Meninges and Ventricular System
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
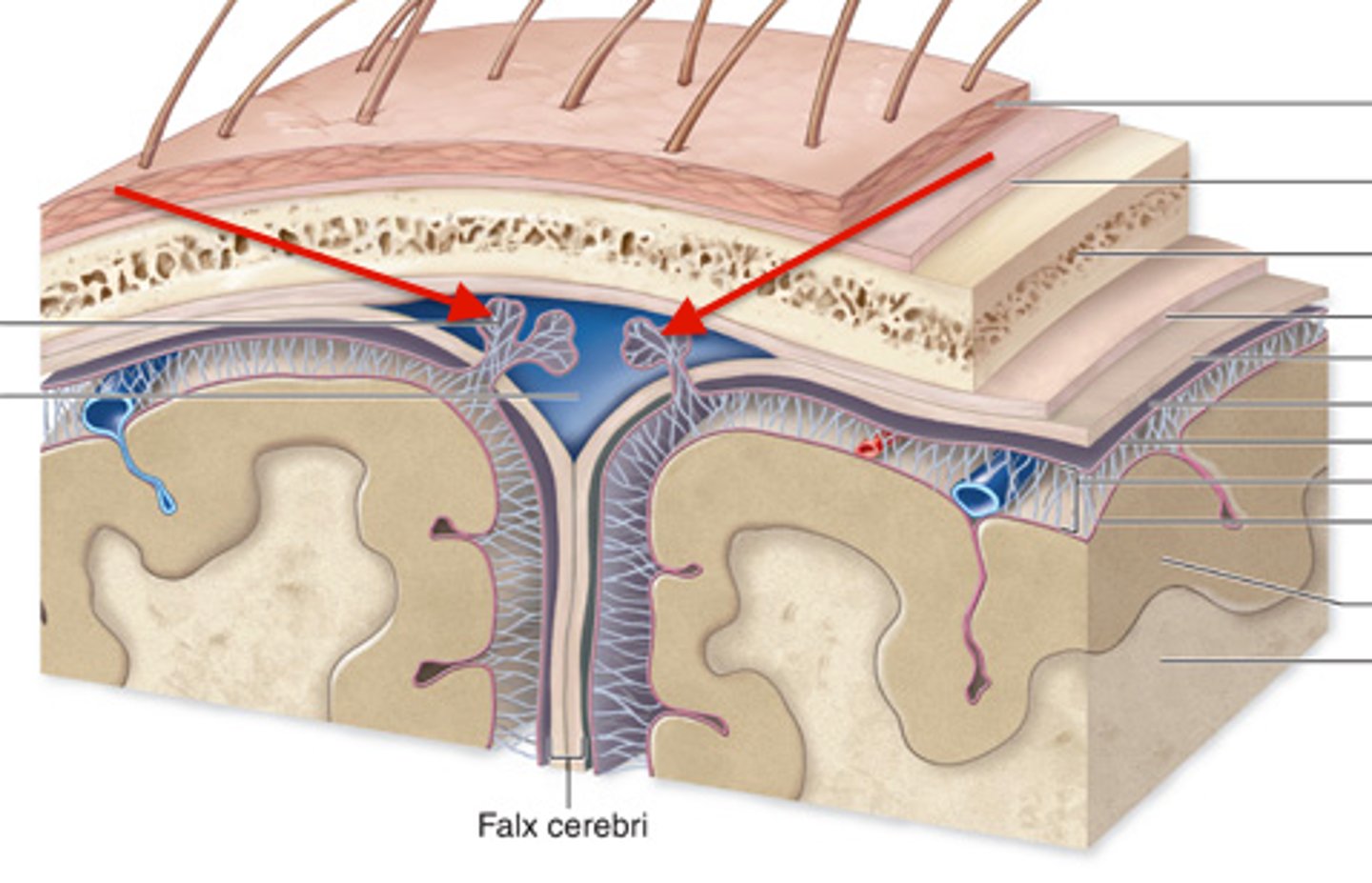
Meninges
three layers of connective tissue that protect the brain and house blood vessels
What are the 3 Meninges layers?
dura mater, arachnoid, pia mater
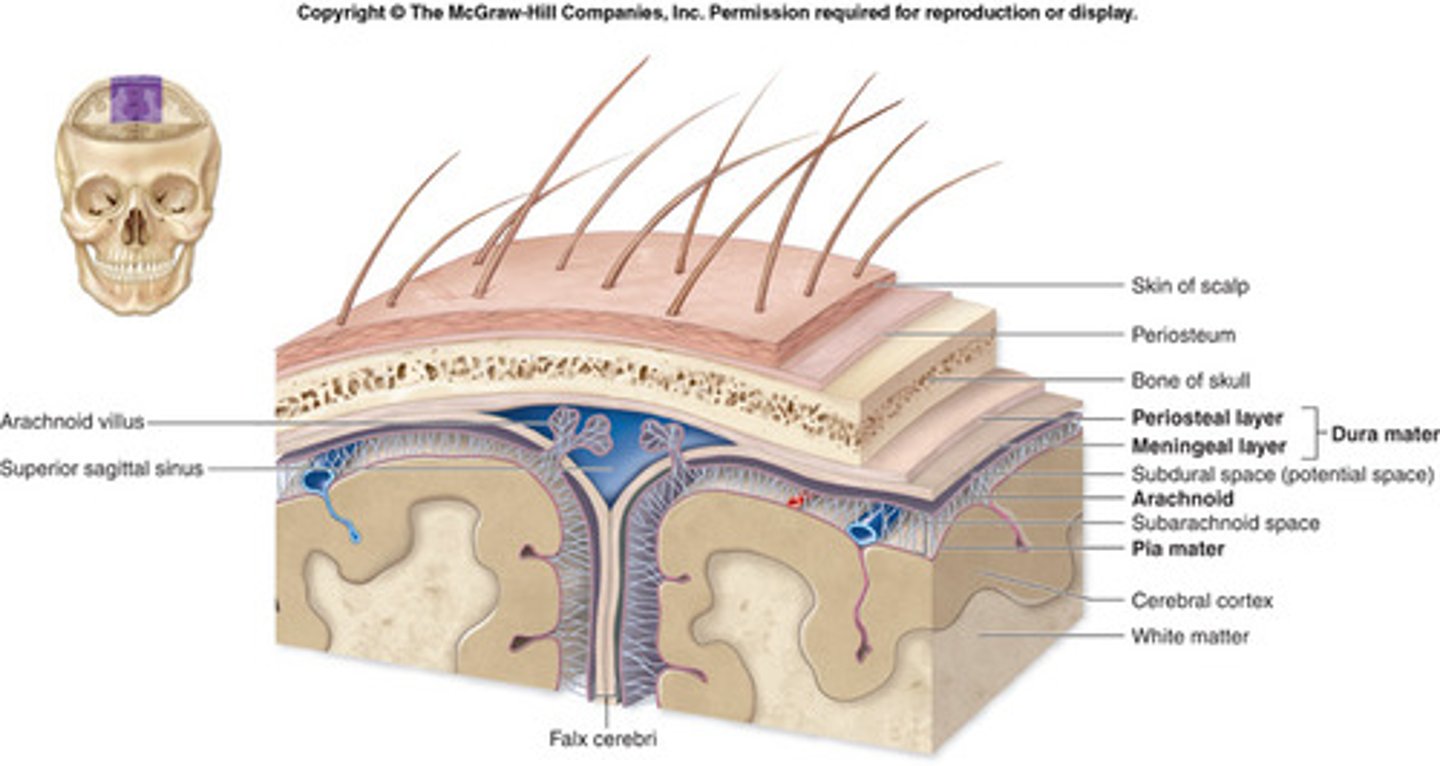
Dura Mater
"tough mother"
outermost layer
connected to skull
contains venous sinuses
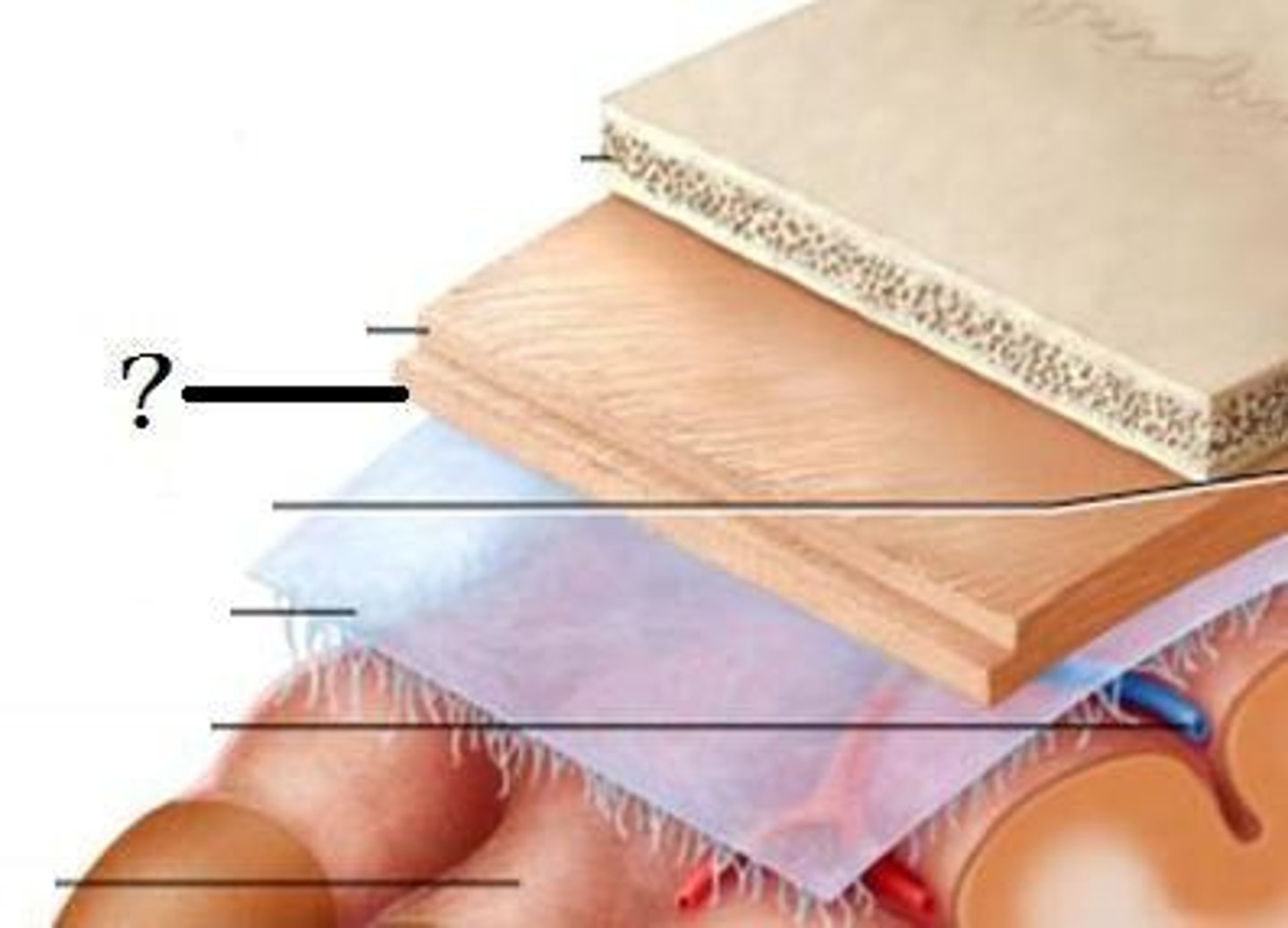
Arachnoid Mater
middle layer
spidery appearance from trabecula
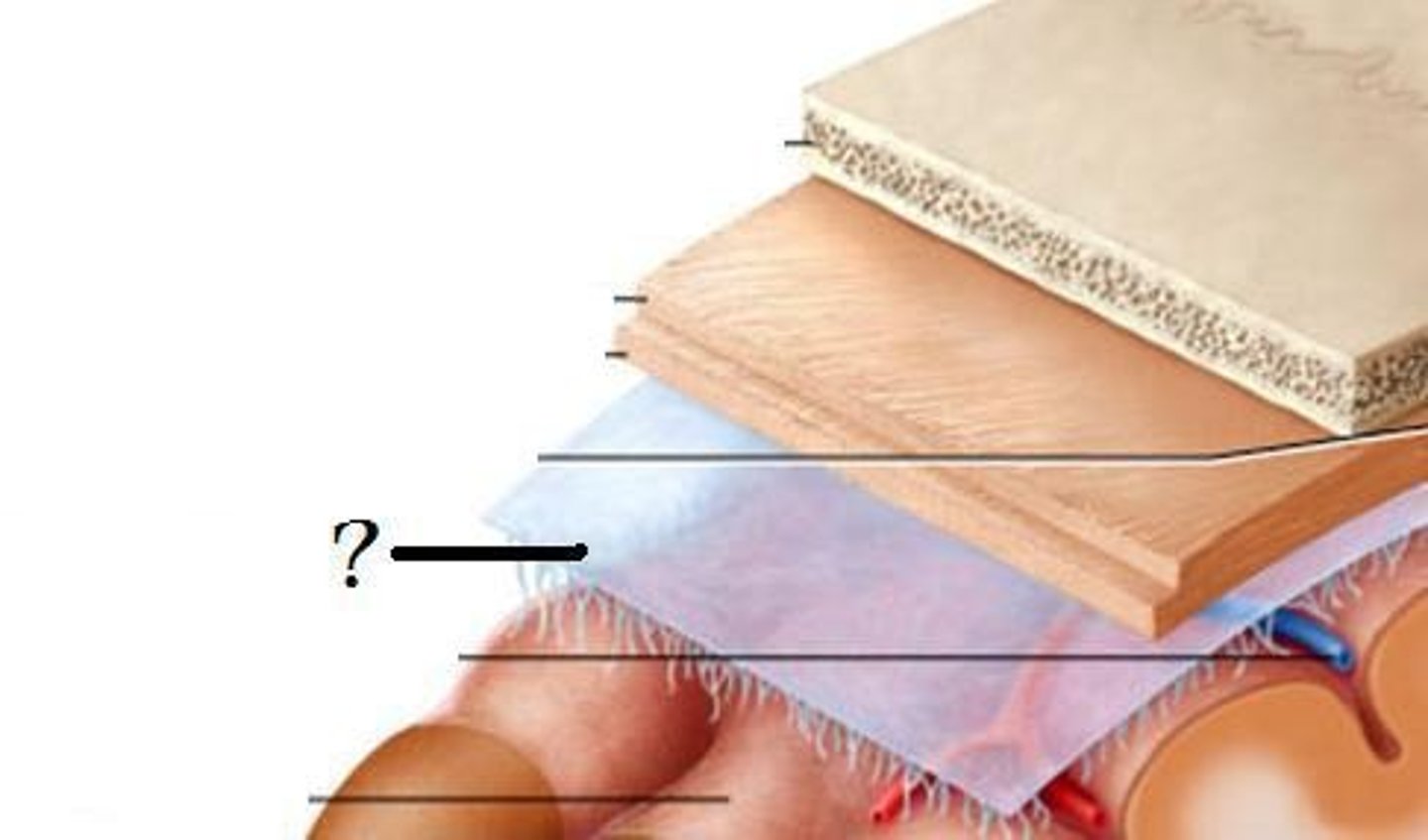
Pia Mater
"soft mother"
fine layer of tissue
directly connected to brain parenchyma
follows gyri and sulci
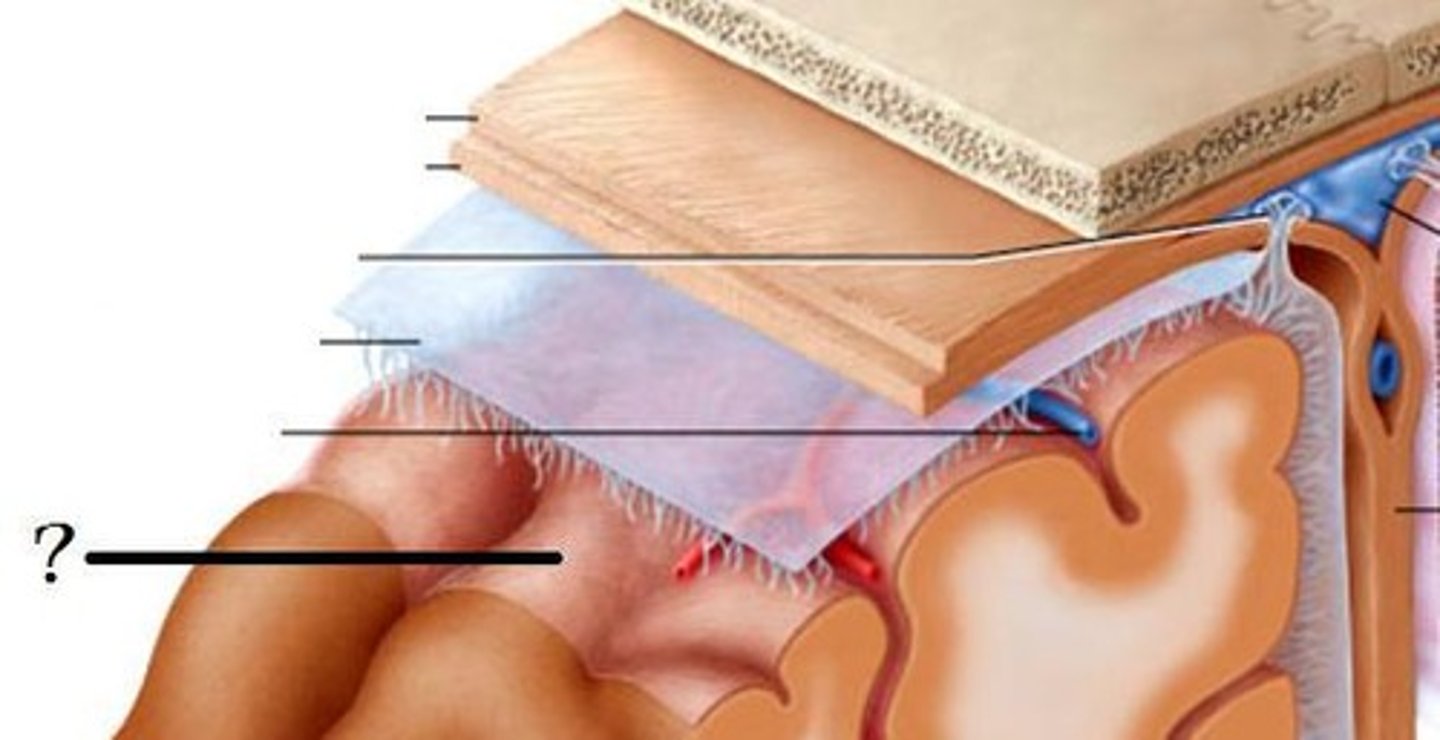
What are the 2 layers of the Dura Mater?
