Ib Biology HL : Protein synthesis - D.1.2
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
transcription
3’ to 5’ is the template strand: the one used by the mRNA.
helicase opens the DNA. RNA polymerase catalyses the production of mRNA. The mRNA is essentially the same as the coding strand
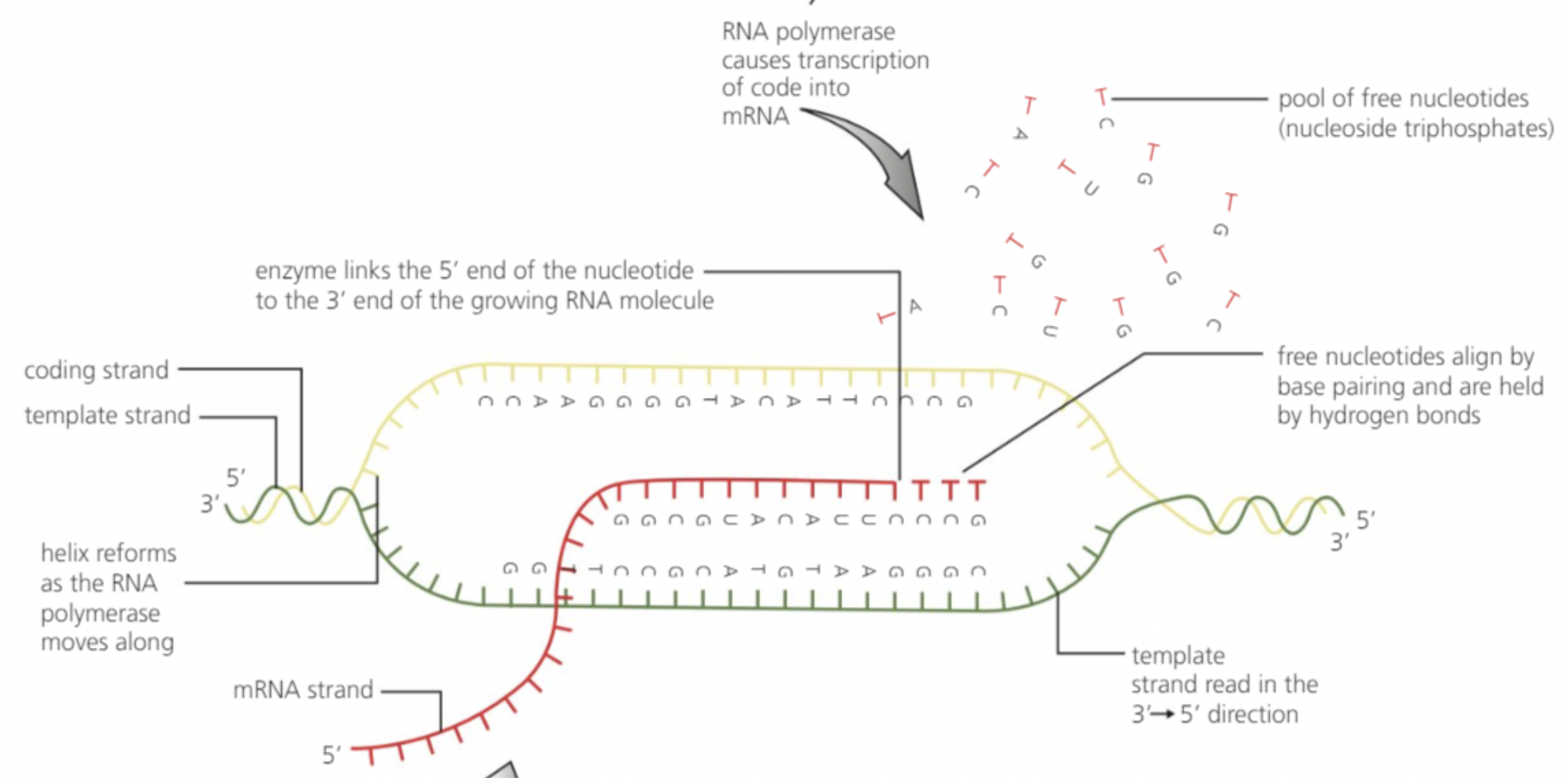
What directions do polymerases read genetic material and how do they produce new ones ?
