4/3/25 the eyes and ear
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
THE EYE
You're looking at the layers of the eye and their components. Here's a breakdown of the layers and structures within the eye:
### Outermost Layers:
- Sclera – The white, tough outer layer of the eyeball that provides structure and protection. It is continuous with the cornea at the front of the eye.
- Cornea – The transparent, dome-shaped structure at the front of the eye that allows light to enter. It also helps focus light as it passes into the eye.
### Inner Layer:
- Retina – The light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye that converts light into neural signals that are sent to the brain via the optic nerve. It contains photoreceptor cells (rods and cones) that help in vision.
### Middle Layer:
- Choroid – The vascular layer between the retina and sclera that provides oxygen and nutrients to the retina. It contains many blood vessels.
- Lens – A transparent, flexible structure behind the iris that helps focus light onto the retina. It changes shape to adjust focus for near or distant objects (a process called accommodation).
- Iris – The colored part of the eye, which controls the size of the pupil and therefore the amount of light entering the eye. It has muscles that can constrict or dilate the pupil.
- Ciliary Body – The muscular structure that controls the shape of the lens and also produces aqueous humor, the fluid that nourishes the eye and maintains intraocular pressure.
WORD PARTS OF THE SENSORY SYSTEM:
EYES & EAR
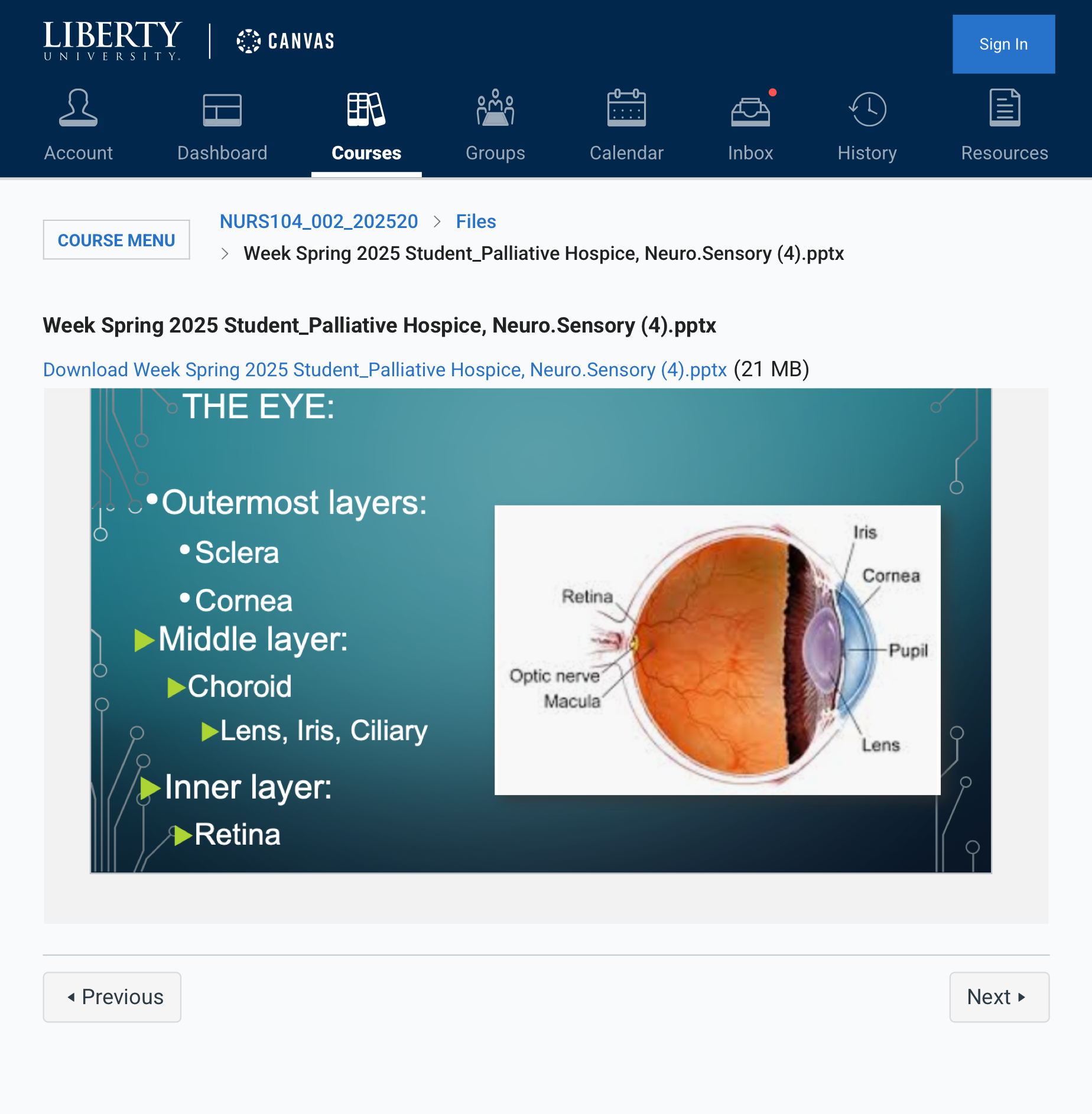
### Eye (Oculo/o, Ophthalm/o, Opt/o)
- Optometrist – A healthcare professional who is trained to examine the eyes, prescribe corrective lenses (glasses or contacts), and detect certain eye conditions, but they are not medical doctors.