periosteal and meningeal
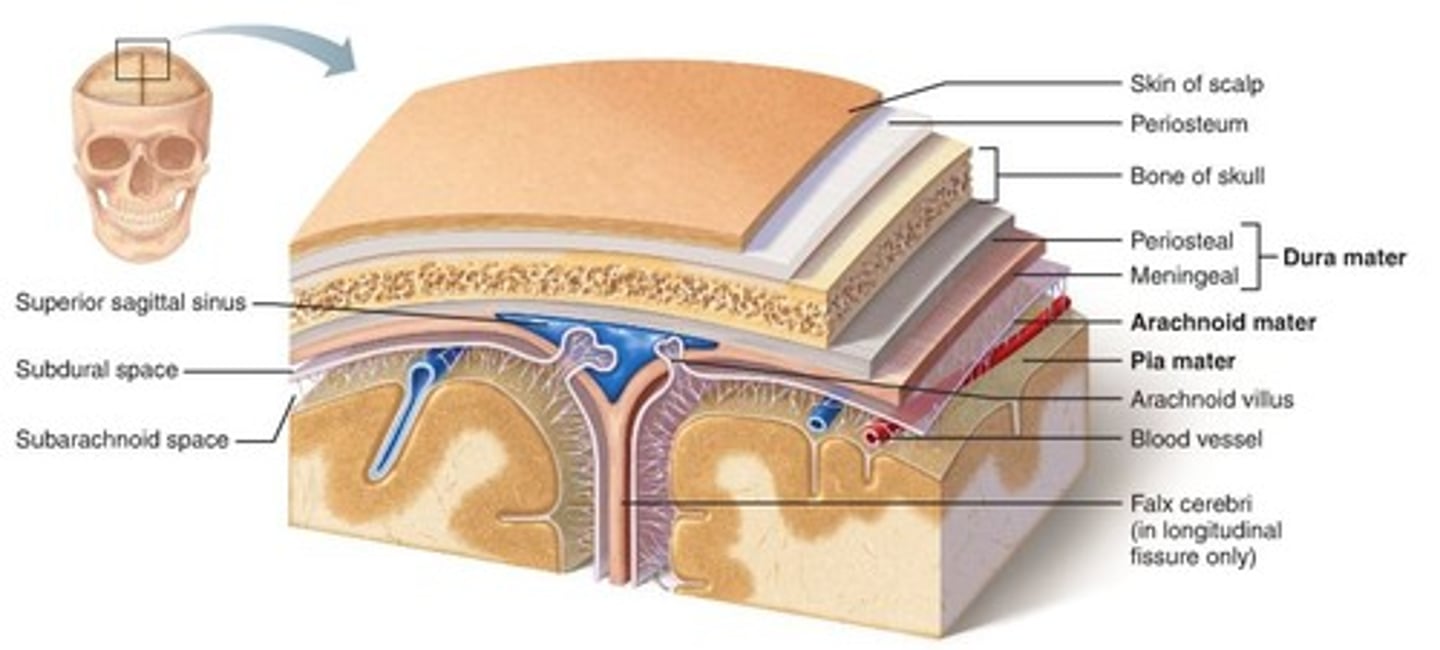
The two layers of the dura mater are what?
generally fused but do separate in some parts
When the two layers of the dura mater separate what does this form?
venous sinuses
What do the venous sinuses drain?
cerebral veins
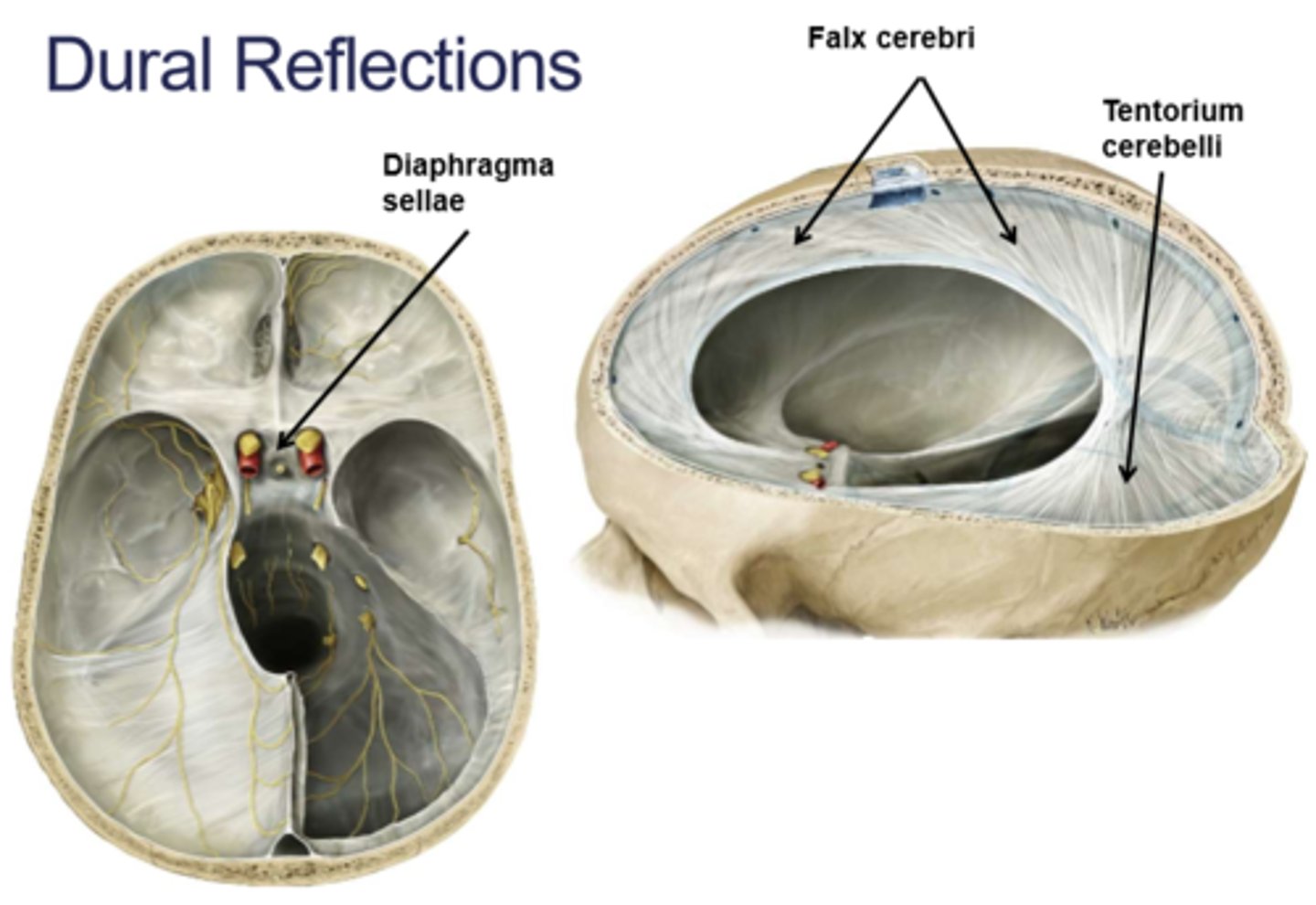
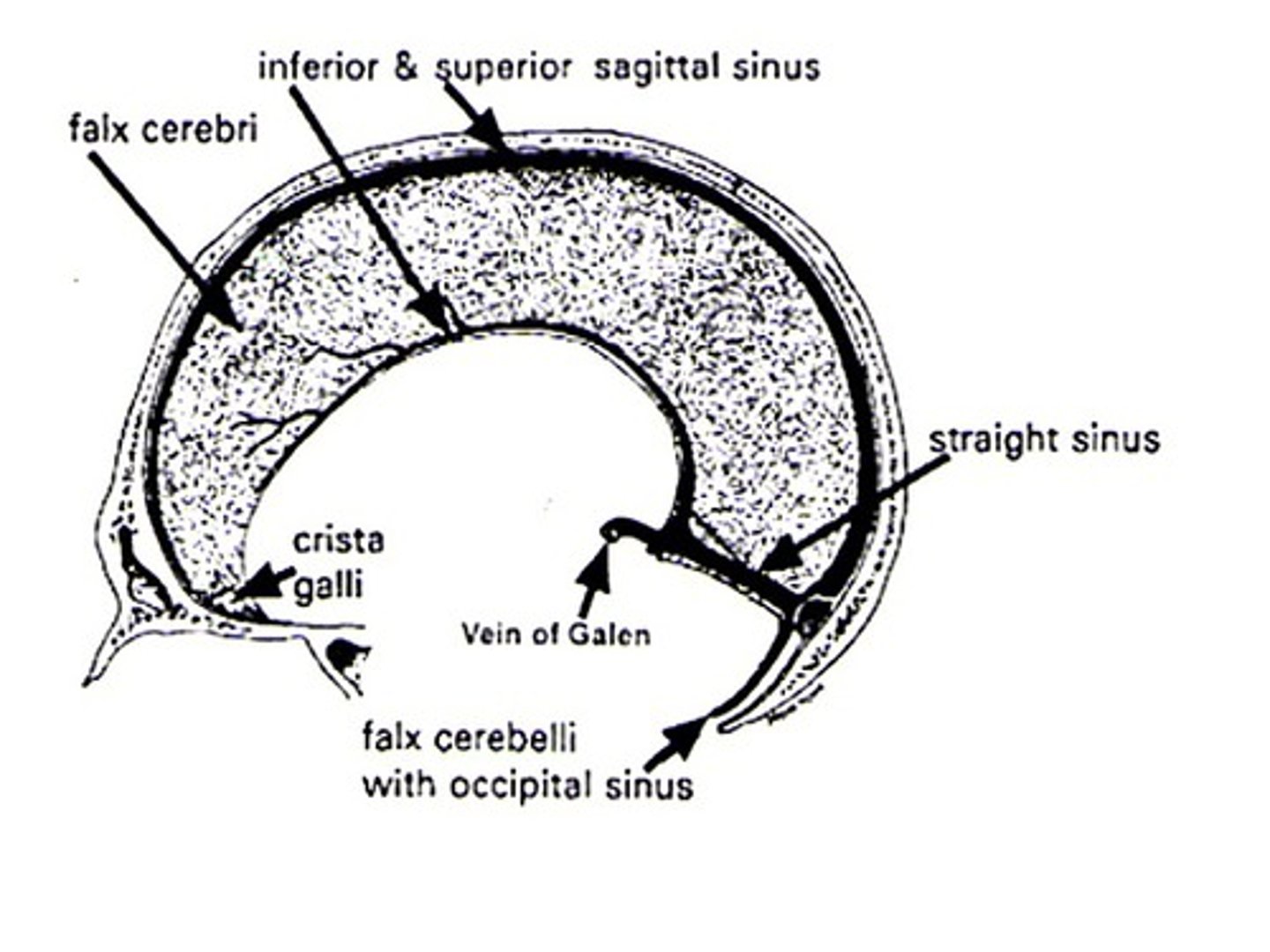
Dural reflections
folds of the meningeal layer that separate different compartments within the brain
The dura mater is pain sensitive because it is innervated by what?
meningeal branches of CN V and CN X
The blood supply of the dura mater is what arteries?
meningeal - mainly the middle meningeal artery
Where does the middle meningeal artery mainly travel?
in the periosteal layer
Areas where two dural sueparates forms what?
venous sinuses
Folds of the inner meningeal layer results in what?
dural reflections
Dural reflections consist of what?
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
falx cerebelli
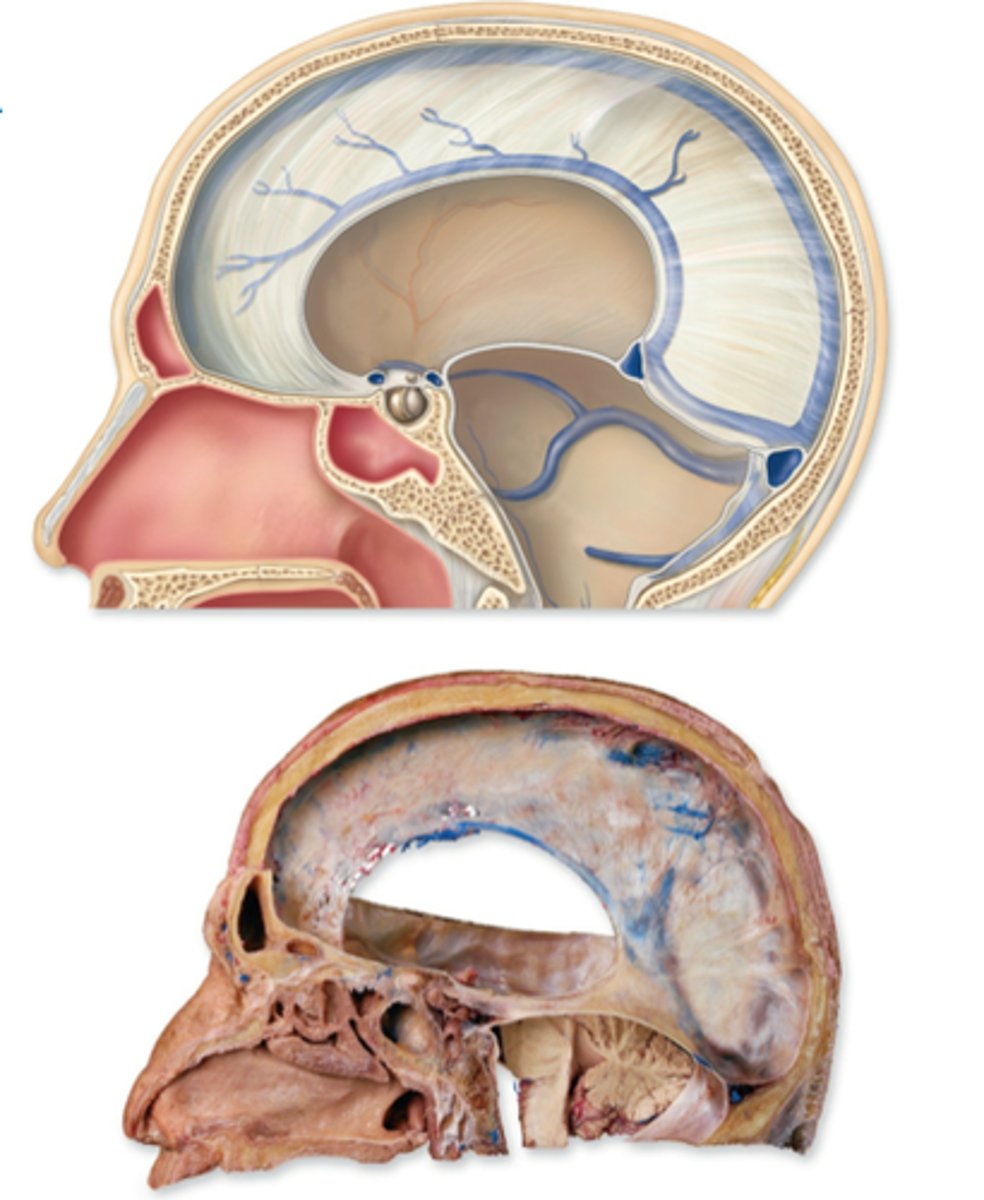
Falx cerebri
separates the two cerebral hemispheres
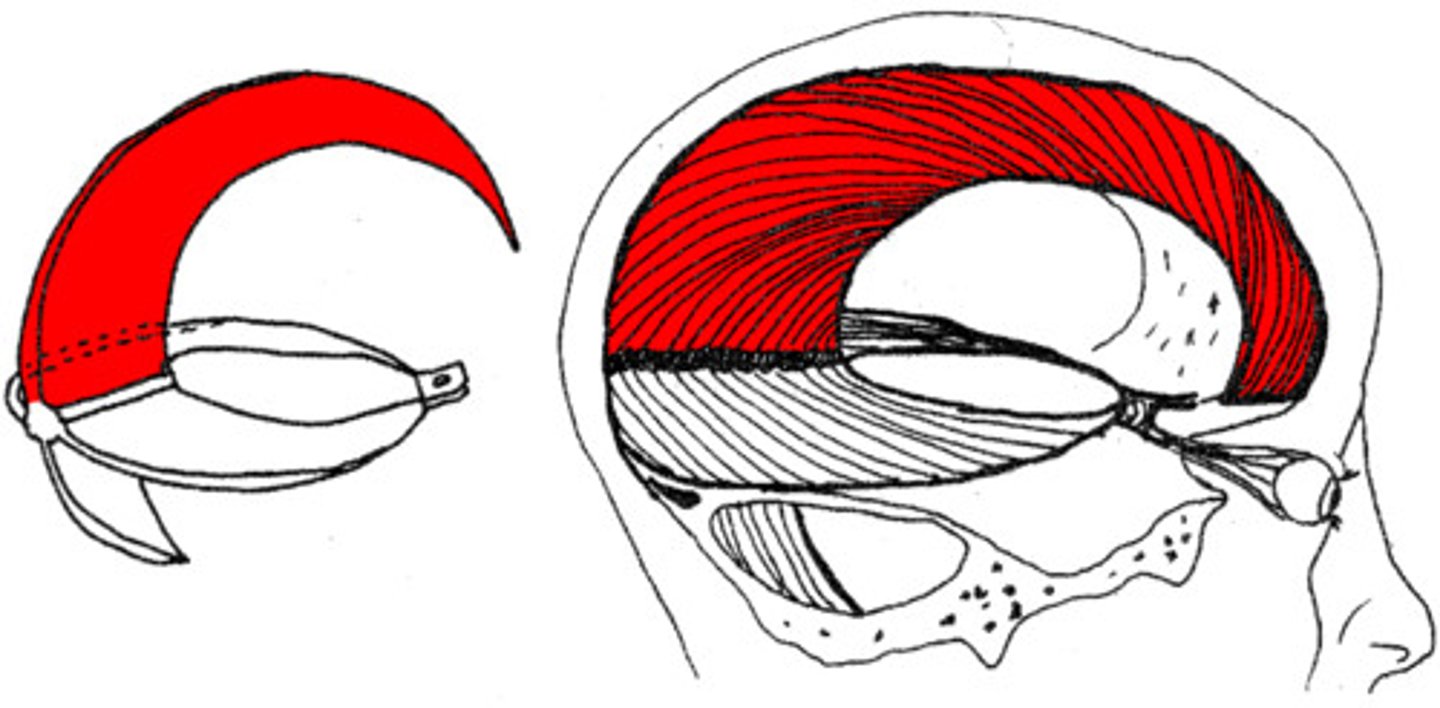
Falx cerebri contains what sinuses?