Read from 3’ to 5’
Produce new strand 5’ to 3’
What order is mRNA read in ribosomes ?
5’ to 3’
percentage of expressed genes
25% - in whole body !
genes expression variation:
genes related to essential metabolic reactions: respiration. always
at later stage: stem→ specialised
matured cells → memory B cells
when signalled to→ insulin production
Point mutation
Mutation in which one nucleotide is changed. Usually happens in dna replication but can also happen in transcription
Types of point mutation
insertion mutation
Deletion mutation
Both of these cause frameshift mutation, meaning that all the following codons are affected by the mutation
substitution mutation: due to code degeneracy, it sometimes is a silent mutation
Élongation of a polypeptide
tRNA comes and bonds to A site
The large subunit of the ribosome catalyses a reaction between the amino acid held by the tRNA in the A site and the one in the P site ( requires energy )
tRNA in P site moves to E site and exits ribosome, and one in A site moves to P site ( requires energy ) which leaves site A available for next tRNA
proteome
All cells used by human body
Proteasome
protease complex which degrades and recycles unwanted proteins: hydrolyses peptide bonds between amino acids
collaborates with ubiquitin, which binds to the unwanted proteins
Stages of translation
initiation: mRNA attaches to small subunit of ribosome
Elongation: peptide bonds are for,Ed
TerminAtion: polypeptide released during termination
stages of elongation
hydrogen bonds to A part of ribosome on tRNA
ATP used up to form covalent/ peptide bond between amino acids
amino acids moves to T
eventually exits
continues until reaches stop codon
The promoter DNA
Non coding region in DNA just before a gene, where proteins known as positive transcription factors can bind, which will allow the RNA polymerase to bind to the dna
Non coding sequences in DNA roles
regulators of gene expression : promoters
Introns: parts of dna that are copied in mRNA but removed in post transcriptional modification
