Histones and transcription (2)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
DNA in the form of a chromosome is…
not naked
DNA complex in the chromosome
Beads on a string→ 30nm nucleosome→ Chromatin loops→ Chromosome
Histones in the nuclosome complex (3)
H2, H3, H4
Heterochromatin/ Repressive chromatin
Condensed
Transcriptionally inactive region
Can be constitutive (telomeres, centromeres) or facultative
Euchromatin
Thread-like so uncondensed
Transcriptionally active region
The MAT locus allows…
to control the mating type in yeast (switch)
Why must HMLα or HMRa be silenced for the yeast to mate?
Because otherwise the cells will be diploid α/a and can’t mate
How is the mating type chosen?
Depending on the silencer sequence in front of the locus that is active = heterochromatin formation
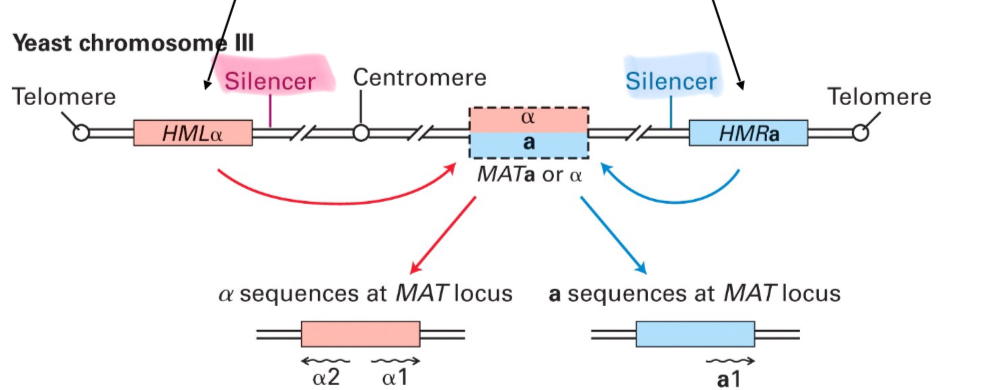
How do telomeres behave similarly to the HML and HMR locus in yeast?
They also have silencer sequences that halt cell division when the chromosome gets too short
Transcription factors (proteins) that a required for MAT locus silencing (3)
RAP1
SIR1
SIR2, 3 and 4
RAP1
Binds to DNA in the silencer/telomere sequences
SIR1
Binds the silencer sequence near the silent mating type loci (can’t put it anywhere) with RAP1
SIR2, 3 and 4
Bind to hypoacetylated histone tails (H3, H4) and recruit more (+ve feedback loop bc SIR2 is a deacetylase)
Rpd3p (and SIR2)
Histone deacetylases
Repressor domain (RD) with DBD=
Transcriptional repression through deacetylation= Rpd3p enzymatic action on histone’s N-terminal tails
Activator domain (AD) with DBD=
Transcriptional activation through hyperacetylation= Gnc5 enzymatic action (HAT)
Why does acetylation of histone tails allow transcription?
Bc it neutralizes electrostatic interactions (negativeDNA and positiveHistones) and permits complex formation
Why co-activator/repressor?
Bc they lack specificity
How is that specificity confered to them?
By the transcription factors (AD/RD+DBD)
Pioneer transcription factors
Have 2 HATs
Can interact with chromatin even in its consensed form + recruitment of co-activators/repressors
What modification of the histone tails allows transcription?
Methylation on H3 K4 (mono, di, tri)
What modification of the histone tails blocks transcription?
Methylation of H3 K9 (mono, di, tri)
ChIP
Used to determine regions of the genome (genes) that are affected by modified histone tails
Epigenetic traits
Characteristics transmitted regardeless of the DNA sequence itself (toxins)
Types of epigenetic traits (3)
Inactive X/histone marks (methylation (Xist))
Developmental restrictions (legs vs antennae (Polycomb))
Imprints/marks (DNA methylations)
Epigenetic writers
Enzymes that add the marks to histones or DNA
Epigenetic readers
Proteins that recognize the imprint/marks/modifications
Example of epigenetic reader AND writer in histones
HMT or histone methyltransferase by recognizing neighbouring naive histones
H3K9me3
Example of mark