superior and inferiorer sagittal sinuses
Tentorium cerebelli
separates middle and posterior cranial fossae, covers upper surface of cerebellum
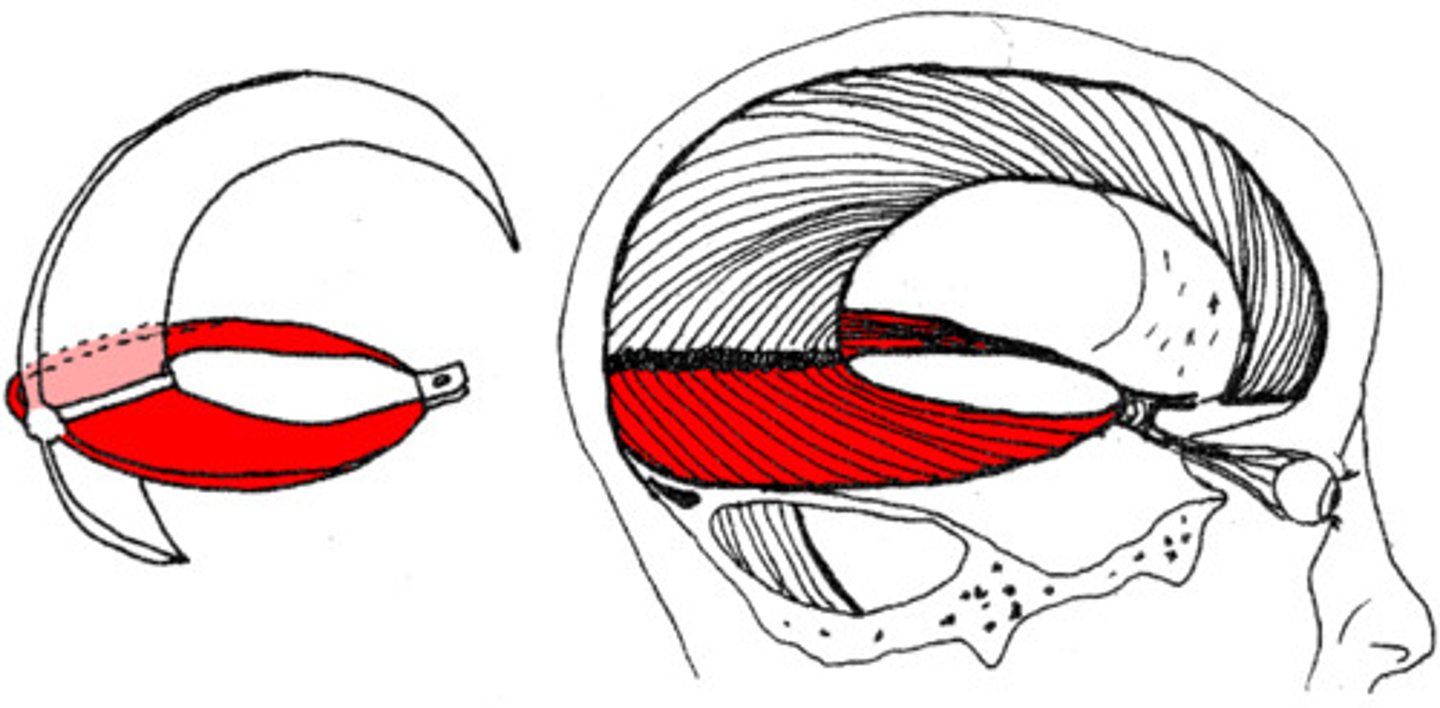
Outer border of Tentorium cerebelli contains what sinsus?
transverse sinus
Falx cerebelli
separates cerebellar hemispheres
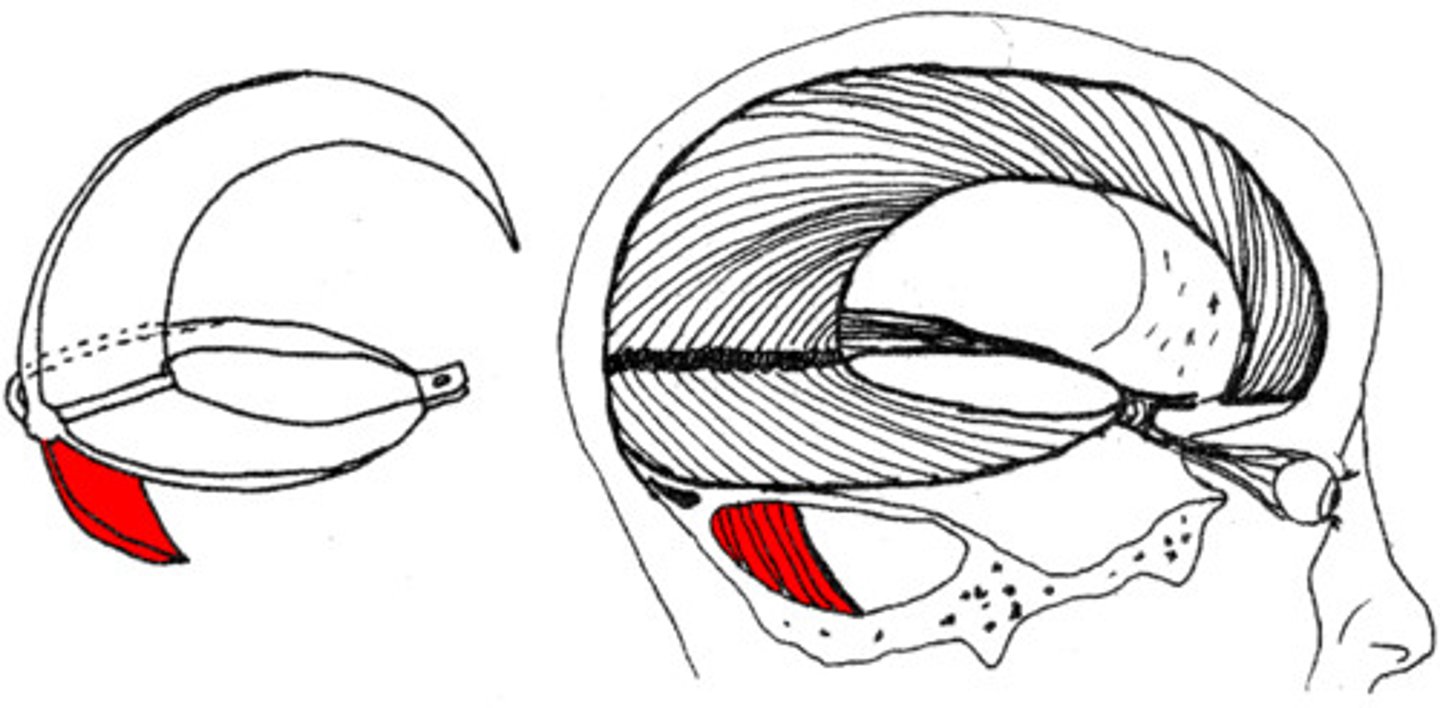
Falx cerebelli contains what sinus?
occipital sinus
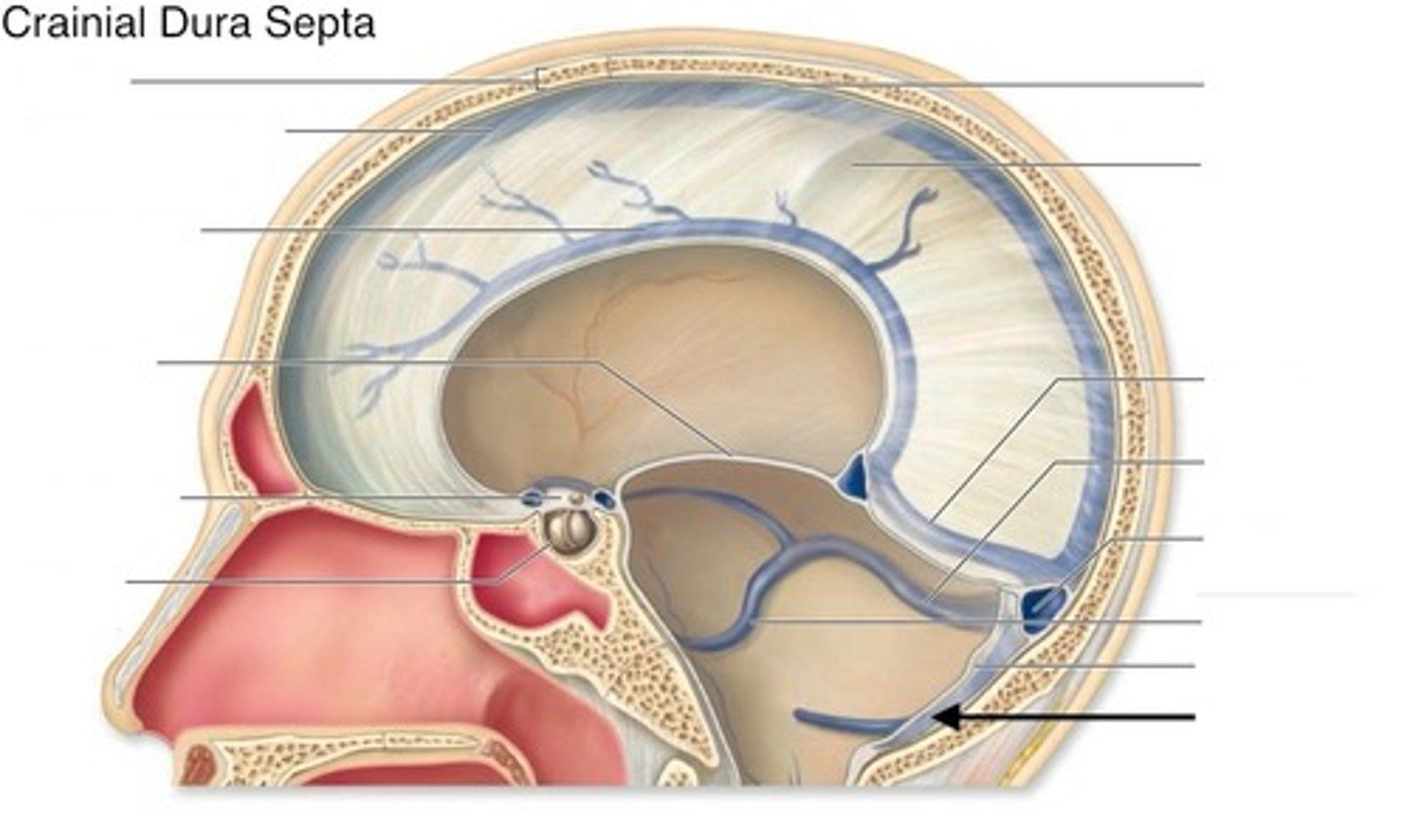
What sinus is between the falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli?
straight sinus
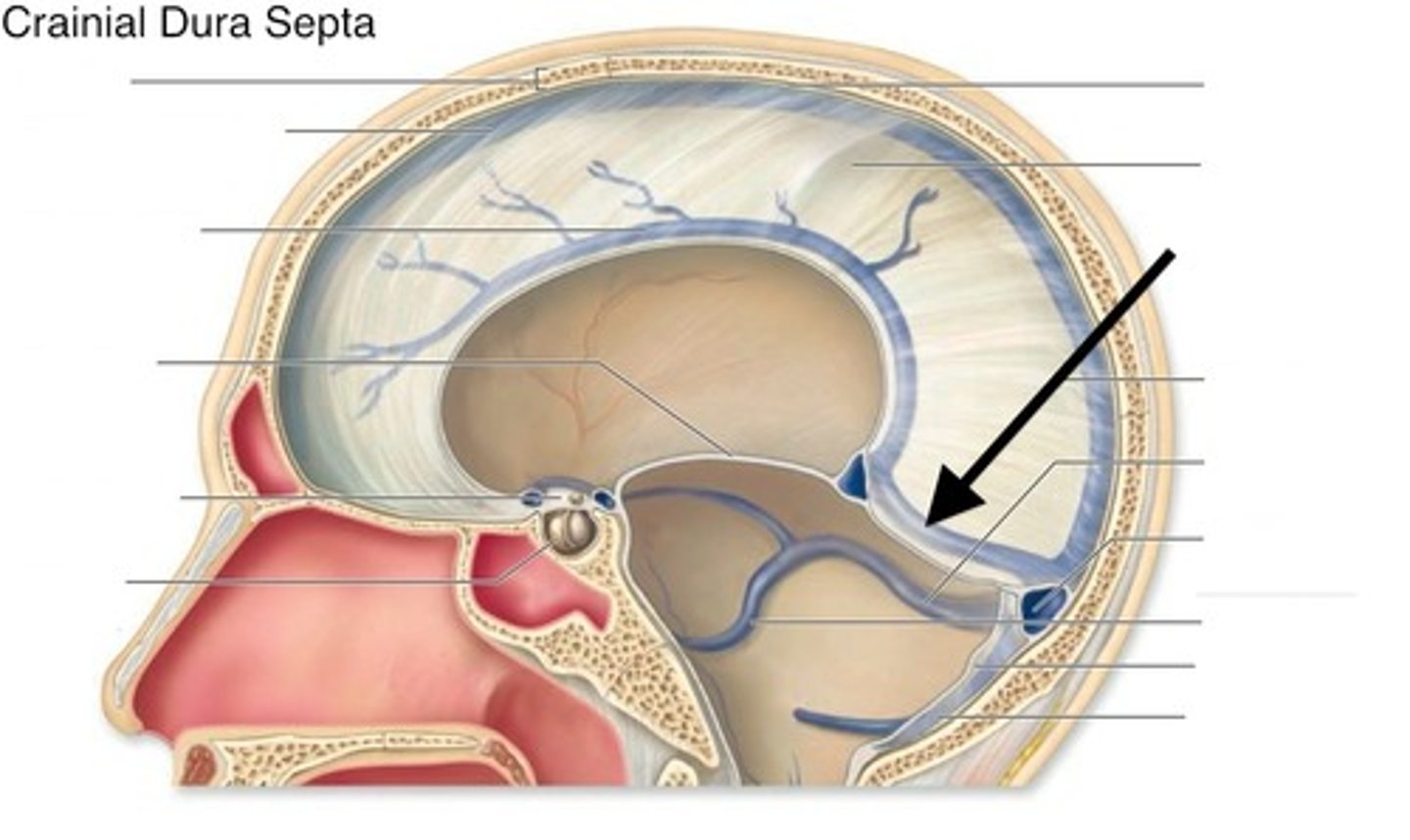
Confluence of sinuses
meeting place of the sinuses where they later go to the transverse sinus to the sigmoid sinus and out of the internal jugular vein
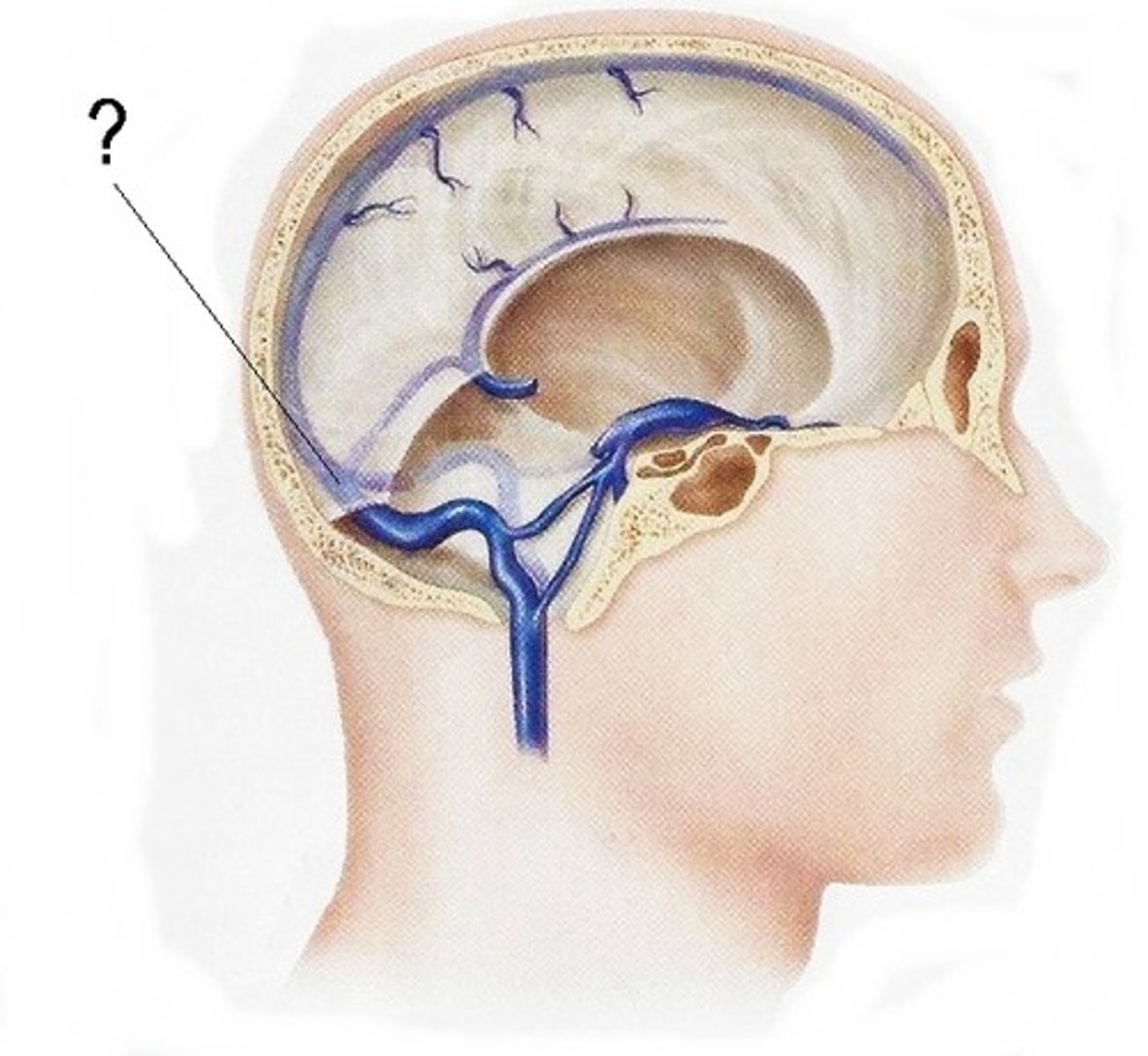
What characteristic within the Arachnoid Mater helps to connect to the pia mater below it?
