Aggregate Demand & Supply - MAC
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Aggregate Demand (Scott’s Lecture)
An economy’s aggregate demand related to output.
Aggregate demand (Fluegge Definition)
the relationship between quantity of real GDP demanded and the price level.
Aggregate Supply (Fluegge Definition)
the relationship between the quantity of real GDP supplied and the price level.
Monetary Policy is- (Scott’s Lecture)
Money supply & interest rates
Fiscal Policy is- (Scott’s Lecture)
government spending
PI stands for - (Scott’s Lecture)
Price of output market
Pf stands for- (Scott’s Lecture)
Price input market
LAS is - (Scott’s lecture)
wavier plan, capital, & technology
SAS is- (Scott’s Lecture)
a function of PI
The quantity of real GDP supplied
the total amount of final goods and services that firms in the United States plan to produce
The price level influences the quantity of real GDP demanded because of-
a change in the price level brings a change in the buying power of money, real interest rate, real prices of exports and imports.
The factors that change aggregate demand are-
Expectations about the future, fiscal policy and monetary policy, the state of the world economy
What are two sources of inflation:
Demand-pull inflation & Cost-push inflation
Aggregate supply
the relationship between the quantity of real GDP supplied and the price level when all other influences on production plans remain the same
Aggregate demand
the relationship between the quantity of real GDP demanded and the price level when all other influences on expenditure plans remain the same.
Recessionary Gap
The economy is below full employment
Inflationary Gap
The economy is above full employment
Real Business Cycle
The resulting cycle
demand-pull inflation
Inflation that starts because aggregate demand increases
cost-push inflation
Inflation that begins with an increase in cost
stagflation
The combination of a decreasing real GDP and a rising price level
Quantity of real GDP supplied depends on the quantities of-
Labor employed, capital, human capital, & the state of technology, land & natural resources, & entrepreneurial talent.
Aggregate supply changes when-
Potential GDP changes, money wage rate changes, & money prices of other resources change.
If aggregate supply price level & quantity of real GDP supplied increase then the-
The real wage rate decreases, & employment increases.
If aggregate supply price level & quantity of real GDP supplied decrease then the-
The real wage rate increases, & employment decreases.
Quantity of real GDP demanded-
The total amount of final goods & services produced in the United States that people, businesses, governments, & foreigners plan to buy.
What formula is the quantity-
Y = C + I + G + X - M
If the aggregate demand price level increases then the quantity of real GDP demanded-
decreases
What is C for?
C is for consumption expenditure
What does I stand for?
I stands for investment
What does G stand for?
G stands for government expenditure on goods and services
What does NX stand for?
net exports of goods and services
What two phases do the business cycle have?
Expansion
Recession
Monetary Policy includes-
1- Nominal money supply ( Interest rates go up, aggregate demand goes up ) Makes supply a positive relationship
2- Interest rests
Fiscal Policy includes-
-Taxes (if taxes go up, demand curve, aggregate goes down) ( -negative relationship)
-Government (if government goes up, demand curve, aggregate goes up) (+ positive relationship)
What type of policies used for aggregate demand tariffs?
Monetary/Fiscal
What does LAS stand for?
Long-run Aggregate Supply
What does SAS stand for?
Short-run Aggregate Supply
What does LAS represent?
the most output that an economy can sustain
What does SAS represent?
supply of the economy in the short run.