- Oculopathy – A general term for eye disease or disorder. It can refer to any disease affecting the eye.
### Tears (Lacrimo/o, Dacry/o)
- Lacrimation – The production of tears, usually in response to irritation or emotions.
- Dacryorrhea – Excessive tearing or the abnormal flow of tears, which can result from irritation, allergies, or other conditions affecting the tear ducts.
### Ear (Aur/o, Ot/o)
- Aural – Related to the ear or hearing.
- Otoscope – A medical device used to examine the ear canal and eardrum. It allows healthcare providers to check for infections, blockages, or other conditions affecting the ear.
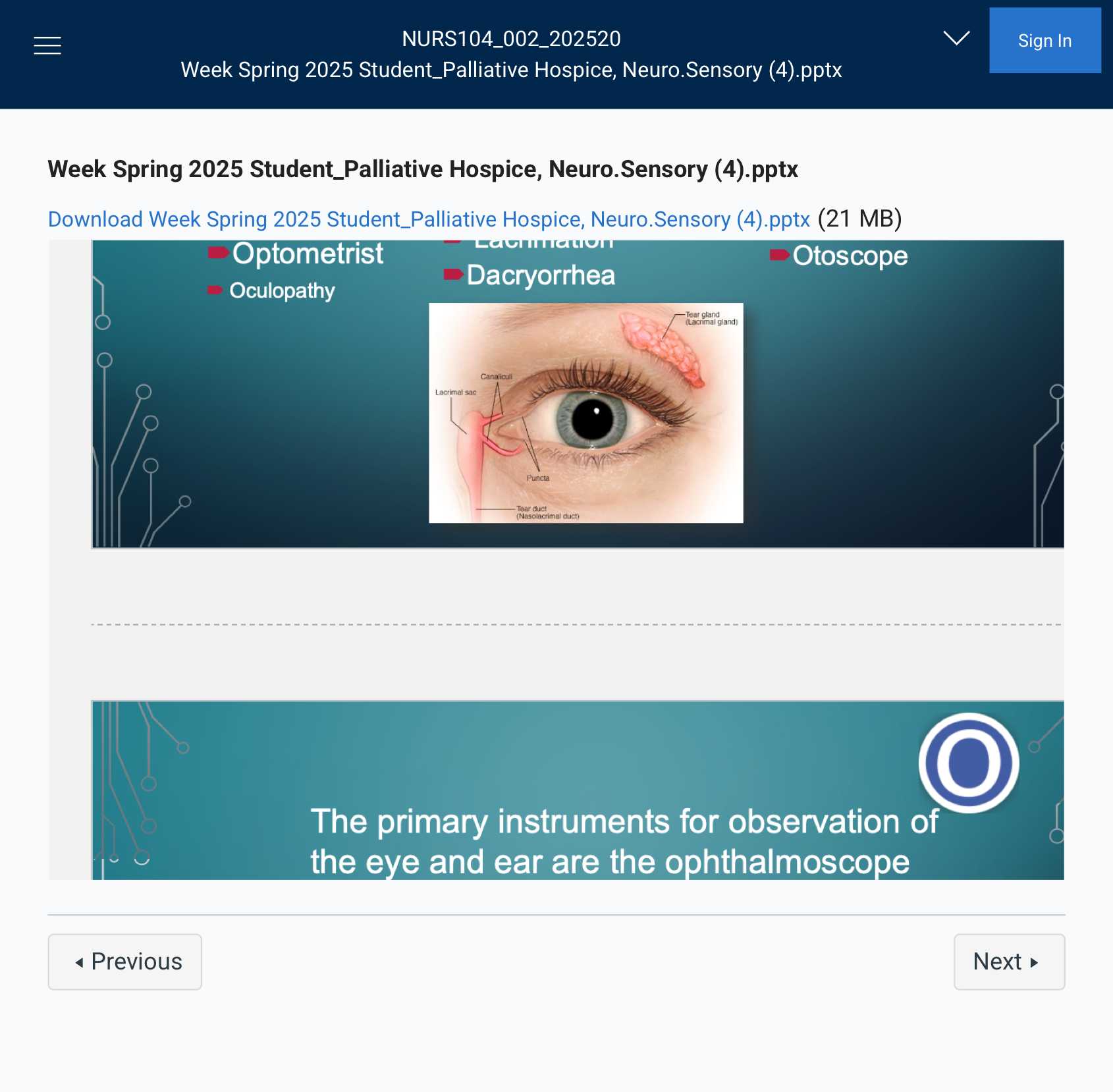
Observations
The primary instruments for observation of
the eye and ear are the ophthalmoscope
and otoscope
Exactly! Here's a quick summary:
- Ophthalmoscope – An instrument used to examine the inside of the eye, especially the retina and optic nerve.