trabeculae (also gives spider appearance)
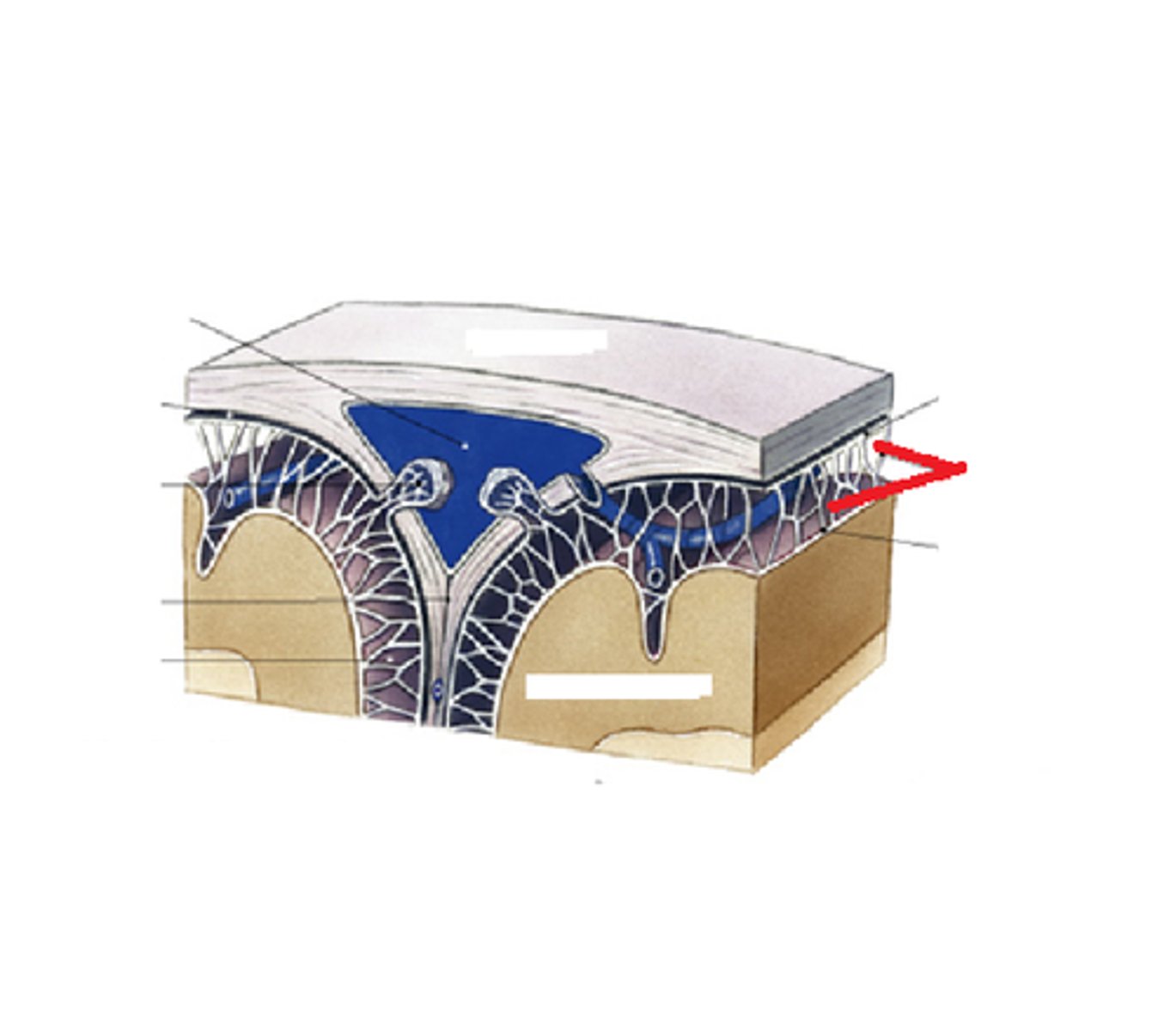
What characteristic within the Arachnoid Mater will protrude into superior sagittal sinus?
granulations
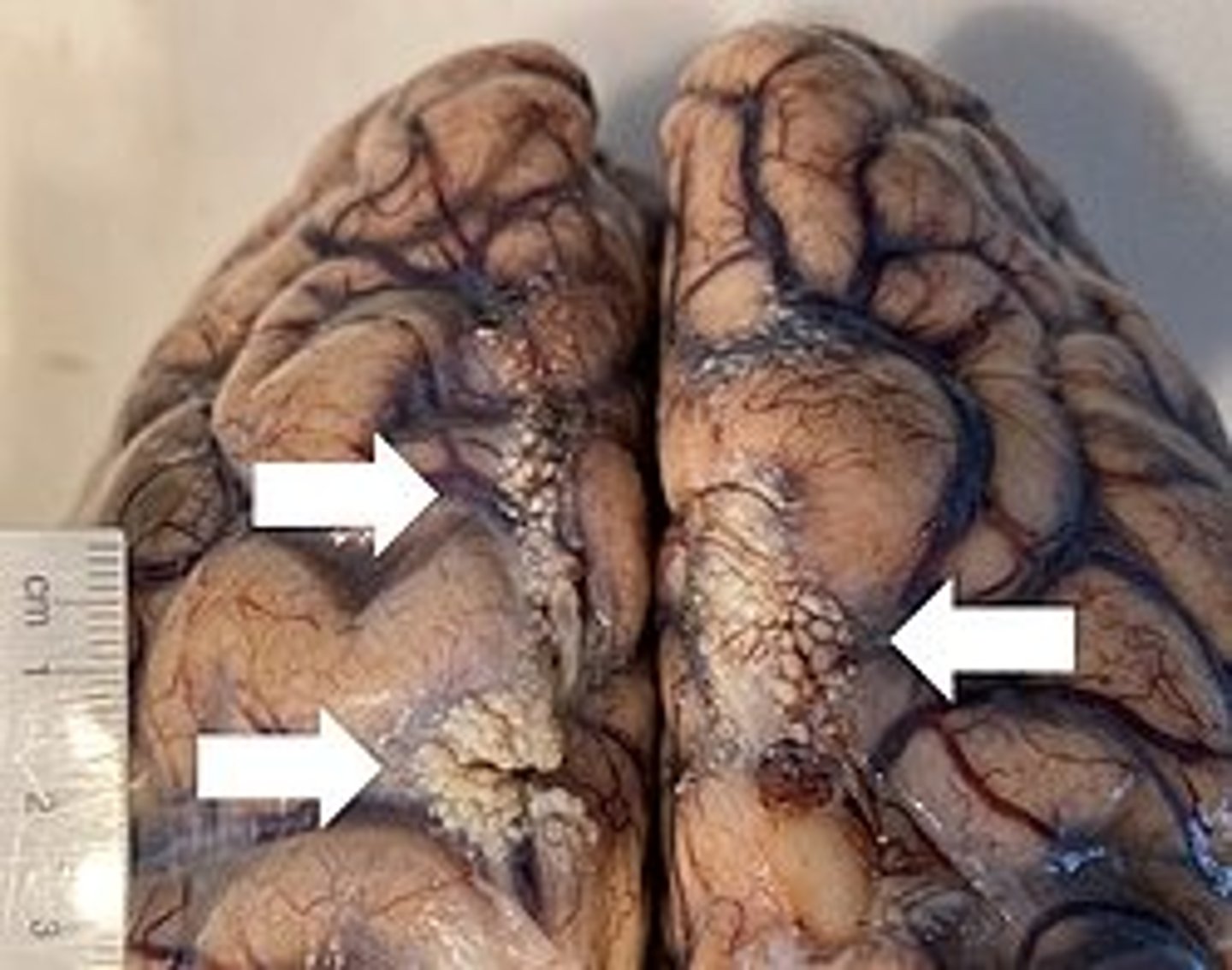
Arachnoid granulations are involved in what?
reabsorption of the CSF
Space between arachnoid mater and pia mater?
subarachnoid space
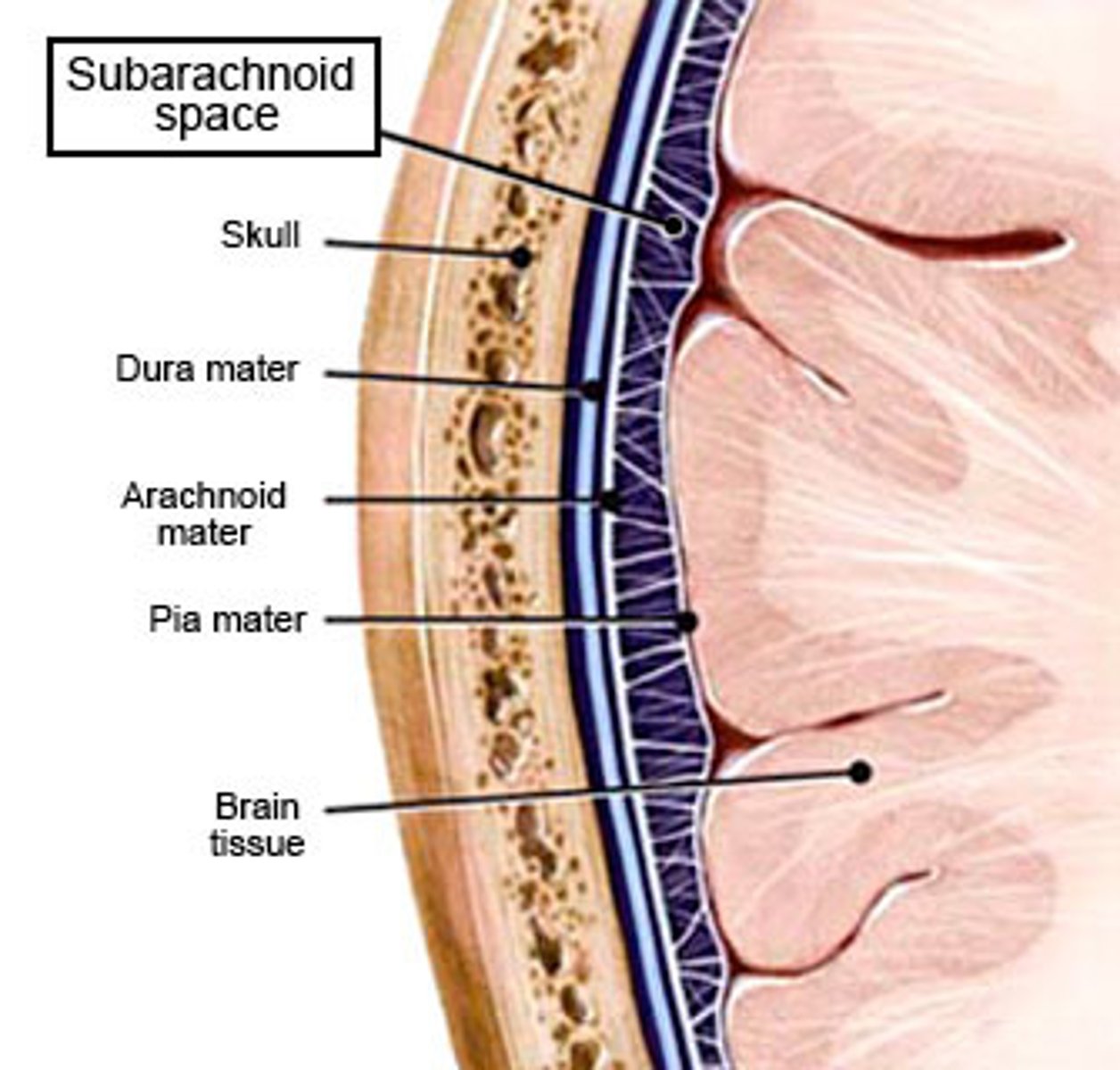
What is the Subarachnoid space filled with?
CSF and cerebral blood vessels
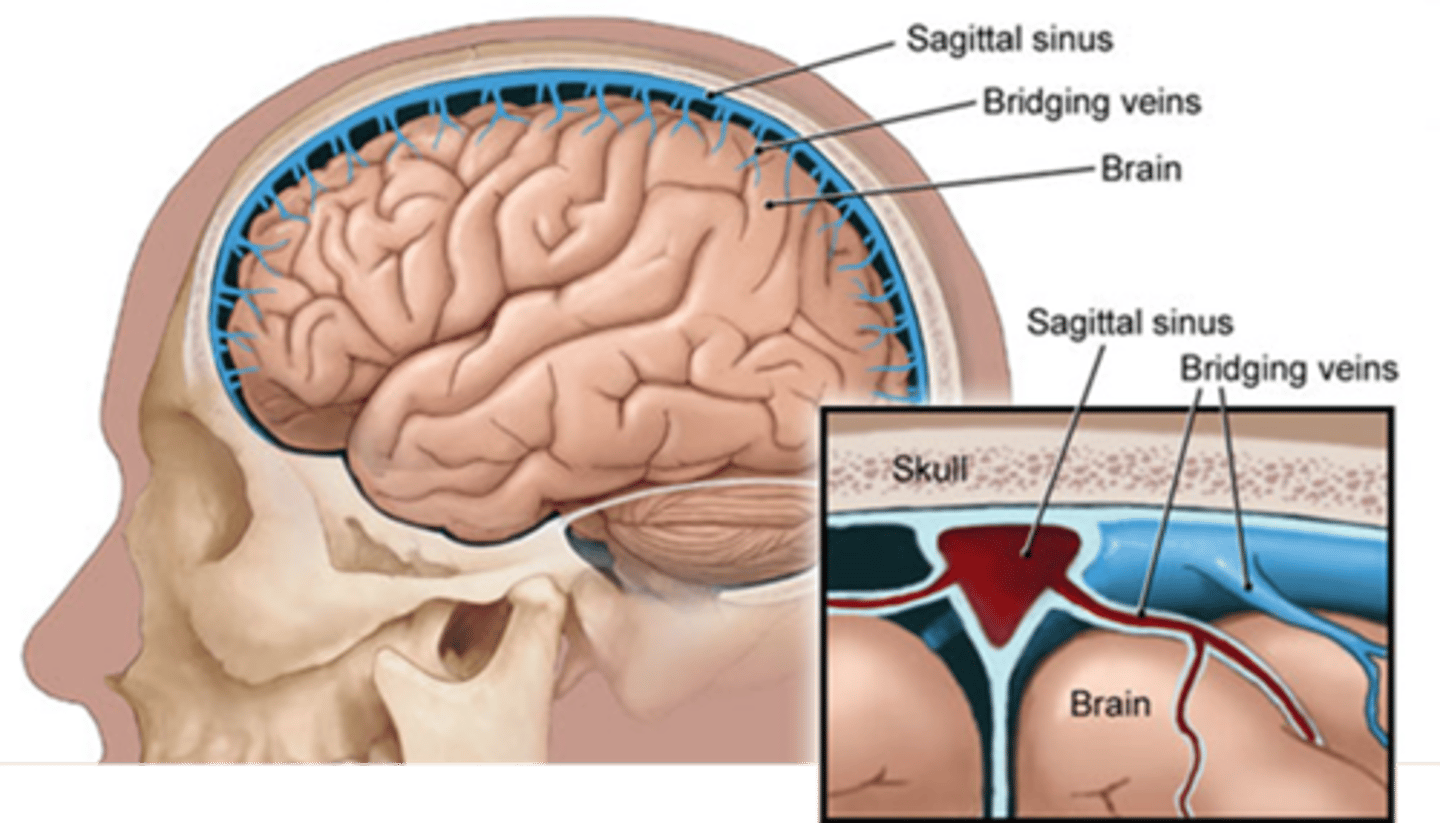
What pierces the arachnoid to connect to the dural sinuses?
bridging veins
Pia Mater separates what?