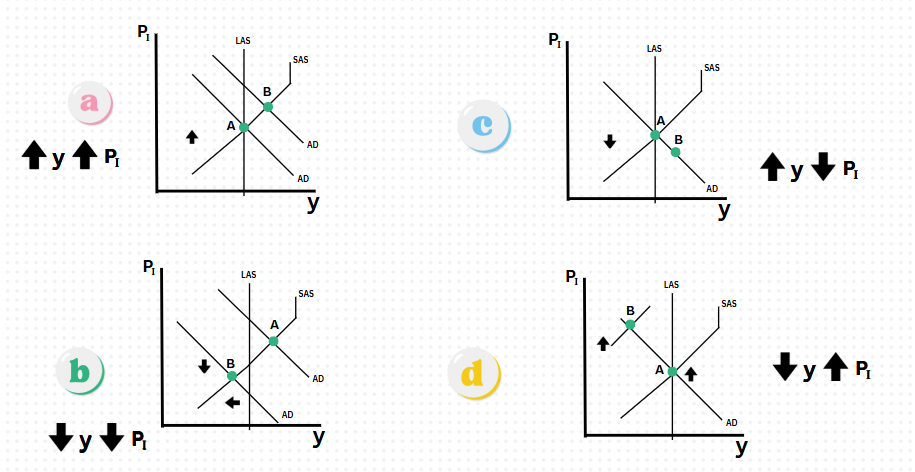
Which graph represents an increase in price level (PI) and increase in Real GDP (y)?
Graph A
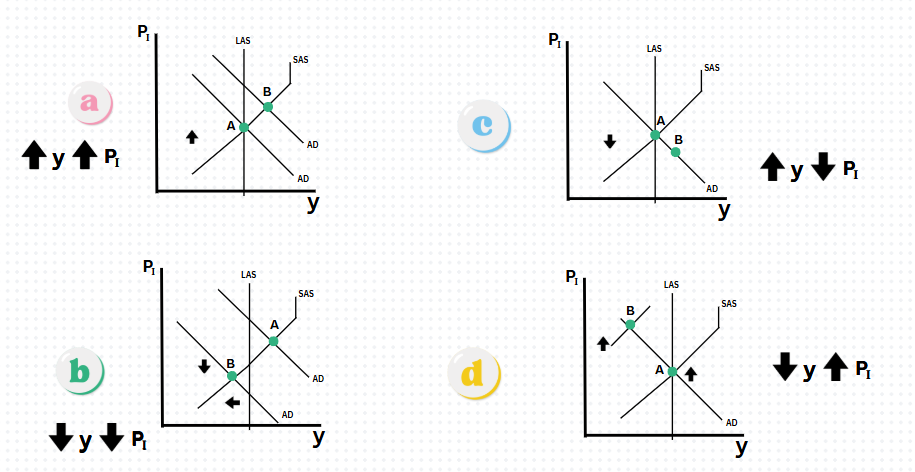
Which graph represents an decrease in price level (PI) and decrease in Real GDP (y)?
Graph B
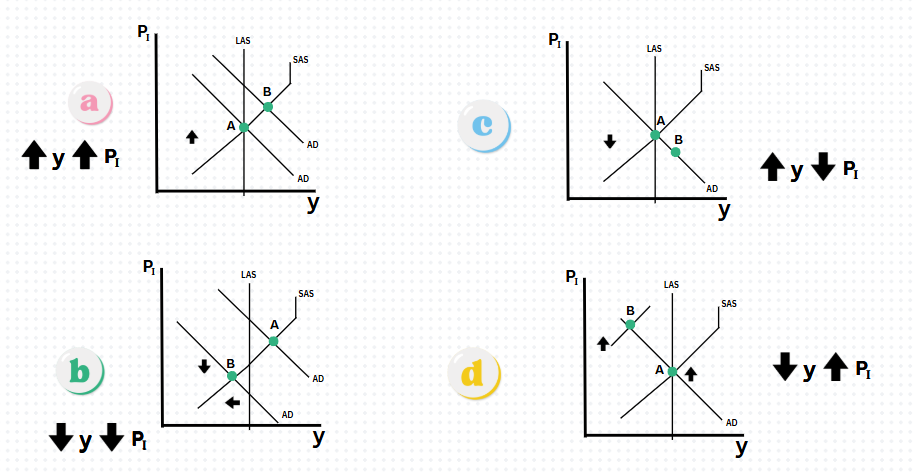
Which graph represents an decrease in price level (PI) and increase in Real GDP (y)?
