Adv. Bio Cellular Respiration
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/74
Last updated 11:59 PM on 1/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
1
New cards
Define autotroph
An organism that creates its own food from inorganic substances
2
New cards
Define heterotroph
An organism that must consume other organisms in order to break them down and create energy for itself.
3
New cards
In eukaryotic cells, what is the main function of cellular respiration?
To break down food molecules (glucose) and release usable chemical energy
4
New cards
What percentage of energy is kept for the cell to use? What happens to the other energy?
39% is kept, the rest is lost from the heat
5
New cards
What is the chemical equation for cellular respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
6
New cards
What are the reactants in cellular respiration?
Glucose and (6)oxygen
7
New cards
What are the products of cellular respiration?
(6)CO2 and (6)H2O
8
New cards
Which reactant is oxidized? What does it turn into once oxidized?
Glucose is oxidized, turns into (6)CO2
9
New cards
Which reactant is reduced? What does it turn into once reduced?
Oxygen is reduced, turns into (6)H2O
10
New cards
Which steps of cellular respiration are anaerobic?
Glycolysis
11
New cards
Which steps of cellular respiration are aerobic?
Krebs Cycle and the ETC
12
New cards
What input is needed for glycolysis to occur?
glucose
13
New cards
Where does glycolysis take place in the cell?
cytoplasm
14
New cards
What are the products of glycolysis?
Pyruvic Acid (Pyruvate), 2 net ATP, and 2 NADH
15
New cards
What types of organisms perform glycolysis reactions for energy production?
ALL LIVING ORGANISMS
16
New cards
Explain the net production of ATP in glycolysis
4 ATP are made overall, but 2 ATP must return to the start of the process in order to power the cycle - meaning only two are kept.
17
New cards
What molecule conversion during the Prep reactions? (Between glycolysis and krebs cycle)
Pyruvate created in glycolysis is broken into acetyl coA.
18
New cards
Where are the Krebs Cycle and Prep Reactions located?
In the matrix of the cell
19
New cards
What molecules are produced from the Krebs Cycle?
(4)CO2, (2)ATP, (6)NADH, and (2)FADH2
20
New cards
What molecule produced from the Krebs Cycle is given off as waste?
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
21
New cards
Which of the molecules produced from the Krebs Cycle continues to the ETC?
NADH and FADH2
22
New cards
What is the function of the NADH and FADH2 molecules?
To transport excited electrons from the Krebs Cycle to the ETC
23
New cards
Where is the Electron Transport Chain located in Eukaryotes?
The inner membrane/cristae of the mitochondria
24
New cards
Where is the Electron Transport chain located in prokaryotes?
The plasma membrane(mesosome)
25
New cards
How does the structure of the ETC help it function more efficiently?
The many folds that make up the cristae increase the surface area / room for reactions
26
New cards
Energy from the ETC is used to pump H+ from ____ to ________.
Matrix, inner membrane
27
New cards
What are the specific inputs to the ETC reactions?
O2, NADH, FADH2, and ADP+P
28
New cards
How is ATP generated in the ETC? What is the process called?
This process is called oxidative phosphorylation. Electrons carried by NADH+H+, and FADH are transferred to oxygen-forming ATP.
29
New cards
Where does the ATP produced in the ETC go?
The ATP diffuses out of the matrix/mitochondria to power the rest of the cell.
30
New cards
Once NADH and FADH2 provide their electrons and hydrogen, what happens to them?
NADH and FADH2 turn into NAD+ and FAD respectively. They then pick up more H+ from the diffusion gradient, and are reused/returned to both Glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle
\
\
31
New cards
How is water produced from cellular respiration?
The hydrogen (from the gradient) bonds with oxygen to form water.
32
New cards
What metabolic pathway is present in both fermentation and cellular respiration?
Glycolysis
33
New cards
What are the two types of fermentation?
Alcoholic Fermentation and Lactic Acid Fermentation
34
New cards
What is the product of Alcoholic fermentation?
Ethyl Alcohol and Carbon Dioxide
35
New cards
What is the product of lactic acid fermentation?
lactic acid
36
New cards
Example of alcoholic fermentation
yeast
37
New cards
Example of lactic acid fermentation?
yogurt, cheese
38
New cards
How much ATP is produced during fermentation?