brain from CSF in the subarachnoid space
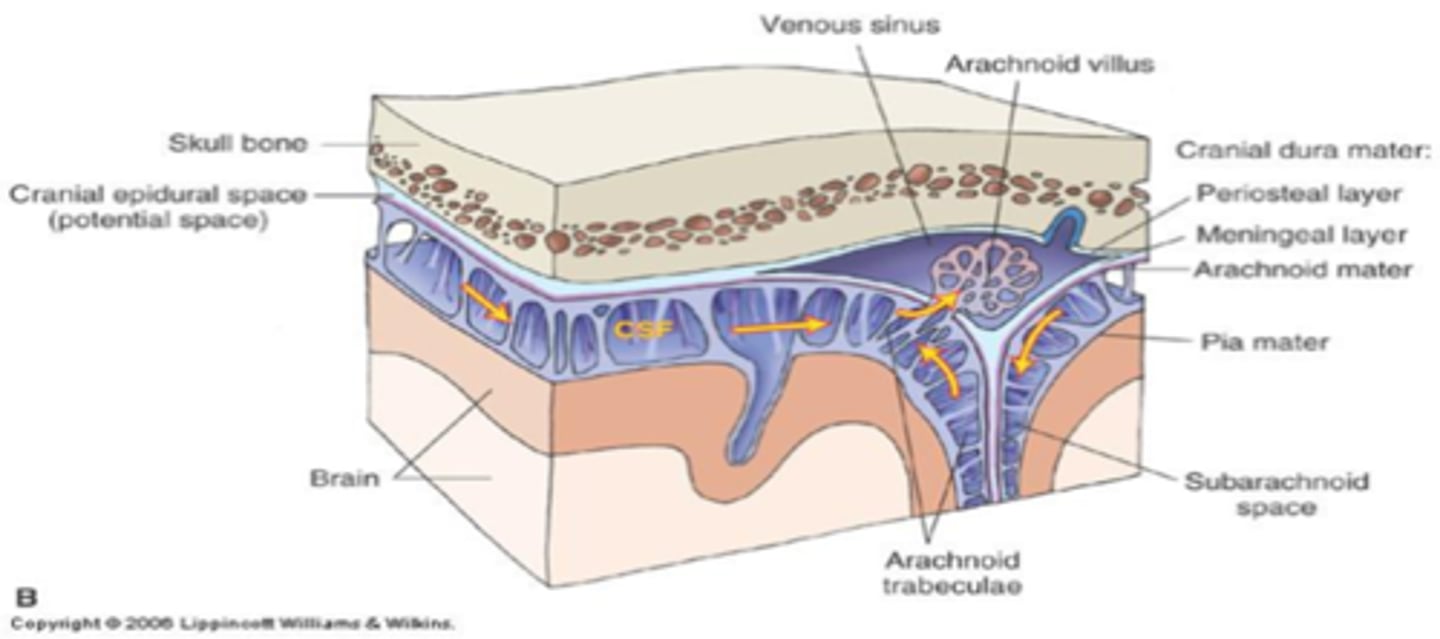
What is the space in the Pia Mater where blood vessels to the cerebrum are covered in a sleeve of pia?
perivascular space
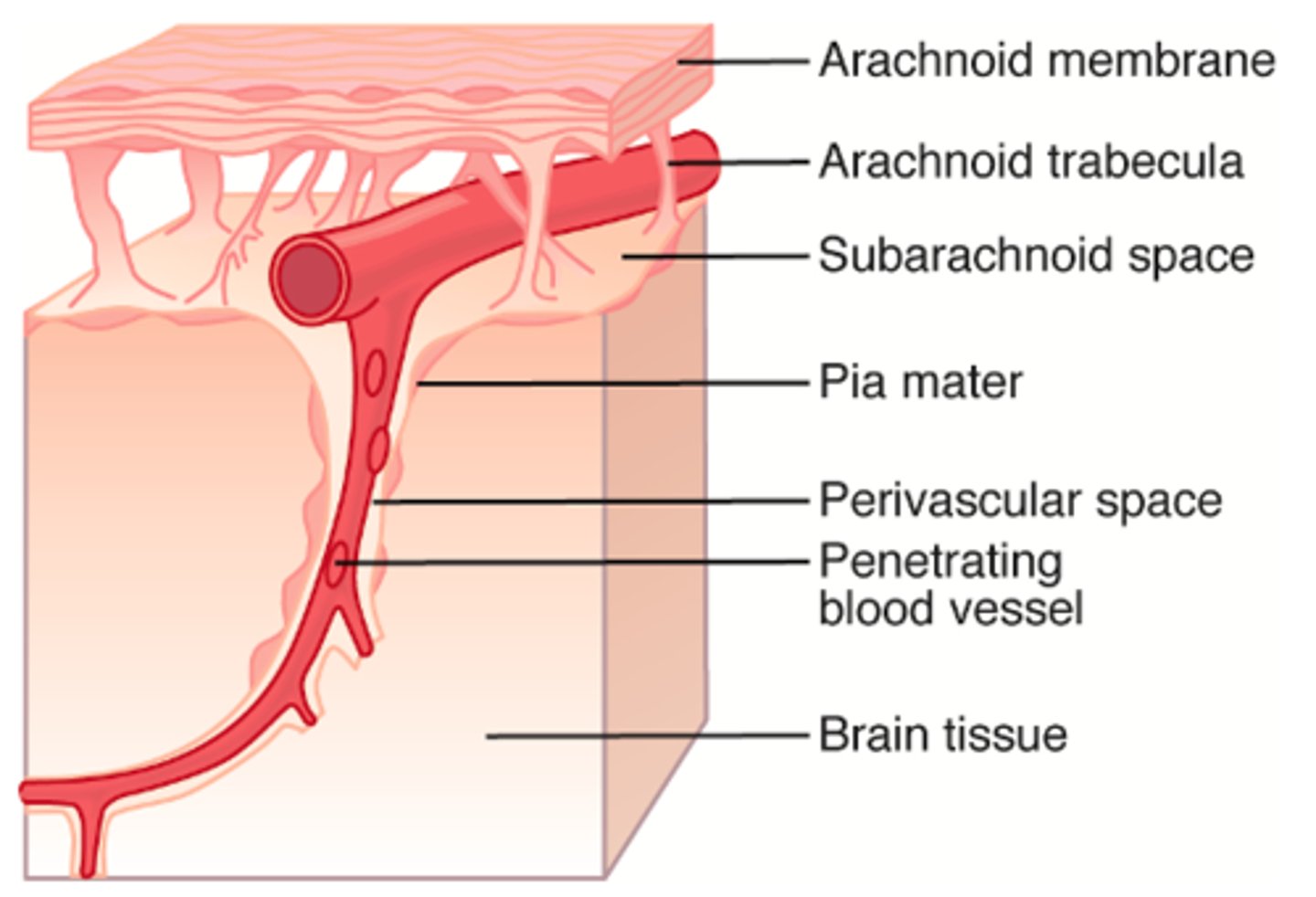
Perivascular space
penetrates the brain parenchyma until the vessel becomes a capillary
Real space
exists under normal conditions
Potential Space
Does not exist under normal conditions; can become a real space pathologically with blood accumulation
Is the Subarachnoid space a true/real or potential space?
true/real space
Is the Epidural space a true/real or potential space?
potential space
Is the Subdural space a true/real or potential space?
potential space but becomes a real space with a meningeal artery bleed
Epidural space
ABOVE THE DURA MATER
houses meningeal arteries, branches of the external carotid artery (which supplies the dura)
Subdural space
BELOW THE DURA MATER
bridging veins connecting cerebral veins in the subarachnoid space to the dural venous sinuses found here
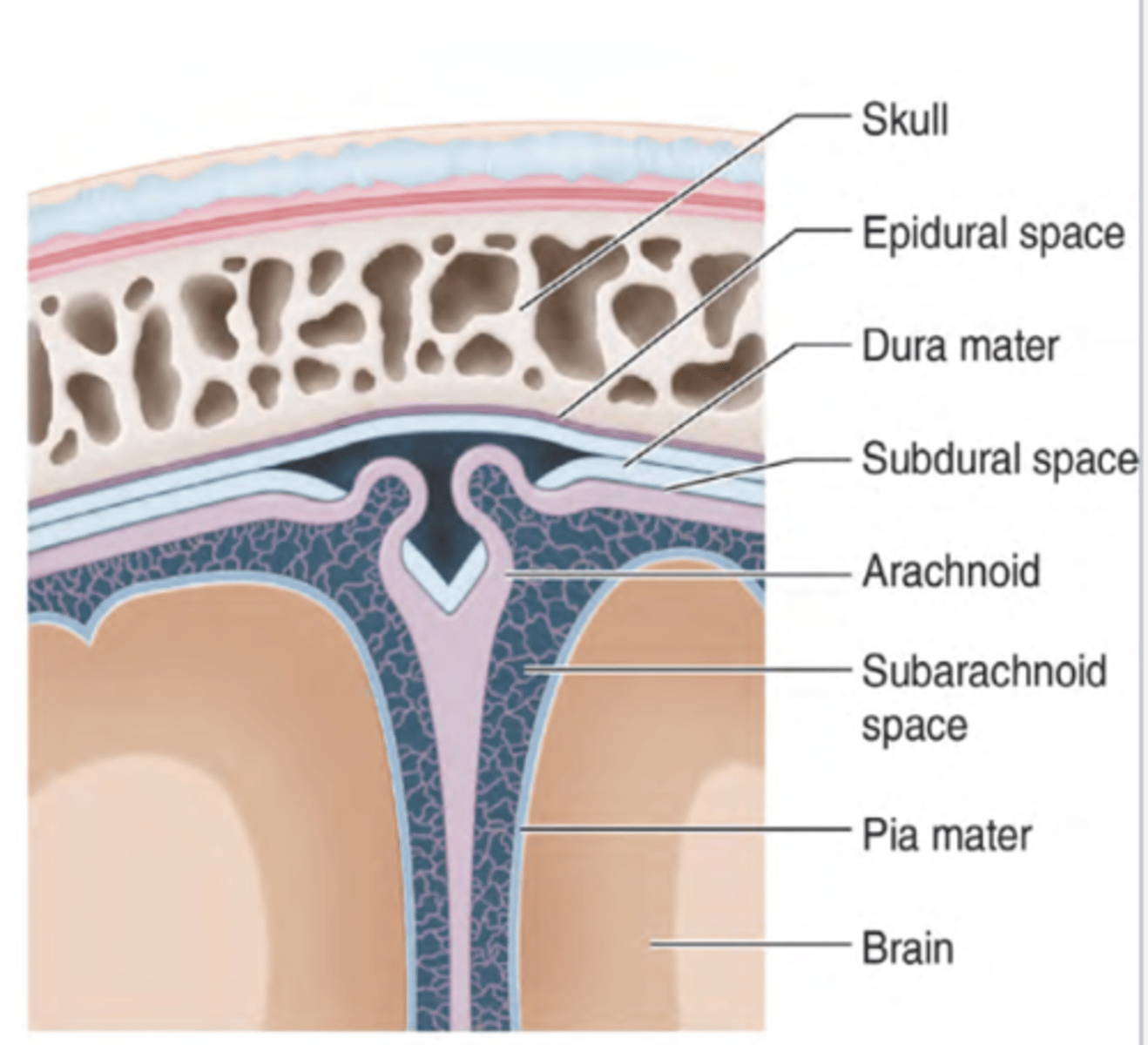
Subarachnoid space
real space filled with CSF that contains major cerebral arteries and veins
