MCAT Missed concepts
1/471
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
472 Terms
In Translation, which step is the most expensive?
tRNA loading because it requires 2 GTP
What affects Vmax directly?
Vmax is directly dependent on concentration of enzyme and enzyme efficiency (kcat)
What affects Vmax indirectly?
Temperature and pH, inhibitors/activators, substrate concentration
What does ADH (vassopressin) do and where do they come to effect in the nephron?
Increase H20 reabsorption in collecting ducts and proximal distal tubules of the kidneys
Where is bile synthesized?
Synthesized in the liver and stored in the gallbladder
What’s the difference between diploid inheritance and Mendelian inheritance?
💡 A:
Diploid inheritance = 2 copies of each chromosome (1 from each parent)
Mendelian inheritance = how traits are passed (dominant/recessive alleles)
Explain what would happen to Vmax and Km if you increased temperature, substrate concentration and enzyme concentration?
Higher temperatures = Vmax ↑ (until denaturation) and no effect on km (think of km as affinity of enzyme to substrate).
Increase [enzyme]= Vmax ↑, Km same
increase [substrate]= no change in Vmax, km same unless inhibitor is present
What does morbidity vs mortality mean?
Incidence of disease vs incidence of death
Would you divide or multiply from ng —→ kg? What about kg —→ ng?
Divide from ng —→ kg
Multiply from kg —→ ng
What does Truncating mutation mean?
Genetic alterations= premature termination (like nonsense mutation) so proteins become truncated (“trancados”)
How do you identify WT vs mutant on a gel?
💡 A:
✅ Look for common bands = likely WT
✅ Smaller bands = possible truncation mutation
Use size & pattern to compare across lanes
Which is the nucleophile and electrophile in DNA/protein synthesis
3' OH = nucleophile (attacks)
5' phosphate = electrophile (gets attacked)
✅ New nucleotides add to the 3' end
What is PCR genotyping?
💡 A:
A technique to find genetic differences using specific primers.
❌ Wrong primer = missed allele = error
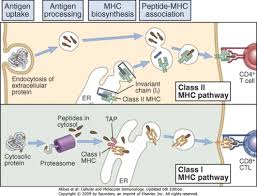
What type of cells are MCH I and II found and how do they intake foreign particles?
MCH I: Found in all cells which presents antigen endogenously to CD8 T cells.
MCH II: Found in APCs (antigen presenting cells like macro/dendritic/ B cells) presents antigen exogenously to CD4 Helper T cells.
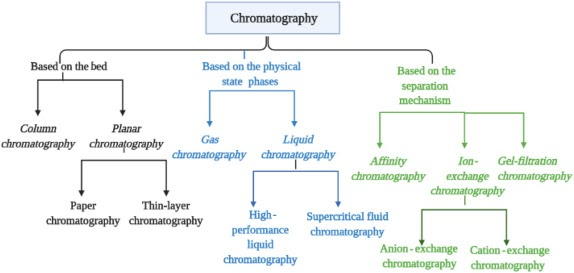
What does Ion Exchange Chromatography separate?
Molecules based on charge (uses charged resin).