Telomeres: parts at end of chromosomes made of repetitions which protects coding DNA; with every cell division 0, end of the telomeres are lost
Genes for tRNA and rRNA ; ?
Directionality of transcription
Direction of RNA polymerase when on DNA (5’ to 3’);
Post transcriptional modification of mRNA
addition of 5’ cap ( so ribosome can work )
a poly-A-tail ( which protects a molecule from degradation )
Splicing : excising introns ( splisosomes ) : and ligating exons to form mature mRNA
Introns and exons
Introns In eukaryotic genomes, don’t contain coding information. Exons do; they code for polypeptides
Alternative splicing
A gene can be modified by combing different exons and removing others; this can results in a different range of proteins which function differently. Like this, from a single gene multiple proteins can be made
polysome
several ribosomes may move along the mRNA at the same time. This structure ( mRNA, ribosomes and protein chains ) is called a polysome
Alternative splicing example
Troponin P, a protein involved in cardiac contraction, is sliced one particular way in foetuses which gives it a greater sensitivity to Ça+2 and acidosis. A few weeks after the birth of the baby, the troponin T gene gets spliced differently and these features are lost
what direction is mRNA synthesised
5’ to 3’ on the template stand which is 3’ to 5’
transcription bubble
RNA polymerase
mRNA strand
template DNA
non coding regions of dna ( list them )
promoter
terminator
promoter
marks the beginning of the protein sequence
in charge of deciding whether or not the gene gets transcribed
makes RNA polymerase bind
terminator
when they are transcribed, the DNA polymerase detaches and therefore stops the transcription process
allows it to not make a huge, useless protein
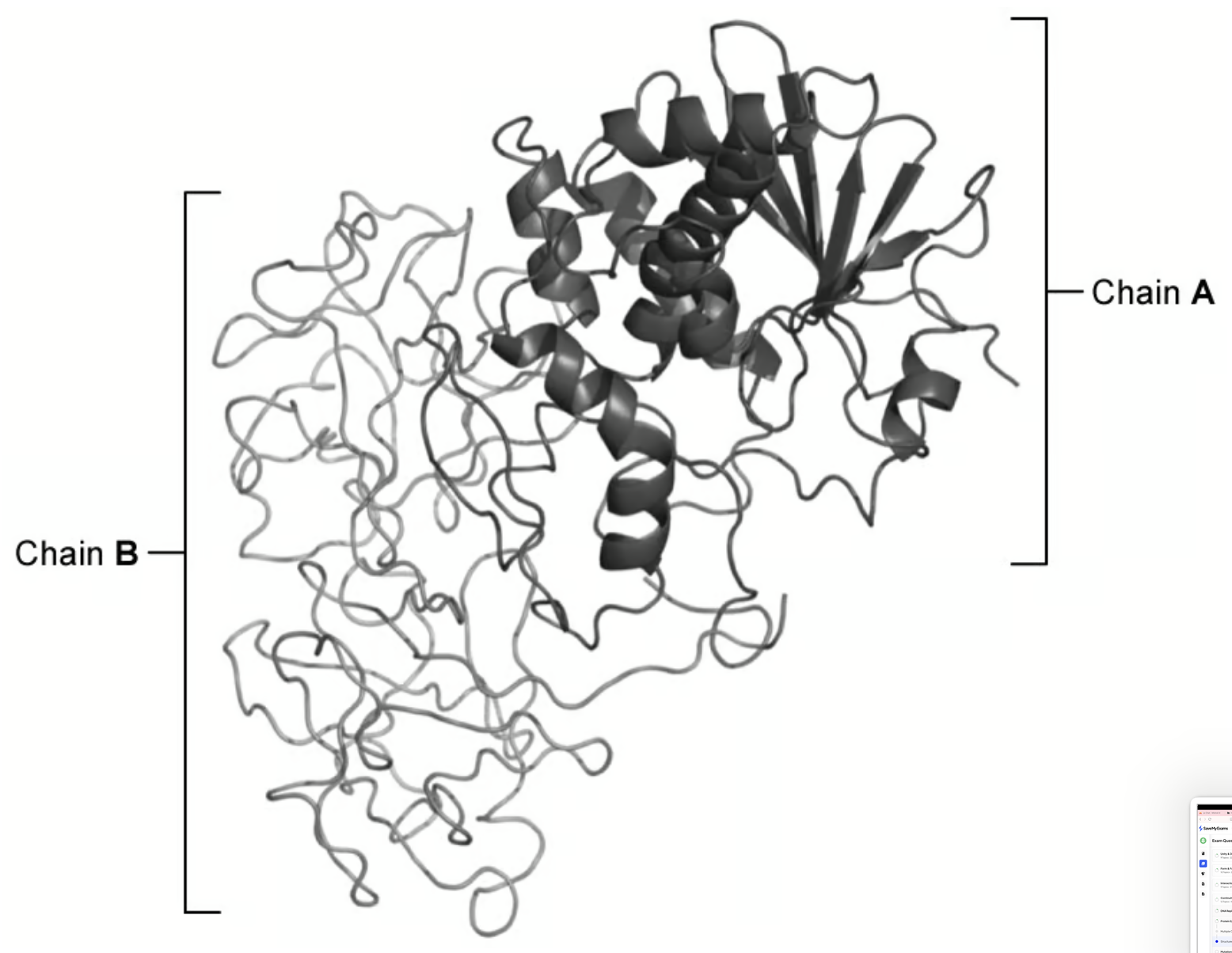
describe structure visible (3)
alpha helixes and beta pleated sheets cause secondary structure
the 3D structure of chain A and chain B shows the secondary structure
the combination of structure A and structure B leading to a globular structure shows quartermary structure