Epidural hematoma
accumulation of blood (meningeal artery) between dura and skull that is from trauma with a biconcave lens shape on CT
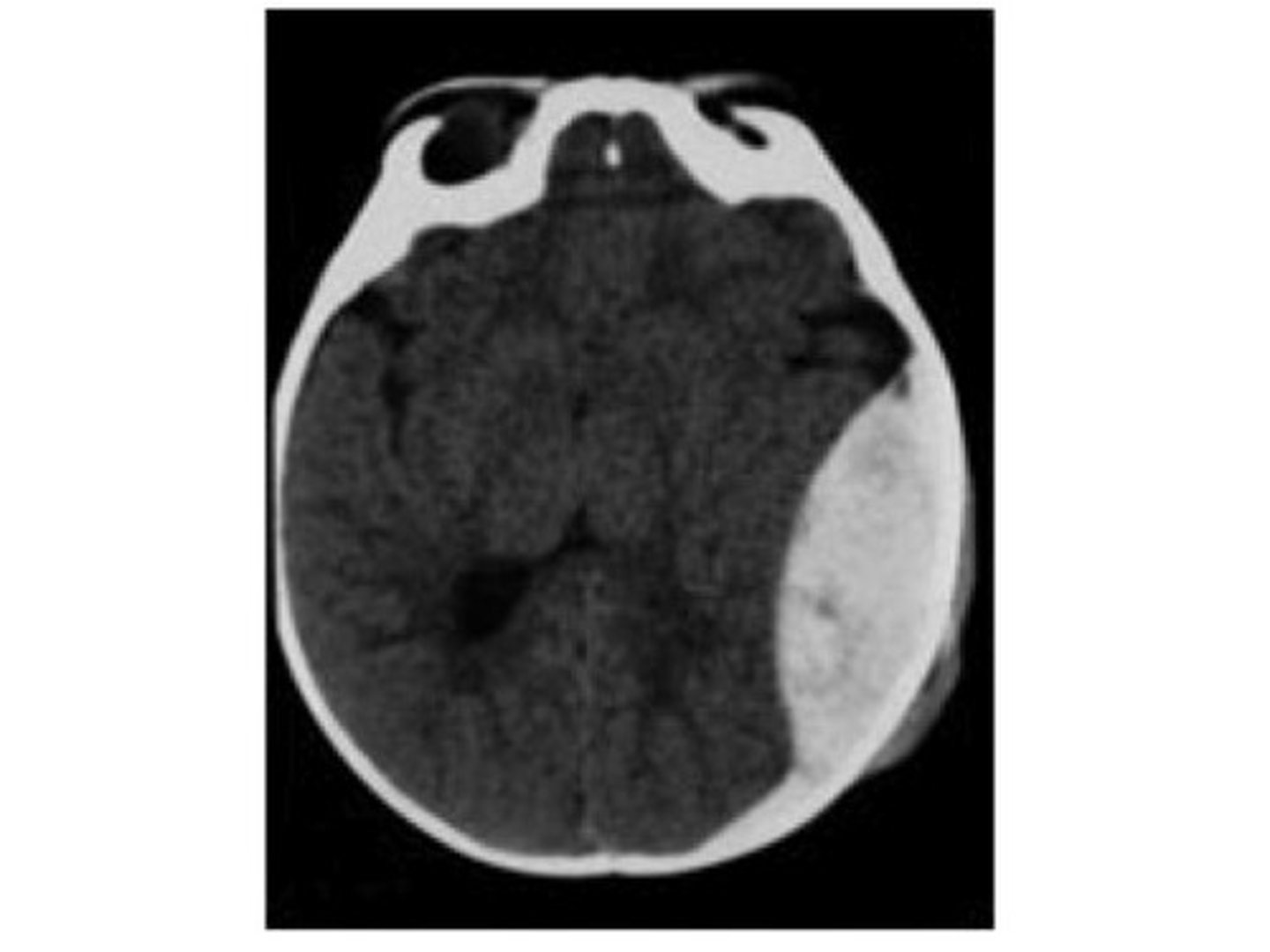
Subdural hematoma
accumulation of blood (bridging veins) between dura and arachnoid mater that is from acute or chronic occurrences with a crescent-shape on CT
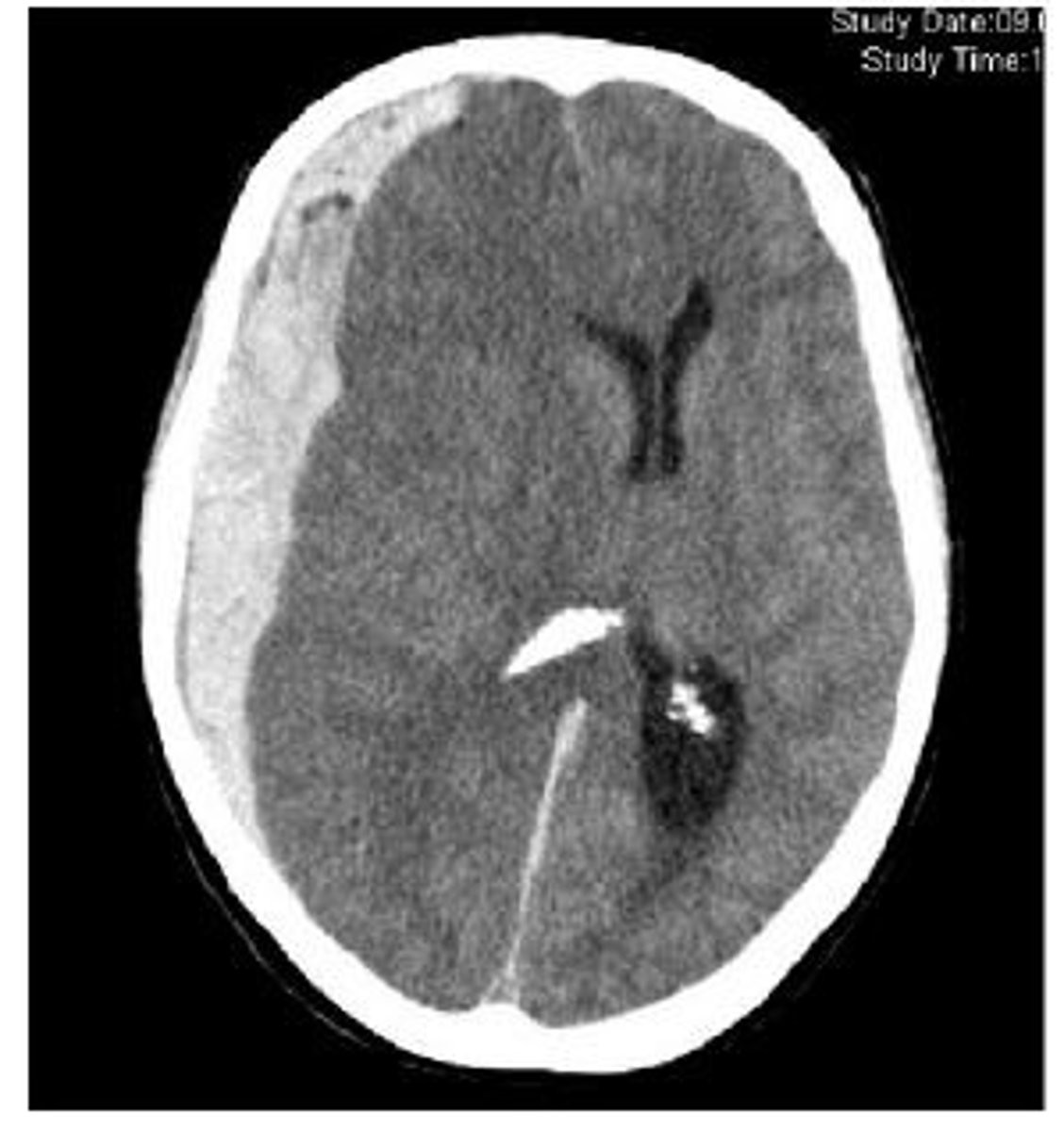
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
bleeding between arachnoid mater and pia mater where the blood replaces the CSF and on CT it shows blood tracing down into sulci
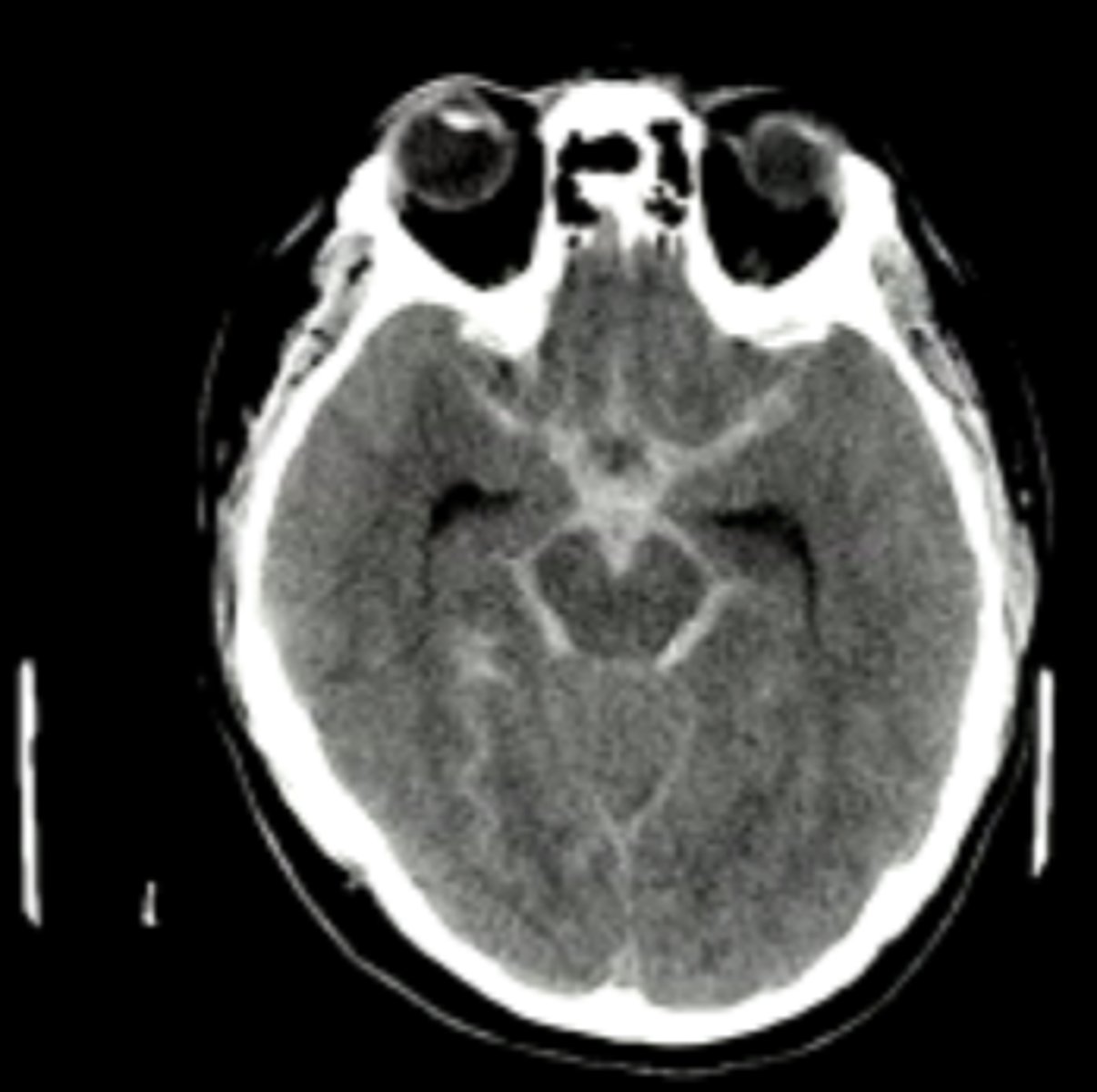
Subarachnoid hemorrhage causes
trauma, rupture of intracranial aneurysm with a severe headache of rapid onset
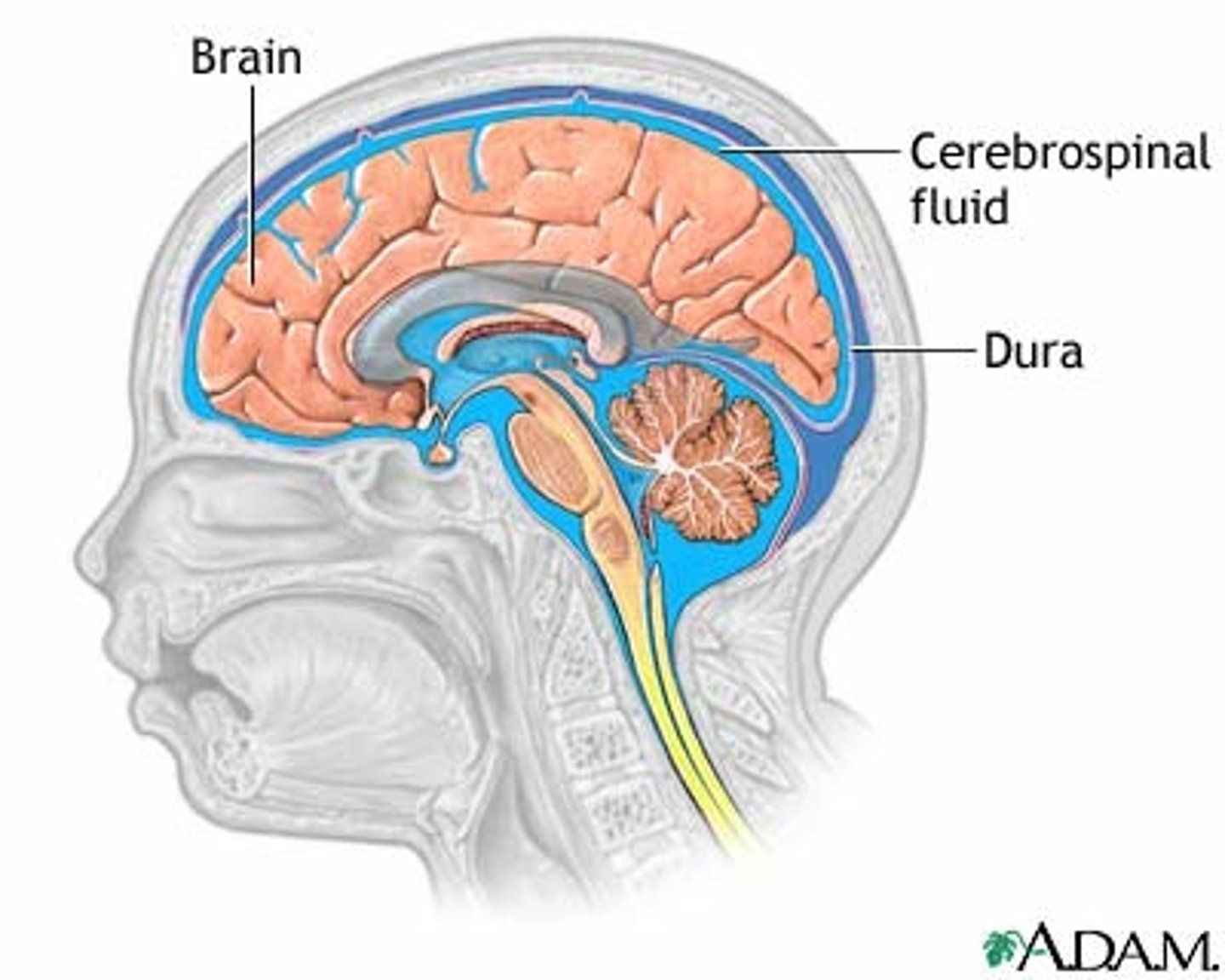
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
clear, colorless fluid that fills the spaces within the cerebrum and spinal cord
Major functions of CSF
- mechanical protection (cushion and shock absorption)
- reduces weight of brain
- distribution of nutrients and neurotransmitters + maintenance of chemical balance
- removal of metabolic waste and toxins
CSF locations
- ventricles (brain)