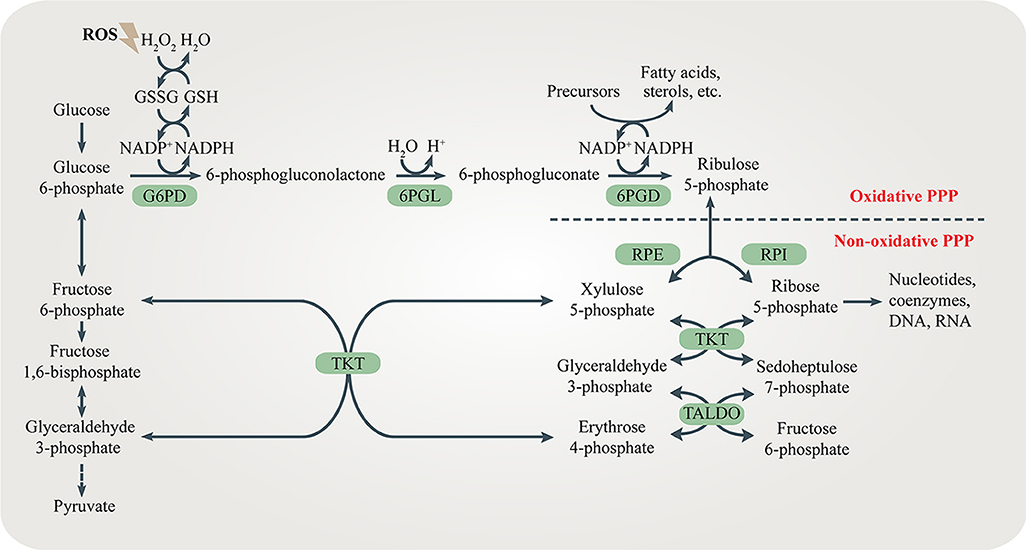
What is NADPH used for?
💡 A:
Made in PPP (from G6P + NADP⁺)
Used for fatty acid synthesis
Used in nucleotide synthesis (ribose)
Acts as a reducing agent in cytoplasm
Could bacteria plasmid participate in conjugation?
No, unless it has the F factor
How could you alter membrane integrity to make it collapse?
Making membrane more rigid to sever strong connections between the membrane and cytoskeleton.
Remember that membrane is naturally flexible so making it have a rigid shape will make it collapse.
Which type of fiber(s) is involved in endurance and sprinting/weight lifting exercise?
Type IIa: Intermediate fast twitch
Type IIx: Fast twitch (sprinting/weightlifting)
Type I: Slow twitch (endurance)
Note: Keep in mind all muscles have these types of fibers but it differs in their concentration
What do Pons and the medulla (in brain) and limbic system do?
Pons: regulate body’s sense of balance
Medulla: regulates homeostatic functions (breathing/cardiac /digestion/ involuntary regions)
Limbic System: Regulates emotions
Where does osmolarity primarily occur in the nephron?
Collecting duct
In Fatty acid synthesis, what would cause acetyl-coa activation?
Synthesis of malonly-coa. It inhibits fatty acids from associating with carnitine and entering mitochondria
What stimulates and inhibits the Krebs cycle?
💡 A:
Stimulates:
ADP
NAD⁺ / FAD
Inhibits:
ATP
NADH
Citrate
Succinyl-CoA
Would morula stem cells be more or less differentiated than inner cell mass stem cells?
Morula stem cells would be less differentiated than ICM stem cells.
What does the thyroid regulate?
Thermal and metabolic rate. Individuals who lack this for idiopathic reasons have weight gain and fatigue
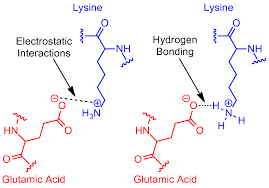
What are Salt bridges in proteins?
non-covalent interactions combining electrostatic attraction and H-bonding between opposite charged AA
What is hydrolase?
Hydrolase is an enzyme that use water to speed up a reaction like hydrolysis
What is the Lineweaver Burk plot equation
1/v0 = (km/Vmax)(1/[S]) + 1/Vmax
relate to y=mx + b
y would be 1/v0
m= slope so km/Vmax
x= 1/[s]
b= 1/Vmax
If a patient that is fasting has hypertriglyceridemia , what happens?
The glycerol from the triglyceride would get converted into ketone bodies in the liver.
Can glucose turn into fat?
💡 A:
✅ Yes!
Glucose can make glycerol and fatty acids for fat storage.
What characteristics make phospholipids unique?
Each have their own mass, charge, and solubility. This is thanks to backbone, polar head, and FAs chain
Why do cells store glucose as glycogen?
To reduce osmotic pressure.
To lower osmotic pressure — free glucose draws in water, glycogen does not.
What is the average weight of 1 AA? (missed this twice)
110 Da or 0.11 KDa
What do electrostatic interactions do?