- Otoscope – A tool used to look inside the ear canal and examine the eardrum.
Let me know if you need flashcards or a quiz to help you study! 😊
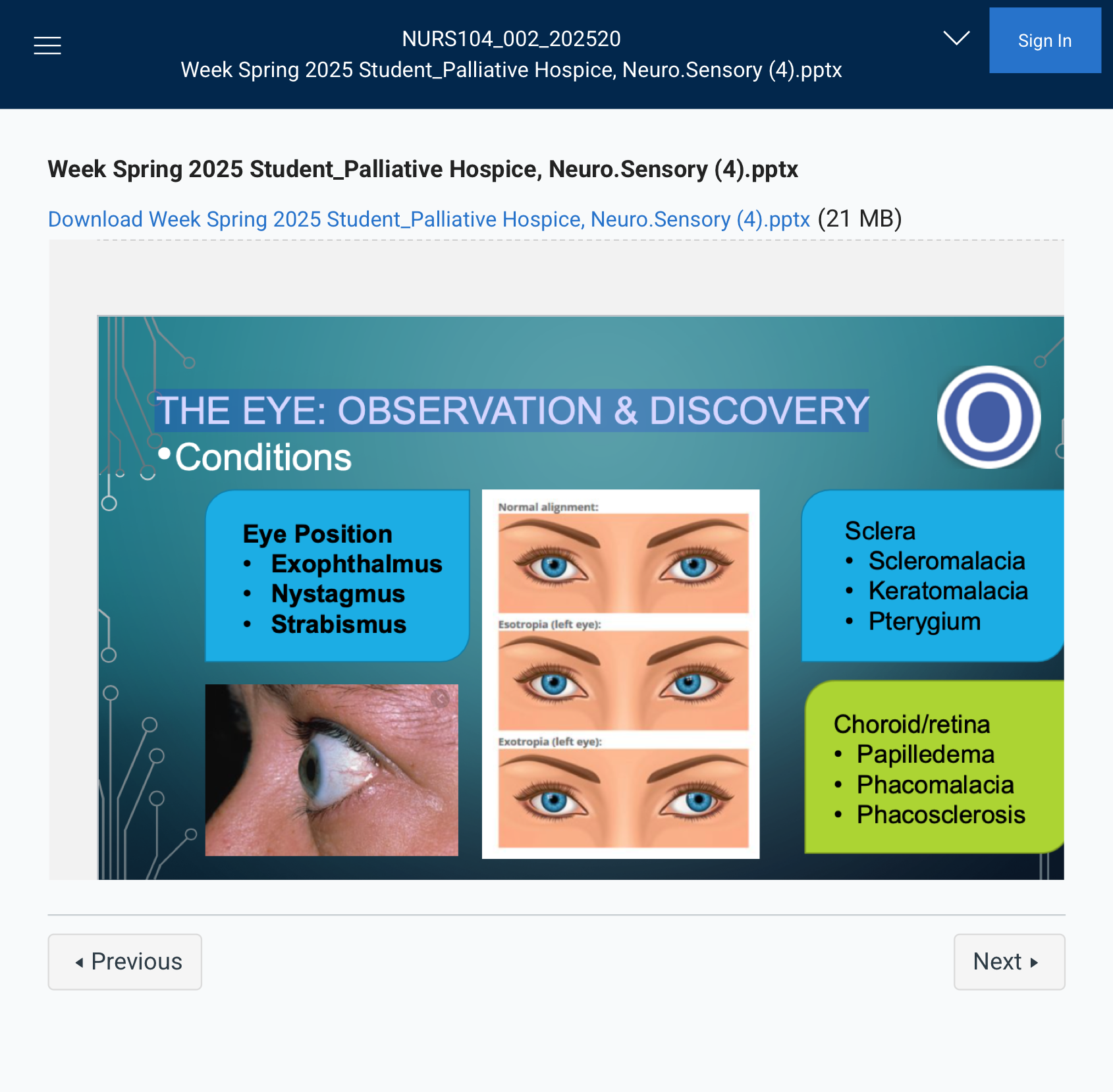
THE EYE: OBSERVATION & DISCOVERY
### Eye Position Conditions
- Exophthalmus – A condition where the eyeballs protrude from the eye sockets, often seen in thyroid disease (e.g., Graves' disease) or other systemic conditions.
