7a. Government failure
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/4
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:07 PM on 4/18/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
1
New cards
Law of unintended consequences
Government intervention can have negative unintended consequences.
E.g. a tax on cigarettes can create a black market where cigarettes are sold without tax.
E.g. a tax on cigarettes can create a black market where cigarettes are sold without tax.
2
New cards
Administration costs
The miscellaneous costs of government intervention.
E.g. paperwork, legal fees, secretaries, managers.
E.g. paperwork, legal fees, secretaries, managers.
3
New cards
Information gaps
When the government lacks the information needed to intervene most efficiently.
E.g. the government doesn’t know what size to set for its carbon tax.
E.g. the government doesn’t know what size to set for its carbon tax.
4
New cards
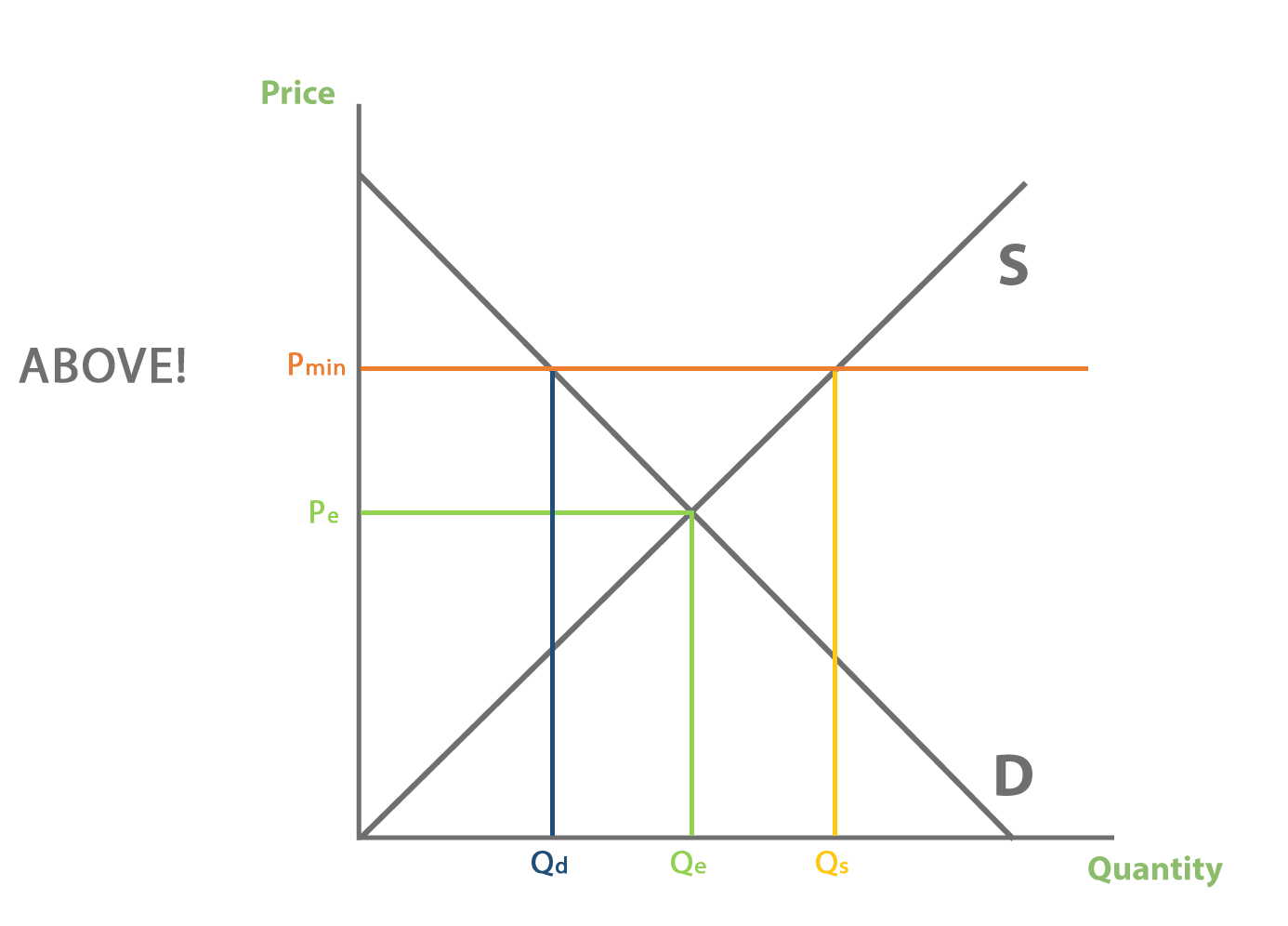
Distortion of the price mechanism
Government intervention can distort the price mechanism.