- subarachnoid space (brain and spinal cord)
- central canal (spinal cord)
Ventricle (brain)
space within brain filled with CSF
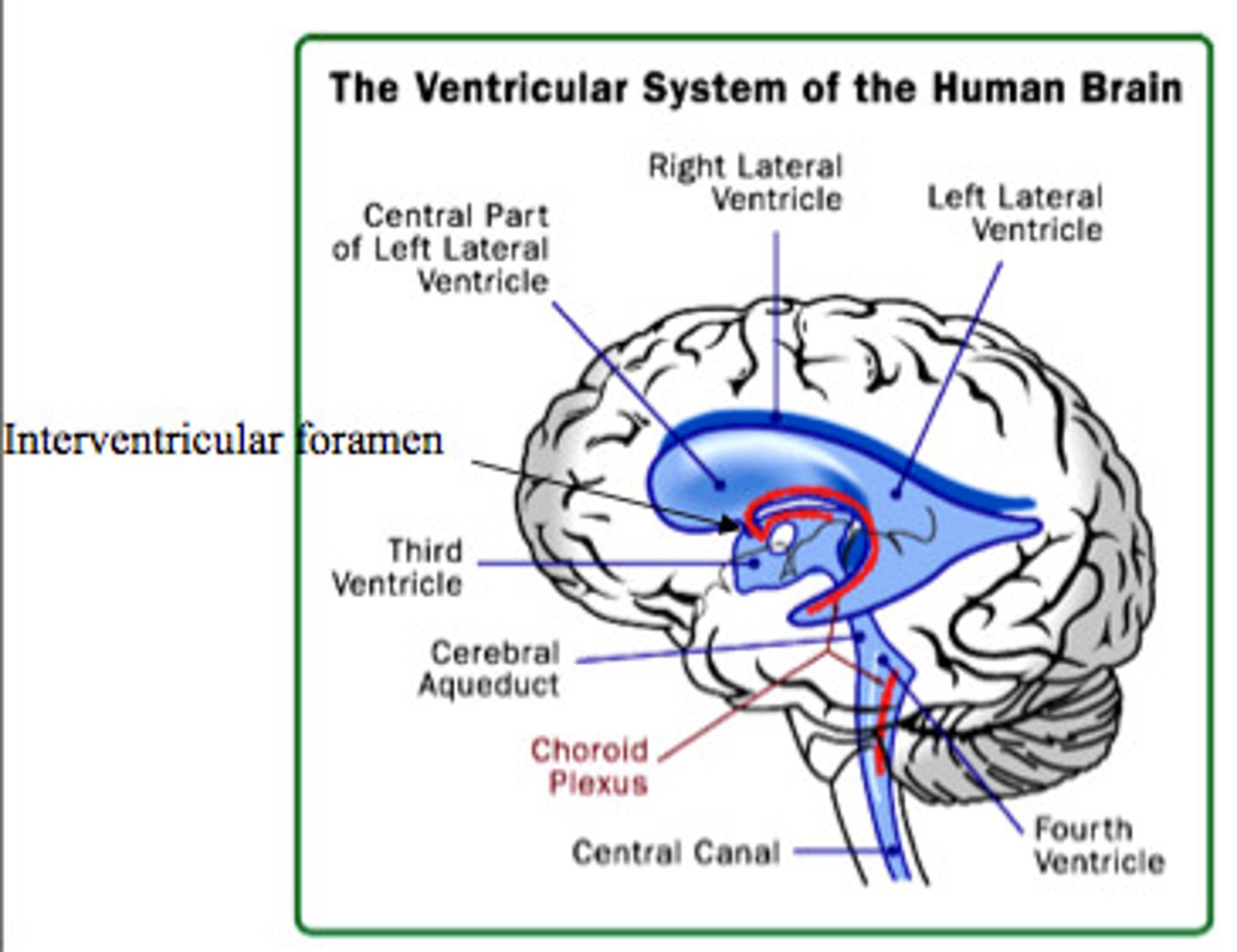
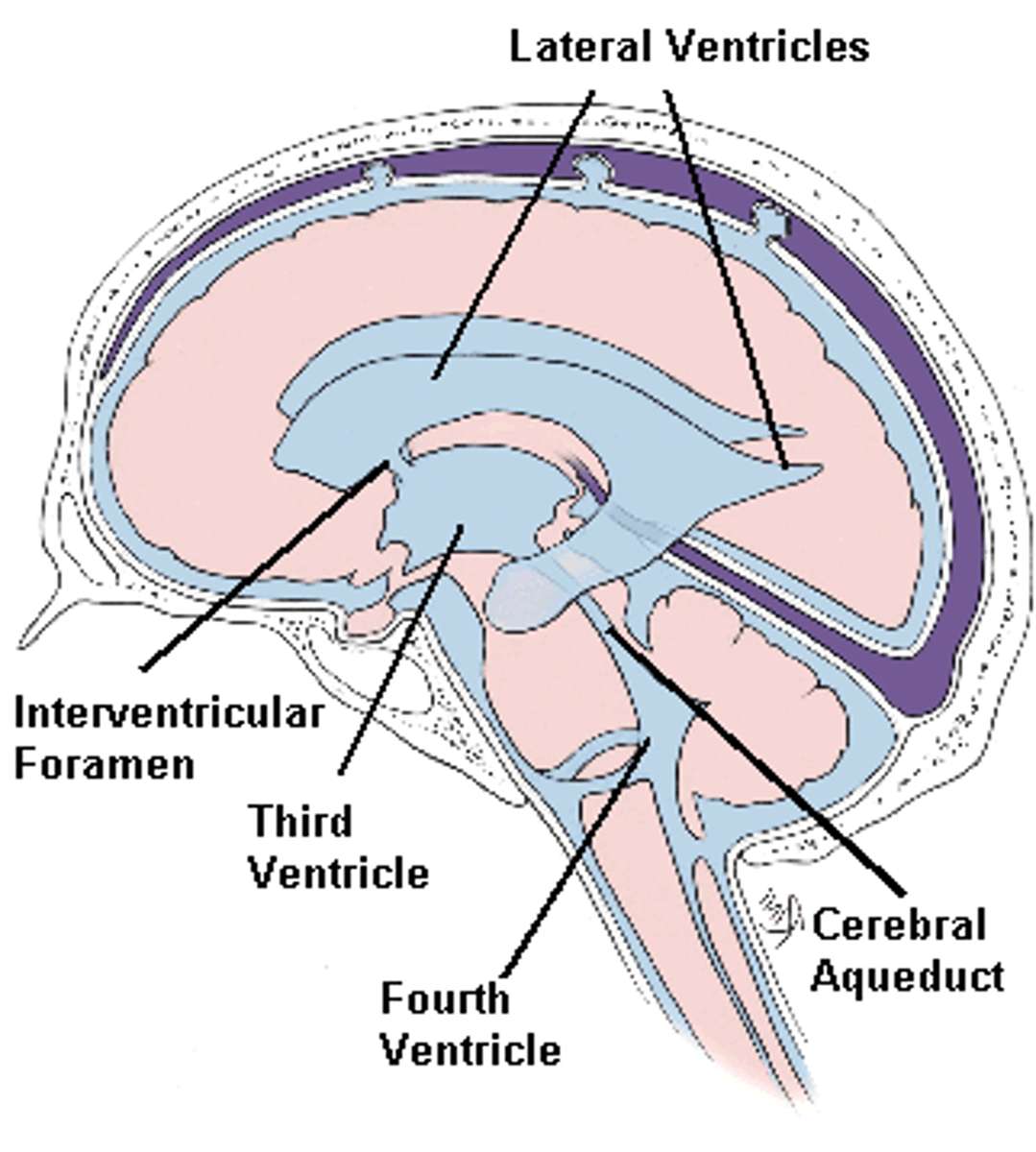
Lateral ventricles
Ventricles located in each cerebral hemisphere
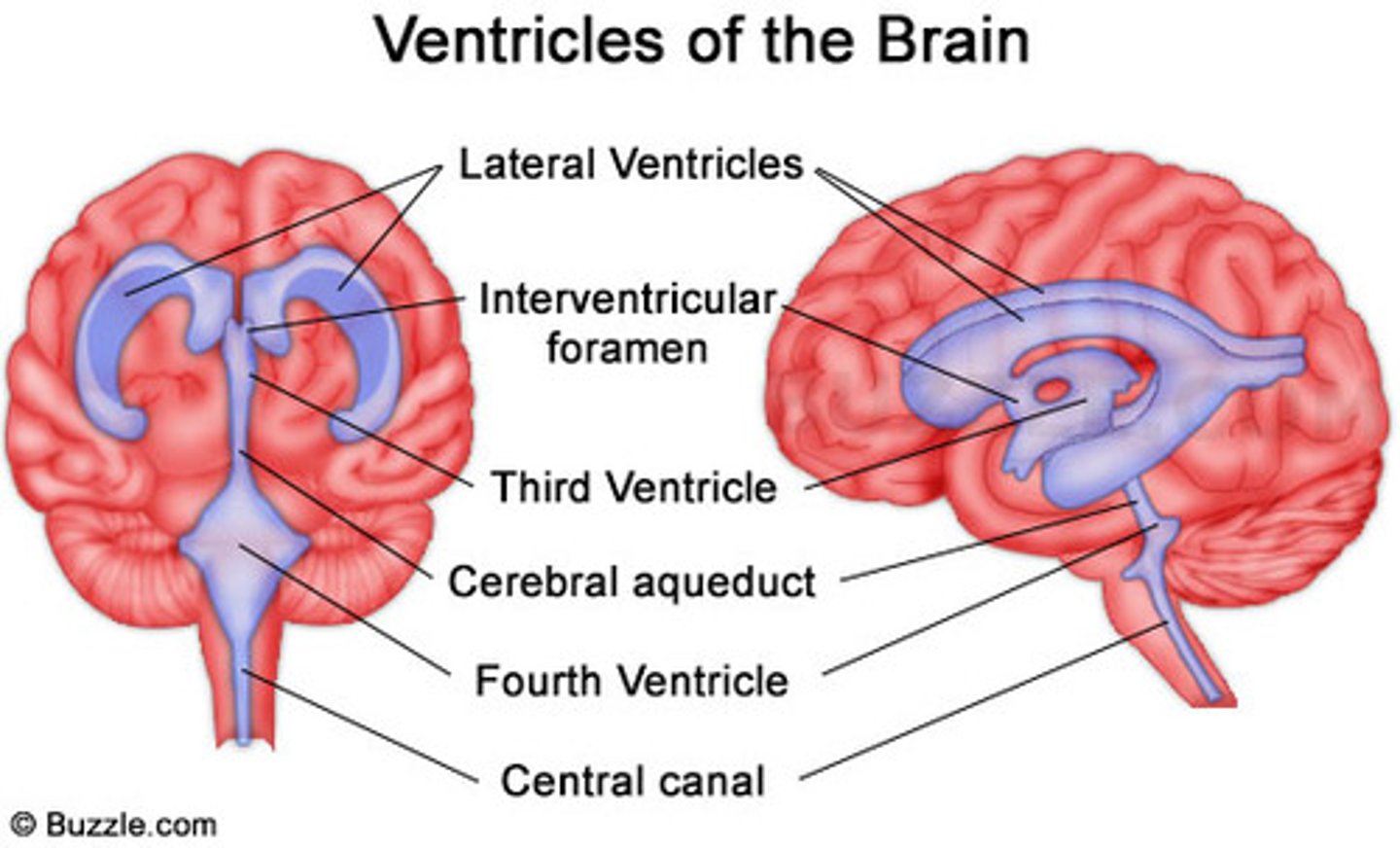
Third ventricle
the ventricle located in the center of the diencephalon
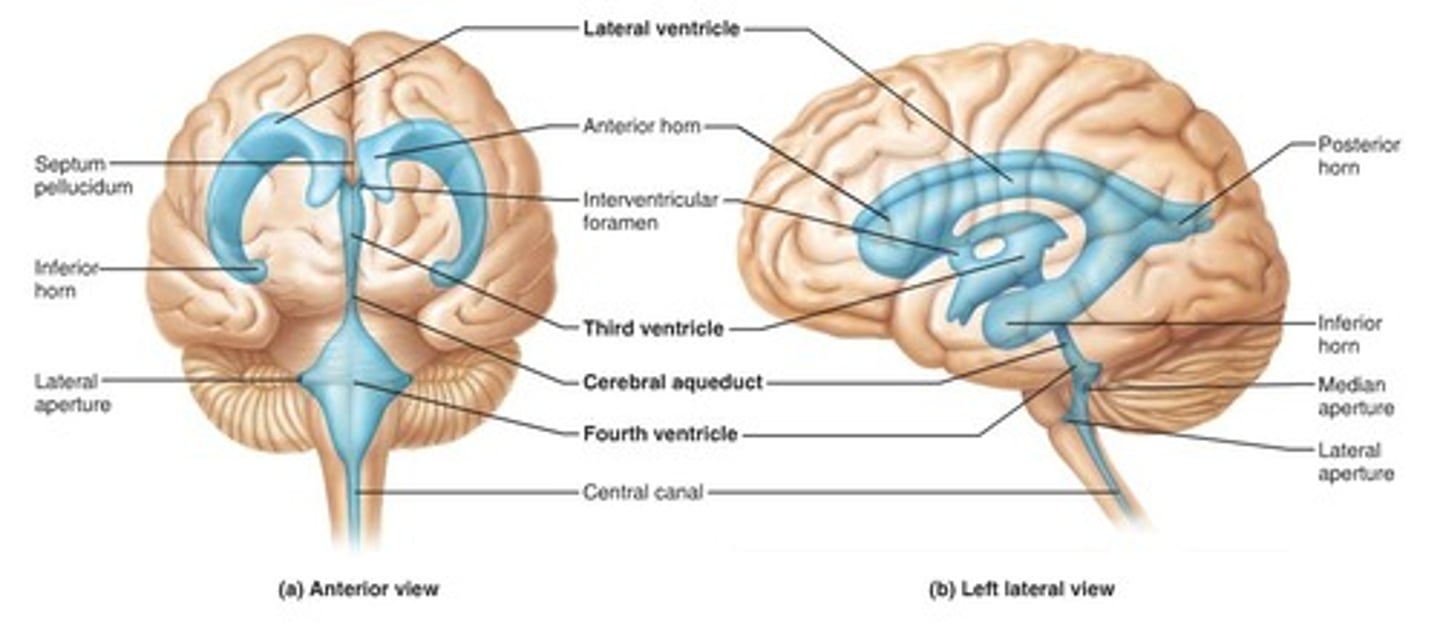
Cerebral aqueduct
connects the third and fourth ventricles
Fourth ventricle
the ventricle located between the cerebellum and the dorsal pons, in the center of the metencephalon
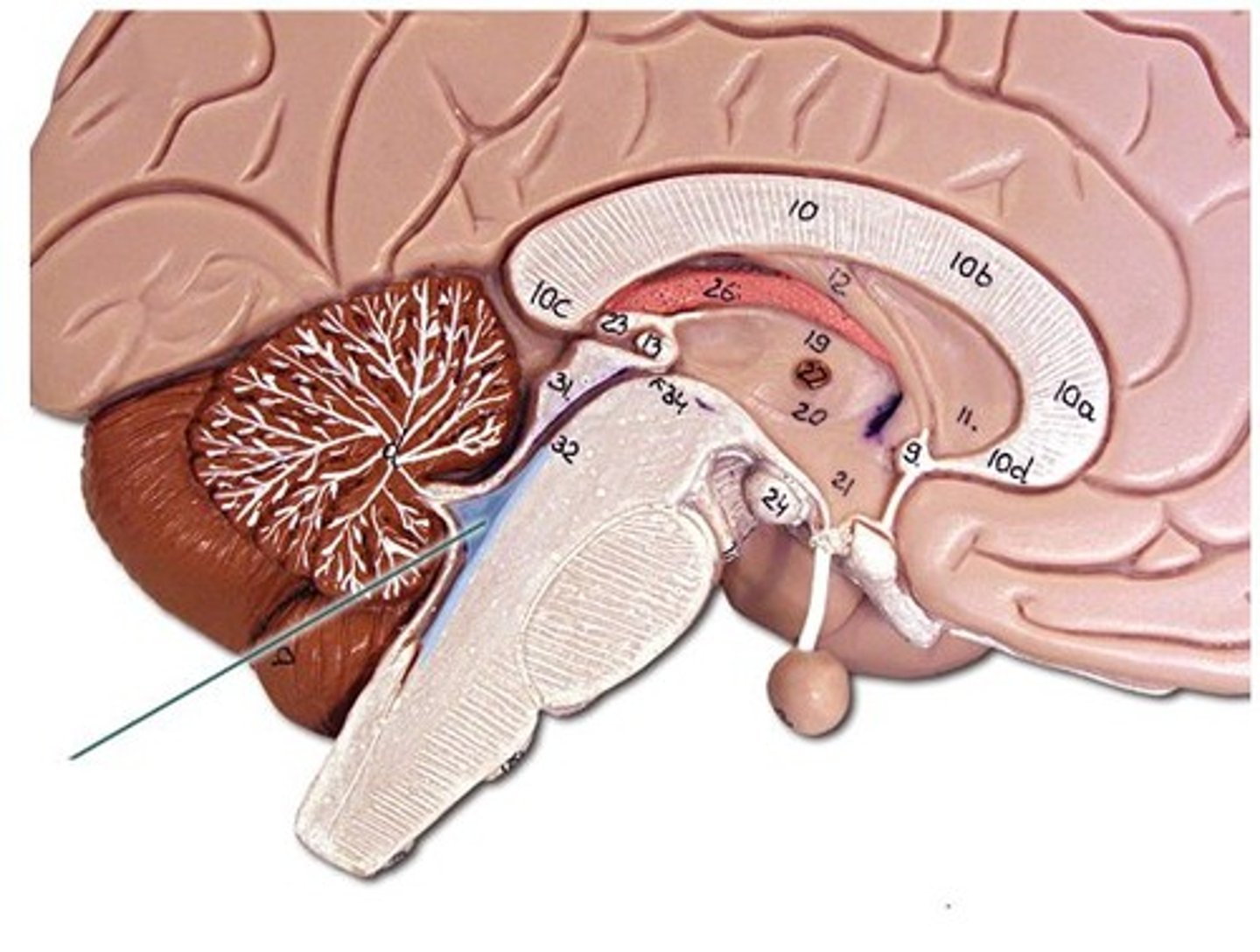
Central canal
a fluid-filled channel in the center of the spinal cord
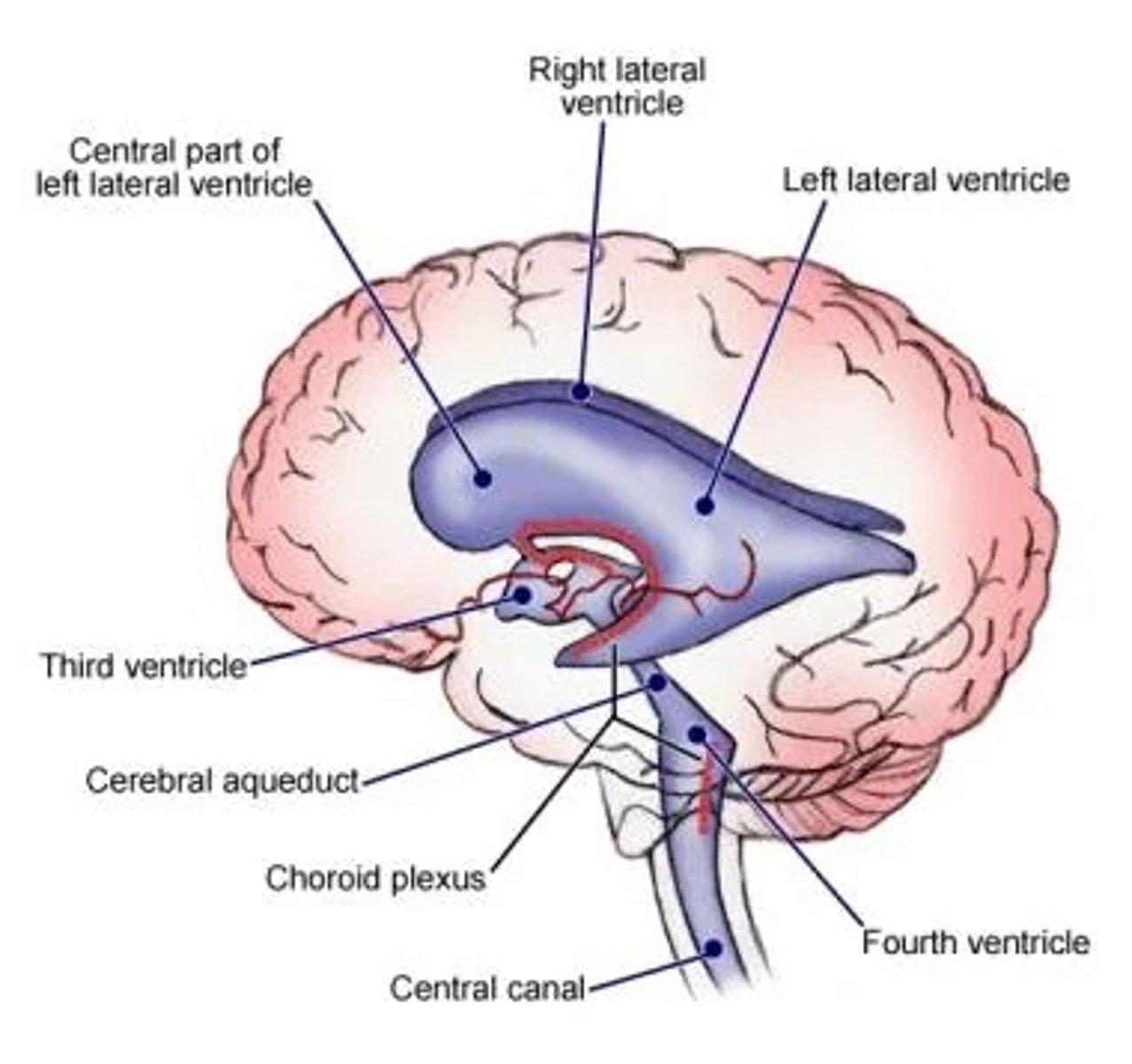
Inter ventricular foramen of Monroe
Passageway between lateral ventricles and third ventricle
Production of CSF is how much and from what daily?
500 ml from the choroid plexus
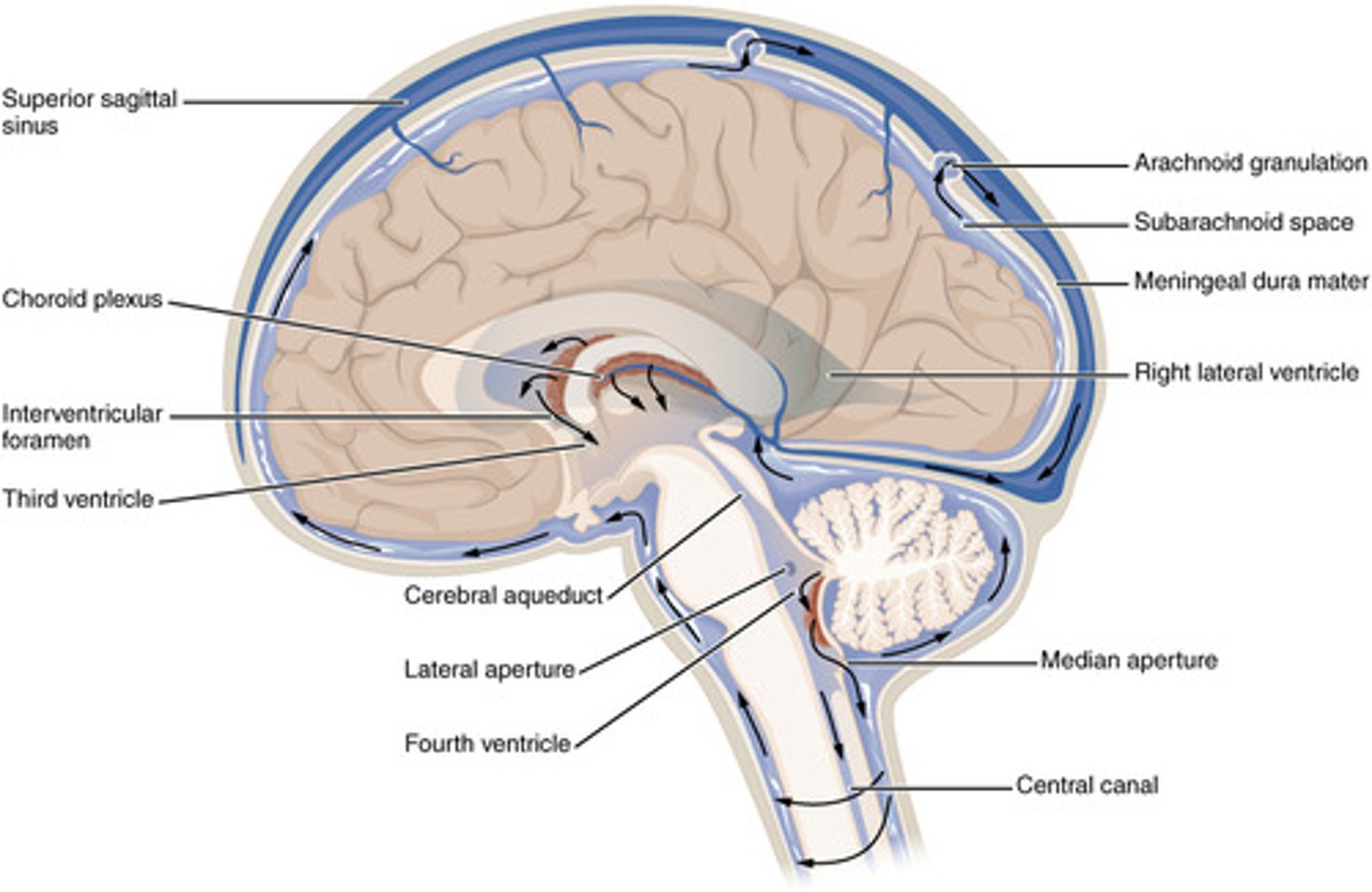
Choroid plexus
lines the ventricles and subarachnoid space
Where does the production of CSF mainly take place?
within the two lateral ventricles and fourth ventricle
What are the 3 layers of the choroid plexus?