- Nystagmus – Involuntary, rhythmic eye movements, which can occur horizontally, vertically, or in a circular motion. It may be a sign of neurological or vestibular issues.
- Strabismus – A condition where the eyes do not align properly. One eye may turn inward (esotropia), outward (exotropia), upward (hypertropia), or downward (hypotropia). This is often referred to as crossed eyes.
Of course! Here are short definitions for each:
- Exophthalmus – Bulging, enlarged or protrusion of the eyeball.
- Nystagmus – Involuntary, rapid eye movement. Eyes moving in circles
- Strabismus – Misalignment of the eyes.
### Sclera Conditions
- Scleromalacia – Softening or thinning of the sclera (the white part of the eye), which can make the eye more vulnerable to injury and other complications.
- Keratomalacia – Softening of the cornea, typically caused by vitamin A deficiency or other severe nutritional deficiencies, leading to vision problems or blindness.
- Pterygium – A benign growth (non cancerous tumor) of tissue on the conjunctiva, usually starting at the inner corner of the eye and extending toward the center of the cornea. It is commonly caused by prolonged exposure to UV light.
### Choroid/Retina Conditions
- Papilledema – Swelling of the optic disc (the point where the optic nerve enters the eye) due to increased intracranial pressure, which can be a sign of conditions such as brain tumors or intracranial hemorrhages.
- Phacomalacia – The softening or degeneration of the lens, which can occur in cataracts or as part of other eye diseases.
- Phacosclerosis – The hardening or sclerosis of the lens, often associated with aging, leading to the development of cataracts.
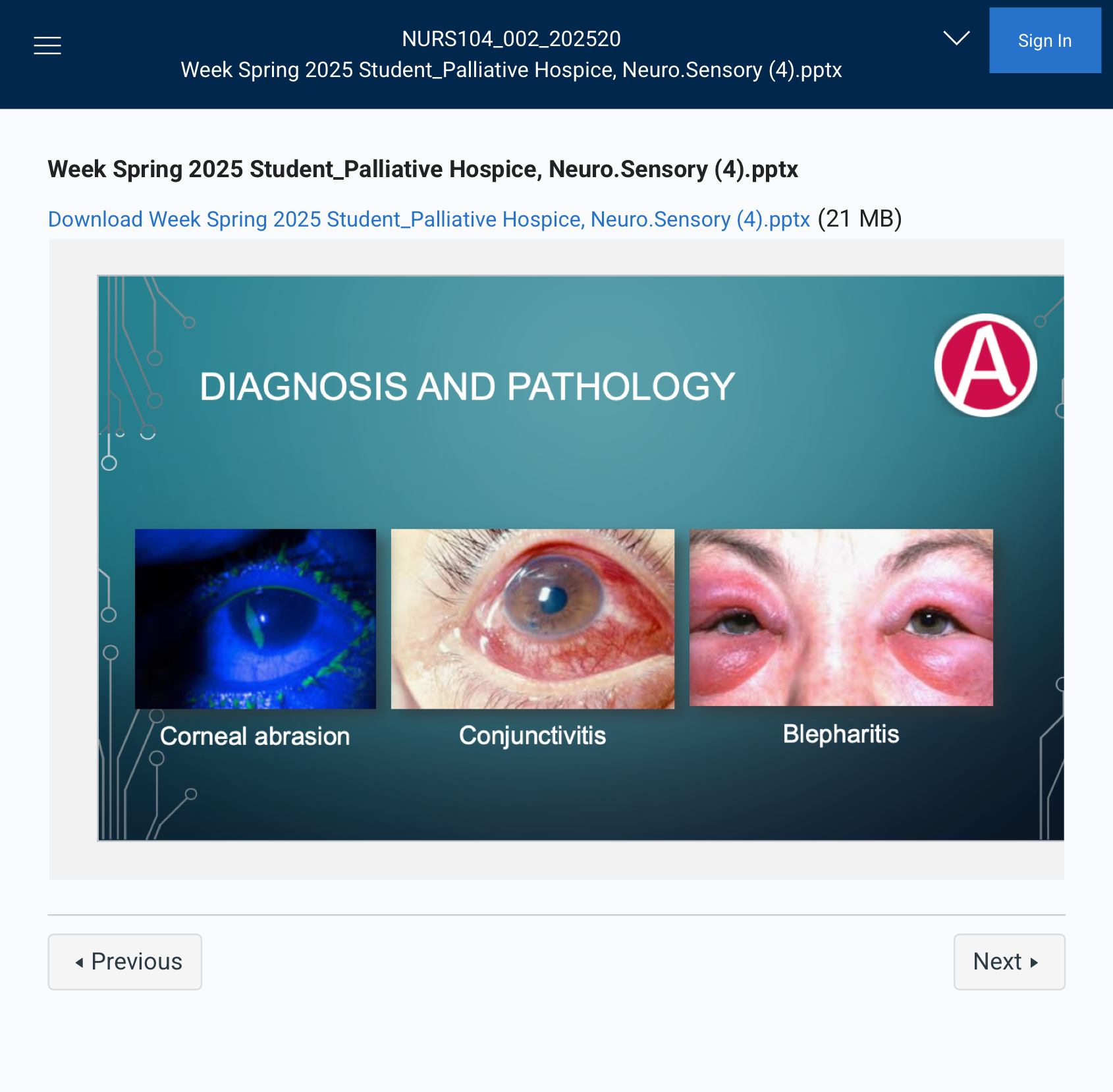
DIAGNOSIS AND PATHOLOGY
### Corneal Abrasion
A scratch or injury to the cornea, causing pain, redness, and tearing.
### Conjunctivitis
Inflammation of the conjunctiva (pink eye), causing redness, itching, and discharge.
### Blepharitis
Inflammation of the eyelids, leading to redness, swelling, and crusty lashes.
THE EYE: CONDITIONS
### Eye Conditions:
- Ophthalmalgia – Eye pain.
- Ophthalmoplegia – Paralysis or weakness of the eye muscles.
- Esotropia – Crossed eyes, where one or both eyes turn inward.
- Exotropia – Outward turning of the eyes (opposite of esotropia).
### Pupil Conditions:
- Miosis – Constricted pupils (small pupils).
- Mydriasis – Dilated pupils (large pupils).
- PERRLA – Pupils Equal, Round, Reactive to Light and Accommodation (a normal finding during eye examination).