They form both hydrogen and ionic bonding
Can cysteines form salt bridges?
No, salt bridges are a non-covalent interaction and cysteines are only involved in covalent interactions
T/F Do Complex I, II, III, IV pump H+ protons into intermembrane space. Would this be against or for concentration gradient.
False: Complex II does not participate in pumping protons into intermembrane space.
H+ are pumped against their [concentration] gradient and contribute to decrease in pH in intermembrane
![<p>False: Complex II <strong>does no</strong>t participate in pumping protons into intermembrane space. </p><p>H+ are pumped <strong>against their [concentration] gradient</strong> and contribute to decrease in pH in intermembrane</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b13df70e-9db1-403d-81e5-dbd9702b5773.jpg)
T/F: Are electrons transferred to carriers with higher oxidation potentials?
False: Electrons transfer to carriers with higher reduction potentials
Which amino acid has an R configuration?
Cysteine has an R configuration, the rest have an S configuration
What enzymes are involved when intaking fructose in skeletal muscle and liver/intestine?
Skeletal muscle: Fructose → using hexokinase→ fructose-6-phosphate. Has feedback inhibition
Liver/intestine: Fructose → using fructokinase → fructose-1-phosphate. Does not have feedback inhibition. Can undergo ATP depletion
Can Fructose bypass PFK?
Yes, it can bypass PFK and lead to unregulated glycolysis and fat production.
Which 2 enzymes are involved in breaking glycogen down?
Phosphorylase + debranching enzyme
What does phosphoglucomutase do?
Phosphoglucomutase is involved in breakdown of glycogen
Converts glucose-1-phosphate → glucose-6-phosphate
What does glucose-6-phosphatase do?
Converts glucose-6-phosphate → glucose
What cofactor is regenerated under aerobic and anerobic conditions?