E.g. a minimum price will create excess supply between Qd and Qs:
*at front*
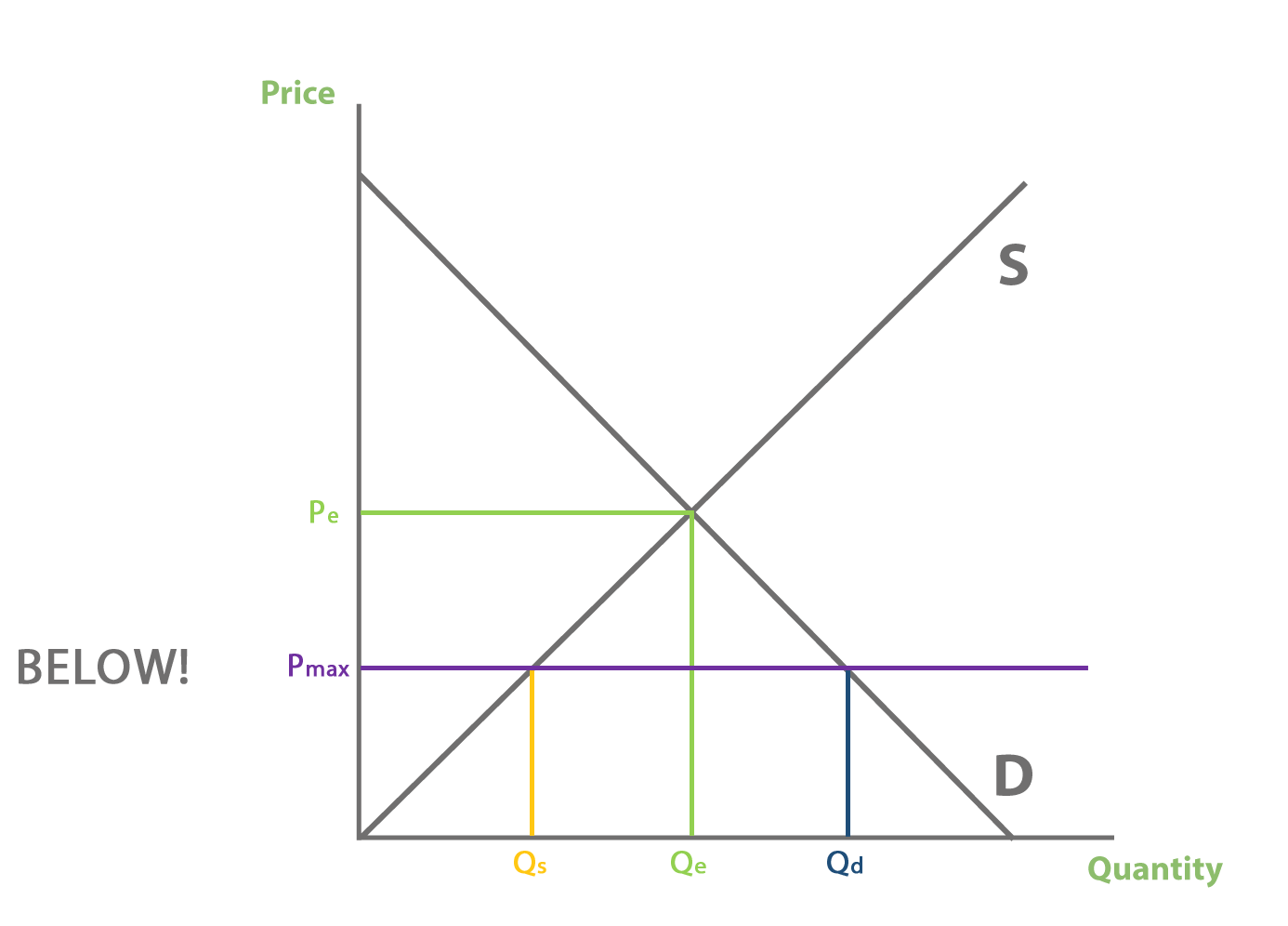
E.g. a maximum price will create excess demand between Qs and Qd:
E.g. a minimum price will create excess supply between Qd and Qs:
*at front*
E.g. a maximum price will create excess demand between Qs and Qd:
5
New cards