### Sclera Conditions:
- Astigmatism – A distorted or blurred vision caused by an irregularly shaped cornea or lens.
- Corneal Xerosis – Dryness of the cornea.
### Visual Field:
- Scotoma – A blind spot or area of reduced vision within the visual field.
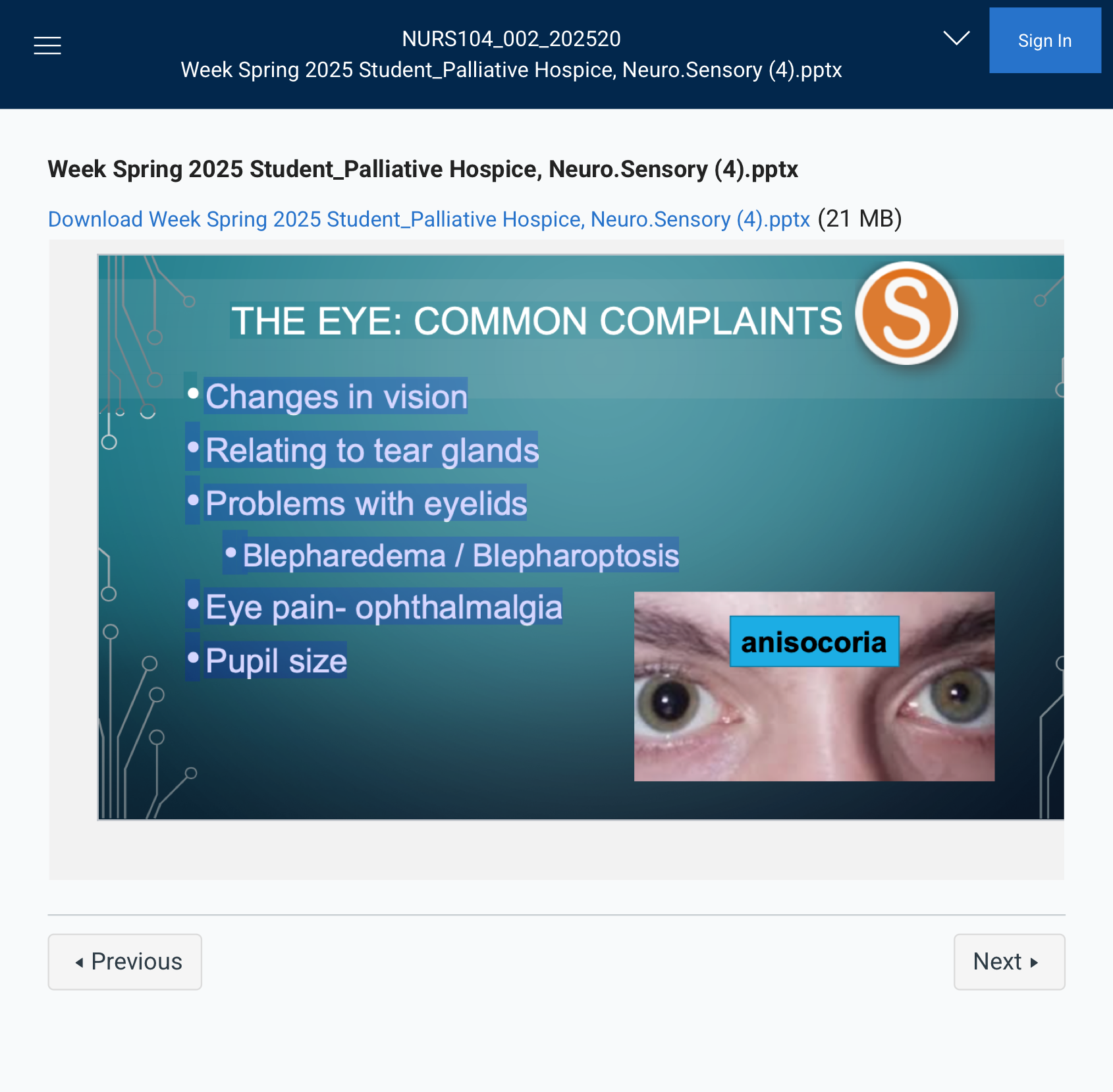
THE EYE: COMMON COMPLAINTS
### Relating to Tear Glands:
- Dacryorrhea – Excessive tearing or watery eyes.
### Problems with Eyelids:
- Blepharedema – Swelling of the eyelid.
- Blepharoptosis – Drooping of the eyelid.
### Eye Pain:
- Ophthalmalgia – Eye pain.
### Pupil Size:
- Miosis – Constricted pupils (small).
- Mydriasis – Dilated pupils (large).
Anisocoria is a condition where there is an unequal size of the pupils in the eyes. It can be a normal variation or may indicate an underlying issue, such as nerve damage, trauma, or neurological disorders.
TREATMENT AND THERAPIES
Usually Ointments or Drops (eye drops)
•Contraction: Miotic
•Dilation: Mydriatic
Here’s the difference between miotic and mydriatic:
- Miotic – Refers to pupil constriction. Miotic drugs cause the pupils to become smaller.
- Mydriatic – Refers to pupil dilation. Mydriatic drugs cause the pupils to become larger.