Under aerobic conditions: NAD+ gets regenerated by oxidation of NADH in ETC
Under anerobic conditions: ETC can’t regenerate enough NAD+ so lactate synthesis takes place and oxidizes NADH to NAD+ as pyruvate is reduced to lactate.
Which AA can’t be converted to glucose?
Leucine and lysine
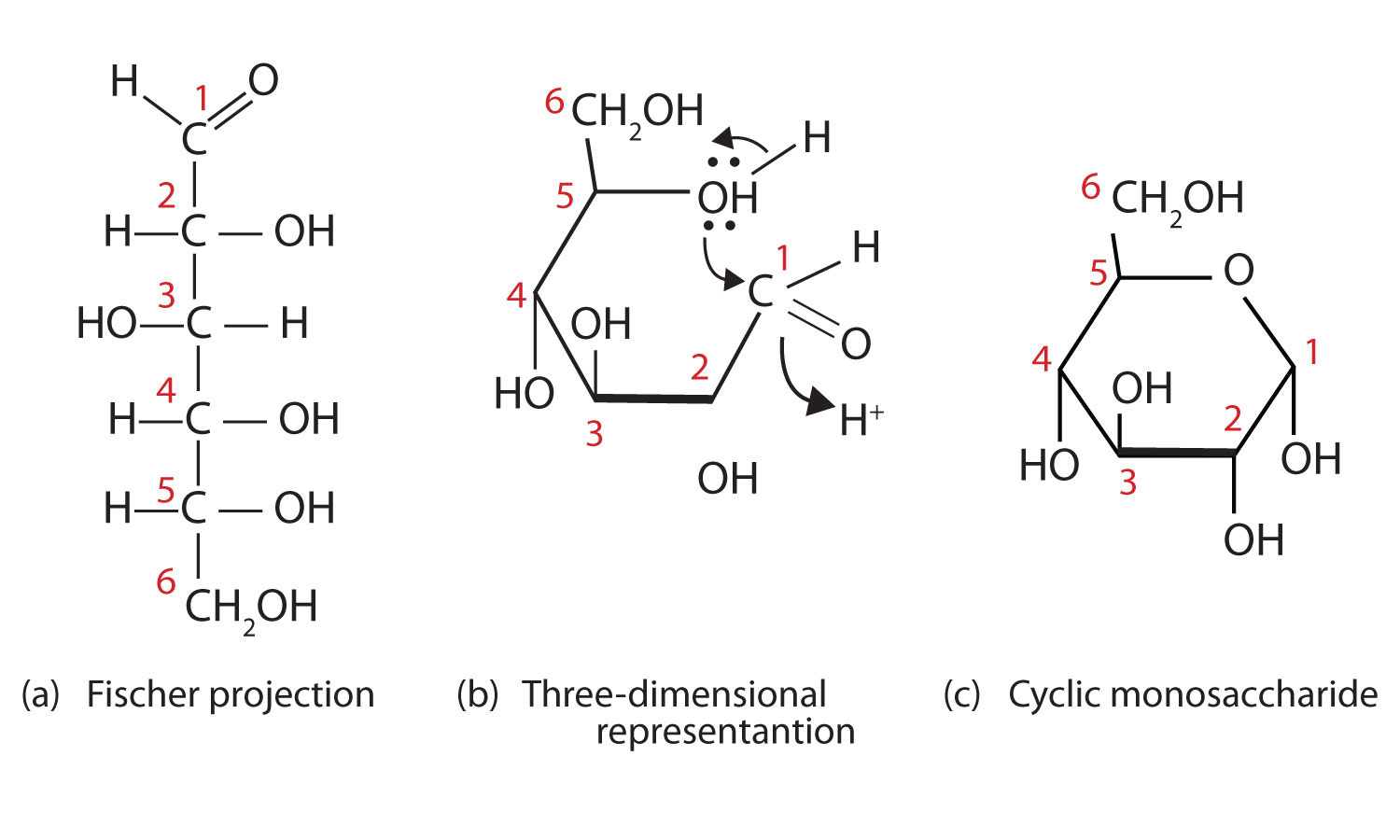
What Fischer projection would glucose be?
Glucose would be beta-D-glucose
What does Clathrin do?
Functions in formation of vesicles to assist in transport within cells (endocytosis)
what is the difference between an amine and amide?
Amine is -NH2 and Amide is NH2 bound to carboxylic acid
What is Chemiosmosis?
Chemiosmosis = Using H⁺ (proton) flow to make ATP as seen in ETC
In genetics when you see the term “and” vs “or” what would you do?
And= multiply
or= add
Which area of the nephron would have the highest reabsorption of water?
Collecting duct of medullary region would have the highest absorption thanks to ADH and absorption of Urea allowing more H20 to be absorbed.
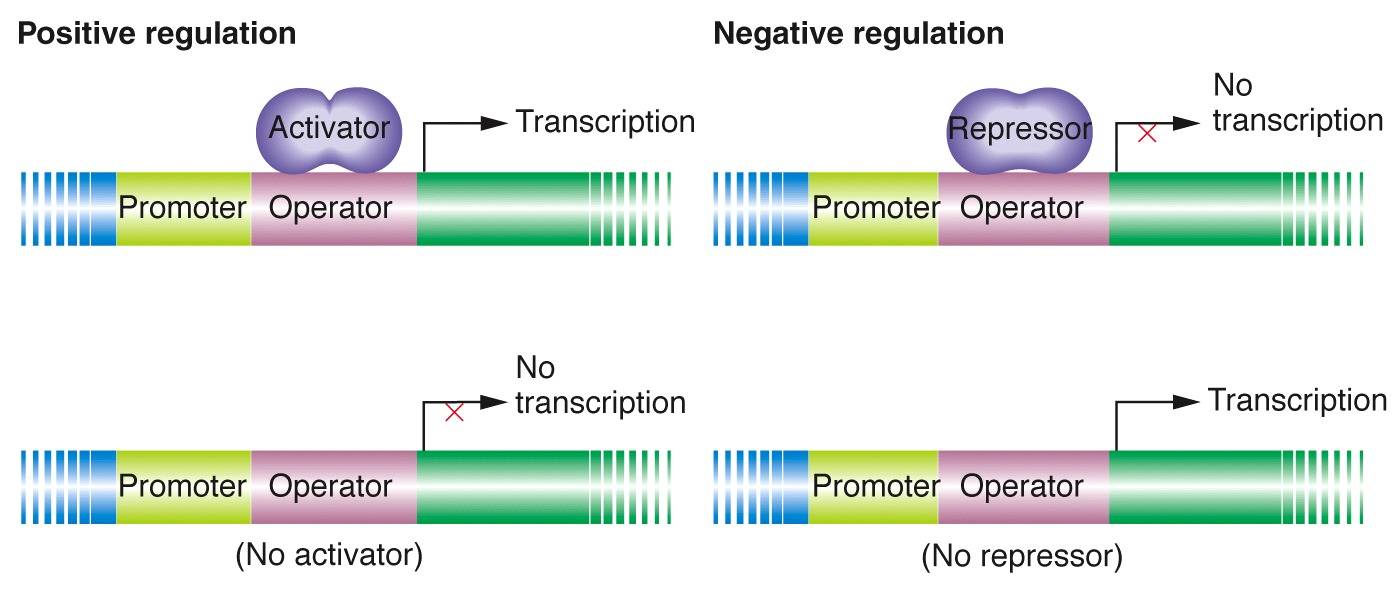
Where would transcription factors, repressors, activators bind on DNA?
Enhancers: Transcription factors which in turn activate the promoter region which RNA polymerase binds to and starts transcription
Repressors/Activators: operator
What is the initial filtration step in glomerulus regulation of filtrate?
Passive flow due to pressure difference
Glomerulus forces solutes out of the blood by pressure
Can enzymes alter local pH?
Yes, they can alter pH in their active site to allow more favorable binding with substrate.
Can enzymes alter substrate primary structures?
No, they can’t change a primary structure (aka AA sequence). Proteases can but in specific cases.
What is an Enzyme Assay?
A lab test that tests how well an enzyme works.
Assays measure how well something behaves or performs