Graph C
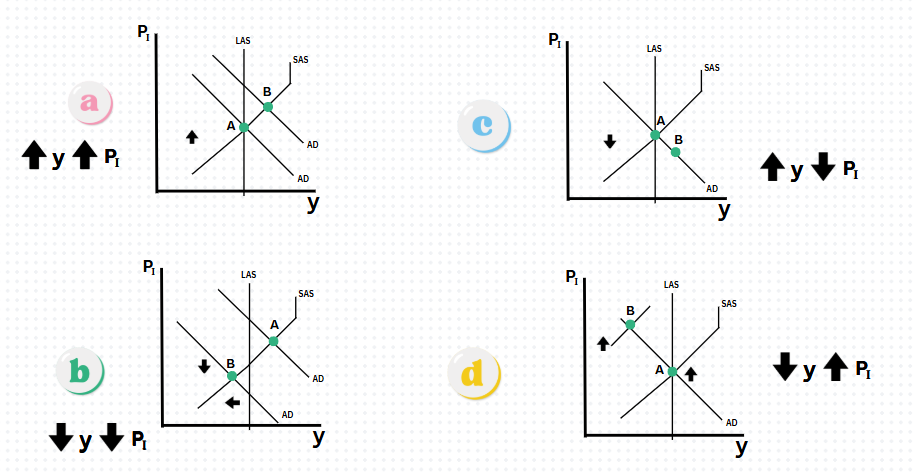
Which graph represents an increase in price level (PI) and decrease in Real GDP (y)?
Graph D
Quantity of Real GDP demanded because a change in the price level brings changes in:
The buying power of money, real interest rate, & real prices of exports & imports.
If the aggregate demand price level decreases then the quantity of real GDP demanded-
increases
When any influence on aggregate demand changes expenditure plans:
changes income, change in income induces a change in consumption expenditure, increase in aggregate demand is the initial increase in expenditure plans plus the induced increase in consumption expenditure.
Aggregate demand is the relationship between the quantity of _____ demanded and the _____ when all other influences on expenditure plans remain the same.
C. real GDP; price level
Which of the following statements illustrates fiscal policy?
C. The US government has proposed a hike in the corporate tax rate.
Which of the following statements illustrates monetary policy?
A. The Fed has raised the federal funds rate by 0.3 percent.
Macroeconomic equilibrium occurs when the quantity of _____ demanded equals the quantity of _____ supplied at the point of intersection of the _____ curve and the _____ curve.
B. real GDP; real GDP; AD; AS
Full-employment equilibrium occurs when equilibrium real GDP _____.
B. equals potential GDP
A recessionary gap is a gap that exists when potential GDP _____ real GDP and that brings a _____ price level. An inflationary gap is a gap that exists when real GDP _____ potential GDP and that brings a _____ price level.
A. exceeds; falling; exceeds; rising
A real business cycle is a cycle that results from fluctuations in the pace of growth of _____ and _____.
D. labor productivity; potential GDP
Demand-pull inflation is an inflation that starts because _____.
A. aggregate demand increases
Cost-push inflation is an inflation that begins with an increase in _____.
B. cost
Which of the following economies is facing stagflation?
A. The European economy is experiencing a decrease in real GDP for three quarters and a rise in the price level.
Aggregate supply is the relationship between the quantity of _____ supplied and the _____ when all other influences on production plans remain the same.
C. real GDP; price level
Aggregate supply increases when _____.
B. the money wage rate falls
When potential GDP increases, _____ .
B. aggregate supply increases
The quantity of real GDP demanded increases if _____ .
C. the price level falls
An increase in expected future income increases _____.
A. consumption expenditure, which increases current aggregate demand
Macroeconomic equilibrium occurs when the quantity of real GDP equals the quantity of _____ .
A. demanded; real GDP supplied
If the economy is at full employment and the Fed increases the quantity of money, _____ .
C. aggregate demand increases, an inflationary gap appears, and the money wage rate starts to rise
Over the past decade, the demand for goods produced in China has brought a sustained increase in the demand for China’s exports that has outstripped the growth of supply. As a result, China has experienced a _____ .
B. rising price level and demand-pull inflation