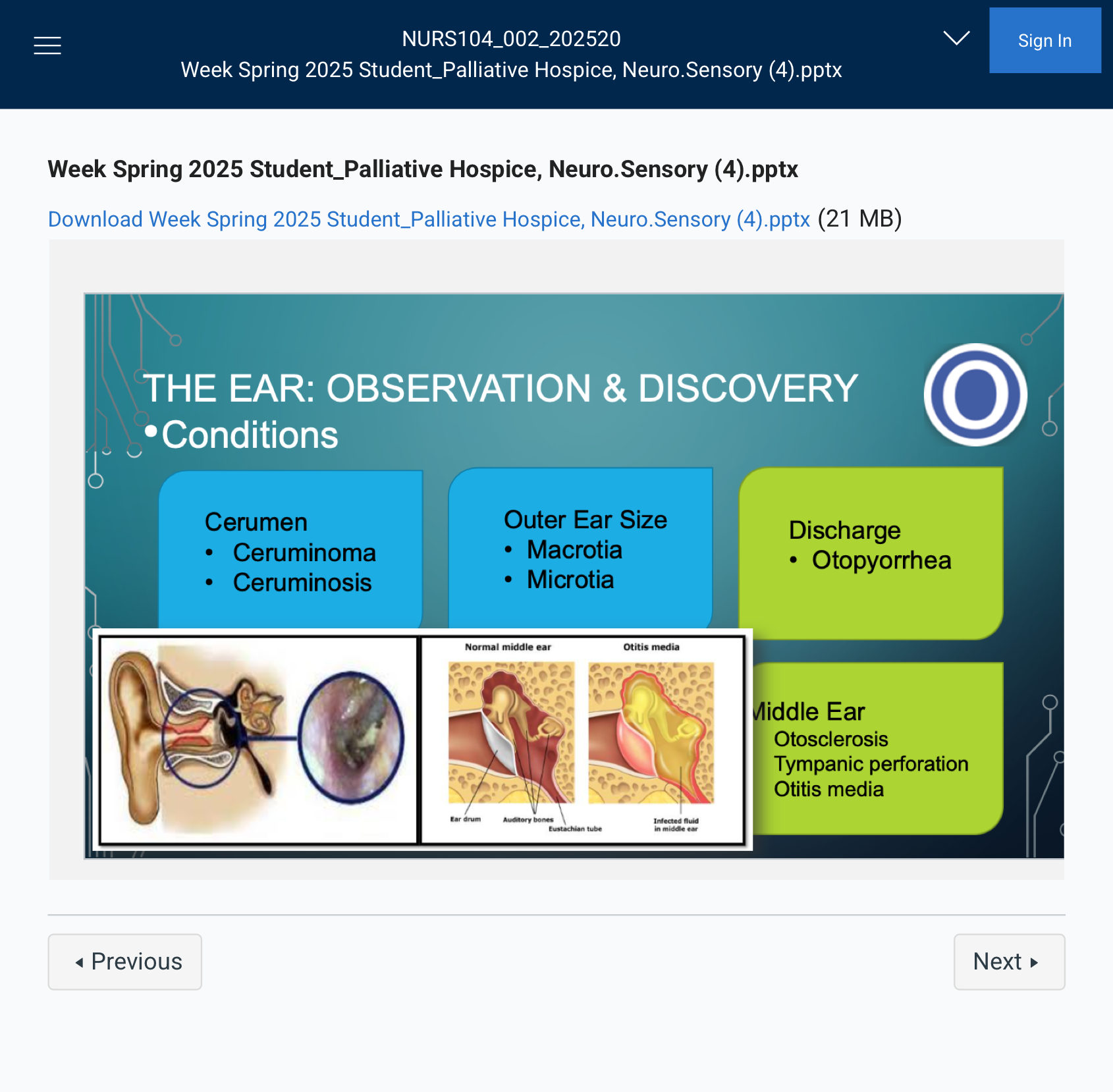
THE EAR: OBSERVATION & DISCOVERY
•Conditions
### Cerumen (Earwax) Conditions:
- Ceruminoma – A tumor or growth in the ear canal, often related to cerumen (earwax).
- Ceruminosis – Excessive earwax buildup, which can cause hearing loss or discomfort.
### Outer Ear Size Conditions:
- Macrotia – Abnormally large ears.
- Microtia – Abnormally small or underdeveloped ears.
### Ear Discharge:
- Otopyorrhea – Discharge of pus from the ear, often due to infection.
### Middle Ear Conditions:
- Otosclerosis – A progressive hearing loss caused by abnormal bone growth in the middle ear, affecting the movement of the stapes bone.
- Tympanic Perforation – A hole or tear in the eardrum, often caused by infection or trauma.
- Otitis Media – Middle ear infection, typically causing ear pain, fever, and possible hearing loss.