T/F: Does aldosterone increase K+ secretion into nephron?
T: aldosterone helps increase K+ secretion into nephron so K+ levels in collecting duct go up
T/F: Does aldosterone help increase absorption of HCO3- ions?
T: Yes, aldosterone does help increase absorption of HCO3- ions
Why is the endomembrane system important and which parts of the cell are the endomembrane system?
Important in modification of translated polypeptide
Seen in ER/ Golgi/ nuclear envelope
Does the brain rely on ketone bodies when insulin resistant?
No, ketone bodies are alternatives during fasting where there is a low glucose supply. There are insulin-independent alternatives when insulin resistant.
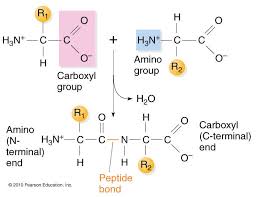
What functional group is formed when AA bond?
Amide bond also known as peptide bond (amide =peptide)
Physics: Tell me the equation that relates power to work
Work= Power x Time. Power can be in watts= J/s, ft x lbs/s
Why is a C–O bond weaker in tertiary alcohols than in primary ones?
More substituents = more crowding = weaker C–O bond (less stable).
How do substitutions affect acid/base strength?
More substitutions on a base = stronger base
More substitutions near an acidic proton = weaker acid
What’s left after an acid or base does its job!
Acid → loses H⁺ → becomes conjugate base
Base → gains H⁺ → becomes conjugate acid
How does resonance affect acid strength? (Aka finding the acidic proton)
If the conjugate base has resonance, it’s more stable, so the acid is stronger and the proton is more acidic.
How do SN1 and SN2 reactions affect stereochemistry?
SN2: Inverts stereochemistry (like flipping a pancake 🥞)
SN1: Makes a racemic mixture (50% R, 50% S) because of the flat intermediate
What is rate law?
The rate law shows how the rate of a reaction depends on the concentration of the reactants involved in the rate-determining step.