1. fenestrated endothelium of choroid arteries
2. pial layer
3. specialized ependymal layer
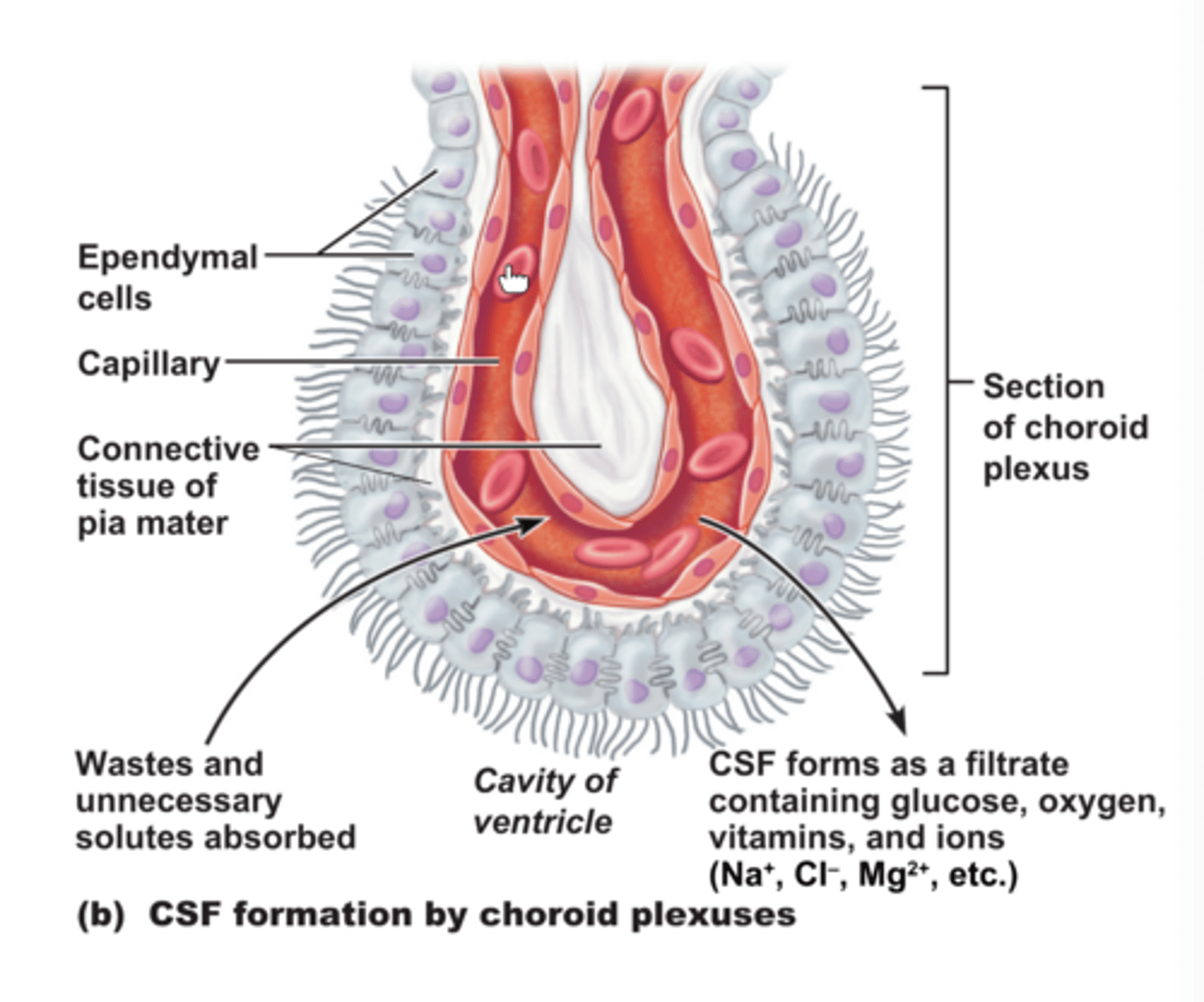
The Blood Brain Barrier prevents what from crossing into the CSF?
large molecules (proteins, glucose)
Bacterial infection means what?
low CSF glucose and high protein
Cisterns
spaces within the subarachnoid space that are filled with CSF and aid in proper circulation
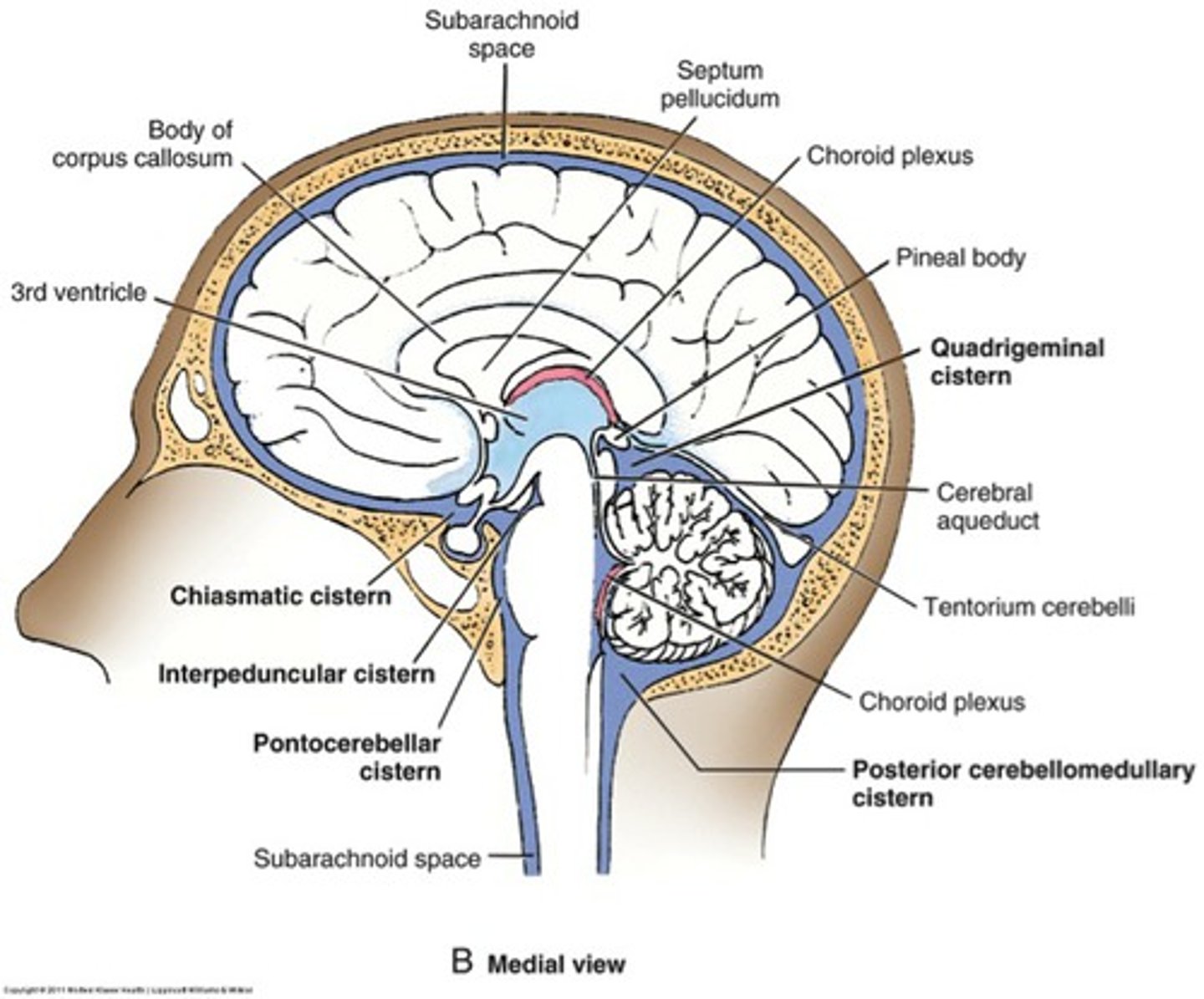
What is the largest cistern?
cisterna magna
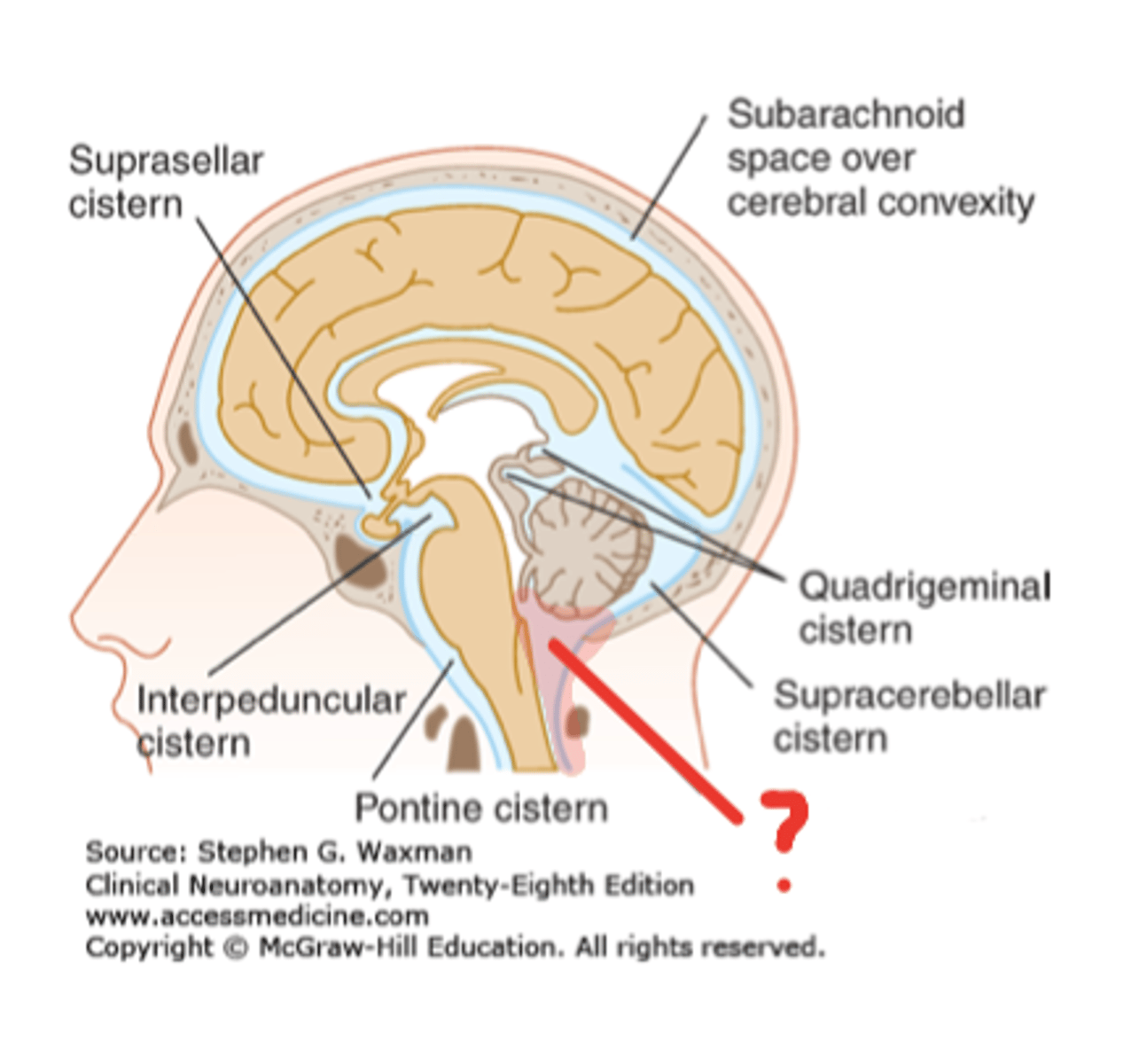
Cisterna magna is located where?
caudal to cerebellum and lying above the foramen magnum
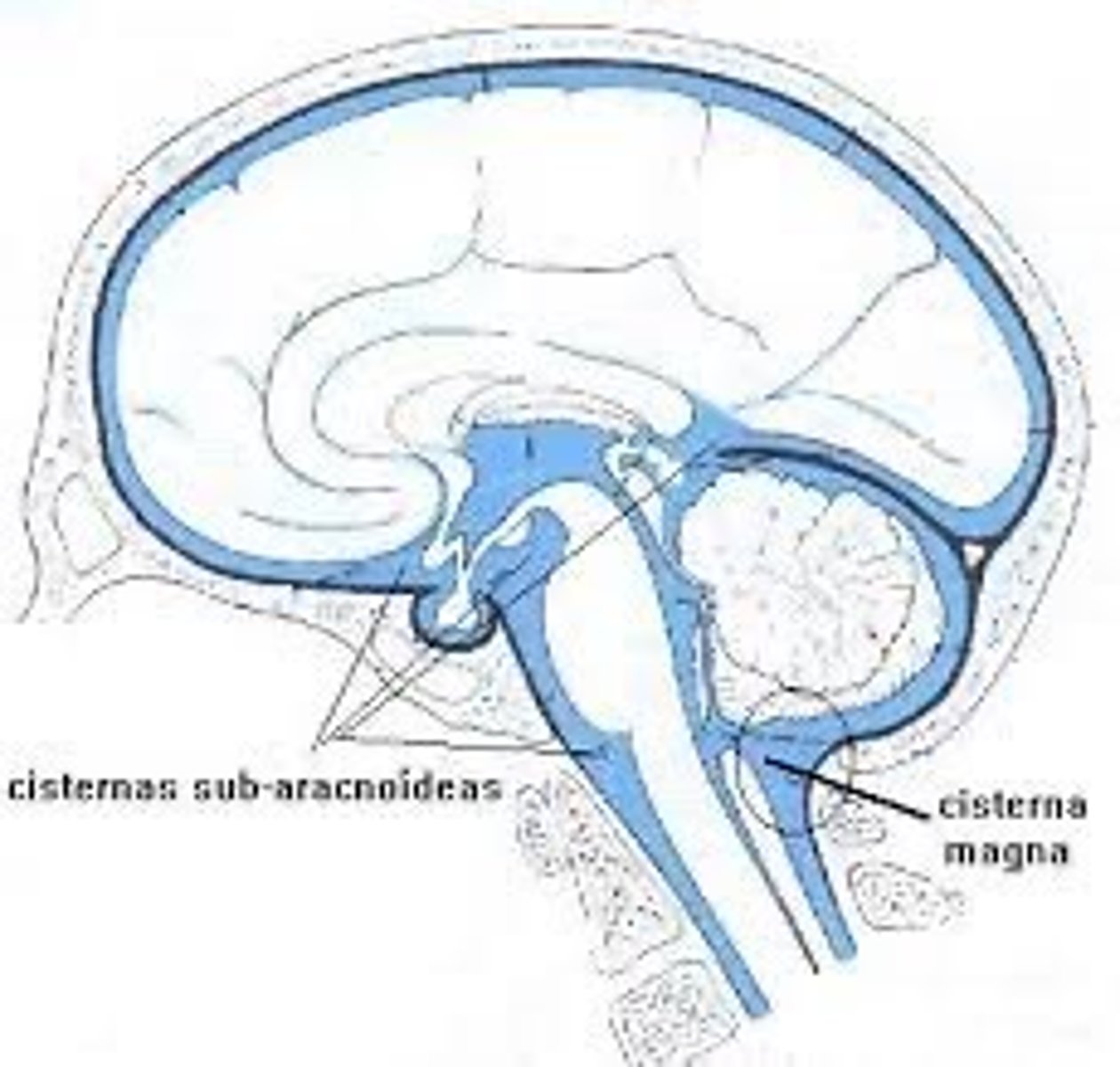
Production of new CSF acts as what?
motor for CSF circulation
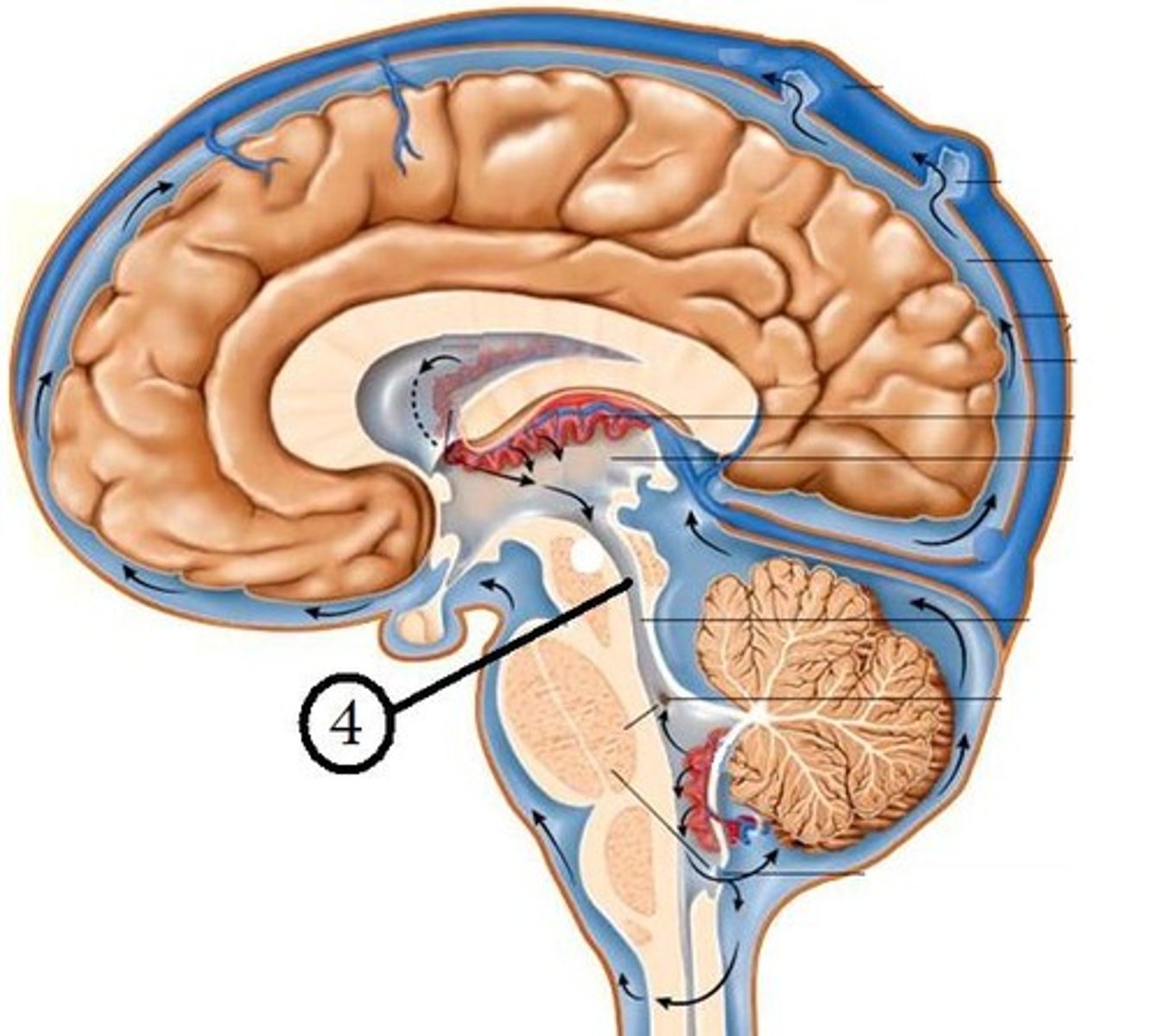
CSF circualtion
flows out of the ventricular system by the medial foramen of Magendie or two lateral foramina of Lushka into subarachnoid space and central canal
In subarachnoid space, CSF circulates until what?
it reaches arachnoid granulations that protrude into superior sagittal venous sinus
How is CSF reabsorbed?
arachnoid granulations/villi
Arachnoid granulations
Extensions of the arachnoid mater that allow excess CSF to be absorbed by the dural sinuses