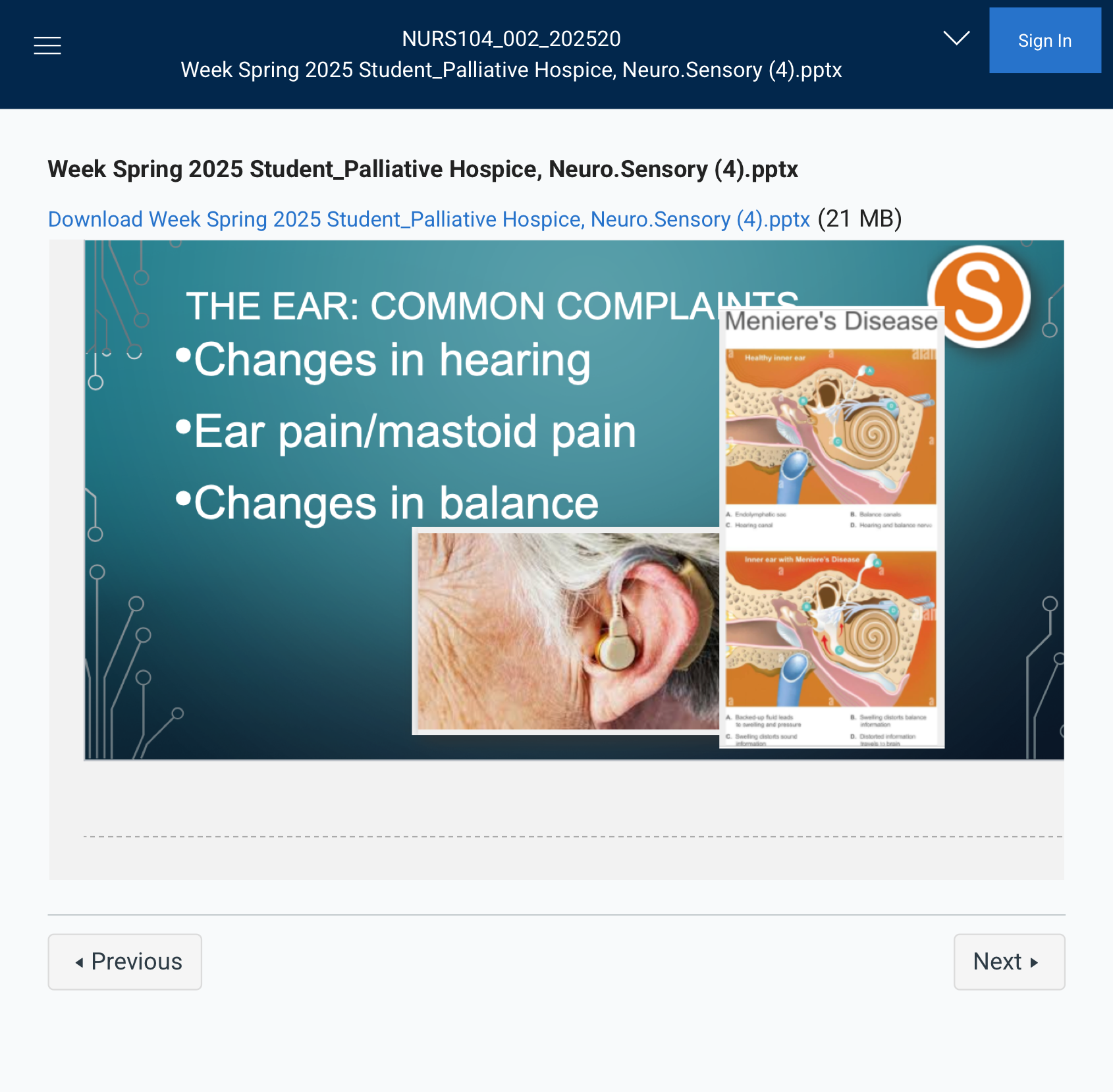
THE EAR: COMMON COMPLAINTS
Changes in hearing
•Ear pain/mastoid pain
•Changes in balance
THE EAR: CONDITIONS
### Inner Ear Conditions:
- Tinnitus – A ringing, buzzing, or hissing sound in the ears, not caused by an external sound.
- Vertigo – A sensation of spinning or dizziness, often related to inner ear problems affecting balance.
Here are concise definitions for the inner ear conditions:
Tinnitus: Ringing or buzzing sound in the ears.
Vertigo: A spinning sensation or dizziness affecting balance.Here are concise definitions for the ear conditions you mentioned:
### Outer/Inner Ear Conditions:
- Otalgia (Otodynia) – Ear pain; can be caused by infections, injuries, or other ear conditions.
- Otorrhea – Discharge from the ear, which could be due to an infection or injury.
Let me know if you need further clarification! 😊
TREATMENT AND THERAPIES
- Ear Drops – Medications applied directly into the ear to treat infections, pain, or inflammation.
- Ototoxic – Harmful to the ear causing ear problems. Medications or substances that can cause damage to the inner ear, leading to hearing loss or balance issues. Common examples include certain antibiotics and chemotherapy drugs.
ABBREVIATIONS
Abbreviation Meaning
HEENT Head, Eyes, Ears, Nose, Throat
OD Right eye
OS Left eye
OU Both eyes
PERRLA pupils are equal, round, and reactive to
light and accommodation
AD Right ear
AS Left ear
AU Both ears
AOM Acute otitis media. (middle ear infection)