Rate law= how many reactant molecules [conc reactant] affects the speed of rxn.
What is a homogeneous catalyst and a downside?
Same phase as reactants.
Downside: Hard to separate.
What is a heterogeneous catalyst and a downside?
Different phase than reactants. Makes it easier to separate and reuse
Downside: Less interaction.
Which metals get oxidized vs. reduced in redox reactions?
Reactive metals (Group 1, 2, Zn, Al) → oxidized
Less reactive metals like transition metals (like Cu, Ag) → reduced
Metals wanna lose e⁻, transition metals are chill taking them 😎
What do hydrolases do?
Use water to break a molecule into two (hydrolysis).
What do lyases do?
Add or remove groups to form or break double bonds.
What do ligases do?
Join two molecules using ATP (bond formation).
What do isomerases do?
Rearrange atoms within a molecule (same formula, different shape).
What do transferases do?
Transfer a functional group from one molecule to another.
What’s ΔG for protein folding vs unfolding?
Folding = −ΔG (spontaneous)
Unfolding = +ΔG (needs energy)
What’s ΔG for peptide bond formation vs breaking?
Forming = +ΔG (needs energy & enzymes)
Breaking = −ΔG
What’s ΔG for general chemical bond formation vs breaking?
Forming = −ΔG (favorable)
Breaking = +ΔG
What does Affinity Chromatography separate?
Proteins based on specific binding (like antibody–antigen).
What does Gas Chromatography separate?
💡 A:
By boiling point and volatility.
High BP = slower.
What does Size-Exclusion Chromatography separate?
💡 A:
By size — large molecules elute first, small get stuck in beads.
What does TLC (Thin Layer Chromatography) separate?
💡 A:
By polarity — nonpolar travels farther.
Rf = spot ÷ solvent front.
What does Column Chromatography separate?
💡 A:
By polarity — nonpolar elutes first in silica gel column.
How does glucose become fat?
Glucose → glycerol-3-phosphate
Glucose → pyruvate → acetyl-CoA → fatty acids
Can fat turn into glucose?
💡 A:
❌ No — fatty acids can’t become glucose
✅ Only glycerol part of fat can → glucose
What happens to fat during fasting?
💡 A:
Fat undergoes β-oxidation to make energy (ATP).
Which enzymes are regulated in krebs cycle (there are 2) and by what ?
Enzyme Regulation:
Isocitrate dehydrogenase: ⬆ by ADP, ⬇ by ATP & NADH
α-Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase: ⬇ by NADH & Succinyl-CoA
What binds after the primer to start elongation?
💡 A:
DNA polymerase III binds to the RNA/DNA duplex to start replication.
What do SSBPs do during DNA replication?
💡 A:
They stabilize single-stranded DNA and keep it open.
What does helicase do in DNA replication?
💡 A:
It unwinds the DNA helix by breaking hydrogen bonds between strands.
💥 Opens up the replication fork like a BOSS.
Where is vitamin D activated into calcitriol?
💡 A:
In the liver and kidney.
💥 Diet/skin → liver → kidney → calcitriol (active form)
How is vitamin D activated in the body?
💡 A:
Skin + sunlight makes vitamin D₃
Liver → first conversion
Kidney → final step → calcitriol (active)
T/F: PTH stimulates phosphate reabsorption.
F: PTH stimulates phosphate excretion!!
What does it mean if there is an overlap between mean and standard error deviation in a graph?
If overlap then means are not statistically different
What happens when ovaries are removed?
💡 A:
⬇ Estrogen & progesterone → menopause irritability, bone loss, infertility, breast atrophy
What is the mean vs median?
💡 A:
The average: add all values, divide by how many.
The middle value when data is in order.
What does a low vs high standard deviation indicate?
How spread out the data is from the mean.
Low SD = Data is close to the mean
High SD = Data is all over the place
What do somatic and autonomic neurons control?
💡 A:
Somatic: controls skeletal muscles (voluntary)
Autonomic: controls BP & involuntary muscles
T/F: Somatic reflexes do not include autonomic neurons
True