2 ATP (because its just glycolysis)
39
New cards
What is the primary purpose of fermentation?
To regenerate NAD+ so glycolysis can continue to happen
40
New cards
Name the four stages of cellular respiration?
Glycolysis, prep reactions, Krebs/Citric Acid Cycle, Electron Transport Chain
41
New cards
Can organic molecules other than glucose be metabolized?
Yes, but they enter the process at a different stage
42
New cards
Define catabolism
Reactions that break down molecules (cellular respiration) (Exergonic)
43
New cards
Define anabolism
reactions that build molecules (endergonic) (photosynthesis)
44
New cards
what are the outputs of cellular respiration
carbon dioxide, water, ATP
45
New cards
what are the inputs of cellular respiration
glucose and oxygen
46
New cards
what is the output of glycolysis
Two pyruvate molecules, 2 net ATP, and 2 NADH
47
New cards
What is the option after glycolysis if no oxygen is available?
fermentation
48
New cards
which metabolic pathway begins with glucose and ends with pyruvate
glycolysis
49
New cards
what can pyruvate be used for if there is oxygen?
Entering the mitochondria for the prepreactions if oxygen is available.
50
New cards
what can pyruvate be used for if NO oxygen is avaliable?
Converting to alcohol or lactic acid in fermentation if oxygen is not available.
51
New cards
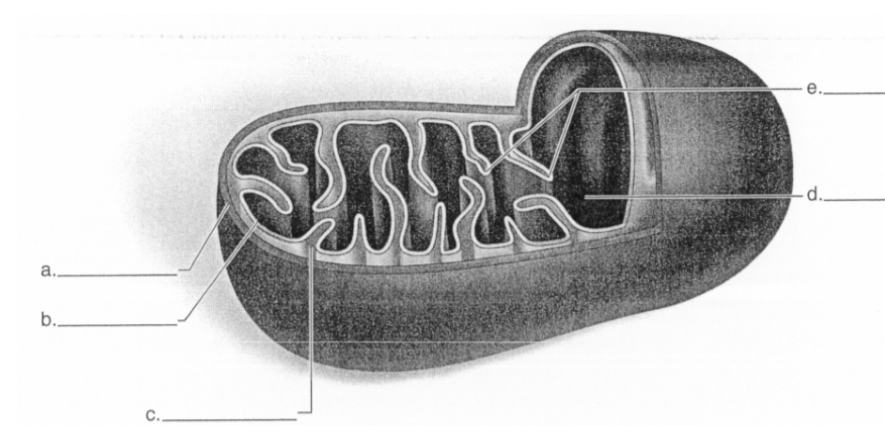
What does letter A represent in the diagram?
outer membrane
52
New cards
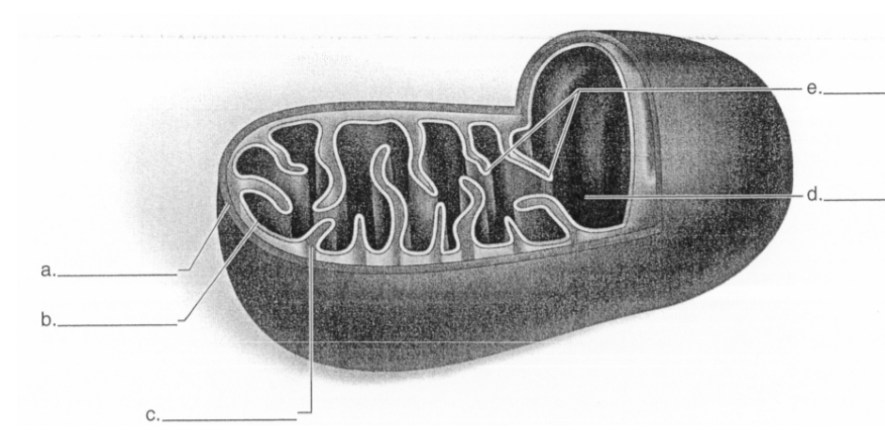
What does letter B represent in the diagram?
inner membrane
53
New cards

What does letter C represent in the diagram?
