / parts of the matrix
Reticular fibers
stabilizes organs, blood vessels, nerves and other structures
Elastic fibers
Found in the air sacs of lungs, dermis, blood vessels, and in-between vertebrate.
Hyaline cartilage vs Elastic cartilage vs fibrocartilage
ends of long bones/between ribs
epiglottis and larynx
Intervertebral disks
Dense regular CT
secures bones - makes up tendons and ligaments
dense irregular CT
dermis of skin - layered around cartilage and bone
order of the epidermis (most superficial to deepest)
corneum, lucidum, granulosum, spinosum, basal
Layers of the dermis
Papillary, reticular, subcutaneous
Acetylcholine
ACh - stimulates muscle contraction
When do LG Na+ channels open?
When a stimulus arrives at the plasma membrane
refractory period
period of time after the action potential has been activated where the neuron cannot be excited
When do VG potassium channels open?
30 mV / same time as Na+ channels are closing
When do sodium VG channels close?
30 mV
When do Na+ channels open
threshold (-55 mV)
how is repolarization accomplished?
K leak channels and the Na/K pump
resting neuron mV
-70 mV
Where on the neuron are graded potentials received?
dendrites
LG channel location
soma and dendrites
VG channel location
axolemma, sarcolemma and synaptic knobs