3.7 Plant Nutrition and Transport
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Water potential
potential energy of water
How do solutes reduce water potential
consuming potential energy in water
How water moves in root cells
difference in water potential
Transpiration
water evaporates from leaves
Why does water evaporate from leaves
cool the leaf
occurs through stomata
main driver of water movement in xylem
creates negative pressure at the leaf surface
Cohesion
pulls nearby water molecules closer to stomata
Cohesion tension theory
transpiration creates negative water potential gradient
water pulled to roots
cohesion and adhesion of water to the cell walls transports water through the xylem up the tree
Turgor Pressure
force of water pushing against cell wall
Turgor Pressure- if water potential is lower outside cells
water moves out of the cells, plant wilts
Turgor Pressure- if water potential is higher outside
water moves into the cells keeping plant errect
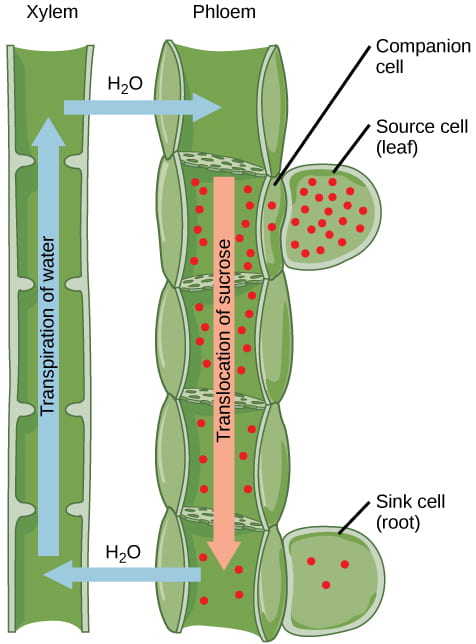
Role of Phloem
creates positive pressure pushing sap from source to a sink
source
produces sugars (leaves)
Sink
receives sugars (roots and fruits0
Pressure Flow Theory
sugars actively transported by companion cells from photosynthetic cells into sieve tube cells
water moves via osmosis from xylem to sieve tube, increasing sieve tube pressure
pressure pushes sugars toward the sink
at the sink, transport proteins move sugars out of sieve tube
because solute conc. in phloem decreased, water leaves sieve tube via osmosis
Translocation
Active transport of sugars from source into phloem
high amount of solute in phloem moves water into phloem
pressure pushes sugars to the sink
water moves back into xylem
Response to light- Chromophores
light absorbing pigments
Photoperiodism
uses light to track time (seasonal, germination, or growth response
Phototropism
reaction to light toward or away from light
positive phototropism
toward light
negative phototropism
away from light
Gravitropism
response to gravity
negative: shoots grow up
positive: roots grow down
Thigmotropism
response to touch
thigmomorphogensis
developmental change in plant change due to mechanical stress
ex: thickened tree trunk on windy coast
Difference between plant hormones and human
plant hormones can be produced in any cell
animal hormones produced in specific glands
Plant defenses
bark/waxy cuticle=barrier
thorns: modified branches and spines: modified leaves
volatile odors
repellent tastes
toxins
Role of cellulose
structure component of cell wall
Parasitism- holoparasites
lack chlorophyll
Parasitism- hemiparasites
have chlorophyll
Insectivorous Plants
uses specialized leaves to attract and digest insects
in acidic environments
Commensalism- epiphyte
grows on other plants, not dependent on other plant for nutrition