intermembrane space
54
New cards
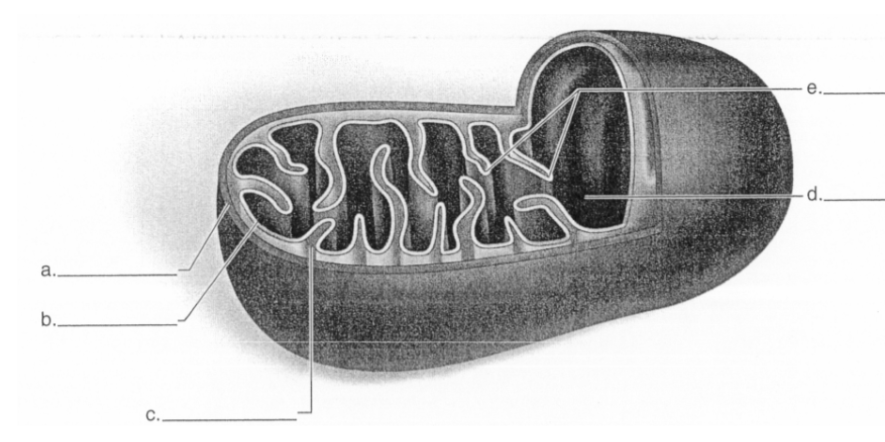
What does letter D represent in the diagram?
matrix
55
New cards

What does letter E represent in the diagram?
cristae
56
New cards
In which part of the cell does the ETC take place?
Inner Membrane/Cristae
57
New cards
Explain the carbon molecule conversion that occurs in the Prep reactions prior to the Krebs Cycle.
The pyruvate that enters the prep reactions after being created in glycolysis is turned into acetyl. This is significant because the pyruvate has 3 carbon, while acetyl has only 2 carbon. Then, CO2 is released. Coenzyme A then forms acetyl coA by adding itself to the acetyl.
58
New cards
what is the input to prep reactions?
pyruvate, coA, and NAD+
59
New cards
what is the output of prep reactions?
Acetyl coA, NADH, and CO2
60
New cards
what molecules are produced from the krebs cycle?
CO2, NADH, FADH2, and 2 ATP
61
New cards
what molecules are the input to the electron transport chain?
FADH2, NADH, Oxygen, and ATP+P
62
New cards
What molecules are the product of the electron transport chain?
Water, NAD+, FAD, and 32-34 ATP
63
New cards
What happens to electrons in the ETC?
High-energy electrons will be released from the electron carriers (NADH and FADH2) and move along the inner membrane of the mitochondria, passing from one carrier protein to the next, giving energy as they go for pumping of H+. Electrons will then be received by oxygen, the final electron acceptor.
64
New cards
Energy from the ETC is used to pump H+ from ________ to _________.
matrix, intermembrane space
65
New cards
What happens as H+ atoms that have gathered in the intermembrane space flow down the concentration gradient?
ATP is produced from ADP+P
66
New cards
explain the importance of oxygen in the ETC
Oxygen is the final electron acceptor and needs to be there to collect the electrons at the end of the ETC. ETC relies on oxygen to be present in order to occur. Since the bulk of ATP is made in the ETC, without oxygen, aerobic cellular respiration could not happen, which greatly reduces the amount of energy that can be released for the cell to use.
67
New cards
Which metabolic pathways use Substrate Level Phosphorylation?
glycolysis and krebs cycle
68
New cards
which metabolic pathways use Oxidative Phosphorylation?
ETC
69
New cards
Which metabolic pathway does NOT result in NADH?
ETC
70
New cards
What is the name of the enzyme that carries the acetyl to the krebs cycle?
coenzyme A
71
New cards
what are the products of lactic acid fermentation?
lactic acid, NAD+
72
New cards
what are the products of alcohol fermentation?
ethyl alcohol, CO2, NAD+
73
New cards
What is the primary function that is shared by both types of fermentation?
To remove electrons from NADH and have a supply of NAD+ to enter glycolysis again (keeps glycolysis going)
74
New cards
What happens to pyruvate during fermentation in humans?
the pyruvate is converted to lactic acid
75
New cards
What happens to pyruvate during fermentation in yeast?
Pyruvate is converted to ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide