Measuring Intelligence
5.0(2)Studied by 6 people
0%Unit 5: Cognitive Psychology Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/53
Last updated 11:42 PM on 4/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
1
New cards
The 3 aspects in designing a good test
1. standardization
2. reliability
3. validity
2
New cards
Standardization
one aspect of designing a good test
= comparing a data point against a data set
\
ex. grades from a harsh teacher vs. an easy teacher, don’t mean anything without _______
so that’s why there are ______ tests (MCAS, SAT, AP)
\
* comparison of a large enough data set of ANY data will usually give a **bell curve**
= comparing a data point against a data set
\
ex. grades from a harsh teacher vs. an easy teacher, don’t mean anything without _______
so that’s why there are ______ tests (MCAS, SAT, AP)
\
* comparison of a large enough data set of ANY data will usually give a **bell curve**
3
New cards
Reliability
one aspect of designing a good test
= score consistency
* IMPORTANT: Reliability is necessary, but NOT SUFFICIENT (you also need validity)
* ex. consider a broken scale, each person that steps on will weigh 100 lbs (very reliable/consistent, but accurate? No.)
= score consistency
* IMPORTANT: Reliability is necessary, but NOT SUFFICIENT (you also need validity)
* ex. consider a broken scale, each person that steps on will weigh 100 lbs (very reliable/consistent, but accurate? No.)
4
New cards
Split-in-Half Technique
One way to establish reliability
= is assessed by splitting the measures/items from the measurement procedure in half, and then calculating the scores for each half separately
\
ex. 100 Q test, see how well students did in first 50 and the last 50 (or split by evens and odds)
if both halves are good = reliable
if one good, one bad = unreliable (b/c one part is \*statistically\* significantly more difficult)
\
* is useful in determining if a test is too long
* ex. if someone got a question right that’s early on in the exam, but got a similar Q wrong later, can maybe account it to **fatigue**)
= is assessed by splitting the measures/items from the measurement procedure in half, and then calculating the scores for each half separately
\
ex. 100 Q test, see how well students did in first 50 and the last 50 (or split by evens and odds)
if both halves are good = reliable
if one good, one bad = unreliable (b/c one part is \*statistically\* significantly more difficult)
\
* is useful in determining if a test is too long
* ex. if someone got a question right that’s early on in the exam, but got a similar Q wrong later, can maybe account it to **fatigue**)
5
New cards
Test-Retest Reliability
One way to establish reliability
= administering the same test (but shuffled a bit to avoid test-retest bias AKA memorization) twice over a period of time
* scores from first and second time can then be correlated to evaluate reliability
\
The __higher the correlation__, the __higher the reliability__!
= administering the same test (but shuffled a bit to avoid test-retest bias AKA memorization) twice over a period of time
* scores from first and second time can then be correlated to evaluate reliability
\
The __higher the correlation__, the __higher the reliability__!
6
New cards
Alternate Forms Reliability
One way to establish reliability
= Does the score you receive correlate with the score on another test covering the same material?
\
ex. taking the October SAT vs. the December SAT: scores shouldn’t change drastically b/c the SAT is reliable
= Does the score you receive correlate with the score on another test covering the same material?
\
ex. taking the October SAT vs. the December SAT: scores shouldn’t change drastically b/c the SAT is reliable
7
New cards
Inter-Rater Reliability
One way to establish reliability
= does the score one grader assigns to your assessment correlate with the score another grader gives for the same test?
\
ex. more than one “blind” grader gives scores for FRQs to ensure _____ reliability where both scores should be the same
= does the score one grader assigns to your assessment correlate with the score another grader gives for the same test?
\
ex. more than one “blind” grader gives scores for FRQs to ensure _____ reliability where both scores should be the same
8
New cards
Intra-Rater Reliability
One way to establish reliability
= Does an individual rater agree with themselves when measuring the same item multiple times?
= the consistency of the data recorded by ONE rater over several trials
= Does an individual rater agree with themselves when measuring the same item multiple times?
= the consistency of the data recorded by ONE rater over several trials
9
New cards
Validity
one aspect of designing a good test
= the extent to which a test actually assesses what it claims to asses
= the extent to which a test actually assesses what it claims to asses
10
New cards
Content Validity
One way to establish validity
= Does the assessment have content relevant to the construct?
\
AKA how representative the results are of the content being tested
\
* exams must include Qs relevant to the topic (represents the material learned in the couse)
= Does the assessment have content relevant to the construct?
\
AKA how representative the results are of the content being tested
\
* exams must include Qs relevant to the topic (represents the material learned in the couse)
11
New cards
Face Validity
One way to establish validity
= at first glance, does the test seem to evaluate what it claims to?
\
ex. a test on musical ability, but the first page is just pictures of food → appropriate here to question the _____ validity
\
ex. AP Psych exam includes a graph of normal distribution, and you (a psych student who didn’t study at all) thinks it looks like a math test, but the graph is actually related to intelligence testing and statistics
* thus, the exam LACKS face validity, but it DOES have content validity
= at first glance, does the test seem to evaluate what it claims to?
\
ex. a test on musical ability, but the first page is just pictures of food → appropriate here to question the _____ validity
\
ex. AP Psych exam includes a graph of normal distribution, and you (a psych student who didn’t study at all) thinks it looks like a math test, but the graph is actually related to intelligence testing and statistics
* thus, the exam LACKS face validity, but it DOES have content validity
12
New cards
Construct Validity
One way to establish validity
= whether or not an assessment measures an idea (or “construct”) that it is designed to measure
\
construct = something intangible, so test makers have to come up with a tool (or “operational definition”)
\
so the main question is: __**Does the operational definition really measure what it’s supposed to?**__
= whether or not an assessment measures an idea (or “construct”) that it is designed to measure
\
construct = something intangible, so test makers have to come up with a tool (or “operational definition”)
\
so the main question is: __**Does the operational definition really measure what it’s supposed to?**__
13
New cards
Criterion Validity
One way to establish validity
= measures how well the test correlates with the outcome
\
ex. student gets “genius” on an inteligens test, BUT always misspells the word inteligens → low criterion validity
ex. you score really high on an inteligens test, BUT, you have trouble multitasking → bad criterion validity
\
has 2 types:
1. predictive validity
2. concurrent validity
= measures how well the test correlates with the outcome
\
ex. student gets “genius” on an inteligens test, BUT always misspells the word inteligens → low criterion validity
ex. you score really high on an inteligens test, BUT, you have trouble multitasking → bad criterion validity
\
has 2 types:
1. predictive validity
2. concurrent validity
14
New cards
Predictive Validity
a type of criterion validity
= does the test accurately predict the level of some future performance?
ex. Does the performance on the SAT correlate with later college performance?
= does the test accurately predict the level of some future performance?
ex. Does the performance on the SAT correlate with later college performance?
15
New cards
Concurrent Validity
a type of criterion validity
= do the results from the test correlate with results from OTHER measures designed to assess similar topics/concepts?
\
ex. if results from my test that I created were similar to the WAIS, then my test has criterion validity (b/c the scores had a positive correlation to another valid measure of intelligence)
= do the results from the test correlate with results from OTHER measures designed to assess similar topics/concepts?
\
ex. if results from my test that I created were similar to the WAIS, then my test has criterion validity (b/c the scores had a positive correlation to another valid measure of intelligence)
16
New cards
Verbal Tests
Tests that use word problems to assess abilities
17
New cards
Abstract tests
Tests that use non-verbal measures to assess abilities
18
New cards
Speed of Processing
= the time it takes a person to do a mental task
19
New cards
Binet Test
an intelligence test that compares a child against what most children their age can do
* ex. an average 7 year old can tie their shoes, ride a bike, do basic math, etc.
* then you compare a 7 year old against the average
* is ratio-based:
\
__Mental age__ X 100 = IQ
Chronological age
\
__7__ X 100 = 100 IQ (the average)
7
\
ex.
__a mental age of 8__ X 100 = 80 IQ (below average)
a biological 10 yr old
* ex. an average 7 year old can tie their shoes, ride a bike, do basic math, etc.
* then you compare a 7 year old against the average
* is ratio-based:
\
__Mental age__ X 100 = IQ
Chronological age
\
__7__ X 100 = 100 IQ (the average)
7
\
ex.
__a mental age of 8__ X 100 = 80 IQ (below average)
a biological 10 yr old
20
New cards
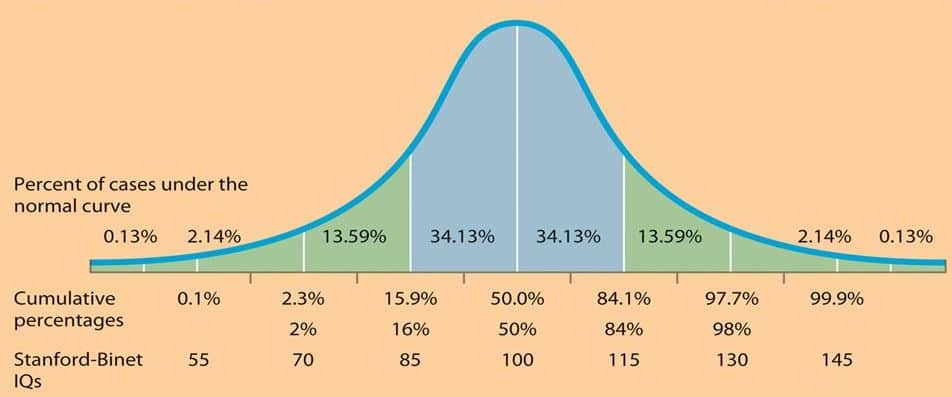
Stanford-Binet Test
= an intelligence test that compares an individual against a large bank of acquired scores on a bell curve
* is based on the Binet Test and addresses the Binet Test’s problem where it gets less accurate as people get older (because age difference isn’t as discretely predictive of age-appropriate skills)
* “what can a 34 yr old do that a 33 yr old couldn’t do?”
\
\
* is based on the Binet Test and addresses the Binet Test’s problem where it gets less accurate as people get older (because age difference isn’t as discretely predictive of age-appropriate skills)
* “what can a 34 yr old do that a 33 yr old couldn’t do?”
\
\
21
New cards
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS)
= an IQ test designed to measure intelligence and cognitive ability
* gives a general intelligence score + 15 subtests
* assesses a range of intellectual abilities
* gives a general intelligence score + 15 subtests
* assesses a range of intellectual abilities
22
New cards
Francis Galton
= this person correlated reaction time to intelligence
\
HOWEVER, this person also used intelligence tests to support eugenics
\
HOWEVER, this person also used intelligence tests to support eugenics
23
New cards
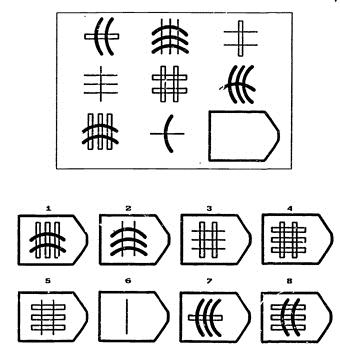
Raven’s Matrices
= a non-verbal IQ test that measures intellectual development + logical thinking
\
* tables given to test pattern-recognition with increasing difficulty
\
* tables given to test pattern-recognition with increasing difficulty
24
New cards
Flynn Effect
= an increase in population Intelligence Quotient (IQ) throughout the 20th century
* characterized by rapid changes (+3 IQ points per decade)
* due to a combination of environmental factors
* characterized by rapid changes (+3 IQ points per decade)
* due to a combination of environmental factors
25
New cards
Growth Mindset
= when you DO believe you can improve intellectually
* self-efficacy
* don’t allow challenges to define you
* more likely to embrace challenges
* appreciates feedback
* self-efficacy
* don’t allow challenges to define you
* more likely to embrace challenges
* appreciates feedback
26
New cards
Fixed Mindset
= when you DON’T believe you can improve intellectually
* ex. \**does bad on math test** → “I’m just not a math person”
* learned helplessness
* ex. \**does bad on math test** → “I’m just not a math person”
* learned helplessness
27
New cards
idk, u think
Are tests predictive?
28
New cards
idk, u think
Are tests biased?
29
New cards
55% of intelligence is heritable (biological/nature)
\
However, intelligence can be modified by changing the environment
ex. improving nutrition, removing toxins, better schools, the ratio of encouraging comments to reprimands, amount of attention from adults, etc.
\
However, intelligence can be modified by changing the environment
ex. improving nutrition, removing toxins, better schools, the ratio of encouraging comments to reprimands, amount of attention from adults, etc.
What portion of intelligence is due to nature? due to nurture?
30
New cards
Between-Group Differences
= the average of group 1 compared to the average of group 2
\
ex. average height of women = 5’4” vs. men = 5’9”
\
ex. average height of women = 5’4” vs. men = 5’9”
31
New cards
Within-Group Differences
= the range of differences within 1 group (individual 1 compared to individual 2)
\
ex. Ms. Georges height vs. Mrs. Silipo’s height (within the female SHS teachers population)
\
ex. Ms. Georges height vs. Mrs. Silipo’s height (within the female SHS teachers population)
32
New cards
Question Familiarity
one criticism of standardized tests
= the Qs are more familiar to middle/upper-middle class than others
or
= the Qs might reflect common knowledge of the majority group / the interests of one specific group
\
ex. only 1 student knowing about Ash Wednesday (majority group = christians)
ex. a Q about using instrumental aggression in football (biased towards men)
ex. MCAS question about snow days given to the Midwest region (probably created by people in northern regions)
= the Qs are more familiar to middle/upper-middle class than others
or
= the Qs might reflect common knowledge of the majority group / the interests of one specific group
\
ex. only 1 student knowing about Ash Wednesday (majority group = christians)
ex. a Q about using instrumental aggression in football (biased towards men)
ex. MCAS question about snow days given to the Midwest region (probably created by people in northern regions)
33
New cards
Motivation
recall Maslow’s hierarchy:
* kids who are worries about meeting basic needs are not going to put energy into esteem needs → won’t test well
\
also:
* in many schools, there’s an anti-intellectual culture → doing well on tests = “Nerd!!”
* kids who are worries about meeting basic needs are not going to put energy into esteem needs → won’t test well
\
also:
* in many schools, there’s an anti-intellectual culture → doing well on tests = “Nerd!!”
34
New cards
Self-fulfilling Prophecy
people often conform to what’s expected of them
35
New cards
Stereotype Threat
tendency for members of the same group for which a negative stereotype exists to perform poorly on an instrument designed to asses an ability related to the negative stereotype
\
AKA members who are *thought* to be ____ will conform to that expectation when tested about _______
\
* this will subconsciously effect a child growing up under this stereotype (will fall prey to the self-fulfilling prophecy)
* you can reduce stereotype threat with deception in experiments!
\
AKA members who are *thought* to be ____ will conform to that expectation when tested about _______
\
* this will subconsciously effect a child growing up under this stereotype (will fall prey to the self-fulfilling prophecy)
* you can reduce stereotype threat with deception in experiments!
36
New cards
Peer Pressure and Group Norms
= different groups have different beliefs about school success
\
based on research from the 200s:
* Black and White kids think school success is due to INNATE INTELLIGENCE
* Asian and Latinx kids think it’s due to HARD WORK
\
based on research from the 200s:
* Black and White kids think school success is due to INNATE INTELLIGENCE
* Asian and Latinx kids think it’s due to HARD WORK
37
New cards
Biological Reactions to Stress
= physical stress reactions (changes in cortisol. blood pressure, etc.) hurt memory, attention, and executive functioning---all necessary components for academic success
38
New cards
Achievement Tests
= any norm-referenced standardized test intended to measure skill/knowledge in a certain subject
39
New cards
Aptitude Tests
= attempts to determine a person’s ability to acquire (through future training) specific skills
* AKA how much potential one has (?)
\
ex. career tests for high school students
* AKA how much potential one has (?)
\
ex. career tests for high school students
40
New cards
Personality Tests
= designed to systematically elicit information about a person's motivations, preferences, interests, emotional make-up, and style of interacting with people and situations
\
ex. MMPI-2, MBTI, etc.
\
ex. MMPI-2, MBTI, etc.
41
New cards
Objective Tests
= tests that are easily scored, can be given in groups, are forced choice (test taker has to choose from multiple choice or true/false)
* answers are then tabulated and the scores determine personality traits
\
ex. Achievement tests (intelligence), Aptitude tests (intelligence), MMPI (personality), MBTI (personality)
* answers are then tabulated and the scores determine personality traits
\
ex. Achievement tests (intelligence), Aptitude tests (intelligence), MMPI (personality), MBTI (personality)
42
New cards
Projective Tests
= tests that are unstructured where the subject is shown ambiguous stimuli
\
ex. Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)
ex. Rorschach inkblot
\
ex. Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)
ex. Rorschach inkblot
43
New cards
Thematic Apperception Test (TAT)
= a type of projective test that involves describing ambiguous scenes to learn more about a person's emotions, motivations, and personality

44
New cards
Rorschach Inkblot
= a projective psychological test in which subjects' perceptions of inkblots are recorded and then analyzed using psychological interpretation, complex algorithms, or both

45
New cards
Intellectual Disability
= limited cognitive and adaptive functioning
= IQ less than 70, needs support to live
* have trouble with executive functioning
= IQ less than 70, needs support to live
* have trouble with executive functioning
46
New cards
Adaptive Functioning
= ability to care for self and meet general social expectations
47
New cards
Executive Functioning
= planning strategies, multi-step problems, metacognition
48
New cards
Intermittent
level 1 of support needed for those with intellectual disabilities
= as needed basis (usually only needed when person starts something new in life)
= as needed basis (usually only needed when person starts something new in life)
49
New cards
Limited
level 2 of support needed for those with intellectual disabilities
= for limited time/activities (ex. job coach)
= for limited time/activities (ex. job coach)
50
New cards
Extensive
level 3 of support needed for those with intellectual disabilities
= long-term involvement (help w/daily living)
= long-term involvement (help w/daily living)
51
New cards
Pervasive
level 4 of support needed for those with intellectual disabilities
= intense, long-term care (possibly needed to keep a person alive) for all parts of their life
= intense, long-term care (possibly needed to keep a person alive) for all parts of their life
52
New cards
Savants
= people (usually with intellectual disabilities) who have a genius-like ability in a very narrow area
53
New cards
Prodigy
= a child with amazing ability
\
IQ > 135
\
IQ > 135
54
New cards
Genius
scoring 2 standard deviations above the man (top 1%)